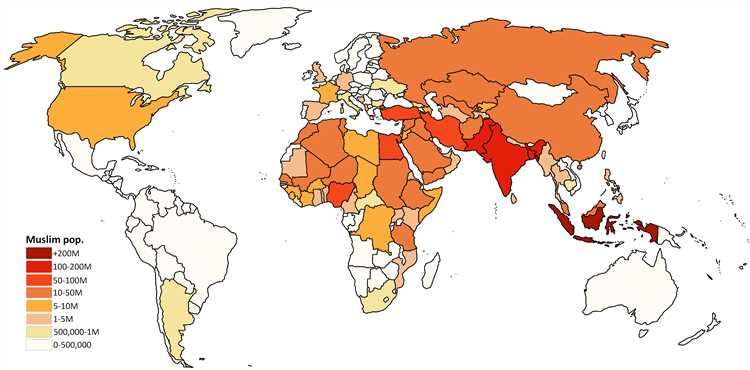
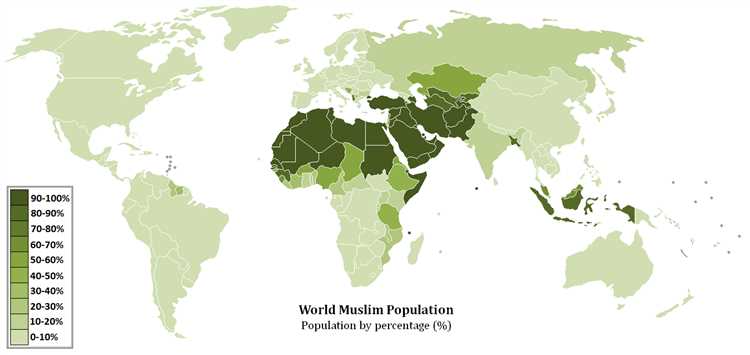
Step into a world of wonder and discovery as we embark on a journey to explore the vibrant culture and rich history of the Islamic world. From the majestic architectural wonders of the Mosque of Cordoba to the bustling markets of Marrakech, this guide will take you on an unforgettable adventure.
One of the defining aspects of Islamic culture is its deep appreciation for art and beauty. From intricate calligraphy to mesmerizing geometric patterns, Islamic art is a sight to behold. Whether you’re admiring the delicate ceramic tiles of the Blue Mosque in Istanbul or marveling at the ornate woodwork of the Alhambra in Granada, you’ll be captivated by the incredible craftsmanship and attention to detail.
But the Islamic world is more than just stunning architecture and artwork. It is also a world of diverse cultures and traditions, with each country offering its own unique experiences. From the vibrant colors and lively music of Morocco to the serene beauty of the Maldives, there is something for everyone to enjoy.
Along with its rich culture, the Islamic world is also steeped in a fascinating history. From the golden age of the Islamic empire to the modern day, the region has been a center of innovation, scholarship, and cultural exchange. Visit the ancient city of Petra in Jordan or explore the historic site of Persepolis in Iran to get a glimpse into the past and uncover the stories of the people who lived there.
Whether you’re a history buff, an art enthusiast, or simply someone who loves to travel, the Islamic world has something to offer everyone. So pack your bags, open your mind, and get ready to embark on a journey of a lifetime. Explore the vibrant culture and rich history of the Islamic world – your ultimate guide awaits.
Islamic Art: A Tapestry of Beauty and Spirituality
Islamic art is a testament to the rich cultural and spiritual heritage of the Islamic world. It is characterized by its intricate designs, vibrant colors, and deep symbolism, reflecting the diverse influences and historical periods that have shaped the Islamic artistic tradition.
One of the key features of Islamic art is its emphasis on geometric patterns. These patterns are not only aesthetically pleasing but also hold symbolic meaning. The use of geometric motifs and designs reflects the Islamic belief in the order and harmony of the universe, as well as the divine nature of creation.
Arabesque is another prominent feature of Islamic art. Arabesque refers to the elaborate and intricate decoration often found in Islamic architecture, calligraphy, and textiles. It typically consists of floral motifs, intertwining vines, and complex geometric patterns. The flowing and interlacing nature of Arabesque represents the unity and interconnectedness of all things in the Islamic worldview.
Calligraphy is another important element of Islamic art. Since the Quran, the holy book of Islam, is written in Arabic, calligraphy has become a highly esteemed art form. Islamic calligraphy is not only a means of conveying text but also an aesthetic expression of the divine word. The intricate and decorative nature of Arabic script adds an additional layer of beauty to Islamic artwork.
Another notable aspect of Islamic art is its rejection of figurative representation. Islam discourages the depiction of living beings in art, as it can be seen as a form of idolatry. Instead, Islamic art focuses on the beauty found in nature, geometry, and abstract symbolism. This unique approach to artistic expression gives Islamic art its distinct character.
Islamic art encompasses a wide range of mediums, including ceramics, metalwork, textiles, and architecture. It is seen as a holistic art form that permeates all aspects of life, from the grandeur of mosques to the intricate designs adorning everyday objects. Each piece of Islamic art is a reflection of the beauty, craftsmanship, and spirituality that define the Islamic world.
| Medium | Description |
|---|---|
| Tilework | Colorful ceramic tiles used to adorn the walls and interiors of mosques and palaces. |
| Miniature Painting | Detailed and intricate paintings often found in illuminated manuscripts, showcasing scenes from daily life and legendary stories. |
| Calligraphy | Beautifully written Arabic script used to convey the word of God and decorate various surfaces. |
| Carpet Weaving | Elaborate hand-woven carpets known for their intricate patterns and vibrant colors. |
In conclusion, Islamic art is a reflection of the rich cultural heritage, spiritual beliefs, and artistic traditions of the Islamic world. Its intricate designs, vibrant colors, and deep symbolism make it a tapestry of beauty and spirituality. Whether in the form of architecture, calligraphy, ceramics, or textiles, Islamic art continues to inspire and captivate audiences around the world.
Islamic Architecture: From Mosques to Palaces
The Islamic world is renowned for its stunning architectural heritage, characterized by intricate designs, geometric patterns, and grand structures. Islamic architecture encompasses a wide range of architectural styles, from mosques to palaces, reflecting the diverse cultural and historical influences of different regions.
Mosques:
Mosques hold a central place in Islamic architecture. They serve as places of worship and community gathering, displaying the beauty and grandeur of Islamic design. The key features of mosques include:
- Minarets: These tall, slender towers serve as visual and auditory focal points for the call to prayer.
- Domes: Many mosques feature domes, which symbolize the heavens and create an impressive interior space.
- Prayer Halls: These large open areas provide space for congregational prayers, often decorated with ornate carpets and intricate patterns.
Palaces:
Islamic palaces are known for their architectural splendor and opulence. They served as residences for rulers and served as symbols of their power and wealth. Key features of Islamic palaces include:
- Courtyards: Palaces often feature spacious courtyards surrounded by graceful arcades and gardens.
- Halls: Palaces typically contain grand halls with high ceilings and ornate decorations, where rulers would receive guests and hold important events.
- Private Quarters: Palaces have private living quarters for the rulers and their families, often lavishly decorated with luxurious materials.
- Water Features: Many palaces incorporate pools, fountains, and intricate water channels, symbolizing beauty and providing a cooling effect.
