Islam is one of the world’s major religions, with over 1.8 billion followers worldwide. It is often misunderstood and confused with the term “Muslim.” While both terms are related to the religion of Islam, they have distinct meanings and contexts.
Islamic refers to anything related to Islam, its teachings, principles, and practices. It is an adjective that describes the religion itself, such as Islamic art, Islamic law, or Islamic culture. The word “Islamic” originates from the Arabic word “Islam,” which means submission or surrender to God’s will.
Muslim is a noun that refers to a person who follows or practices Islam. It is an identity term used to describe individuals who believe in and adhere to the teachings of Islam. The word “Muslim” also comes from the Arabic language and means “one who submits to God.”
While all Muslims are followers of Islam, not all things related to Islam are exclusive to Muslims. For example, Islamic art can be appreciated and studied by people of all faiths and backgrounds. Understanding this difference between “Islamic” and “Muslim” is crucial to avoid generalizations and stereotypes when discussing the religion of Islam and its followers.
It is important to respect the diversity within the Muslim community and recognize that Islam is a religion that encompasses various cultural practices and interpretations.
In conclusion, “Islamic” refers to anything related to the religion of Islam, while “Muslim” refers to an individual who practices Islam. By understanding the difference between the two terms, we can foster a better understanding and appreciation for the beliefs and practices of Muslims around the world.
Understanding the Difference Between Islamic and Muslim
Islamic and Muslim are terms that are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings.
Islamic refers to anything related to the religion of Islam. It encompasses the beliefs, practices, and principles that are based on the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad as recorded in the holy book of Islam, the Quran.
Muslim, on the other hand, refers to an individual who follows Islam. A Muslim is someone who believes in and submits to the teachings of Islam, practices the various rituals and obligations prescribed by the religion, and seeks to lead a life in accordance with Islamic principles.
In simpler terms, Islamic pertains to the religion itself, while Muslim is used to describe the followers of that religion.
Here are a few key points to better understand the difference:
- Islamic: Relating to the religion of Islam as a whole.
- Muslim: A person who practices Islam and follows Islamic teachings.
It is also worth noting that not all Muslims are the same. There are different sects and interpretations within Islam, leading to variations in practices and beliefs. Some of the major sects include Sunni, Shia, and Sufism.
Furthermore, it is important to approach discussions about Islam and Muslims with respect and cultural sensitivity. It is always best to learn from reliable sources and engage in dialogue to gain a better understanding of both the religion and its followers.
Acknowledging and understanding the difference between Islamic and Muslim can help foster better interfaith relations, combat stereotypes, and promote religious tolerance and mutual respect.
The Origins of Islam and Muslim
Islam: Islam is a monotheistic religion that originated in the 7th century CE in the Arabian Peninsula. It was founded by the Prophet Muhammad, who is considered the last and final messenger of God in Islam. Muhammad received revelations from God through the angel Gabriel and composed the holy book of Islam, the Quran. Islam is based on the teachings and beliefs outlined in the Quran and the Hadith (sayings and actions of the Prophet Muhammad).
Muslim: The term “Muslim” refers to an individual who follows or practices Islam. Muslims believe in the teachings of Islam as outlined in the Quran and the Hadith. They believe in the oneness of God and the prophethood of Muhammad. In addition to the Quran and the Hadith, Muslims also follow the teachings and interpretations of Islamic scholars and jurists.
It is important to note that Islam and Muslim are two distinct terms. Islam refers to the religion itself, while Muslim refers to the individuals who follow and practice the religion. Not all individuals from Islamic countries or regions are necessarily Muslims, as there are other religious and ethnic groups present in these areas.
Islam has a rich history and has spread to various regions around the world. The religion played a significant role in shaping the cultures, societies, and civilizations in these areas. Today, Islam is one of the major religions in the world, with millions of followers globally.
Key Principles of Islam and Muslim
1. Monotheism:
Islam is based on the belief in the oneness of God, known as Tawhid. Muslims believe that there is only one God, Allah, and reject the idea of Trinity or multiple gods.
2. Submission to God:
The word “Islam” itself means “submission” or “surrender”. Muslims strive to submit themselves completely to the will of God and follow His commandments as revealed in the Quran.
3. Quran as the Final Revelation:
According to Muslims, the Quran is the word of God and the final revelation to humanity. It is considered the ultimate source of guidance for all aspects of life, including spiritual, moral, and social matters.
4. Prophethood:
Muslims believe in the prophethood of Muhammad, who is considered the last and final messenger of God. They also believe in the earlier prophets, including Abraham, Moses, and Jesus, and honor them as highly respected figures.
5. Five Pillars of Islam:
- Shahada: The declaration of faith, which states that there is no god but Allah and Muhammad is His messenger.
- Salah: The five daily prayers performed facing the Kaaba in Mecca.
- Zakat: The giving of a specific portion of one’s wealth to the poor and needy.
- Sawm: Fasting during the month of Ramadan, from dawn to sunset.
- Hajj: The pilgrimage to Mecca, which every able-bodied and financially capable Muslim is expected to make at least once in their lifetime.
6. Moral and Ethical Guidelines:
Islam places a strong emphasis on moral and ethical values, including honesty, compassion, justice, and respect for others. Muslims are encouraged to lead a righteous and virtuous life, following the teachings of Islam.
7. Importance of the Afterlife:
Belief in the afterlife is a fundamental principle of Islam. Muslims believe in the Day of Judgment, where individuals will be held accountable for their actions in this world. Life after death is seen as eternal, with Paradise as the reward for the righteous and Hell as the punishment for the wicked.
8. Brotherhood and Unity:
Islam promotes the concept of brotherhood and unity among its followers. Muslims are encouraged to treat each other with kindness, fairness, and respect, regardless of their race, nationality, or social status. The ummah, or the worldwide Muslim community, is seen as one unified entity.
9. Role of Women:
Islam recognizes the equal spiritual worth of men and women, but also assigns them different roles and responsibilities based on their nature and abilities. Women have specific rights and obligations within the family and society, including the right to education, work, and inheritance.
10. Continuous Seek for Knowledge:
Islam emphasizes the importance of knowledge and encourages Muslims to seek knowledge throughout their lives. This includes both religious and secular knowledge, as the pursuit of knowledge is seen as a way to understand and appreciate the signs of God’s creation.
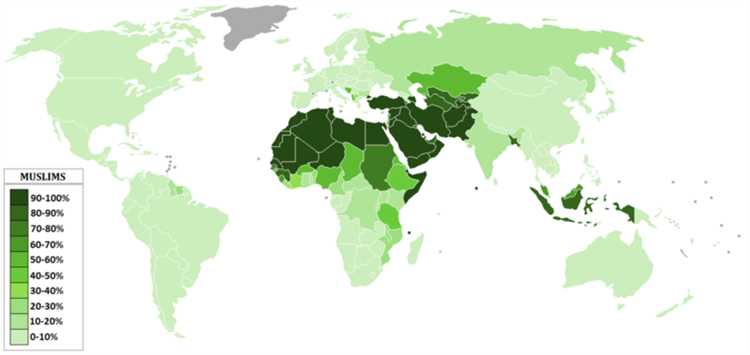
Different Geographical Distribution of Islam and Muslim
Islam is a religion that originated in the 7th century in the Arabian Peninsula, specifically in present-day Saudi Arabia. It was founded by Prophet Muhammad, who is considered the last and final prophet by Muslims. Since its inception, Islam has spread across the world and has become one of the major religions.
The distribution of Islam is not evenly spread across the globe. It has a strong presence in certain regions while being a minority in others. Geographical distribution is influenced by various factors, including historical, cultural, and political reasons.
