Islamic mortgages, also known as halal mortgages, have gained popularity among Muslims seeking home financing options that are compliant with Shariah law. Shariah compliance is a fundamental principle for many practicing Muslims, as it ensures adherence to Islamic principles in all aspects of life, including financial transactions.
Traditional mortgages, which involve the payment of interest, are considered haram (prohibited) in Islam due to the belief that charging or receiving interest goes against the principles of fairness and justice. Islamic mortgages, on the other hand, are structured in a way that avoids the payment or receipt of interest and instead employs alternative mechanisms that are considered halal.
One common method used in Islamic mortgages is known as murabaha, which is a cost-plus-profit arrangement. In this arrangement, the lender purchases the property and sells it to the borrower at a higher price, allowing the borrower to repay the loan in installments over an agreed-upon period. This method ensures that the lender receives a profit without charging interest.
Another popular option is ijara, which is a form of lease-to-own agreement. Under this arrangement, the lender purchases the property and leases it to the borrower for a specified period. The borrower makes regular lease payments, which may include a portion that goes towards the eventual purchase of the property. At the end of the lease term, the borrower has the option to buy the property at an agreed-upon price.
While Islamic mortgages offer an alternative to traditional mortgages that aligns with the principles of Shariah law, there are ongoing debates among scholars regarding the true compliance of these financial products. It is important for individuals considering Islamic mortgages to consult with knowledgeable scholars or experts to ensure that the specific product they choose adheres to the necessary criteria set forth by Shariah law.
What Are Islamic Mortgages and How Do They Work?
An Islamic mortgage, also known as a Shariah compliant mortgage or home financing option, is a form of financial arrangement that adheres to the principles of Islamic law (Shariah). It provides an alternative to conventional mortgages for Muslims who wish to abide by their religious beliefs when purchasing a home.
In Islamic finance, the charging of interest (riba) is prohibited, as it is considered exploitative and unjust. Therefore, Islamic mortgages are structured in a way that avoids the payment or receipt of interest. Instead, they utilize various Islamic financial concepts to achieve a similar outcome.
One common type of Islamic mortgage is the Murabaha mortgage. This involves the bank purchasing the property and then selling it to the customer at a higher price on deferred payment terms. The customer pays the bank in installments over an agreed-upon period, effectively repaying the loan without any interest charges.
Another type of Islamic mortgage is the Ijara mortgage, which functions similarly to a lease-to-own arrangement. The bank purchases the property and leases it to the customer for a specific term. During this period, the customer pays rent, a portion of which is used to gradually transfer ownership of the property to the customer. At the end of the term, the ownership is fully transferred, and the customer becomes the sole owner.
Islamic mortgages may also utilize other concepts such as Musharaka (partnership) and Diminishing Musharaka (gradual partnership). These concepts involve joint ownership and profit sharing arrangements between the bank and the customer, allowing for a gradual transfer of ownership and repayment of the loan over time.
It is important to note that Islamic mortgages require stringent compliance with Shariah principles, as oversight by a Shariah board is typically involved in reviewing and approving the structures and terms of the financing. This ensures that the mortgage is in accordance with Islamic law and free from any prohibited elements.
Overall, Islamic mortgages offer Muslim individuals and families an ethical and Shariah compliant option for purchasing a home. They provide an alternative to conventional mortgages that aligns with Islamic principles and values.
Understanding Shariah-Compliant Home Financing
Shariah-compliant home financing, also known as Islamic mortgages, is a type of financing that adheres to Islamic principles and is considered halal (permissible). It offers an alternative to conventional mortgages, which are based on interest (riba) and other aspects that may be prohibited in Islam.
One of the key principles of Shariah-compliant financing is the absence of interest. In Islamic finance, earning interest is seen as exploitative and unjust. Instead, a Shariah-compliant home financing option seeks to provide a fair and mutually beneficial agreement between the lender and the borrower.
Islamic mortgages utilize different structures to ensure compliance with Islamic principles. Some common structures include:
- Murabaha: In this structure, the lender purchases the property and sells it to the borrower at an agreed-upon price, with the borrower making installment payments over an agreed-upon period.
- Ijarah: This structure involves the lender purchasing the property and leasing it to the borrower for a specific period. The borrower pays rent, which may include an additional fee to eventually obtain ownership of the property.
- Musharaka: In this structure, the lender and the borrower enter into a partnership where both parties contribute capital and share the risks and rewards of the investment. The property is jointly owned, with the borrower purchasing the lender’s share over time.
These structures ensure that the financing arrangement is compliant with Shariah principles by avoiding interest and promoting shared risk and benefits.
Additionally, Shariah-compliant home financing options may also incorporate ethical considerations. For example, the property being financed should be free from any unethical or prohibited activities, such as alcohol sales or gambling. This ensures that the borrower is not indirectly involved in haram (prohibited) activities.
It is important for individuals considering Shariah-compliant home financing to work with knowledgeable and reputable financial institutions that offer such options. These institutions typically have a Shariah board or committee that ensures the compliance of their products with Islamic principles.
In conclusion, Shariah-compliant home financing provides an alternative to conventional mortgages for Muslims who seek to adhere to Islamic principles. By avoiding interest and incorporating principles of fairness and shared risk, these financing options offer a halal solution for home ownership.
Are Islamic Mortgages Halal?