Influence on Other Architectural Styles:
The beauty and elegance of Islamic architecture have had a profound influence on various other architectural styles around the world. For example:
- Moorish Architecture: Moorish architecture in Spain is heavily influenced by Islamic architecture, characterized by intricate filigree work, horseshoe arches, and decorative tilework.
- Mughal Architecture: Mughal architecture in India showcases the fusion of Islamic, Persian, and Indian architectural styles, featuring grand mosques, forts, and mausoleums.
- Ottoman Architecture: Ottoman architecture, prevalent in Turkey, combines Byzantine, Persian, and Islamic elements, known for its grand mosques and imperial palaces.
Conclusion:
Islamic architecture is a testament to the rich cultural heritage and artistic craftsmanship of the Islamic world. From the majestic domes of mosques to the grandeur of palaces, Islamic architecture continues to captivate with its timeless beauty and intricate details.
Islamic Calligraphy: The Art of the Written Word
Islamic calligraphy is a unique art form that holds deep cultural and religious significance within the Islamic world. It is considered one of the highest forms of artistic expression and a way to connect with the divine through the written word.
In Islamic calligraphy, the Arabic script is used as the primary medium to create visually stunning and intricate designs. This ancient art form dates back to the 7th century and has been influenced by various cultures and artistic traditions throughout history.
Islamic calligraphy holds a central place in Islamic art and is prominently featured in religious texts, architecture, and decorative objects. The art form is not limited to the Quran, but also extends to poetry, proverbs, and other forms of written expressions.
One of the key principles of Islamic calligraphy is the idea that the word of God should be revered and treated with the utmost respect. Calligraphers undergo years of training to master the various styles and techniques of writing, ensuring that every stroke and curve is precisely executed.
There are several different styles of Islamic calligraphy, each with its own distinct characteristics and aesthetic appeal. Some of the most well-known styles include Naskh, Thuluth, Nasta’liq, and Kufic. Each style has its own rules and guidelines for proportions, spacing, and ornamentation.
The beauty of Islamic calligraphy lies in its ability to transform words into visual art. Calligraphers carefully consider the composition of each piece, balancing the elements of form, rhythm, and harmony. The resulting artwork is a testament to the skill and devotion of the calligrapher.
Islamic calligraphy is not just limited to professionals. Many people from all walks of life practice calligraphy as a form of meditation and spiritual expression. It is a versatile art form that has the power to captivate and inspire both artist and viewer.
In conclusion, Islamic calligraphy is a vital part of the Islamic world’s cultural and artistic heritage. It serves as a visual representation of the beauty and power of the written word, connecting individuals to their faith and inspiring awe and wonder in all who encounter it.
Islamic Music: Melodies that Transcend Borders
Islamic music is an integral part of the rich cultural heritage of the Islamic world. With its origins deeply rooted in the sacred texts of the Quran, Islamic music holds a special place in the hearts of Muslims around the globe. It encompasses a wide range of genres, styles, and instruments, reflecting the diverse traditions and histories of different Muslim communities.
Spiritual Significance:
Islamic music is primarily recognized for its spiritual significance. It is used as a means of connecting with the divine and expressing devotion to Allah. The lyrics often incorporate verses from the Quran or Hadiths, fostering a connection to the Islamic faith and fostering a sense of unity among believers. The melodies and rhythms are carefully crafted to inspire feelings of tranquility, contemplation, and inner peace.
Diverse Genres and Styles:
Islamic music encompasses a wide array of genres and styles that vary across different regions and cultures. From the uplifting sounds of Nasheeds, which are acapella songs praising Allah and His prophet Muhammad, to the soulful melodies of Qawwali, a genre prominent in South Asia that combines Persian and Indian influences, Islamic music offers a rich tapestry of sounds and rhythms.
Instruments:
Islamic music incorporates a variety of traditional instruments, each adding depth and character to the compositions. The oud, a pear-shaped string instrument, is widely regarded as the “king” of Islamic musical instruments. Other commonly used instruments include the ney (a reed flute), the daf (a frame drum), and the qanun (a zither-like instrument). The combination of these instruments creates a harmonious blend of sounds that resonates with listeners.
Regional Influences:
Islamic music is not limited to a specific geography or language. It spans across borders, with each region adding its own unique flavor and cultural influences. The music of North Africa, also known as Maghreb, incorporates Berber, Arabic, and African elements. In contrast, the music of the Middle East reflects a fusion of Arabic, Persian, and Turkish traditions. Central Asia is known for its mesmerizing Sufi music, while South Asia has its distinctive qawwali and Sufi music traditions.
Celebratory Music:
Islamic music is not only meant for spiritual contemplation but also plays a vital role in joyous celebrations and communal gatherings. Weddings, religious festivals, and other special occasions are often accompanied by lively musical performances that uplift the spirits and create a sense of unity among the participants. Dances are often a part of these celebrations, showcasing the rhythm and harmony of Islamic music in action.
In conclusion, Islamic music is a vibrant and diverse art form that transcends borders and connects people through its melodies and spiritual essence. It not only reflects the rich history and cultural traditions of the Islamic world, but also holds deep meaning and significance for Muslims worldwide. From sacred chants to joyful celebrations, Islamic music continues to captivate and inspire listeners across the globe.
Islamic Literature: Stories that Inspire
Islamic literature is a treasure trove of stories that have been passed down through generations. These stories not only entertain but also inspire and educate. They provide insight into the values, beliefs, and history of the Islamic world. From epic poems to moral fables, Islamic literature encompasses a wide range of genres and styles. Here are some notable examples:
- The Qur’an: The holy book of Islam is considered the most important piece of literature in the Islamic world. It contains the revelations from Allah to Prophet Muhammad, offering guidance and wisdom to Muslims.
- The Thousand and One Nights: Also known as Arabian Nights, this collection of Middle Eastern and South Asian stories has captivated readers worldwide. It features tales such as Aladdin, Sinbad, and Ali Baba, showcasing the rich storytelling tradition of the Islamic world.
- Rumi’s Poetry: Jalal ad-Din Muhammad Rumi, a 13th-century Persian poet, is widely regarded as one of the greatest mystical poets in history. His poetry explores themes of love, spirituality, and the search for truth.
- Ibn Battuta’s Travelogues: Ibn Battuta was a 14th-century Moroccan scholar and explorer who documented his extensive travels in a series of travelogues. His writings provide valuable insights into the social, cultural, and political landscape of the Islamic world during the medieval period.
These are just a few examples of the vast body of Islamic literature that exists. Islamic literature not only reflects the cultural heritage of the Islamic world but also serves as a source of inspiration and moral guidance for Muslims. Through these stories, readers can gain a deeper understanding of the rich history and vibrant culture of the Islamic world.
Islamic Philosophy: Seeking Knowledge and Wisdom
The Islamic world is renowned for its contributions to the field of philosophy. Islamic philosophy emerged in the 9th century and flourished during the Islamic Golden Age, when scholars from different cultures and backgrounds came together to exchange knowledge and ideas.
One of the key principles of Islamic philosophy is the importance of seeking knowledge and wisdom. Islam encourages its followers to actively seek knowledge throughout their lives and to use that knowledge to benefit themselves and society. This pursuit of knowledge is not limited to religious studies, but encompasses all areas of human understanding.
Islamic philosophy has a rich history, with numerous scholars making significant contributions to a wide range of fields. Some of the most notable Islamic philosophers include Al-Farabi, Avicenna, and Averroes. These philosophers explored a variety of topics, including metaphysics, ethics, and logic.