Majority Muslim Countries
The largest Muslim populations are found in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. These regions are home to countries with a majority Muslim population. Some of the countries with the highest Muslim populations include:
- Indonesia: With around 230 million Muslims, Indonesia has the largest Muslim population in the world.
- Pakistan: With approximately 210 million Muslims, Pakistan is the second most populous Muslim-majority country.
- India: Despite being a Hindu-majority country, India has the third-largest Muslim population in the world, with over 190 million Muslims.
- Bangladesh: With over 160 million Muslims, Bangladesh is another country with a significant Muslim population.
- Egypt: Egypt is the most populous Arab country and has a large Muslim population of around 100 million.
Minority Muslim Populations
In addition to the majority Muslim countries, there are also countries where Muslims are a minority. These include countries in Europe, the Americas, and other parts of the world. Some examples of countries with a significant Muslim minority population are:
- United States: Islam is one of the fastest-growing religions in the United States, with an estimated 3.45 million Muslims.
- France: Due to historical ties with North Africa, France has a significant Muslim population, estimated to be around 5-6 million.
- United Kingdom: The United Kingdom is home to approximately 3 million Muslims.
- China: China has a significant Muslim population, concentrated primarily in the western regions such as Xinjiang and Ningxia.
Impact on Culture and Society
The geographical distribution of Islam and Muslim populations has had a significant impact on the cultures and societies of different regions. It has influenced art, architecture, language, cuisine, and various other aspects of daily life.
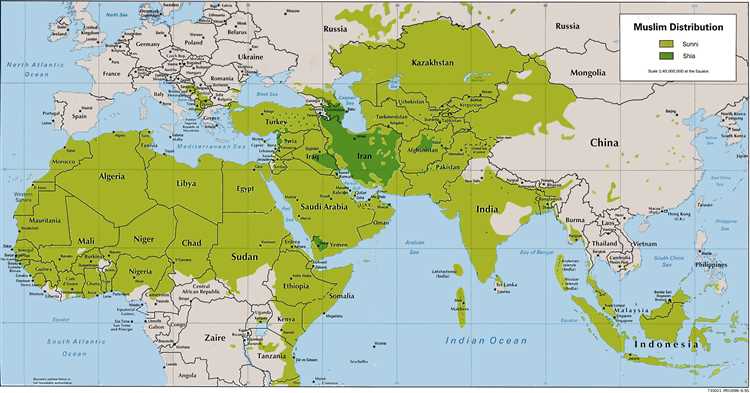
Islamic traditions and practices vary across different regions, influenced by local customs and traditions. This diversity is reflected in the different sects and schools of thought within Islam, ranging from Sunni to Shia to Sufism.
The geographical distribution of Islam and Muslims continues to evolve as a result of migration, globalization, and other factors. Understanding these demographic patterns helps in appreciating the diverse nature of the Islamic faith and its followers around the world.
Similarities and Differences in Religious Practices of Islam and Muslim
While Islam and Muslim are often used interchangeably, it is important to understand that Islam refers to the religion itself, whereas Muslim refers to the people who follow Islam. In terms of religious practices, there are both similarities and differences between Islam and its followers, the Muslims.
Similarities:
- The Five Pillars: Both Islam and Muslims adhere to the Five Pillars, which are the foundational acts of worship in Islam. These pillars include the declaration of faith (Shahada), prayer (Salat), giving to charity (Zakat), fasting during Ramadan (Sawm), and pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj) for those who are able.
- The Qur’an: The Qur’an serves as the holy book for both Islam and Muslims. It is believed to be the word of God as revealed to the Prophet Muhammad.
- Prophet Muhammad: Both Islam and Muslims hold Prophet Muhammad in high regard. They believe that he was the final prophet sent by God to guide humanity.
- Mosques: Mosques serve as places of worship for both Islam and Muslims. They are used for congregational prayers, religious gatherings, and educational purposes.
Differences:
- Sects: Islam is comprised of different sects, such as Sunni and Shia, while the term Muslim does not specify any particular sect. Each sect may have its own distinct religious practices and traditions.
- Prayer Practices: Although prayer is a common practice in both Islam and among Muslims, there might be differences in the way prayers are performed. For example, some sects may have variations in the number of units (rak’ahs) or the recitation of supplications.
- Religious Holidays: While both Islam and Muslims celebrate religious holidays, different sects may observe specific holidays or commemorate certain events in different ways. For example, Shia Muslims have additional days of mourning to commemorate the martyrdom of Imam Hussein.
- Legal Schools of Thought: Islam encompasses different legal schools of thought, known as madhahib, which might result in subtle differences in religious practices among Muslims. These differences can include interpretations of religious texts, laws, and customs.
Overall, while there are certain similarities in religious practices between Islam and Muslims, it is important to recognize and respect the diversity within the Muslim community in terms of sects, prayer practices, holidays, and legal schools of thought.
Different Interpretations of Islam and Muslim
Islam is a religion that has various interpretations and understandings. Muslims, as followers of Islam, also have diverse perspectives and beliefs that shape their understanding and practice of the religion.
One of the major differences in interpretations of Islam lies in the understanding of Islamic law, known as Sharia. Sharia is derived from the Quran and the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad. However, different scholars and sects interpret and apply these principles in various ways. This has led to different schools of thought within Islam, such as Sunni, Shia, and Ibadi, each with its own interpretations of Islamic law.
The Sunni sect is the largest branch of Islam and follows the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad and his companions. They believe in following the consensus of the Muslim community and rely on sources such as the Quran and Hadith (sayings and actions of the Prophet) for guidance. On the other hand, the Shia sect holds the belief that the leadership of the Muslim community should be derived from the lineage of the Prophet Muhammad through his cousin, Ali, and his descendants.
Another area of difference in interpretations is the role of women in Islam. While the Quran and Hadith provide guidelines for the treatment and rights of women, different interpretations can lead to varied practices. Some interpretations may restrict women’s roles to traditional gender roles, while others advocate for gender equality and women’s rights.
Additionally, interpretations of jihad, which is often misunderstood as a holy war, can vary. Some interpret jihad as an internal spiritual struggle to purify oneself, while others view it as an external struggle to defend Islam or fight oppression. The different interpretations of jihad have led to diverse approaches to violence and conflict among Muslims.
It is important to recognize and respect the diversity of interpretations within Islam and the Muslim community. These variations highlight the complexity and richness of the religion and emphasize the individual agency of Muslims to determine their own beliefs and practices within the framework of Islam.
Historical Background of Islam and Muslim
The history of Islam and the Muslim community can be traced back to the 7th century CE. The religion of Islam was founded by Prophet Muhammad, who was born in the city of Mecca in present-day Saudi Arabia. Muhammad received revelations from God, which were later compiled into the holy book of Islam known as the Quran.
The early years of Islam were challenging, as Prophet Muhammad faced opposition from the ruling tribes of Mecca. However, the Muslim community gradually grew in number and strength. In 622 CE, Muhammad and his followers migrated to the city of Medina, in an event known as the Hijra, marking the beginning of the Islamic calendar.
During Muhammad’s lifetime, Islam spread rapidly in the Arabian Peninsula. After his death in 632 CE, the Muslim community expanded beyond the Arabian Peninsula and conquered vast territories, establishing one of the largest empires in history.
The spread of Islam was not only through military conquest but also through peaceful means, as Muslim traders and scholars carried the message of Islam to different parts of the world. Islam reached regions as far as Spain in the West and India in the East.
Over time, different empires and dynasties were formed by Muslim rulers, such as the Umayyads, Abbasids, and Ottomans. These empires had significant contributions to Islamic art, science, and culture.