Islamic mortgages, also known as halal mortgages, are home financing options that are designed to be Shariah-compliant. Shariah is the law of Islam, derived from the teachings of the Quran and the Hadith, and it governs all aspects of a Muslim’s life, including financial matters.
In Islamic finance, the charging or paying of interest is forbidden, as it is seen as exploitative and unfair. Therefore, traditional mortgages that charge interest are not considered halal. Islamic mortgages, on the other hand, are structured in a way that allows Muslims to purchase homes without resorting to interest-based financing.
There are several types of Islamic mortgages available, each with its own structure and features. One common type is the murabaha mortgage, which involves the bank buying the property and then selling it to the buyer at a higher price on a deferred payment basis. This allows the bank to earn a profit without charging interest.
Another type is the ijara mortgage, which is similar to a lease-to-own arrangement. The bank buys the property and then leases it to the buyer, who makes monthly payments that include both rent and a portion that goes toward purchasing the property. Once the full amount is paid, ownership is transferred to the buyer.
Islamic mortgages also often involve the concept of shared ownership, where the bank and the buyer jointly own the property until the buyer has fully paid off the mortgage. This ensures that the bank shares in the risk and rewards of the investment, as is required by Shariah.
Overall, Islamic mortgages are considered halal as long as they comply with the principles of Shariah. However, it is important for individuals to do their own research and consult with scholars or experts in Islamic finance to ensure that the specific mortgage product they are considering is truly halal.
Exploring the Principles of Islamic Home Financing
Islamic home financing is based on the principles of Shariah, the Islamic law derived from the Quran and the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad. These principles guide Muslims in their financial transactions and ensure that they are conducted in a manner that is considered halal or permissible in Islam.
The following are some key principles of Islamic home financing:
-
Riba (Usury) Prohibition:
Islamic finance prohibits the charging or paying of interest, as it is considered usury. This principle is in line with the Quranic verse that states, “Those who consume interest cannot stand [on the Day of Resurrection] except as one stands who is being beaten by Satan into insanity” (Quran 2:275). Instead, Islamic home financing uses alternative methods such as profit-sharing, rent-to-own, or cost-plus financing.
-
Asset-Backed Financing:
Islamic home financing requires that the financing be backed by real assets, such as the property being purchased. This ensures that the financing is tied to a tangible asset and not based on speculative or uncertain transactions. In some cases, Islamic banks may purchase the property and sell it to the buyer at a higher price, allowing the buyer to pay in installments.
-
Shared Risk and Profit:
Islamic home financing promotes the concept of sharing risks and profits between the buyer and the financier. Unlike conventional mortgages where the lender receives fixed interest payments regardless of the property’s performance, Islamic home financing structures involve sharing both the risks and rewards of owning the property. This aligns the interests of the financier with the buyer and encourages responsible and ethical lending practices.
-
Avoidance of Haram Activities:
Islamic home financing avoids entering into any contracts or transactions that involve haram (forbidden) activities according to Islamic law. This includes transactions related to alcohol, gambling, pork, and other prohibited substances or activities. Islamic banks and financial institutions follow strict ethical guidelines to ensure that the financing offered is free from any haram elements.
-
Ethical and Social Responsibility:
Islamic home financing takes into account ethical and social responsibility aspects in its operations. This includes promoting fairness, transparency, and accountability in all financial transactions. Islamic banks are also encouraged to invest in socially responsible projects that benefit the community, such as affordable housing initiatives, renewable energy projects, and education programs.
Overall, Islamic home financing adheres to the principles of Shariah and offers Muslims a halal alternative to conventional mortgages. It allows individuals to fulfill their dream of owning a home while adhering to their religious beliefs and values. By understanding the principles behind Islamic home financing, individuals can make informed decisions about their financial matters and ensure that their transactions are in compliance with Islamic law.
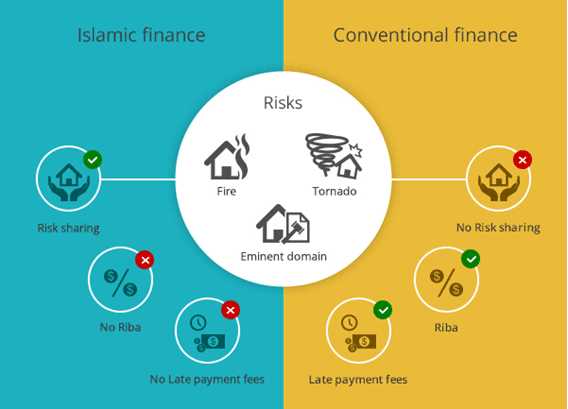
The Role of Riba in Conventional Mortgages
One of the key issues when examining the Islamic and conventional mortgage systems is the concept of riba. Riba is an Arabic term that refers to any form of interest or usury. In Islamic finance, riba is strictly prohibited, as it is considered exploitative and harmful to individuals and society as a whole.
In conventional mortgage systems, interest plays a central role. Banks and financial institutions provide loans to homebuyers, expecting repayment with interest over a specified period of time. However, from an Islamic perspective, this interest is viewed as riba, as it involves the lender receiving a predetermined amount of money regardless of the underlying risk or effort involved.
The prohibition of riba in Islamic finance stems from the Quran, where it is explicitly mentioned in several verses. For example, in Surah Al-Baqarah (2:275), it states, “Those who consume interest cannot stand [on the Day of Resurrection] except as one stands who is being beaten by Satan into insanity. That is because they say, ‘Trade is [just] like interest.’ But Allah has permitted trade and has forbidden interest.”