One of the central concepts in Islamic philosophy is the idea of tawhid, which refers to the oneness of God. Islamic philosophers believe that all knowledge and wisdom ultimately comes from God, and that human beings are meant to use their intellect to uncover this divine wisdom.
Islamic philosophy also emphasizes the importance of reason and rationality in the pursuit of knowledge. Muslims are encouraged to use their critical thinking skills and apply reason to all aspects of life, including their understanding of religion.
Islamic philosophy also places a strong emphasis on ethics and morality. Islamic philosophers have explored the nature of good and evil, and the role that humans play in determining their own moral actions. Islamic ethics is based on the principle of justice, and encourages individuals to act in a way that is fair and just towards others.
Another area of focus in Islamic philosophy is the nature of reality. Islamic philosophers have explored questions about the nature of existence, the relationship between the physical and spiritual worlds, and the purpose of life.
In conclusion, Islamic philosophy is a rich and diverse field that encompasses a wide range of topics and ideas. It emphasizes the importance of seeking knowledge and wisdom, and encourages individuals to use reason and rationality in their pursuit of understanding. Islamic philosophy has had a profound influence on the development of numerous scientific, philosophical, and ethical ideas throughout history.
Islamic Science: Contributions to the World
The Islamic world has a rich history of scientific advancements and contributions that have significantly influenced the development of various fields of knowledge. Islamic science emerged during the Islamic Golden Age, which spanned from the 8th to the 14th centuries. During this period, scholars in the Islamic world made groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in various scientific disciplines, including astronomy, mathematics, medicine, chemistry, and optics.
Astronomy: Islamic astronomers made significant contributions to the field, both in terms of observation and theoretical understanding. They built upon the knowledge of ancient civilizations and devised more accurate instruments for observing celestial bodies. Prominent astronomers like Al-Farabi, Al-Battani, and Al-Zarqali made significant discoveries in areas such as celestial mechanics, astrolabes, and the determination of planetary orbits.
Mathematics: Islamic mathematicians made fundamental contributions to the development of algebra and trigonometry. Scholars like Al-Khwarizmi and Omar Khayyam were pivotal in introducing the decimal system and algorithms, which revolutionized mathematics as a whole. They also made advancements in geometry, number theory, and calculus.
Medicine: Islamic physicians made significant contributions to the field of medicine, building upon the works of ancient Greek and Roman physicians. Scholars like Al-Razi and Ibn Sina (Avicenna) made groundbreaking advancements in the understanding and treatment of diseases. They compiled extensive medical encyclopedias, which became standard textbooks in medical schools throughout Europe for centuries.
Chemistry: Islamic chemists made significant advancements in the field, particularly in the areas of distillation, chemical reactions, and pharmacology. They developed new techniques for extracting and purifying substances, which laid the foundation for modern chemistry. Alchemist scholars such as Jabir ibn Hayyan contributed to the development of experimental scientific methods.
Optics: Islamic scientists played a crucial role in the development of optics. Scholars like Ibn al-Haytham made significant advancements in understanding the nature of light and how it interacts with different materials. Their work on optics laid the foundation for modern understanding of lenses, vision, and the principles of light refraction.
This is just a glimpse of the immense contributions made by scientists in the Islamic world. Their achievements in various scientific fields not only advanced knowledge but also influenced subsequent scientific endeavors in Europe and other parts of the world. Islamic science continues to be a vital part of the global scientific heritage.
Islamic Mathematics: The Foundation of Modern Calculations
Islamic mathematics refers to the mathematical advancements made in the Islamic world during the Golden Age of Islam, which lasted from the 8th to the 14th century. During this period, Islamic scholars made significant contributions to various branches of mathematics, laying the foundation for modern calculations and shaping the development of mathematics as a whole.
One of the most notable contributions of Islamic mathematics is the introduction of the decimal system. Islamic mathematicians adopted the Indian numeral system, which included the concept of zero and the use of place value. This revolutionary system made calculations more efficient and accurate, paving the way for modern arithmetic.
Islamic mathematicians also made substantial progress in algebra. They built upon the existing knowledge of the Greeks and Indians and developed algebra as a distinct branch of mathematics. The renowned Persian mathematician Al-Khwarizmi is often referred to as the “Father of Algebra” for his work on equations and solving unknowns. His masterpiece, “Al-Kitab al-mukhtasar fi hisab al-jabr wa’l-muqabala,” provided a comprehensive introduction to algebraic methods and laid the groundwork for future advancements.
In addition to algebra, Islamic mathematicians excelled in geometry. They expanded upon the Greek geometric traditions and developed new concepts and theorems. The most famous Islamic mathematician in this field is Al-Hasan Ibn al-Haytham, commonly known as Alhazen. His book “Book of Optics” not only explored optics but also contributed to the development of geometric optics and served as a vital resource for scientists and mathematicians around the world.
Another crucial aspect of Islamic mathematics was the preservation and translation of ancient Greek and Roman mathematical works. Islamic scholars translated these texts into Arabic, preserving them for future generations. These translations were instrumental in transmitting ancient mathematical knowledge to medieval Europe, where it had a significant impact on the development of Western mathematics.
To facilitate their mathematical explorations, Islamic mathematicians also introduced various mathematical tools and notations. They invented numerous instruments like astrolabes and quadrant, which were used for astronomical and trigonometric calculations. Islamic mathematicians also developed symbols and notations, including the familiar symbols for addition (+) and subtraction (-). These innovations made complex calculations more accessible and contributed to the development of modern mathematical notations.
In conclusion, Islamic mathematics played a crucial role in the foundation of modern calculations. Through their contributions to the decimal system, algebra, geometry, preservation of ancient works, and the invention of mathematical tools, Islamic scholars laid the groundwork for the advancements that followed. Their achievements continue to influence mathematics today, making Islamic mathematics an integral part of the rich history of mathematics and the Islamic world.
Islamic Medicine: Advancements in Health and Healing
Islamic civilization has made remarkable contributions to the field of medicine, which have had a lasting impact on the world. Drawing on knowledge from ancient civilizations such as Greece, Egypt, and Persia, Islamic scholars and physicians made significant advancements in understanding the human body, diagnosing diseases, and developing effective treatments.
1. Preservation and Translation of Ancient Medical Texts
One of the key contributions of Islamic medicine was the preservation and translation of ancient medical texts. Islamic scholars dedicated themselves to translating Greek, Roman, and Persian medical works into Arabic, making them accessible to a wider audience. This facilitated the accumulation of medical knowledge and laid the foundation for further advancements in medical practices.
2. Hospitals and Healthcare Centers
The establishment of hospitals and healthcare centers by Islamic rulers played a significant role in improving healthcare. These institutions provided medical care to all, regardless of their social status or religious beliefs. Hospitals were equipped with pharmacies, libraries, and lecture halls, promoting the exchange of ideas and the dissemination of medical knowledge.
3. Specializations in Medicine
Islamic medicine recognized the importance of specialization in different fields of medicine. Scholars developed specializations in various branches, such as ophthalmology, dentistry, surgery, and pharmacology. This division of labor led to advancements in each field and improved the overall quality of healthcare.