The diversity within the Muslim community grew as Islam expanded and encountered different cultures and civilizations. Today, Muslims come from various ethnic backgrounds and live in different parts of the world.
The historical background of Islam and Muslims is rich and complex, encompassing a wide range of events and developments over the centuries. Understanding this history is crucial for gaining a comprehensive understanding of the Islamic faith and the Muslim community.
Significance of Islamic and Muslim Holidays
Islamic and Muslim holidays hold a significant place in the lives of individuals who follow the religion of Islam. These holidays serve as a means to commemorate important events and celebrate fundamental beliefs of the faith. They also provide an opportunity for Muslims to come together in prayer, reflection, and the strengthening of their community bonds.
Eid al-Fitr: This holiday marks the end of Ramadan, the holy month of fasting. Muslims worldwide celebrate this occasion by gathering for special prayers, exchanging gifts, and partaking in festive meals. It is a time of joy and gratitude, as individuals express their appreciation for the blessings they have received throughout the month of Ramadan.
Eid al-Adha: Also known as the Feast of Sacrifice, Eid al-Adha commemorates the willingness of Ibrahim (Abraham) to sacrifice his son as an act of obedience to God. Muslims celebrate this holiday by performing the ritual of animal sacrifice, distributing meat to the less fortunate, and engaging in acts of charity and goodwill.
Mawlid al-Nabi: This holiday is observed to commemorate the birth of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Muslims honor Muhammad’s life and teachings by reciting prayers, participating in processions, and engaging in acts of charity. It is a time of reflection and gratitude for the role that Muhammad played in spreading the message of Islam.
Ashura: Ashura is a day of fasting that commemorates various significant events in Islamic history, including the liberation of the Israelites from Egypt, the deliverance of Prophet Muhammad’s grandson Imam Husayn from captivity, and the day Noah’s Ark settled on Mount Ararat. It is a day of reflection, mourning, and self-discipline for Muslims.
Islamic New Year: The Islamic New Year marks the migration of Prophet Muhammad from Mecca to Medina. Muslims reflect on this event and use it as an opportunity to set spiritual goals, make resolutions, and seek personal growth in the upcoming year.
Laylatul Qadr: Laylatul Qadr, also known as the Night of Power, is considered the holiest night in the Islamic calendar. Muslims spend this night in prayer, seeking forgiveness, guidance, and blessings from God. It is believed to be the night when the first verses of the Quran were revealed to Prophet Muhammad.
These holidays are not only of religious importance but also provide Muslims with an opportunity to connect with their faith, reflect on their spiritual journey, and strengthen their relationships with others. They serve as reminders of the core values of Islam, such as gratitude, compassion, and self-discipline.
| Holiday | Date |
|---|---|
| Eid al-Fitr | 1st day of Shawwal (10th month of the Islamic lunar calendar) |
| Eid al-Adha | 10th day of Dhu al-Hijjah (12th month of the Islamic lunar calendar) |
| Mawlid al-Nabi | 12th day of Rabi’ al-Awwal (3rd month of the Islamic lunar calendar) |
| Ashura | 10th day of Muharram (1st month of the Islamic lunar calendar) |
| Islamic New Year | 1st day of Muharram (1st month of the Islamic lunar calendar) |
| Laylatul Qadr | Last 10 nights of Ramadan (9th month of the Islamic lunar calendar) |
Islamic and Muslim Dietary Restrictions
Islamic and Muslim dietary restrictions play a significant role in the daily lives and practices of followers of Islam. These restrictions are based on the principles outlined in the Quran (the holy book of Islam) and the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad. Understanding and adhering to these dietary restrictions is considered an essential aspect of practicing Islam.
Halal:
Halal is an Arabic word that translates to “permissible” in English. In terms of food, halal refers to any item or product that is allowed or lawful according to Islamic law. Halal dietary restrictions are derived from specific guidelines set forth in the Quran.
Some key points regarding halal dietary restrictions:
- All meats consumed by Muslims must be from animals that have been slaughtered in accordance with Islamic principles. This involves pronouncing the name of Allah and using a sharp instrument to swiftly sever the animal’s throat, ensuring a quick and humane death.
- Pork and pork products are strictly prohibited in Islam. Muslims are not allowed to consume any food that contains pork or its by-products.
- Alcohol and intoxicating substances are also forbidden in Islam. This includes consuming, selling, or facilitating the use of such substances in any form.
Haram:
Haram is the opposite of halal, meaning “forbidden” in Arabic. Haram refers to any food or substance that is prohibited by Islamic law. Muslims are obliged to avoid consuming anything that is considered haram.
Some examples of haram food items include:
- Pork and pork products
- Alcohol and intoxicating substances
- Meat from animals that have not been slaughtered according to Islamic principles
- Any food items containing ingredients derived from animals not slaughtered in the halal manner
Eating Etiquette:
In addition to dietary restrictions, there are also guidelines and etiquette that Muslims follow while eating:
- Bismillah: Before consuming any food, Muslims typically say “Bismillah” (In the name of Allah) as a way of acknowledging and seeking the blessings of Allah.
- Eating with the right hand: It is customary for Muslims to eat with their right hand, as the left hand is considered unclean.
- Sharing food: Sharing food with others, especially those in need, is highly encouraged in Islam as an act of charity and generosity.
Conclusion:
Islamic and Muslim dietary restrictions form an integral part of Islamic practice and have significant cultural and religious importance for Muslims worldwide. Adhering to these restrictions not only reflects a commitment to religious beliefs but also promotes self-discipline, mindfulness, and respect for the environment.
Islamic and Muslim Role Models
Islamic and Muslim role models are individuals who exemplify the teachings and values of Islam and serve as inspiring figures for others in the Muslim community. These role models are recognized for their piety, character, contributions to society, and adherence to Islamic principles.
Role models play a crucial role in shaping the behavior and aspirations of individuals, especially for younger Muslims who look up to them for guidance. By following the footsteps of these role models, Muslims strive to cultivate a deep connection with their faith, strengthen their moral character, and make positive contributions to their communities.
Islamic history and literature are replete with stories of great individuals who serve as role models for Muslims worldwide. Here are a few examples of some prominent Islamic and Muslim role models:
- Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him): The Prophet Muhammad is considered the ultimate role model for Muslims. His life and teachings serve as a guide and inspiration for Muslims in all aspects of their life, including faith, worship, family, and social conduct.
- Khadijah bint Khuwaylid: Khadijah was the first wife of Prophet Muhammad and a prominent figure in early Islamic history. She was a successful businesswoman known for her intelligence, compassion, and unwavering support for the Prophet Muhammad.
- Omar ibn Al-Khattab: Omar ibn Al-Khattab was the second caliph of Islam and known for his strong leadership, justice, and commitment to upholding the principles of Islam. His reign was marked by social welfare programs, expansion of Islamic territories, and establishment of a fair judicial system.
- Rabi’a al-Adawiyya: Rabi’a al-Adawiyya was a renowned female Islamic mystic and poet. She is remembered for her devotion to God, asceticism, and her teachings on selfless love and the pursuit of inner spirituality.
In addition to these historical figures, contemporary Islamic and Muslim role models also exist. These individuals are often scholars, activists, professionals, or community leaders who embody Islamic values and principles in their daily lives.
| Name | Field/Contribution |
|---|---|
| Malala Yousafzai | Education and advocacy for girls’ rights |
| Tariq Ramadan | Islamic scholar and advocate for interfaith dialogue |
| Ibtihaj Muhammad | Olympic fencer and advocate for Muslim representation in sports |
| Mohamed Salah | Professional footballer and role model for young Muslims |
It is important to note that Islamic and Muslim role models can differ from one individual to another, depending on personal experiences, cultural backgrounds, and the specific areas of inspiration sought after. Nevertheless, these role models collectively inspire Muslims to strive for excellence, uphold their faith, and make a positive impact in the world.