According to Islamic scholars, riba not only leads to economic inequality but also hampers economic growth and stability. It encourages excessive debt, speculation, and risks, which can have adverse effects on individuals and the larger society. Islamic finance aims to provide alternative financial solutions that promote fairness, transparency, and social justice.
In contrast, Islamic mortgages are designed to be Shariah-compliant and avoid the use of riba. Instead of charging interest, Islamic financial institutions utilize various alternative financing structures, such as murabaha, musharakah, and ijara. These structures adhere to Islamic principles and involve profit sharing, cost-plus financing, and leasing arrangements, respectively.
| Characteristics of Conventional Mortgages | Characteristics of Islamic Mortgages |
|---|---|
|
|
It is important to note that the legality and effectiveness of Islamic mortgages may vary between jurisdictions. Islamic scholars and financial institutions work together to ensure compliance with Shariah principles while adapting to the legal frameworks of different countries.
In conclusion, the role of riba in conventional mortgages is a fundamental distinction between Islamic and conventional home financing options. Islamic mortgages provide an alternative solution that adheres to Shariah principles and avoids riba. These alternative financing structures allow Muslims to fulfill their housing needs while remaining faithful to their religious beliefs.
Comparing Islamic and Conventional Home Financing Methods
When it comes to purchasing a home, individuals have various financing options available to them. Two common methods are Islamic home financing and conventional home financing. While both options provide individuals with the means to purchase a home, there are some key differences between them.
1. Interest
- In conventional home financing, interest is charged on the loan amount borrowed. This interest is predetermined and remains fixed over the course of the loan.
- Islamic home financing, on the other hand, adheres to the principles of Islamic law. Islamic financing does not charge interest, as it is considered usury (riba) and is forbidden. Instead, an Islamic lender will typically charge a profit margin, which is agreed upon by both parties.
2. Ownership
- In conventional home financing, the lender provides the loan amount, and the borrower repays the loan gradually over a fixed term. However, the ownership of the property remains with the borrower throughout the repayment period.
- In Islamic home financing, the lender and borrower have a shared ownership arrangement. The lender purchases the property and then transfers a portion of ownership to the borrower through a leasing or rent-to-own agreement. As the borrower makes payments, their ownership share increases until they become the sole owner of the property.
3. Risk Sharing
- In conventional home financing, the borrower bears the full risk of any loss or damage to the property. If the borrower defaults on the loan, the lender may choose to foreclose on the property.
- In Islamic home financing, the risk is shared between the lender and the borrower. If the borrower faces financial difficulties, the lender may offer assistance or extend the repayment period. Foreclosure is usually seen as a last resort in Islamic financing.
4. Transparency
- In conventional home financing, the terms and conditions of the loan may not always be fully transparent. The borrower may not be fully aware of the exact amount of interest they will be charged or the total cost of the loan.
- In Islamic home financing, transparency is emphasized. The terms and conditions of the financing are clearly communicated to the borrower, including the profit margin charged by the lender.
5. Socially Responsible
- In conventional home financing, the focus is primarily on profit maximization for the lender.
- In Islamic home financing, there is a greater emphasis on ethical and socially responsible practices. Islamic financing aims to support the development of the community and adhere to principles of justice and fairness.
In conclusion, Islamic home financing differs from conventional home financing in various aspects, including the treatment of interest, ownership structure, risk sharing, transparency, and social responsibility. Individuals seeking home financing options should carefully consider their beliefs and values to determine which method aligns best with their needs.
Shariah Compliance in Islamic Home Financing
Islamic home financing, also known as Islamic mortgages, is a financial tool that adheres to the principles of Shariah law. Shariah compliance is a fundamental aspect of Islamic finance, and it ensures that financial transactions are carried out in accordance with Islamic principles and values.
When it comes to home financing, Shariah compliance requires a number of key principles to be followed:
- No interest (riba): Islamic home financing prohibits the charging or receiving of interest. Instead, the financial institution and the homeowner enter into a partnership agreement where the profits and risks are shared.
- Asset-backed: Shariah-compliant financing is required to be asset-backed, meaning that the financing must have a tangible underlying asset, such as the property being purchased.
- Absence of excessive uncertainty (gharar): Islamic home financing should avoid any excessive uncertainty or ambiguity in the terms and conditions of the contract.
- Avoidance of prohibited activities: Shariah-compliant financing should not involve any prohibited activities, such as investing in alcohol, gambling, or other forbidden industries.
In addition to these general principles, Islamic home financing also incorporates specific Islamic contract structures that comply with Shariah law. Some common structures include:
- Murabaha: In a murabaha contract, the financial institution purchases the property and then sells it to the homeowner at a higher price on a deferred payment basis.
- Ijarah: In an ijarah contract, the financial institution purchases the property and leases it to the homeowner for a specific period. The homeowner pays rent, and at the end of the lease term, ownership of the property may be transferred.
- Musharakah: In a musharakah contract, the financial institution and the homeowner enter into a partnership where both parties contribute capital and share profit and loss.
- Mudarabah: In a mudarabah contract, the financial institution provides the capital while the homeowner manages the property. Profits are shared based on a pre-agreed ratio.
Overall, the Shariah compliance of Islamic home financing ensures that Muslims have access to financial products that align with their religious beliefs. These financing options provide an alternative to conventional mortgages while adhering to the principles and values of Shariah law.