4. Diagnostic Techniques
Islamic physicians developed innovative diagnostic techniques that revolutionized the understanding and treatment of diseases. They conducted detailed examinations of patients, including taking their medical history, monitoring their pulse, and observing physical symptoms. This comprehensive approach to diagnosis laid the foundation for modern medical practices.
5. Pharmacology and Drug Development
Islamic scholars made significant contributions to the field of pharmacology and drug development. They identified and studied medicinal plants, minerals, and animal products to develop effective and safe treatments. Their work in pharmacology laid the foundation for later developments in the field, influencing medicine in both the Islamic world and beyond.
6. Surgical Procedures
Islamic surgeons made notable advancements in surgical procedures and techniques. They developed sophisticated tools and instruments for surgeries and pioneered new procedures, such as cataract surgery and lithotomy (the removal of urinary stones). These advancements in surgical techniques paved the way for modern surgical practices.
7. Public Health Initiatives
Islamic rulers recognized the importance of public health and implemented initiatives to improve the overall well-being of their communities. They established quarantine measures, clean water systems, and public bathhouses, among other measures. These initiatives helped prevent the spread of diseases and promoted general hygiene.
| Name | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Ibn Sina (Avicenna) | Canon of Medicine – comprehensive medical encyclopedia |
| Ibn al-Nafis | Discovery of pulmonary circulation |
| Ibn al-Haytham | Contributions to ophthalmology |
| Al-Razi (Rhazes) | Classifying and describing various diseases |
| Ibn Zakariya al-Razi | First to identify and describe smallpox |
The advancements in Islamic medicine had a profound impact on the development of modern healthcare systems. The knowledge and practices developed by Islamic physicians paved the way for the scientific revolution in Europe, influencing medical education, research, and patient care. Today, the principles and techniques developed during the Islamic Golden Age continue to shape the field of medicine.
Islamic Astronomy: Exploring the Cosmos
Islamic Astronomy, also known as Arabic Astronomy, refers to the scientific study of celestial objects and phenomena that was developed and practiced in the Islamic world from the 8th to the 15th centuries. It was during this time that Islamic scholars made significant contributions to the field of astronomy, expanding upon earlier Greek, Persian, and Indian astronomical knowledge.
Islamic astronomers were driven by a desire to accurately determine the positions and movements of celestial bodies, as well as to understand the nature of the universe. They played a crucial role in developing sophisticated instruments and mathematical techniques for astronomical observations, and their findings paved the way for future scientific advancements.
Contributions to Astronomy
Islamic astronomers made numerous contributions to the field, some of which are still highly regarded today. Here are a few key advancements:
- Development of Observational Techniques: Muslim astronomers refined existing observational techniques and introduced new methods for determining the positions of stars, planets, and other celestial bodies. They made precise measurements of angles and distances using instruments like astrolabes and quadrants.
- Star Catalogues: Islamic astronomers compiled detailed star catalogues containing the positions and magnitudes of thousands of stars. One of the most famous catalogues, the Zij al-Sindhind, was created by the Persian astronomer Al-Khwarizmi.
- Advancement of Mathematical Models: Islamic astronomers developed and improved upon mathematical models to accurately predict the movements of celestial bodies. They refined the use of trigonometry and spherical geometry, making significant strides in the study of planetary motion.
- Advancement of Astrolabes and Other Instruments: Islamic astronomers played a critical role in the development and refinement of astronomical instruments such as astrolabes, celestial globes, and sundials. These tools greatly facilitated celestial observations.
- Preservation and Translation of Ancient Texts: Islamic scholars played a vital role in the translation and preservation of ancient Greek, Persian, and Indian astronomical texts. They translated and commented upon works by astronomers such as Ptolemy and contributed to the preservation of scientific knowledge.
Legacy and Impact
The contributions of Islamic astronomers had a lasting impact on the field of astronomy and the scientific community as a whole. Their discoveries and advancements laid the groundwork for future developments in astronomy, mathematics, and other scientific disciplines.
Islamic astronomy also played a significant role in the European Renaissance, as many Islamic scientific texts were translated into Latin and used to educate European scholars. The knowledge gained from Islamic astronomers helped pave the way for the Copernican revolution and the heliocentric model of the solar system.
| Name | Country | Contributions |
|---|---|---|
| Al-Khwarizmi | Iran (Persia) | Star catalogue, trigonometry |
| Al-Farabi | Iran (Persia) | Astrolabe, mathematical models |
| Ibn Yunus | Egypt | Astrolabe, accurate observations |
| Al-Battani | Iraq | Improved planetary tables, solar observations |
| Al-Zarqali | Spain | Astrolabe, Almanac |
In conclusion, Islamic astronomy played a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of the cosmos. Islamic astronomers made significant contributions to various aspects of the field, from observational techniques and mathematical models to the development of instruments and the translation of ancient texts. Their work continues to inspire and influence astronomers around the world.
Islamic Fashion: Traditional and Contemporary Styles
The Islamic world has a rich and diverse fashion scene that encompasses both traditional and contemporary styles. Islamic fashion is influenced by cultural and religious beliefs, and it is often characterized by modesty and elegance. Let’s explore some of the traditional and contemporary styles in Islamic fashion.
Traditional Styles
Traditional Islamic fashion is rooted in the cultural and historical traditions of the Muslim-majority countries. It includes garments such as the hijab, abaya, thobe, and kaftan.
- Hijab: The hijab is a headscarf worn by Muslim women to cover their hair and neck. It comes in various styles and can be accessorized with pins and brooches.
- Abaya: The abaya is a loose-fitting robe-like garment worn by women. It typically covers the entire body and is often black in color.
- Thobe: The thobe is a traditional Arab garment worn by men. It is a long robe usually made of white fabric and is worn with a head covering known as a keffiyeh.
- Kaftan: The kaftan is a flowing, loose-fitting garment worn by both men and women. It is often made of silk or cotton and is adorned with intricate embroidery and patterns.
Contemporary Styles
Contemporary Islamic fashion blends modern designs with traditional elements, catering to the evolving tastes and needs of Muslim fashion enthusiasts.
- Modest Fashion: Modest fashion is a growing trend in Islamic fashion that emphasizes covering the body while incorporating fashionable and trendy designs. Modest fashion designers often work with long sleeves, high necklines, and loose-fitting silhouettes.
- Islamic Street Style: Islamic street style is a fusion of urban fashion and Islamic modesty. It includes trendy items such as wide-legged pants, maxi dresses, and oversized tops paired with headscarves or turbans.
- Muslim Athleisure: Muslim athleisure combines sportswear with modesty. It includes items like sports hijabs, long-sleeved workout tops, and loose-fitting athletic pants.
The Rise of Islamic Fashion
The rise of Islamic fashion has been fueled by the increasing demand for modest clothing options, as well as the growing awareness and representation of Muslim fashion designers and influencers. Fashion events, such as Dubai Modest Fashion Week and London Modest Fashion Week, have also contributed to the visibility and acceptance of Islamic fashion on a global scale.
| Traditional Styles | Contemporary Styles |
| • Hijab | • Modest Fashion |
| • Abaya | • Islamic Street Style |
| • Thobe | • Muslim Athleisure |
| • Kaftan |
Islamic fashion reflects the diverse and vibrant culture of the Islamic world. Whether it’s traditional styles or contemporary trends, Islamic fashion offers a wide range of options for individuals seeking modest yet stylish clothing choices.