Islamic and Muslim Places of Worship
Islamic and Muslim places of worship play a significant role in the lives of Muslims. These places serve as community centers, educational institutions, and spiritual sanctuaries. There are a few different names for these places of worship, depending on the cultural and regional context.
Mosque: The most commonly used term for a Muslim place of worship is “mosque.” Mosques are considered the central gathering places for Muslims, where they come together for daily prayers, Friday sermons, and community events. They usually have an open hall with a designated area for prayer, often called a prayer hall or musalla. Mosques can vary in size and architectural styles, reflecting the cultural diversity of the Muslim world.
Masjid: “Masjid” is another term used to refer to a Muslim place of worship. The word “masjid” is of Arabic origin and is commonly used in many parts of the world. It has the same meaning as “mosque” and is often used interchangeably.
Jamia Mosque: A “jamia mosque” refers to a mosque that serves as a central hub for a Muslim community. It is usually larger in size and often includes additional facilities such as educational institutes, libraries, and community centers. The term “jamia” means “unification” or “congregation” in Arabic, emphasizing the role of these mosques in fostering unity and community cohesion.
Masjid al-Haram: Known as the “Sacred Mosque,” Masjid al-Haram is one of the holiest sites in Islam. Located in Mecca, Saudi Arabia, it surrounds the Kaaba, which is considered the most sacred site in Islam. Muslims from all over the world come to Masjid al-Haram to perform the Hajj pilgrimage and the Umrah, as well as to pray and seek spiritual blessings.
Masjid an-Nabawi: Also known as the “Prophet’s Mosque,” Masjid an-Nabawi is located in Medina, Saudi Arabia. It is the second holiest site in Islam after Masjid al-Haram. The mosque holds immense religious and historical significance as it houses the tomb of the Prophet Muhammad. Muslims visit Masjid an-Nabawi to offer prayers and pay their respects to the Prophet.
Masjid-e-Nabawi: The term “Masjid-e-Nabawi” is commonly used in South Asia to refer to Masjid an-Nabawi. The addition of “-e-” in the name is a grammatical feature in many South Asian languages.
Islamic Center: While not specifically a place of worship, Islamic centers are important institutions within the Muslim community. They serve a range of purposes, including offering religious education, hosting community events, and providing social services. Islamic centers often have prayer halls, classrooms, libraries, and recreational facilities, catering to the diverse needs of the Muslim community.
Overall, Islamic and Muslim places of worship serve as focal points for the Muslim community, providing spiritual guidance, fostering a sense of belonging, and promoting social cohesion among Muslims.
Islamic and Muslim Contributions to Art and Culture
The Islamic and Muslim civilizations have made significant contributions to art and culture throughout history. These contributions have helped shape various art forms and cultural practices that we see today.
1. Calligraphy:
Islamic calligraphy, also known as “beautiful writing,” is an important art form within the Islamic tradition. It is characterized by its elaborate designs and intricate lettering. Calligraphy has been used to beautify religious texts, architectural structures, and everyday objects such as pottery and textiles.
2. Architecture:
Islamic architecture is renowned for its distinctive features, such as domes, minarets, and intricate geometric patterns. The design of mosques and palaces often incorporates these elements to create visually stunning structures. Notable examples include the Taj Mahal in India and the Alhambra in Spain.
3. Music:
Muslim musicians have played a significant role in developing classical music traditions. One example is the maqam system in Arabic music, which consists of specific scales and melodic patterns. Muslim musicians have also contributed to the development of instruments such as the oud (a stringed instrument similar to a lute) and the tabla (a pair of drums).
4. Literature:
Islamic literature encompasses a wide range of genres, including poetry, prose, and religious texts. One of the most famous works is the Quran, which is considered the holy book of Islam. Muslim writers and poets have made significant contributions to literature in various languages, such as Arabic, Persian, and Urdu.
5. Science and Mathematics:
The Islamic Golden Age, a period from the 8th to the 14th centuries, saw significant advancements in science and mathematics. Muslim scholars made groundbreaking contributions in fields such as astronomy, medicine, chemistry, and algebra. Their discoveries and theories had a lasting impact on scientific knowledge.
6. Textiles and Carpets:
Islamic civilizations have a rich tradition of textile and carpet weaving. Intricate patterns and designs are woven into textiles and carpets using a variety of techniques. These textiles are not only decorative but also serve as a means of self-expression and cultural identity.
Summary:
The Islamic and Muslim civilizations have made substantial contributions to art and culture. From calligraphy to architecture, music to literature, science to textiles, their impact can be seen in various art forms and cultural practices that continue to thrive today.
Islamic and Muslim Influence in Science and Technology
The Islamic civilization has made significant contributions to various fields of science and technology throughout history. The advancements made during this era greatly influenced the development of modern scientific and technological knowledge.
- Astronomy: Islamic scholars played a crucial role in advancing astronomy. They built observatories, developed sophisticated astronomical instruments, and made significant discoveries. For example, the famous Iranian astronomer, Al-Khwarizmi, accurately calculated the length of a year and contributed to trigonometry.
- Mathematics: Islamic mathematicians introduced the concept of algebra, revolutionizing the field of mathematics. Scholars such as Al-Khwarizmi and Al-Kindi laid the foundation for modern algebraic notation and algorithms. They also made significant advancements in areas like geometry and trigonometry.
- Medicine: Muslim physicians made remarkable progress in medicine. The renowned physician Ibn Sina (Avicenna) wrote the influential medical encyclopedia, “The Canon of Medicine.” The book became a standard medical textbook in Europe for several centuries and greatly contributed to the understanding of human anatomy and the development of pharmacology.
- Engineering: The Islamic world witnessed remarkable achievements in engineering. Islamic engineers constructed grand buildings, mosques, and palaces with innovative architectural techniques. They developed systems like irrigation, water management, and techniques in hydraulic engineering that revolutionized agriculture and irrigation practices.
- Chemistry: The field of chemistry also flourished during the Islamic Golden Age. Scholars like Jabir Ibn Hayyan (Geber) greatly contributed to the development of alchemy and laid the groundwork for modern chemistry. Their experiments and discoveries led to advancements in areas such as distillation and chemical processes.
The Muslim world’s emphasis on education, scholarship, and scientific inquiry fostered an environment conducive to these advancements. Scholars and researchers from diverse backgrounds exchanged knowledge and ideas, leading to a rich scientific and technological heritage.
| Field | Contributions |
|---|---|
| Astronomy | Observatories, accurate calculations, astronomical instruments |
| Mathematics | Introduction of algebra, advancements in geometry and trigonometry |
| Medicine | Medical encyclopedias, understanding human anatomy, pharmacology |
| Engineering | Innovative architectural techniques, irrigation systems, hydraulic engineering |
| Chemistry | Advancements in alchemy, distillation, chemical processes |
In conclusion, the Islamic and Muslim influence in science and technology is substantial and has greatly shaped the progress and development of various fields. The contributions made by Islamic scholars and researchers during the Islamic Golden Age continue to resonate and inspire advancements in science and technology today.
Islamic and Muslim Attire
In Islamic culture, modesty in dress is highly valued. Both men and women are expected to dress in a manner that is modest, loose-fitting, and covers the body appropriately. The specific attire varies among different Muslim communities and cultures, but there are some common aspects that can be seen across the Islamic world.