Key Features of Shariah-Compliant Mortgages
Shariah-compliant mortgages, also known as Islamic mortgages, have several key features that differentiate them from conventional mortgages. These features ensure that the mortgages are in accordance with Islamic principles and are considered halal:
- No interest: Islamic mortgages operate on the principle of profit sharing rather than charging interest. This is because charging or paying interest (riba) is prohibited in Islam. Instead, the mortgage provider and the homeowner enter into a partnership where profits and risks are shared.
- Asset-based financing: Shariah-compliant mortgages are based on the concept of asset ownership. The mortgage provider purchases the property and retains ownership until the mortgage is fully paid off. The homeowner then pays rent (ijarah) for the use of the property, which gradually enables them to acquire full ownership.
- Transparency and fairness: Islamic mortgages emphasize transparency and fairness in their terms and conditions. The terms of the mortgage must be clearly communicated to the homeowner, ensuring that they fully understand the obligations and rights associated with the financing. The profit-sharing arrangement is determined upfront, enabling both parties to enter into the agreement with full knowledge.
- Avoidance of prohibited activities: Shariah-compliant mortgages avoid involvement in activities that are considered haram (prohibited) in Islam. For example, the mortgage provider cannot invest in businesses related to alcohol, gambling, or pork products. This ensures that the mortgage is free from any taint of unethical or forbidden practices.
- Independent Shariah board: Islamic mortgages are typically overseen by an independent Shariah board. This board consists of scholars well-versed in Islamic finance and ensures that the mortgage product complies with Shariah principles. Their role is to review and approve the contracts and operations of the mortgage provider to ensure compliance.
These key features help to ensure that Shariah-compliant mortgages align with Islamic principles and provide a halal alternative to conventional mortgages for Muslim homeowners.
Benefits of Choosing an Islamic Mortgage
An Islamic mortgage, also known as a Shariah-compliant mortgage, is a financing option that complies with the principles of Islamic law. It offers several benefits for individuals looking to purchase a home while adhering to their religious beliefs:
- Interest-free financing: One of the fundamental principles of Islamic finance is the prohibition of charging or paying interest (riba). Islamic mortgages are structured in a way that eliminates the accrual or payment of interest. Instead, they rely on profit-sharing agreements or rent-to-own arrangements, making them a halal alternative to conventional mortgages.
- Shariah compliance: By choosing an Islamic mortgage, individuals ensure that their home financing is compliant with the principles of Islamic law. This provides peace of mind and aligns with the ethical and moral values of Muslim borrowers.
- Shared risk and reward: Islamic mortgages operate on the basis of shared risk and reward between the lender and the borrower. Any profit or loss from the investment is shared between the two parties, creating a sense of partnership rather than a traditional lender-borrower relationship.
- Flexibility: Islamic mortgages offer flexibility in terms of payment structures and terms. Lenders may offer various options such as flexible payment schedules, early repayment options, and refinancing opportunities. This allows borrowers to customize their mortgage to better suit their financial situations.
- Transparency: Islamic mortgages promote transparency in the lending process. The terms and conditions are clearly outlined, and borrowers have a better understanding of how their financing works. This transparency fosters trust and reduces the likelihood of misunderstandings or hidden fees.
- Ethical investment: Islamic mortgages ensure that the financing is used for a lawful and ethical purpose, such as purchasing a home. This aligns with the principles of Islamic finance, which emphasize the importance of avoiding investments in sectors or activities that are prohibited under Shariah.
- Community development: Islamic mortgages often have provisions for community development funds or charitable contributions. A portion of the profits generated from the financing may be allocated towards social causes or initiatives that benefit the community, contributing to the greater good.
In conclusion, Islamic mortgages offer several advantages for individuals seeking Shariah-compliant home financing. They provide interest-free options, align with Islamic principles, operate on shared risk and reward, offer flexibility, promote transparency, facilitate ethical investment, and contribute to community development.
Common Misconceptions About Islamic Home Financing
Islamic home financing, also known as Islamic mortgages, is a topic that has generated numerous misconceptions and misunderstandings. These misconceptions often arise due to a lack of knowledge about the principles and practices of Islamic finance. In this section, we will explore some of the common misconceptions about Islamic home financing:
- Islamic mortgages are more expensive than conventional mortgages: This is a common misconception that arises from the perception that Islamic home financing involves additional costs due to its compliance with Shariah principles. However, it is important to note that the pricing structure of Islamic mortgages is based on different principles compared to conventional mortgages. While the initial costs may vary, it is not necessarily true that Islamic mortgages are always more expensive.
- Islamic mortgages are only available to Muslims: Another misconception is that Islamic home financing is exclusively for Muslims. In reality, Islamic mortgages are available to people of all faiths who wish to have a Shariah-compliant option for purchasing a home. Lenders who offer Islamic mortgages can provide these financing options to anyone who meets their eligibility criteria, regardless of their religious background.
- Islamic mortgages involve paying rent to the lender: This misconception arises from a misunderstanding of the concept of ijara or lease-based financing. In Islamic home financing, the lender purchases the property and leases it to the buyer for an agreed-upon period. The buyer pays regular installments that comprise both the repayment of the principal amount and a predetermined profit margin. Once the lease period ends, the buyer becomes the owner of the property. Therefore, Islamic mortgages do not involve paying rent to the lender.