Islamic Cuisine: A Delicious Fusion of Flavors
Islamic cuisine is a reflection of the vibrant cultures and rich history of the Islamic world. It is a delicious fusion of flavors, blending the traditions and techniques of various regions into mouthwatering dishes that have captivated taste buds for centuries.
One of the unique aspects of Islamic cuisine is its emphasis on halal food. Halal, which means “permissible” in Arabic, refers to food and drink that is prepared according to Islamic dietary laws. It involves the use of specific ingredients and careful preparation to ensure that the food is clean, pure, and free from any forbidden substances or practices.
Islamic cuisine features a wide range of dishes that vary from region to region. It is heavily influenced by the diverse cultures and culinary traditions of the Islamic world, including the Middle East, North Africa, Central Asia, and South Asia. Each region has its own distinctive flavors, spices, and cooking techniques that contribute to the rich tapestry of Islamic cuisine.
Common ingredients in Islamic cuisine include grains, such as rice and wheat, legumes, such as lentils and chickpeas, vegetables like eggplant and okra, and meats like lamb, chicken, and beef. Spices like cumin, coriander, turmeric, and cinnamon are also widely used to add depth and complexity to the dishes.
The Islamic world is also famous for its sweet treats and desserts. From the rich pastries of the Ottoman Empire to the delicate sweets of Persia, Islamic desserts are a feast for the senses. Ingredients like honey, nuts, rose water, and saffron are commonly used to create unique and indulgent flavors that are sure to satisfy any sweet tooth.
To fully experience the flavors of Islamic cuisine, an essential part of the dining experience is communal eating. Sharing a meal with family and friends is a cherished tradition in Islamic culture and is often accompanied by lively conversation and hospitality. The act of breaking bread together fosters a sense of unity and connection among those sharing the table.
In conclusion, Islamic cuisine is a delectable fusion of flavors that reflects the rich heritage and diverse cultures of the Islamic world. Whether it’s a savory kebab, a fragrant biryani, or a decadent baklava, Islamic cuisine offers a truly gastronomic adventure that will leave you craving for more.
Islamic Festivals: Celebrations of Faith and Culture
Islamic festivals play a significant role in the lives of Muslims around the world. These celebrations are not only moments of religious significance but also serve as opportunities for communities to come together and express their faith and culture. Here are some of the most important Islamic festivals celebrated across the globe:
Eid al-Fitr
Eid al-Fitr, also known as the “Festival of Breaking the Fast,” marks the end of the holy month of Ramadan. During Ramadan, Muslims fast from dawn to sunset, and Eid al-Fitr is a joyous occasion that signifies the successful completion of this spiritual journey. On this day, Muslims gather for prayers at the mosque, exchange gifts, and share meals with family and friends. It is a time of forgiveness, gratitude, and celebration.
Eid al-Adha
Eid al-Adha, also known as the “Festival of Sacrifice,” commemorates the willingness of Prophet Ibrahim to sacrifice his son as an act of obedience to Allah. As a sign of gratitude and devotion, Muslims worldwide perform the ritual of sacrificing an animal, usually a sheep, cow, or camel. The meat is then divided into three parts, one for the family, one for friends and relatives, and one for those in need. This festival emphasizes the importance of selflessness, charity, and compassion.
Mawlid al-Nabi
Mawlid al-Nabi, also known as the “Birth of the Prophet Muhammad,” is celebrated to honor the birth of the founder of Islam. Muslims express their love and admiration for Prophet Muhammad by engaging in various activities such as reading poetry, holding religious gatherings, and sharing stories about his life and teachings. This festival serves as a reminder of the Prophet’s exemplary character and teachings, promoting unity and brotherhood among Muslims.
Ashura
Ashura is a solemn day of remembrance for Muslims. It commemorates the martyrdom of Imam Hussein, the grandson of Prophet Muhammad, in the Battle of Karbala. This day holds great significance for the Shia Muslim community, who mourn the tragedy in various ways, including processions, reenactments, and recitations of elegies. It is a time for reflection, self-purification, and showing solidarity with those who sacrificed their lives for the greater good.
Ramadan
While not specifically a festival, Ramadan is a month of fasting and spiritual reflection observed by Muslims worldwide. It is a time of self-discipline, increased prayer, and acts of charity. During Ramadan, Muslims abstain from food, drink, and other physical needs from dawn to sunset, focusing on spiritual growth and seeking Allah’s blessings. This month fosters personal growth, self-control, and empathy for those less fortunate.
Islamic festivals are not only occasions for religious observance but also serve as vivid expressions of the rich and diverse Islamic culture. These celebrations reinforce the values of community, compassion, and devotion within the Islamic faith and provide opportunities for Muslims to connect with one another and strengthen bonds.
Islamic Traditions: Customs and Rituals
Islamic traditions encompass a wide range of customs and rituals that are deeply rooted in the religion of Islam. These traditions play a significant role in the daily lives of Muslims and provide a framework for their spiritual and social practices. Let’s explore some of the key customs and rituals that are observed by Muslims around the world.
Prayer
Prayer, or Salah, is one of the fundamental rituals in Islam. Muslims are required to pray five times a day, facing the Kaaba in Mecca, Saudi Arabia. The prayers are performed at specific times throughout the day and consist of recitations from the Quran, physical movements such as standing, bowing, and prostrating, and supplications to Allah. Prayer is seen as a means of connecting with Allah and seeking His guidance and mercy.
Fasting
Fasting, or Sawm, is another important Islamic tradition observed during the holy month of Ramadan. Muslims abstain from food, drink, and other physical needs from dawn until sunset. Fasting is seen as a way to purify the soul, practice self-discipline, and develop empathy for those less fortunate. The fast is broken each day with a meal called Iftar, usually with family and friends, and it is common for Muslims to gather for additional prayers and recitations during Ramadan.
Pilgrimage
The pilgrimage to Mecca, known as Hajj, is considered one of the five pillars of Islam and is a significant ritual for Muslims worldwide. Every year, millions of Muslims from around the world travel to Mecca to perform the Hajj, following the footsteps of Prophet Muhammad. The pilgrimage involves various rituals, including circumambulating the Kaaba, running between the hills of Safa and Marwa, and spending a day in the plain of Arafat. Hajj is a time of spiritual reflection and unity, as Muslims from different backgrounds come together to worship Allah.
Charity
Charity, or Zakat, is an integral part of Islamic tradition and is seen as a means of purifying one’s wealth and benefiting those in need. Muslims are required to donate a portion of their wealth to charity, which is used to support the poor, orphans, widows, and other vulnerable members of society. Zakat is not only a way to fulfill one’s obligation towards the less fortunate but also a means of remembering and appreciating the blessings provided by Allah.
Eid Celebrations
Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha are the two main annual festivals celebrated by Muslims worldwide. Eid al-Fitr marks the end of Ramadan and is a time of joy and gratitude. Muslims gather for special prayers, exchange gifts, visit family and friends, and enjoy festive meals. Eid al-Adha commemorates the willingness of Prophet Ibrahim to sacrifice his son as an act of obedience to Allah. Muslims mark this occasion by performing the ritual sacrifice of an animal, such as a sheep or cow, and distributing the meat to the needy.
Islamic Calligraphy
Islamic calligraphy is an art form that holds great significance in the Islamic world. It involves the artistic representation of verses from the Quran using intricate designs and beautiful Arabic script. Islamic calligraphy is not only visually appealing but also carries a spiritual message, as the words of Allah are honored and showcased through this art form.