Hijab: One of the most well-known aspects of Muslim attire for women is the hijab. The hijab is a headscarf that covers the hair, neck, and shoulders. It is worn by many Muslim women as a symbol of modesty and religious piety. The style of hijab can vary from region to region, with different fabrics, colors, and designs, but the basic concept remains the same.
Abaya: The abaya is a loose-fitting, full-length robe worn by some Muslim women to cover their entire body. It is often black in color, although it can also be found in other colors and styles. The abaya is typically worn over regular clothing and is commonly seen in countries such as Saudi Arabia and the Gulf region.
Jubba/Thobe: The jubba, also known as thobe or dishdasha, is a long, loose-fitting robe worn by Muslim men. It is commonly worn in Arab countries and can vary in style and color. The jubba is usually made of lightweight fabric and is worn as an everyday garment or for special occasions.
Niqab/Burqa: The niqab and burqa are garments worn by some Muslim women to cover their face. The niqab covers the face except for the eyes, while the burqa covers the entire face with a mesh screen to see through. These garments are worn for the purpose of maintaining modesty and privacy.
Kufi: The kufi is a cap worn by Muslim men, often as a part of traditional attire or as a sign of religious devotion. It is a simple, round-shaped cap that is typically made of fabric or crocheted. The kufi can be worn by men of all ages and is especially common during religious ceremonies or Friday prayers.
While these are some of the commonly seen garments in Islamic and Muslim attire, it is important to note that there is diversity among Muslim communities and cultures. The specific style and interpretation of modest clothing can vary widely, and individuals may choose to wear different types of clothing based on personal preference, cultural traditions, and religious beliefs.
Islamic and Muslim Symbols and Icons
Islamic and Muslim symbols and icons are important elements that represent the faith and culture of Muslims. These symbols hold significant meanings and are often used in various contexts, including religious rituals, visual arts, and everyday life.
- Star and Crescent: One of the most widely recognized symbols of Islam is the star and crescent. The star represents guidance and divinity, while the crescent symbolizes the lunar calendar and the beginning of each Islamic month.
- Kaaba: The Kaaba is a sacred black cube-shaped structure located at the center of the Grand Mosque in Mecca, Saudi Arabia. It is the holiest site in Islam and serves as the focal point for Muslims during the Hajj pilgrimage.
- Calligraphy: Arabic calligraphy is a highly regarded art form in the Islamic world. It is a decorative writing style that is often used to transcribe verses from the Quran or express various Islamic concepts and prayers. Calligraphy is frequently seen in mosques, manuscripts, and other Islamic artworks.
- Minaret: A minaret is a tall, slender tower typically found alongside mosques. It serves as a visual marker of Islamic architecture and is used to make the call to prayer (adhan) five times a day.
- Hijab: The hijab is a headscarf worn by many Muslim women as a symbol of modesty and devotion to their faith. It is an important aspect of Islamic dress code and is interpreted differently across cultures and regions.
- Crescent Moon: The crescent moon is often associated with Islam and is often used to announce the beginning of the Islamic month of Ramadan or Eid festivals. It is seen as a symbol of renewal and signifies the lunar-based Islamic calendar.
- Quran: The Quran, also spelled as Koran, is the holy book of Islam. It is believed to be the literal word of God, as revealed to the Prophet Muhammad. The Quran is considered the ultimate source of guidance for Muslims and is recited and studied extensively.
- Five Pillars of Islam: The Five Pillars of Islam are the core principles and practices of the faith. These pillars include the declaration of faith (Shahada), prayer (Salat), giving of alms (Zakat), fasting during Ramadan (Sawm), and pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj). They serve as the foundation for every Muslim’s spiritual life.
- Islamic Geometric Patterns: Islamic geometric patterns are intricate designs that are commonly found in Islamic art and architecture. They often consist of repeated geometric shapes and are used to symbolize the infinite nature of God.
- Crescent and Star Flag: The crescent and star flag is commonly associated with Muslim-majority countries. It is often seen as a symbol of identity and represents the unity and pride of the Muslim community.
These symbols and icons play a pivotal role in reflecting the cultural and religious heritage of Muslims worldwide. They are not only visually striking but also deeply meaningful, holding centuries of tradition and devotion. Understanding these symbols can help foster better understanding and appreciation of Islamic culture and its diverse manifestations.
Perceptions and Misconceptions about Islam and Muslim
Islam is one of the fastest-growing religions in the world, yet it is also one of the most misunderstood. Many people often associate Islam with negative images and stereotypes, which contributes to misconceptions about Muslims. It is important to separate fact from fiction and challenge these perceptions to promote understanding and tolerance.
Perception: Islam promotes violence and terrorism.
Reality: Islam is a religion of peace and compassion. The vast majority of Muslims condemn terrorism and violence, just as followers of any other religion would. Acts of violence committed by individuals or groups should not be attributed to an entire religion or community.
Perception: Muslim women are oppressed and have no rights.
Reality: Islam grants women numerous rights and privileges. The misconception of Muslim women as oppressed often stems from cultural practices rather than religious teachings. Islamic teachings emphasize the equality of men and women, and Muslim women hold important roles both within their families and society.
Perception: Muslims do not integrate into western societies.
Reality: Muslims, like followers of any other religion, are diverse and have different levels of integration. Many Muslims successfully integrate into Western societies, contributing to their communities and practicing their faith in peace. Negative perceptions often arise due to the actions of a small minority or media bias.
Perception: Islam is incompatible with democracy and human rights.
Reality: Islam is compatible with democracy and respects human rights. Islamic principles encourage justice, equality, and respect for the rights of individuals. Like any other religion, interpretations may vary, but the core values of Islam do not contradict democratic principles or human rights.
Perception: All Muslims are the same.
Reality: Muslims, like followers of any other religion, are diverse. They come from different ethnic backgrounds, cultures, and have varying interpretations of their faith. Generalizations about all Muslims based on the actions of a few individuals are unfair and perpetuate stereotypes.
Perception: Muslims do not contribute to society.
Reality: Muslims make significant contributions to various fields, including science, medicine, arts, literature, and more. They are active members of their communities and contribute to the betterment of society. Like any other group, Muslims should be evaluated based on their individual actions and achievements, rather than stereotypes.
It is essential to dispel these misconceptions and strive for understanding and respect between people of different faiths and cultures. By challenging stereotypes and promoting dialogue, we can build a more inclusive and tolerant society.
Media Representations of Islam and Muslim
Media plays a significant role in shaping public opinion and perception, and this includes its representation of Islam and Muslims. Unfortunately, media often perpetuates negative stereotypes and misconceptions about Islam and Muslims, contributing to the rise of Islamophobia.
Stereotyping and Misrepresentation
One common way that media misrepresents Islam and Muslims is through stereotyping. Muslims are often portrayed as terrorists, extremists, or oppressors, which creates a distorted view of the religion and its followers. This portrayal not only perpetuates harmful stereotypes but also fuels fear and hatred towards Muslims.
Another form of misrepresentation is the tendency of the media to only focus on negative stories involving Muslims. Positive contributions and achievements by Muslims are often overlooked, reinforcing the negative narrative surrounding Islam. This reinforces the idea that Muslims are inherently dangerous or anti-Western, adding to the culture of fear.
Lack of Diversity
The media also tends to present a monolithic view of Islam and Muslims, ignoring the diversity within the faith. Islam is a global religion with followers from various ethnicities, cultures, and backgrounds. However, the media often portrays Muslims as a homogeneous group, disregarding the numerous sects, practices, and interpretations that exist within the religion.