- Islamic mortgages are not widely available: Some people believe that Islamic home financing options are limited and not widely available. While it is true that the availability of Islamic mortgages may vary across different regions, countries, and financial institutions, there has been a significant growth in the availability of Islamic home financing in recent years. Numerous financial institutions around the world now offer Islamic mortgages to meet the growing demand for Shariah-compliant financing options.
- Islamic mortgages are only for low-income individuals: This is a misconception that arises from the fact that Islamic finance has often been associated with microfinance initiatives and poverty alleviation efforts in some parts of the world. However, Islamic home financing is available to individuals of all income levels. Whether someone is a low-income earner or a high-net-worth individual, they can explore Islamic home financing options that suit their financial needs and circumstances.
It is important to dispel these misconceptions and increase awareness about the principles and practices of Islamic home financing. By understanding the truth behind these misconceptions, individuals can make informed decisions when considering Islamic mortgages as a viable option for purchasing a home.
Islamic Mortgages and the Global Real Estate Market
The global real estate market is a vast and lucrative industry that attracts investors from all over the world. However, for devout Muslims, investing in real estate can be a challenge because conventional mortgages often involve interest payments, which are prohibited in Islamic finance. This has led to the development of Islamic mortgages, also known as halal mortgages, which adhere to the principles of Shariah law.
Islamic mortgages offer a Shariah-compliant alternative to conventional mortgages, allowing Muslims to purchase homes without violating their religious beliefs. These mortgages are structured in a way that avoids charging interest, which is considered usury in Islam. Instead, the lender and the borrower enter into a partnership where the lender shares in the profits and risks of the property. This partnership model ensures that both parties share in the benefits and responsibilities of property ownership.
The popularity of Islamic mortgages has been on the rise in recent years, as more Muslims seek ways to finance their homes while remaining faithful to their religious principles. This has led to the growth of Islamic mortgage products and services in countries with significant Muslim populations, such as Malaysia, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates.
However, Islamic mortgages are not limited to these countries alone. In fact, they have gained traction in the global real estate market, with financial institutions in Western countries also offering Islamic mortgage products. For example, in the United Kingdom, several banks and lenders have introduced Shariah-compliant home finance options to cater to the growing demand from Muslim homebuyers.
This global acceptance of Islamic mortgages reflects the increasing recognition of Islamic finance as a viable alternative to conventional finance. As a result, the real estate market has become more inclusive and accessible to Muslim investors, who can now participate in the property market without compromising their beliefs.
Furthermore, the growth of Islamic mortgages has had a positive impact on the real estate industry, stimulating demand and expanding the pool of potential buyers. This has led to increased competition among lenders, which has in turn driven innovation and the development of new financing products tailored to the needs of Muslim homebuyers. The availability of Islamic mortgages has also helped to fuel the growth of the global real estate market, attracting new investors and contributing to economic development.
In conclusion, Islamic mortgages have become an integral part of the global real estate market, allowing Muslims to invest in properties while adhering to the principles of Shariah law. The acceptance and growth of Islamic mortgages worldwide demonstrate the increasing recognition and acceptance of Islamic finance as a viable and ethical alternative to conventional finance.
How Can Non-Muslims Benefit from Islamic Home Financing?
Islamic home financing, also known as sharia-compliant mortgages, offers a unique and ethical alternative for homeownership that can be beneficial for both Muslims and non-Muslims alike. While Islamic home financing follows the principles of Islamic law, it is not exclusive to Muslims and can be utilized by anyone interested in a fair and ethical home financing solution.
Here are some ways in which non-Muslims can benefit from Islamic home financing:
- Ethical and Fair Principles: Islamic home financing operates on the principles of fairness, transparency, and ethical conduct. The contracts used in Islamic home financing, such as murabaha (cost-plus financing) and ijara (leasing), ensure that all parties involved are treated fairly and that there are no hidden fees or unjust practices. Non-Muslims can appreciate the ethical standards upheld by Islamic home financing institutions.
- Avoidance of Interest: Islamic finance prohibits the charging or paying of interest, which is seen as exploitative. Instead, Islamic home financing relies on profit-sharing arrangements or rental agreements. Non-Muslims who prefer to avoid interest-based transactions can find Islamic home financing appealing.
- Flexible Financing Options: Islamic home financing offers various structures to suit different homeowner needs. For example, the murabaha structure allows the financing institution to purchase the property and sell it back to the homeowner at a profit, paid over a specified period. This allows non-Muslims to have access to flexible financing options that cater to their individual circumstances.
- Community Development: Islamic finance promotes the concept of collective prosperity and community development. Islamic home financing institutions often invest in socially responsible projects that benefit the community, such as affordable housing initiatives, hospitals, and educational institutions. Non-Muslims can participate in these initiatives and contribute to the overall development of society.
- Competitive Rates: Islamic home financing institutions aim to provide competitive rates and terms to attract customers. Non-Muslims can benefit from these competitive rates, which may be comparable or even better than conventional mortgage options.
In conclusion, Islamic home financing is not limited to Muslims and offers a range of benefits that can be attractive to non-Muslims as well. The ethical and fair principles, avoidance of interest, flexible financing options, community development initiatives, and competitive rates make Islamic home financing a viable and appealing choice for anyone seeking an ethical and transparent home financing solution.
Research and Studies on the Shariah Compliance of Islamic Mortgages
Islamic mortgages, also known as Islamic home financing options, have gained popularity among Muslims as an alternative to conventional mortgages. These mortgages are designed to be Shariah-compliant, adhering to the principles of Islamic finance. Various research and studies have been conducted to evaluate the Shariah compliance of these home financing options. The findings of these studies are crucial for individuals seeking halal alternatives for their housing needs.