Conclusion
Islamic traditions, customs, and rituals form an essential part of the rich cultural heritage of the Islamic world. From the daily prayers to the annual festivals, these traditions help Muslims deepen their connection to Allah, foster community bonds, and promote values of compassion, charity, and unity.
Islamic Education: Nurturing the Mind and Soul
The Islamic world has a rich tradition of valuing knowledge and education. Islamic education is not just about acquiring information, but it also plays a significant role in nurturing the mind and soul of individuals. It encompasses a holistic approach to learning that seeks to develop a person’s intellectual, spiritual, and moral dimensions.
In Islamic education, the Qur’an is considered the primary source of knowledge and guidance. It is revered as the word of God and serves as a comprehensive guide for Muslims in all aspects of life. The study of the Qur’an is a fundamental part of Islamic education, with students memorizing and analyzing its verses under the guidance of qualified teachers.
Islamic education also emphasizes the study of Hadith, which are the sayings and actions of the Prophet Muhammad. The Hadith provide further insights into how Muslims should live their lives and serve as a source of wisdom and guidance.
Islamic education is not limited to religious studies. It also encompasses various disciplines, including mathematics, science, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy. Islamic scholars made significant contributions to these fields, building upon the knowledge gained from ancient civilizations and their own unique perspectives.
Islamic educational institutions, such as madrasas and universities, have played a crucial role in preserving and transmitting knowledge throughout history. These institutions have not only served as centers of learning but also as hubs of cultural exchange and intellectual development.
In addition to formal education, informal education plays a vital role in Islamic societies. Sufi orders, for example, emphasize spiritual development through practices such as meditation, chanting, and self-reflection. These practices aim to cultivate a deep connection with God and enhance one’s spiritual well-being.
One unique aspect of Islamic education is its focus on character development. Islamic teachings emphasize virtues such as honesty, kindness, compassion, and patience. Students are taught to embody these qualities in their daily lives and interactions with others.
The principles of Islamic education continue to be relevant in the modern world. Islamic educational institutions, both traditional and contemporary, seek to empower individuals to become well-rounded and ethical members of society. They strive to instill a love for learning, critical thinking skills, and a strong moral compass.
In conclusion, Islamic education goes beyond the acquisition of knowledge. It aims to nurture the mind and soul, combining intellectual, spiritual, and moral development. The Islamic world’s rich educational tradition has contributed to diverse fields of study and continues to shape individuals’ lives, fostering a deep connection with God and inspiring a commitment to righteousness.
Islamic Heritage Sites: Preserving the Past
Islam has a rich and diverse history that spans over 1,400 years. Throughout the centuries, Islamic civilization has produced countless architectural marvels and cultural treasures that are testament to the creativity and ingenuity of Muslim societies. Today, these Islamic heritage sites stand as a reminder of the past and provide a glimpse into the vibrant history and culture of the Islamic world.
One of the most iconic Islamic heritage sites is the Hagia Sophia in Istanbul, Turkey. Originally built as a Christian basilica in the 6th century, it was later converted into a mosque during the Ottoman Empire. The Hagia Sophia is a masterpiece of Byzantine architecture and is known for its grand dome and intricate mosaics. Today, it serves as a museum and attracts millions of visitors who come to admire its beauty and historical significance.
Another remarkable Islamic heritage site is the Alhambra in Granada, Spain. Built during the Muslim rule in the 14th century, it is a splendid example of Islamic architecture and design. The Alhambra consists of a fortress, palaces, and gardens, all adorned with intricate geometric patterns, arabesques, and calligraphy. It is considered a masterpiece of Islamic art and a symbol of the rich Islamic heritage in Spain.
Moving eastward, we find the Taj Mahal in Agra, India. Built in the 17th century by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan, it is a mausoleum dedicated to his beloved wife. The Taj Mahal is renowned for its stunning white marble façade, delicate inlays, and symmetrical gardens. It is considered a masterpiece of Mughal architecture and is recognized as one of the Seven Wonders of the World.
In the heart of the Middle East, we find the city of Jerusalem, which is home to several Islamic heritage sites of immense importance. The Dome of the Rock, built in the 7th century, is one of the most recognizable landmarks in Jerusalem. It is a revered site for Muslims as it is believed to be the place where Prophet Muhammad ascended to heaven. The Al-Aqsa Mosque, adjacent to the Dome of the Rock, is one of the holiest sites in Islam and holds great religious significance.
Preserving these Islamic heritage sites is of utmost importance to ensure that future generations can appreciate and learn from the rich history and culture they represent. Governments and organizations play a vital role in their conservation and restoration efforts. Through these initiatives, these sites can continue to inspire and educate visitors from around the world, fostering a greater understanding and appreciation of the Islamic world’s vibrant cultural heritage.
Islamic Contributions to World History
The Islamic world has made significant contributions to world history in various fields, including science, mathematics, art, architecture, medicine, and philosophy. These contributions have had a lasting impact on the development of human civilization.
- Science: During the Islamic Golden Age, Muslim scholars made remarkable contributions to the field of science. They preserved and translated ancient Greek texts, advancing knowledge in fields such as astronomy, physics, chemistry, and biology. Muslim scientists, such as Ibn al-Haytham and Ibn Sina, made groundbreaking discoveries and laid the foundations for modern scientific methods.
- Mathematics: The Islamic world played a crucial role in the development of mathematics. Scholars like Al-Khwarizmi introduced the decimal system and algebra to the world. They also made significant contributions to trigonometry and geometry, which had a profound impact on the European Renaissance.
- Art and Architecture: Islamic art and architecture are known for their intricate designs, geometric patterns, and arabesque motifs. The Alhambra in Spain, the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem, and the Taj Mahal in India are just a few examples of the stunning Islamic architectural achievements.
- Medicine: Muslim physicians such as Ibn Sina (Avicenna) and Ibn al-Nafis made significant advancements in the field of medicine. Their works were translated into Latin and influenced European medical practices during the Middle Ages. They also developed sophisticated medical instruments and introduced the concept of hospitals as centers for healthcare.
- Philosophy: Islamic philosophy flourished during the medieval period, with scholars like Al-Farabi, Ibn Rushd (Averroes), and Ibn Sina contributing to the fields of metaphysics, ethics, and political philosophy. Their works not only preserved ancient Greek philosophy but also provided new insights into these subjects.
The Islamic world’s contributions to world history are diverse and far-reaching, shaping various aspects of human knowledge and culture. By recognizing and appreciating these contributions, we can gain a better understanding of the vibrant culture and rich history of the Islamic world.
Islamic Women: Empowerment and Equality
In the Islamic world, women play a significant role in society, culture, and history. Contrary to popular misconceptions, Islam promotes women’s empowerment and advocates for gender equality. Islamic teachings emphasize the importance of treating women with respect, dignity, and fairness.
1. Historical Contributions: Throughout history, Islamic women have made significant contributions to various fields such as art, literature, science, and politics. Renowned figures like Fatima al-Fihri, who founded the world’s oldest university in Morocco, and Razia Sultana, the first female ruler of Delhi Sultanate, serve as inspiring examples of empowered women in Islamic history.