By homogenizing Muslims, the media fails to accurately represent the complexities of their experiences, beliefs, and identities. This lack of diversity perpetuates misunderstandings and misjudgments about Islam and its followers.
Islamophobia and sensationalism
Sensationalism and fear-mongering are frequently used by the media when reporting on Islam and Muslims. This is particularly evident in news coverage of terrorist attacks or conflicts involving Muslim-majority countries. The emphasis on the religious background of those involved often overshadows other factors, such as politics or socioeconomic issues.
Such coverage reinforces negative stereotypes and fuels Islamophobia by associating Islam with violence and terrorism. This not only perpetuates a biased narrative but also has real-world consequences, such as increased discrimination and hate crimes against Muslims.
The role of responsible journalism
It is crucial for the media to take responsibility for its representation of Islam and Muslims. Journalists and reporters should strive to provide accurate and unbiased coverage, representing the diversity and complexity of the Muslim community. They should challenge stereotypes, avoid sensationalism, and provide context to help audiences better understand the nuances of Islam.
In an interconnected world, media has the power to shape attitudes and opinions. By portraying Islam and Muslims in a fair and balanced manner, the media can play a significant role in fostering understanding, tolerance, and respect among different communities.
Islamic and Muslim Organizations and Institutions
- Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC): The OIC is an international organization consisting of 57 member states that are predominantly Muslim. It aims to promote cooperation and solidarity among its member states in various fields, including political, economic, social, and cultural.
- Islamic Development Bank (IDB): The IDB is a multilateral development financing institution that provides financial assistance to its member countries for economic development projects. It aims to foster the socioeconomic progress of Muslim communities and promote economic cooperation among member countries.
- Islamic Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (ISESCO): ISESCO is a specialized agency of the OIC that focuses on education, science, and culture. It aims to enhance these areas within member states and promote cooperation and exchange in these fields.
- Muslim World League (MWL): The MWL is a non-governmental organization that operates globally to promote Islamic teachings, strengthen Islamic unity, and support Muslim communities. It provides humanitarian aid, educational programs, and cultural exchanges to foster understanding and cooperation.
- Islamic Relief Worldwide: Islamic Relief is an international humanitarian organization that provides assistance to people in need, irrespective of their race, religion, or gender. It operates in many countries and focuses on emergency response, healthcare, education, and sustainable development.
- Fiqh Council of North America (FCNA): The FCNA is an Islamic scholarly organization that provides guidance on religious and legal matters for Muslims living in North America. It aims to address contemporary issues and promote a better understanding of Islamic teachings in the context of the North American Muslim community.
Islamic and Muslim Political Movements
Islamic and Muslim political movements have played a significant role in shaping the political landscape of many countries with significant Muslim populations. These movements are characterized by their adherence to Islamic principles and their aim to establish Islamic governance.
Some of the most well-known Islamic political movements include:
- Muslim Brotherhood: The Muslim Brotherhood is an influential Islamic political organization founded in Egypt in 1928. It seeks to promote Islamic principles and values in society and has been involved in various social and political activities.
- Hizb ut-Tahrir: Hizb ut-Tahrir, also known as the “Party of Liberation,” is an international political organization. Its primary objective is to establish an Islamic caliphate and work towards the unification of Muslim-majority countries under a single Islamic state.
- Jamaat-e-Islami: Jamaat-e-Islami is a political party in Pakistan founded in 1941. It advocates for the implementation of Islamic law and has been involved in various political and social activities in the country.
These Islamic political movements often participate in electoral politics, form political parties, and advocate for the implementation of Islamic law. They have varying degrees of success and influence depending on the country’s political climate and the level of support they have among the population.
It is important to note that not all Muslims support or are affiliated with these political movements. There is a wide spectrum of political beliefs and ideologies among Muslims, ranging from secularism to various forms of Islamic political activism.
Overall, Islamic and Muslim political movements play a significant role in shaping the political discourse in many Muslim-majority countries. They seek to promote Islamic values and principles in governance and society, though their approaches and goals may differ.
Islamic and Muslim Minority Communities
Islamic and Muslim minority communities exist in many countries around the world, including non-Muslim majority countries. These communities are made up of individuals who follow the Islamic faith and identify as Muslims.
Being part of a minority group can present unique challenges for Islamic and Muslim communities. Discrimination and prejudice can affect their daily lives and limit their opportunities in employment, education, and other areas of society.
Despite these challenges, Islamic and Muslim minority communities often strive to maintain their religious and cultural practices. This includes building mosques and community centers where they can gather for prayer and other religious activities.
In some countries, Islamic minority communities also face restrictions on certain religious practices, such as wearing religious attire, practicing certain customs, or publicly expressing their faith. These restrictions can lead to feelings of marginalization and a sense of being misunderstood by the larger society.
To address these challenges, many Islamic and Muslim minority communities have formed organizations and advocacy groups that aim to protect their rights and promote understanding and acceptance. These groups work towards fostering interfaith dialogue, educating the public about the Islamic faith, and challenging stereotypes and misconceptions.
Additionally, Islamic and Muslim minority communities often create support networks within their own communities. They provide assistance to individuals and families facing discrimination, offer educational resources, and organize social events to foster a sense of belonging and unity.
It is important for society as a whole to recognize and respect the diversity of religious beliefs and practices. By promoting tolerance and understanding, we can create a more inclusive and harmonious society for Islamic and Muslim minority communities and all religious groups.
Challenges and Opportunities for Islam and Muslim
Islam and Muslims face various challenges and opportunities in the modern world, which shape their future and influence their interactions with other cultures and societies. These challenges and opportunities encompass both internal issues within the Muslim community and external factors that impact their perception in the global context.
Internal Challenges:
- Moderation vs Extremism: One of the major internal challenges faced by Islam and Muslims is the struggle to find a balance between embracing moderate interpretations of their faith and countering extremism. This challenge becomes crucial in the face of radical ideologies that seek to undermine the true teachings of Islam.
- Unity and Diversity: Islam encompasses diverse ethnicities, languages, and cultural traditions. The challenge lies in maintaining unity among Muslims while embracing this diversity. Differences in interpretation, sectarian affiliations, and cultural practices can sometimes lead to divisions within the Muslim community, hindering collective progress.
- Education and Literacy: Promoting education and literacy within the Muslim community is another essential challenge. By enhancing access to quality education and promoting critical thinking, Muslims can overcome misconceptions and contribute more effectively to various fields of knowledge in the modern world.
- Gender Equality: Addressing gender disparities and promoting gender equality within the Muslim community is an ongoing challenge. It involves overcoming cultural traditions and interpretations that may restrict women’s rights and opportunities for meaningful participation in society.
External Challenges:
- Islamophobia: Muslims face the challenge of combating Islamophobia, which includes prejudice, discrimination, and stereotyping based on their religious identity. By promoting interfaith dialogue, dispelling misconceptions, and emphasizing the true values of Islam, Muslims can work towards a more inclusive and tolerant society.
- Global Security Concerns: Islam and Muslims often face the challenge of being associated with terrorism and extremism due to the actions of a minority. This perception can lead to heightened security measures and limited opportunities for Muslim individuals and communities. It is essential to address these concerns through collaborative efforts, emphasizing the peaceful teachings of Islam.
- Integration and Assimilation: Muslims living in non-Muslim-majority countries face the challenge of integrating and assimilating into different cultural contexts while maintaining their religious identity. Finding a balance between preserving their own traditions and adapting to local norms can be a complex but necessary challenge for Muslims in such societies.
- Socioeconomic Empowerment: Ensuring socioeconomic empowerment for Muslims is another significant challenge. Muslims in many regions face socio-economic disparities, which can perpetuate marginalization and limited opportunities. Efforts should be made to promote equal access to education, employment, and resources.