1. Islamic Scholars’ Opinions: Some studies have focused on exploring the opinions and viewpoints of Islamic scholars regarding Islamic mortgages. These studies have delved into the Islamic legal principles and interpretations related to the elements of Islamic home financing, such as the concept of Murabaha (cost-plus financing), Musharaka (partnership), and Ijarah (leasing).
2. Comparative Analysis: Researchers have also conducted comparative analyses to evaluate the similarities and differences between conventional mortgages and Islamic mortgages. These studies have examined the contractual structures, pricing mechanisms, risk-sharing arrangements, and underlying legal frameworks of both financing options.
3. Legal Framework: Some studies have concentrated on analyzing the legal framework surrounding Islamic mortgages, including the regulatory environment and legal documentation. These studies aim to ensure that the home financing options comply with Shariah principles while adhering to local laws and regulations.
4. Transparency and Disclosure: Researchers have examined the transparency and disclosure practices of Islamic mortgage providers. These studies evaluate the clarity and comprehensibility of the terms and conditions, allowing potential borrowers to make informed decisions about their home financing options.
5. Consumer Awareness and Perception: Several studies have focused on understanding the awareness and perception of consumers towards Islamic mortgages. These studies explore the knowledge, preferences, and motivations of Muslim homebuyers, contributing to the development of marketing strategies and educational campaigns.
6. Islamic Financial Institutions: Researchers have also evaluated the practices and approaches of Islamic financial institutions offering home financing options. These studies assess the Shariah compliance of the institutions’ operations, products, and services to ensure that they meet the ethical and religious requirements of their clients.
7. Risk Management: Lastly, some studies have examined the risk management practices associated with Islamic mortgages. These studies aim to identify and address potential risks, such as credit risk, market risk, and operational risk, ensuring the financial stability and sustainability of Islamic mortgage providers.
Conclusion
Research and studies on the Shariah compliance of Islamic mortgages play a vital role in ensuring that Muslims have access to housing finance options that align with their religious beliefs and principles. By evaluating the legal, ethical, and operational aspects of these financing options, researchers contribute to the development of transparent and trustworthy Islamic home financing practices.
Regulations and Oversight of Shariah-Compliant Home Financing
Shariah-compliant home financing options are subject to regulations and oversight to ensure their compliance with Islamic principles. These regulations aim to safeguard the interests of both the borrowers and the financial institutions offering the Islamic mortgages.
In most countries, Islamic financial institutions are regulated by specific supervisory bodies, such as central banks or financial authorities, which are responsible for overseeing and monitoring the operations of these institutions.
One of the key regulations governing Shariah-compliant home financing is the requirement to establish a Shariah board or committee. This board consists of Islamic scholars who have expertise in Islamic finance and are responsible for ensuring that the products and services offered by the financial institution are in compliance with Shariah principles.
The Shariah board reviews and approves the home financing products, ensuring that they adhere to the principles of equity, fairness, and social justice. The board also helps in the interpretation and application of Shariah principles in the context of modern financial transactions.
To ensure transparency and accountability, Islamic financial institutions are also required to disclose the terms and conditions of their home financing products to borrowers. This includes providing information on profit rates, fees, and potential risks associated with the financing arrangements.
In addition to these regulatory requirements, Islamic financial institutions may also have their own internal control mechanisms and risk management frameworks in place. These measures help to further ensure compliance with Shariah principles and protect the interests of both parties involved in the home financing transaction.
Overall, the regulations and oversight of Shariah-compliant home financing play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of Islamic finance and ensuring its compliance with Shariah principles. By providing a framework for accountability and transparency, these regulations help to build trust and confidence in Islamic home financing options among the Muslim community.
The Growth and Future of Islamic Mortgages
The concept of Islamic mortgages, or home financing that complies with Shariah law, has been gaining popularity in recent years. Islamic mortgages offer an alternative for Muslims who wish to purchase a home without engaging in interest-based transactions, which are prohibited in Islam.
Islamic mortgages have seen significant growth in many countries with large Muslim populations, such as the United Kingdom, Canada, and Malaysia. This growth can be attributed to several factors:
- Increased demand: As more Muslims become aware of the availability of Islamic mortgages and the importance of adhering to Shariah principles, the demand for these products has been steadily increasing.
- Financial institutions’ response: Many banks and financial institutions have recognized the potential market for Islamic mortgages and have started offering Shariah-compliant home financing options to cater to this demand.
- Supportive regulatory environment: Governments in countries with large Muslim populations have taken steps to create a supportive regulatory environment for Islamic finance, including mortgages. This has included the development of guidelines and regulations that enable Islamic financial institutions to operate and offer Shariah-compliant products.
- Educational initiatives: Various educational initiatives have been launched to raise awareness about Islamic mortgages and the principles behind them. These initiatives help potential homebuyers understand the benefits and features of Islamic mortgages and make informed decisions.
The future of Islamic mortgages looks promising, as the market continues to grow and evolve. Financial institutions are increasingly investing in research and development to improve and innovate Islamic mortgage products, making them more accessible and competitive.
Furthermore, as the global Muslim population continues to increase, the demand for Shariah-compliant financial products, including mortgages, is expected to rise. This creates opportunities for the expansion of Islamic mortgage offerings in both Muslim-majority countries and non-Muslim majority countries.