2. Education and Knowledge: Islam places a strong emphasis on education, regardless of gender. The Prophet Muhammad himself encouraged both men and women to seek knowledge. Today, Muslim women are actively pursuing higher education and making substantial progress in various academic and professional fields. The achievements of Nobel laureate Malala Yousafzai and Arab mathematician Maryam Mirzakhani are testament to the potential and capabilities of Islamic women.
3. Equal Rights and Legal Protection: Islamic teachings emphasize the equality of all individuals, regardless of their gender. Islam grants women various rights, including the right to education, property ownership, and participation in public affairs. The implementation of Sharia law in many Islamic countries ensures legal protection for women’s rights, safeguarding their interests and promoting gender equality.
4. Professional Endeavors: Islamic women are actively participating in various professional endeavors. They serve as doctors, engineers, architects, teachers, lawyers, and entrepreneurs, among other professions. Their contributions have a significant impact on the socioeconomic development of their communities and play a vital role in shaping the future of the Islamic world.
5. Modesty and Empowerment: Modesty is an essential aspect of Islamic culture, and it is often misconstrued as oppressive to women. However, Islamic teachings regarding modesty are a source of empowerment for Muslim women. Modesty allows women to be recognized for their intellect, skills, and character rather than their physical appearance, providing them with a sense of inner confidence and strength.
In conclusion, Islamic women are strong, empowered, and actively contribute to society’s progress in various fields. Islam advocates for gender equality, providing women with the tools and opportunities necessary to succeed. By recognizing and celebrating the achievements of Islamic women, we can challenge stereotypes and foster a more inclusive and diverse society.
Islamic Charity: Giving Back to the Community
In Islam, giving to those in need is not only encouraged but considered a fundamental aspect of faith. Muslims around the world engage in various forms of charity to contribute to their communities and help those less fortunate. Islamic charity, known as “Sadaqah” or “Zakat,” plays a significant role in promoting social justice and alleviating poverty. Let’s explore the concept of Islamic charity and its impact on individuals and society.
Zakat: An Obligatory Form of Charity
Zakat is one of the Five Pillars of Islam and requires Muslims to give a percentage of their wealth to the needy. It is considered an obligatory act of worship and a means of purifying one’s wealth. The collected Zakat is distributed among various categories of recipients, including the poor, debtors, orphans, and travelers in need.
Sadaqah: Voluntary Acts of Charity
In addition to Zakat, Muslims are encouraged to engage in voluntary acts of charity known as Sadaqah. Sadaqah can take various forms, such as giving money, providing food, clothing, or offering help to those in need. It is seen as a way to enhance one’s spiritual growth and purify the soul.
The Impact of Islamic Charity
Islamic charity has a profound impact on both individuals and communities. It fosters a sense of compassion, generosity, and social responsibility among Muslims. By giving back to the community, Muslims contribute to the well-being of society and help create a more equitable and harmonious environment.
Islamic Charitable Institutions
To facilitate charitable giving and ensure efficient distribution of funds, various Islamic charitable institutions exist worldwide. These organizations work to collect and distribute Zakat and Sadaqah to the needy. They also provide a means for individuals to contribute to larger-scale projects, such as building schools, hospitals, and orphanages.
Examples of Islamic Charitable Practices
Islamic charity is not limited to monetary donations. Muslims also engage in other forms of charitable practices, such as volunteering their time and skills to help those in need. They actively participate in community service initiatives, disaster relief efforts, and other philanthropic activities.
Conclusion
Islamic charity is deeply rooted in the teachings of Islam and serves as a means to create a more compassionate and just society. Through acts of giving and service, Muslims contribute to uplifting their communities and helping those who are most vulnerable. By embodying the spirit of Islamic charity, individuals can experience personal growth and strengthen their connection with their faith and fellow human beings.
Islamic Environmentalism: Protecting the Earth
Islam places a strong emphasis on the protection and preservation of the environment. This belief is rooted in the Quran and the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad, who emphasized the importance of sustainable living and responsible stewardship of the Earth. Today, Islamic environmentalism is a growing movement that seeks to raise awareness about environmental issues and promote eco-friendly practices within Muslim communities.
1. The Quranic Teachings
The Quran, the holy book of Islam, acknowledges the Earth as a divine creation and emphasizes the responsibility of humans to be its custodians. It encourages believers to reflect on the intricate balance and beauty of nature as signs of God’s wisdom and power. Numerous verses in the Quran emphasize the importance of preserving the environment and avoiding wastefulness.
2. Conservation and Sustainable Practices
In line with the teachings of the Quran, Muslims are encouraged to adopt conservation and sustainable practices. This includes conserving water, reducing waste, and avoiding pollution. The concept of “Halal” extends to the environment as well, promoting the consumption of ethically sourced and eco-friendly products.
3. Tree Planting and Reforestation
Planting trees is highly regarded in Islamic teachings. Muslims are encouraged to plant trees and participate in reforestation efforts. The practice stems from the Hadith, the sayings and actions of the Prophet Muhammad, who emphasized the importance of planting trees for future generations.
4. Environmental Organizations
Islamic environmental organizations have emerged around the world to promote eco-friendly practices within Muslim communities. These organizations raise awareness about environmental issues, conduct educational programs, and implement sustainability initiatives.
5. Eco-Friendly Mosques
Mosques, as centers of worship and community, have also taken steps towards becoming more sustainable. Many mosques have implemented eco-friendly initiatives such as using renewable energy sources, recycling, and conserving water. These efforts serve as examples of how religious institutions can contribute to environmental preservation.
6. Sustainable Agriculture
Islamic teachings stress the importance of ethical treatment towards animals and the environment. This extends to agriculture, with concepts such as organic farming and animal welfare being encouraged. Islam promotes practices that ensure the well-being of livestock, protect biodiversity, and maintain soil fertility.
Conclusion
Islamic environmentalism is grounded in the Quranic teachings and the example set by Prophet Muhammad. It promotes responsible stewardship of the Earth and encourages Muslims to adopt sustainable practices in their daily lives. By raising awareness, implementing practical solutions, and advocating for environmental protection, Islamic environmentalism contributes to the global effort of preserving our planet for future generations.
Islamic Spirituality: The Path of Inner Peace
The Islamic faith is not just a set of beliefs and rituals, but a way of life that encompasses all aspects of an individual’s being. One of the key aspects of Islamic life is spirituality, which focuses on the inner journey of the soul towards God. Islamic spirituality provides a comprehensive framework for achieving inner peace, tranquility, and a deep connection with the divine.
At the heart of Islamic spirituality is the concept of Tawhid, which is the belief in the oneness of God. Muslims believe that there is no god but Allah, and that He is the creator of the universe and everything within it. This belief forms the foundation of Islamic spirituality and guides Muslims in their quest for spiritual growth and enlightenment.
The path of Islamic spirituality is marked by various practices and teachings, which help individuals cultivate a stronger connection with Allah and attain inner peace:
- Prayer (Salah): Muslims are required to pray five times a day, facing the Kaaba in Mecca. Prayer is not only a means of worshipping God, but also a way to seek His guidance, forgiveness, and blessings. It serves as a constant reminder of the presence of Allah and helps individuals stay connected to Him throughout the day.
- Recitation of the Quran: The Quran is the holy book of Islam and is considered the word of Allah. Muslims are encouraged to recite and reflect upon its verses regularly. This practice helps individuals deepen their understanding of the Islamic teachings and provides spiritual nourishment for the soul.