Overall, addressing these challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities they present can contribute to the growth and prosperity of both the Muslim community and Islamic teachings. It requires internal reflection, engagement with the global community, and a commitment to the true principles of Islam.
Islamic and Muslim Perspectives on Gender Equality
The question of gender equality is a complex and highly debated topic within Islamic and Muslim communities. While there are varying beliefs and interpretations, it is important to note that Islam as a religion and Muslims as individuals hold diverse perspectives on gender roles and equality.
Islam, as a comprehensive faith, encompasses a wide range of teachings and principles regarding gender. While some interpretations emphasize traditional gender roles with distinct responsibilities for men and women, others argue for more egalitarian readings of Islamic texts.
One of the central sources for understanding gender in Islam is the Quran, the holy book of Muslims. While some verses are seen as supporting gender equality, others can be interpreted as prescribing specific roles for men and women. The Quran also contains stories of women who played active and influential roles in society, such as the Prophet Muhammad’s first wife, Khadijah.
Islamic scholars and theologians have debated and provided interpretations of these verses and historical examples throughout history. These interpretations often vary based on cultural context, reflecting the diverse practices and beliefs of Muslims around the world.
In some Islamic societies, traditional gender roles are emphasized, with men typically assuming leadership and decision-making positions, while women are expected to prioritize their roles as wives and mothers. However, it is essential to note that these practices are not universal and are influenced by cultural, social, and historical factors.
On the other hand, there are Muslims who advocate for gender equality within the framework of Islam. They draw upon teachings such as the concept of human dignity, justice, and the spiritual equality of all believers. This perspective encourages equal opportunities for education, employment, and political participation for both men and women.
Furthermore, many Muslim women have been at the forefront of challenging patriarchal norms and advocating for women’s rights within their communities. Organizations and activists, both male and female, are working towards women’s empowerment and gender equality from their Islamic faith perspectives.
It is important to recognize that there is a diversity of opinions among Muslims on gender equality. While some adhere to traditional interpretations, others argue for a more inclusive and progressive understanding of gender roles in Islam. These varying perspectives contribute to an ongoing and dynamic conversation within Muslim communities and shape the way gender equality is understood and practiced.
Islamic and Muslim Views on Human Rights
Human rights are a central topic of discussion in today’s world, and understanding the perspectives of different religions and cultures is crucial to fostering mutual respect and understanding. In the context of Islam and Muslim belief, human rights hold a significant place.
Islamic Perspective:
- Equality: Islam emphasizes the equality of all individuals, regardless of their race, gender, or social status. The Quran explicitly states that all human beings are equal and that the most honored among them are those who are the most righteous.
- Dignity: Islam recognizes the inherent dignity of every human being. The Islamic concept of ‘karamah’ refers to the sanctity and inviolability of human life and the belief that each person possesses inherent worth and deserves to be treated with respect and dignity.
- Justice: Islam emphasizes the importance of justice and fairness. The Quran states that Muslims should stand up for justice, even if it is against their family members, and that they should not let their personal biases or prejudices affect their judgment.
- Freedom: Islam promotes the idea of freedom of belief, expression, and conscience. Muslims are encouraged to seek knowledge and engage in intellectual pursuits, and they have the right to express their opinions and beliefs within the bounds of respect and peaceful dialogue.
- Protection: Islam places a strong emphasis on the protection of human life and prohibits acts of violence or harm against others. Muslims are called upon to promote peace and harmony in society and to protect the rights and well-being of all individuals.
Muslim Perspectives:
It is important to note that the views on human rights may vary among different Muslims due to cultural, social, and political contexts. However, some common perspectives within the Muslim community include:
- Sharia Law: Some Muslims believe that human rights are best protected and upheld through the implementation of Sharia law, which is derived from Islamic teachings and principles. They argue that Sharia law provides a comprehensive framework for justice, equality, and protection of human rights.
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights: Many Muslims believe that the principles outlined in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) are compatible with Islamic teachings. They advocate for the interpretation and implementation of human rights within an Islamic context, taking into account the specific values and principles of the faith.
- Reform and Progress: Some Muslims urge for reform within Muslim-majority countries to address issues related to human rights. They advocate for social progress, gender equality, freedom of speech, and protection of minorities, while still upholding Islamic values and teachings.
- Interpretation and Dialogue: There is a growing emphasis within the Muslim community on promoting dialogue and interpretation of Islamic teachings to ensure the protection of human rights. Many scholars and activists work towards reconciling traditional interpretations of Islamic texts with contemporary understandings of human rights.
- Individual and Community Responsibility: Some Muslims stress the importance of individual and community responsibility in upholding human rights. They believe that it is the duty of Muslims to actively promote and protect the rights and well-being of all individuals, both within the Muslim community and in society at large.
| Islamic Perspective | Muslim Perspectives |
|---|---|
| Equality | Sharia Law |
| Dignity | Universal Declaration of Human Rights |
| Justice | Reform and Progress |
| Freedom | Interpretation and Dialogue |
| Protection | Individual and Community Responsibility |
In conclusion, Islam and Muslims hold a strong emphasis on human rights, including equality, dignity, justice, freedom, and protection. While interpretations may vary among individuals and communities, there is a common belief in the importance of upholding and promoting these rights, both within an Islamic framework and in the broader context of universal human rights.
Islamic and Muslim Stances on Violence and Extremism
Islam and Muslims, often mistakenly associated with violence and extremism, possess multifaceted viewpoints on these subjects. It is crucial to differentiate between the religion of Islam and the actions of individuals who claim to follow it.
Islamic Perspective on Violence: Islam as a religion condemns violence and promotes peace, harmony, and justice. The Quran, the central religious text of Islam, advocates for resolving conflicts peacefully and avoiding aggression. It emphasizes the sanctity of life and the principles of justice and fairness.
The Quranic verse (5:32) states, “Whoever kills an innocent person, it is as if he has killed all of humanity; and whoever saves a person, it is as if he has saved all of humanity.” This verse highlights the importance of preserving human life and discourages any form of violence or aggression towards others.
Islamic Perspective on Extremism: Islam categorically rejects extremism and radicalism. Extremism is not endorsed by Islamic teachings, which promote balance and moderation in all aspects of life. Muslims are advised to follow the middle path (Quran 2:143) and not indulge in extremism in their beliefs or actions.
Extremist ideologies that promote violence and terrorism are often rooted in political, social, or economic factors rather than religious teachings. It is essential to differentiate between genuine Islamic principles and the distorted interpretations of individuals or groups.
Muslim Role in Combating Violence and Extremism: Muslims play a significant role in combating violence and extremism through various means:
- Education and Awareness: Many Islamic scholars and institutions actively promote peaceful teachings of Islam, educating individuals about the true essence of the religion and dispelling misconceptions.
- Interfaith Dialogue: Muslims engage in dialogue with people from different religions and backgrounds, fostering understanding, tolerance, and mutual respect.
- Social Work: Muslims contribute to society by undertaking charitable activities, supporting disadvantaged communities, and advocating for social justice.
- Religious Leadership: Imams and religious leaders condemn violence and extremism, guiding Muslims towards a peaceful and ethical way of life.
The Importance of Context: It is crucial to remember that acts of violence or extremism committed by individuals who identify as Muslims do not represent the entire religion or its followers. Such actions must be analyzed within their specific historical, political, and sociological contexts.
| Key Points: | |
|---|---|
| Islam: | Islam condemns violence and promotes peace, harmony, and justice. |
| Extremism: | Islam categorically rejects extremism and radicalism. |
| Muslim Role: | Muslims actively work to combat violence and extremism through education, interfaith dialogue, social work, and religious leadership. |
| Context: | Acts of violence or extremism must be analyzed within their specific historical, political, and sociological contexts. |
By understanding the true teachings of Islam and recognizing the efforts of Muslims in promoting peace, we can overcome stereotypes and bridge the gap of misunderstanding between different cultures and religions.