However, challenges remain. One of the main challenges is the lack of standardized regulations and guidelines for Islamic mortgages, resulting in variations in product structures and practices across different financial institutions and jurisdictions. Efforts are being made to address these challenges and establish more standardized frameworks to ensure the consistent application of Shariah principles in Islamic mortgages.
In conclusion, the growth of Islamic mortgages has been driven by increased demand, financial institutions’ response, a supportive regulatory environment, and educational initiatives. The future of Islamic mortgages looks promising, with opportunities for expansion and innovation. However, challenges such as standardization need to be addressed to ensure the continued growth and sustainability of Islamic mortgages.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Islamic Home Financing
In recent years, Islamic home financing has gained momentum and proved to be a viable option for Muslims seeking Shariah-compliant mortgages. In this section, we will explore a few case studies of successful implementation of Islamic home financing.
Case Study 1: XYZ Islamic Bank
XYZ Islamic Bank, a leading financial institution offering dedicated Islamic financial products, successfully implemented an Islamic home financing solution. The bank structured its financing based on the principles of Musharakah and Ijara, making it compliant with Shariah law.
Under the Musharakah structure, the bank and the customer enter into a partnership to purchase the property jointly. The customer makes a down payment, and the bank contributes the remaining funds. The property’s ownership is shared between the bank and the customer, with the customer gradually buying out the bank’s share over time.
Simultaneously, the bank leases its share of the property to the customer through the Ijara contract. The customer pays rent to the bank, which gradually decreases as the customer buys out the bank’s share. Once the customer has fully acquired the property, the lease agreement ends, and the customer becomes the sole owner.
This case study demonstrates an effective implementation of Islamic home financing principles, allowing customers to purchase homes without compromising their religious beliefs.
Case Study 2: ABC Islamic Mortgage Company
ABC Islamic Mortgage Company, a dedicated Islamic mortgage provider, offers a unique home financing solution based on the Murabaha structure. This structure allows customers to buy a property without resorting to conventional interest-based loans.
Under the Murabaha structure, the company purchases the property from the seller, adding a profit margin to the purchase price. The customer then buys the property from the company at the inflated price, which is paid in installments over an agreed-upon period.
This case study demonstrates how the use of the Murabaha structure enables customers to acquire homes in a Shariah-compliant manner without the need for conventional interest-based loans.
Case Study 3: PQR Islamic Credit Union
PQR Islamic Credit Union, a member-owned financial cooperative, offers a unique home financing solution based on the diminishing Musharakah structure.
Under this structure, the credit union and the member enter into a partnership to purchase the property jointly. The member makes a down payment, and the credit union contributes the remaining funds. The ownership of the property is shared between the credit union and the member, with the member gradually buying out the credit union’s share over time.
Unlike the traditional Musharakah structure, the share of the credit union diminishes over time, reducing the rental payments required from the member. Eventually, the member becomes the sole owner of the property.
This case study illustrates how the diminishing Musharakah structure offers a unique and flexible approach to Islamic home financing, allowing members of the credit union to gradually acquire full ownership of their homes.
These case studies showcase the successful implementation of Islamic home financing by various financial institutions, providing Muslims with Shariah-compliant alternatives to conventional mortgages. By offering innovative structures such as Musharakah, Ijara, Murabaha, and diminishing Musharakah, these institutions have paved the way for home ownership for the Muslim community while adhering to the principles of Shariah law.
Challenges and Issues in Shariah-Compliant Home Financing
Shariah-compliant home financing, also known as Islamic mortgages, have gained popularity among Muslims seeking to adhere to Islamic principles when it comes to acquiring their own homes. While these financing options offer an alternative to conventional mortgages, they also come with their own set of challenges and issues.
- Availability: One of the main challenges with Shariah-compliant home financing is the limited availability of these options. In many countries, conventional mortgages dominate the market and finding Islamic financing can be difficult. This lack of availability can make it challenging for Muslims to find suitable home financing options that align with their religious beliefs.
- Complexity: Shariah-compliant home financing structures can be more complex compared to conventional mortgages. This complexity stems from the need to adhere to Islamic principles and avoid riba (interest) and gharar (uncertainty). The intricate nature of these financing structures can make it difficult for individuals to fully understand the terms and conditions associated with Islamic mortgages.
- Cost: Shariah-compliant home financing options may come with higher costs compared to conventional mortgages. This is because Islamic financial institutions operate based on profit-sharing and risk-sharing principles, which can lead to higher financing costs for borrowers. The higher costs associated with Islamic mortgages can make it challenging for some individuals to afford homeownership.
- Lack of Standardization: Another challenge in Shariah-compliant home financing is the lack of standardization within the industry. Different Islamic financial institutions may structure their mortgages differently, which can make it challenging for borrowers to compare options and make informed decisions. The lack of standardization can also create confusion and uncertainty among borrowers.
- Affordability: Shariah-compliant home financing may not always be feasible or affordable for all individuals. The strict adherence to Islamic principles and avoidance of interest can limit the financing options available, especially for low-income or first-time homebuyers. This affordability issue can make it challenging for individuals to find suitable Islamic mortgages that meet their financial needs.
In conclusion, while Shariah-compliant home financing offers a way for Muslims to adhere to Islamic principles when acquiring their own homes, it is not without its challenges and issues. Limited availability, complexity, higher costs, lack of standardization, and affordability concerns are some of the challenges that individuals may face when considering Islamic mortgages. It is important for individuals to carefully assess their options and seek advice from qualified professionals before making any decisions regarding home financing.