- Charity (Zakat): Giving to the poor and needy is an integral part of Islamic spirituality. Muslims are required to give a portion of their wealth to those less fortunate, which helps cultivate feelings of compassion, empathy, and gratitude. It is believed that acts of charity not only benefit the recipients but also purify the giver’s heart and increase spiritual growth.
- Fasting (Sawm): Muslims fast from dawn to sunset during the holy month of Ramadan. Fasting is not only an act of self-discipline and self-control but also a means of purifying the soul. It helps individuals develop empathy for the less fortunate, increase mindfulness and self-awareness, and strengthen their connection with Allah.
- Pilgrimage (Hajj): Performing the Hajj, or pilgrimage to the holy city of Mecca, is a significant spiritual journey for Muslims. It is a physical and spiritual journey that symbolizes unity, humility, and submission to Allah. The pilgrimage serves as a powerful reminder of the ultimate purpose of life and reinforces the spiritual bond between Allah and His worshipers.
In addition to these practices, Islamic spirituality emphasizes the importance of cultivating virtuous qualities such as patience, gratitude, humility, and forgiveness. It encourages individuals to lead a balanced life, seeking both worldly success and spiritual growth.
Islamic spirituality offers a transformative path towards inner peace and spiritual enlightenment. It provides practical guidance and tools for individuals seeking a deeper connection with Allah and a greater understanding of the purpose of life. By following the teachings and practices of Islam, one can embark on a journey of self-discovery, self-improvement, and spiritual fulfillment.
Islamic Diversity: Unity in Differences
Islamic culture and civilization are known for their incredible diversity. Though united by their common faith in Islam, Muslims around the world have developed unique customs, traditions, and practices influenced by their history, geography, and local culture.
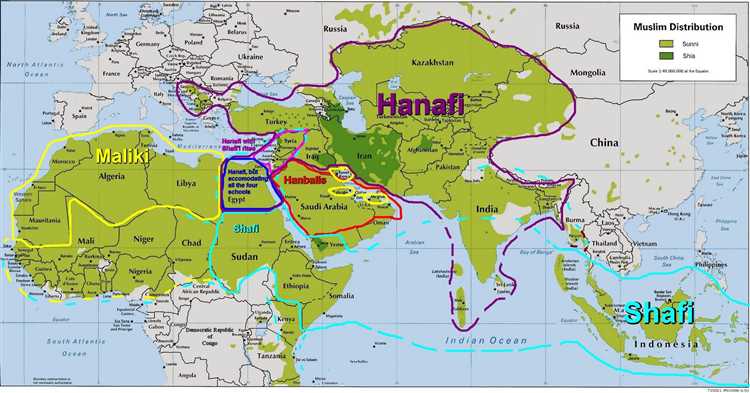
One of the most striking examples of Islamic diversity can be seen in the different interpretations and traditions within the religion itself. While all Muslims follow the fundamental teachings of the Quran and the Prophet Muhammad, they may have varying beliefs and practices based on different schools of thought or sects, such as Sunni and Shia. This diversity within Islam adds richness and depth to the religion, allowing for a wide range of perspectives and understandings.
Along with these theological differences, the Islamic world showcases remarkable cultural diversity. Islam spread from its origins in the Arabian Peninsula across Africa, Asia, and Europe, leading to the blending of various cultures and traditions. As a result, Islamic art, architecture, music, and cuisine reflect the influences of different regions and societies.
For example, the Moorish architecture of Spain, with its intricate geometric patterns and stunning tilework, is a testament to the Islamic influence in the region. The use of calligraphy as a form of artistic expression is also a distinctive feature of Islamic culture, whether in the beautiful Quranic manuscripts of the Ottoman Empire or the ornate inscriptions in mosques and religious buildings across the Arab world.
The diverse traditions of Islamic music and dance are another testament to the richness of Islamic culture. From the soulful Sufi music and dance ceremonies in Turkey and Pakistan to the vibrant sound of qawwali in India and the rhythmic beats of Gnawa music in Morocco, each region has developed its own unique musical style, reflecting its local customs and heritage.
Furthermore, Islamic culture encompasses a wide range of traditional clothing styles, with various forms of dress being influenced by local customs, climate, and social norms. For instance, the abaya and hijab worn by women in Saudi Arabia differ from the vibrant and embroidered sarees worn by Muslim women in countries like India and Pakistan.
This cultural diversity extends beyond the boundaries of the Islamic world, as Muslim communities have migrated and settled in different parts of the globe. These diaspora communities have preserved their Islamic identity while assimilating with their host cultures, resulting in unique expressions of Islam that reflect the diversity of the countries they now call home.
In conclusion, Islamic diversity is a reflection of the rich history and cultural heritage of the Islamic world. It manifests in a variety of forms, including theological differences, artistic expressions, musical traditions, and clothing styles. Despite these differences, there is a sense of unity among Muslims, as they are bound by a shared faith and the core principles of Islam. Embracing this diversity allows for a greater appreciation and understanding of the vibrant culture and traditions of the Islamic world.
FAQ
What are some key historical events in the Islamic world?
The Islamic world has a rich and diverse history, with several key events that have shaped its culture. Some of these include the birth of Islam, the expansion of the Muslim empire, the Caliphate, the Crusades, the Ottoman Empire, and the Age of Exploration.
What are some popular tourist destinations in the Islamic world?
The Islamic world is home to numerous popular tourist destinations. Some of the most well-known include the Taj Mahal in India, the Pyramids of Egypt, the Alhambra in Spain, the Blue Mosque in Turkey, and the Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque in Abu Dhabi. These destinations offer a glimpse into the vibrant culture and architectural wonders of the Islamic world.
How can I experience the vibrant culture of the Islamic world?
To experience the vibrant culture of the Islamic world, you can visit markets, or souks, where you can shop for traditional handicrafts, spices, and textiles. You can also try traditional cuisine, such as kebabs, hummus, and baklava. Additionally, attending a traditional music or dance performance, or visiting a mosque and witnessing religious rituals, can also provide insight into the rich culture of the Islamic world.
What is the significance of calligraphy in the Islamic world?
Calligraphy holds a significant place in Islamic culture. It is considered a visual representation of the divine word and is widely used in the decoration of mosques, manuscripts, and other Islamic art forms. Calligraphy has its roots in the Qur’an, as Muslims believe that the words of the Qur’an are directly from God and should be beautifully written and respected.
What are some famous Islamic scholars?
The Islamic world has produced many notable scholars throughout history. Some of the most famous include Ibn Sina (Avicenna), who was a philosopher and physician in the 11th century, and Ibn Rushd (Averroes), who was a prominent philosopher and jurist in the 12th century. Other notable scholars include Al-Farabi, Al-Ghazali, and Ibn Khaldun.
How has Islamic art influenced the world?
Islamic art is known for its intricate geometric patterns, arabesques, and calligraphy. These art forms have had a significant influence on the world, particularly in areas such as architecture, textiles, and carpet weaving. The beauty and craftsmanship of Islamic art have inspired artists and designers from various cultures, leading to the incorporation of Islamic artistic elements into different art forms.
What are some similarities and differences between the different Islamic cultures?
While the Islamic world is diverse, there are a few similarities that can be seen across different Islamic cultures. These include a shared religious faith in Islam, the importance of community and family, and the veneration of Prophet Muhammad. However, there are also notable differences, such as variations in language, customs, and traditions. For example, the dress, cuisine, and music may differ between different Islamic cultures.