Current Issues and Debates within Islamic and Muslim Communities
The Islamic and Muslim communities are diverse and have their own set of current issues and debates. These issues and debates can vary across different countries and cultures, but they often revolve around important topics such as interpretation of religious texts, gender roles, political involvement, and social justice.
Interpretation of Religious Texts
One ongoing debate within the Islamic and Muslim communities is the interpretation of religious texts, particularly the Quran and Hadiths. Different scholars and individuals may have different interpretations of certain verses or teachings, which can lead to disagreements and debates. Some may argue for a more literal interpretation, while others may advocate for a more contextual and nuanced approach.
These debates often center around issues such as the role of women in society, punishment for crimes, and the treatment of non-Muslims. The interpretation of religious texts is an important aspect of Islamic and Muslim communities, as it shapes beliefs, values, and practices.
Women’s Roles
The role of women in Islamic and Muslim communities is another significant topic of discussion and debate. There are differing views on issues such as modesty, education, and participation in public and political life. Some argue for more traditional interpretations that advocate for gender segregation and limited roles for women, while others argue for a more progressive approach that promotes equality and empowerment for women.
This debate extends beyond religious texts and involves discussions about cultural norms, societal expectations, and the importance of women’s voices and contributions within the community. It is an ongoing conversation with different perspectives and opinions.
Political Involvement
Political involvement is another important issue within Islamic and Muslim communities. Some individuals and groups advocate for active engagement in the political process to promote their interests, protect their rights, and have a voice in decision-making processes.
However, there are also debates about the appropriate role of Islam in government and the relationship between religious and political authority. Some argue for a more secular approach, while others support the implementation of Islamic law or governance based on Islamic principles.
Social Justice
Social justice is a topic of concern and debate within Islamic and Muslim communities. Many individuals and groups are actively involved in advocating for social justice, fighting against poverty, discrimination, and oppression.
Some of the key issues discussed include poverty alleviation, human rights, environmental responsibility, and equality. These debates often center around finding ways to address these issues in accordance with Islamic principles and values.
Conclusion
Current issues and debates within Islamic and Muslim communities encompass a wide range of topics. Interpretation of religious texts, women’s roles, political involvement, and social justice are just a few areas where ongoing discussions and debates take place.
These debates highlight the diversity and complexity within these communities, with different perspectives and opinions shaping the conversations. The willingness to engage in dialogue and understand different viewpoints is crucial for fostering understanding and unity within these communities and promoting positive change.
Unity and Diversity within Islam and Muslim
Islam is a religion with a rich history and diverse traditions. Despite the various interpretations and practices within the Islamic faith, there is a sense of unity that binds Muslims together. This unity is primarily rooted in the Five Pillars of Islam, which serve as the foundation of the faith.
The Five Pillars of Islam include:
- Shahada: The declaration of faith, affirming that there is no god but Allah and Muhammad is his messenger
- Salah: The ritual prayer that Muslims are required to perform five times a day
- Zakat: The giving of alms or charity to support the poor and needy
- Sawm: The observance of fasting during the holy month of Ramadan
- Hajj: The pilgrimage to the holy city of Mecca that Muslims should undertake at least once in their lifetime, if physically and financially able
These pillars provide Muslims with a common set of beliefs and practices, fostering a sense of unity and shared identity within the global Muslim community.
However, it is important to recognize that Islam is not a monolithic religion. Muslims come from various cultural backgrounds and countries, resulting in a great diversity of practices and traditions within the faith. For example, while the Five Pillars are universally recognized, the way Muslims observe them can differ based on regional customs and interpretations.
Furthermore, there are different sects within Islam, such as Sunni and Shia, which have distinct theological and ideological differences. These differences can sometimes lead to tensions and conflicts, but they also demonstrate the diverse and dynamic nature of Islam.
In addition to diverse practices and sects, Islam also embraces a wide range of cultural expressions. Islamic art, literature, music, and architecture vary across different regions and reflect the unique traditions and histories of Muslim communities around the world.
Despite this diversity, there is a shared sense of identity and community among Muslims, underpinned by the belief in one God and the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad. This unity within diversity is a testament to the strength and resilience of Islam as a global religion.
In conclusion, Islam and Muslims are characterized by both unity and diversity. The Five Pillars of Islam serve as a unifying force, while cultural differences and theological variations contribute to the rich diversity within the Muslim community. Recognizing and appreciating this unity and diversity is essential in promoting understanding and respect among people of different faiths and backgrounds.
The Future of Islam and Muslim
As one of the world’s fastest-growing religions, Islam holds a significant role in shaping the future of societies and individuals. The Islamic faith and the Muslim community have continuously evolved throughout history and will continue to do so in the future. Here are some key aspects to consider when discussing the future of Islam and Muslim:
-
Evolving Interpretations: Islam, like any other religion, is subject to evolving interpretations based on cultural, social, and intellectual changes. As time progresses, Muslims will continue to reinterpret Islamic teachings, adapting them to the modern world while remaining rooted in their faith. This process will shape the future of Islam, allowing it to remain relevant and responsive to the needs of Muslims around the world.
-
Globalization: The increasing interconnectedness of the world plays a significant role in shaping the future of Islam and Muslim communities. Globalization facilitates the exchange of ideas, enabling Muslims to connect with each other and share their religious practices and beliefs. This interconnectedness fosters cultural exchange and dialogue, leading to the emergence of diverse Islamic practices and perspectives.
-
Role of Women: The role of women within Islam has been a topic of great debate over the years. In the future, it is expected that women will continue to play a more prominent role in Islamic societies. Muslim women are increasingly asserting their rights and challenging traditional gender norms, which will lead to a more inclusive and egalitarian Islamic community. This shift will undoubtedly impact the future direction of Islam.
-
Social and Political Changes: The ever-changing social and political landscapes across the globe will influence the future of Islam. Muslims living in different countries and under various political systems will inevitably experience different realities and challenges. This diversity will contribute to the emergence of new interpretations and practices within the Islamic faith.
-
Emerging Technology: The rapid development of technology will undoubtedly impact the future of Islam and the Muslim community. From online platforms facilitating Islamic education and virtual communal gatherings to the utilization of social media for advocacy and outreach, technology will provide new avenues for Muslims to connect, learn, and spread awareness about their faith.
In conclusion, the future of Islam and the Muslim community will be shaped by a range of factors, including evolving interpretations, globalization, the role of women, social and political changes, and emerging technology. With each passing year, Islam will continue to adapt to the ever-changing world while remaining rooted in its fundamental principles.
FAQ
Can Islamic and Muslim be used interchangeably?
No, Islamic and Muslim cannot be used interchangeably. Islamic refers to the religion of Islam, while Muslim refers to a person who practices Islam.
What are the main beliefs of Islam?
The main beliefs of Islam include the belief in one God (Allah), the belief in the prophets (including Muhammad as the final prophet), the belief in divine books (such as the Quran), the belief in angels, and the belief in the Day of Judgment.
Are all Muslims Islamic?
Yes, all Muslims are Islamic. Being a Muslim means adhering to the religious practices, beliefs, and values of Islam.
Are there different sects within Islam?
Yes, there are different sects within Islam. The two main sects are Sunni and Shia, which have different interpretations of Islamic teachings and practices.