The Impact of Islamic Mortgages on Society
Islamic mortgages, also known as halal mortgages, have had a significant impact on society. These financial products provide an alternative for Muslims who want to adhere to shariah principles while buying a home. Here are some of the key impacts of Islamic mortgages:
- Empowering Muslim Homeowners: Islamic mortgages allow Muslim individuals and families to purchase a home without compromising their religious beliefs. This empowers them to take control of their housing needs and become homeowners, which is an important aspect of personal and family stability.
- Promoting Financial Inclusion: Islamic mortgages contribute to financial inclusion by providing access to housing finance for Muslims who might otherwise be excluded from conventional mortgage options due to shariah restrictions. This helps reduce economic disparities and promotes social equality.
- Encouraging Ethical Financing Practices: Islamic mortgages operate based on the principles of fairness and ethical finance. They prohibit interest (riba) and engage in asset-based financing, which ensures that the transactions are fair and transparent. This encourages a more ethical approach to financing, fostering trust and integrity in the financial system.
- Supporting Islamic Finance Industry Growth: The popularity and demand for Islamic mortgages have contributed to the growth of the Islamic finance industry. This has led to the emergence of new Islamic financial institutions and products, creating more options for Muslims seeking shariah-compliant financial services.
- Facilitating Real Estate Development: The availability of Islamic mortgages has stimulated real estate development in areas with large Muslim populations. This is because the demand for shariah-compliant financing has increased the number of potential homebuyers, leading to the construction of new houses and the overall development of the housing market.
In conclusion, Islamic mortgages have had a positive impact on society by empowering Muslim homeowners, promoting financial inclusion, encouraging ethical financing practices, supporting the growth of the Islamic finance industry, and facilitating real estate development. These mortgages provide a viable alternative for Muslims to fulfill their housing needs while adhering to shariah principles.
Alternative Shariah-Compliant Home Financing Options
Islamic mortgages, also known as Halal mortgages, are a popular choice for Muslims looking to purchase a home in compliance with Shariah law. However, they are not the only option available. There are other Shariah-compliant home financing options that provide alternatives to conventional mortgages. Here are a few of them:
- Ijarah: This is a form of lease-to-own financing. The bank purchases the property and leases it to the individual with the option to buy it at the end of the lease term. The monthly payments consist of a combination of rent and a portion of the purchase price.
- Musharakah Mutanaqisah: This is a partnership or joint venture agreement between the individual and the bank. Both parties contribute to the financing of the property, and the individual pays rent on the bank’s share of the property. Over time, the individual can buy out the bank’s share, ultimately owning the property outright.
- Bai Bithaman Ajil: This is a deferred payment sale agreement. The bank purchases the property and sells it to the individual at a higher price, which is payable in installments over a specified period. The individual takes possession of the property immediately and pays the bank in installments.
- Murabaha: This is a cost-plus sale agreement. The bank purchases the property and sells it to the individual at a higher price, which is payable in installments over a specified period. The individual takes possession of the property immediately and pays the bank in installments.
These alternative Shariah-compliant home financing options provide Muslims with additional choices when it comes to purchasing a home. Each option has its own advantages and considerations, so it is important for individuals to carefully evaluate and compare them before making a decision. Consulting with an Islamic financial advisor can also be valuable in understanding the intricacies and suitability of each option based on individual circumstances.
Exploring the Spiritual and Ethical Dimensions of Islamic Home Financing
Islamic home financing is a concept that adheres to the principles of Shariah law, which is based on the teachings of the Quran and the tradition of Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him). It aims to provide Muslims with a way to purchase homes while also maintaining their religious and ethical values.
The spiritual dimension of Islamic home financing is rooted in the belief that all aspects of a Muslim’s life should be governed by faith. This includes financial matters, such as purchasing a home. By seeking Shariah-compliant financing options, Muslims ensure that their actions align with their religious beliefs and contribute to a sense of spiritual well-being.
Islamic home financing is considered ethical because it prohibits the payment or receipt of interest, which is seen as exploitative and unfair. Instead, Islamic financial institutions offer alternative models that are based on profit-sharing or equity participation. These models ensure that both the buyer and the institution share in the risks and rewards of the investment, promoting fairness and equality.
Additionally, Islamic home financing encourages responsible and sustainable practices. Islamic financial institutions are obligated to assess the social and environmental impact of their investments, ensuring that they comply with Islamic principles of justice, equity, and sustainability. This consideration of broader societal and environmental well-being aligns with the ethical values promoted by Islam.
Furthermore, Islamic home financing promotes personal and communal responsibility. Islamic financial institutions encourage homeownership as a means of stability and responsibility, promoting a sense of belonging and investment in one’s community. This fosters a culture of mutual support and cooperation among Muslims, strengthening the bonds of the community.
In conclusion, Islamic home financing not only provides Muslims with a means to purchase homes in accordance with their religious beliefs, but it also encompasses spiritual and ethical dimensions. By adhering to the principles of Shariah law, Islamic home financing promotes fairness, sustainability, and communal responsibility, ensuring that Muslims can achieve their dreams of homeownership while also maintaining their religious and ethical values.
FAQ
What is the concept of Islamic mortgages?
Islamic mortgages, also known as halal mortgages, are home financing options that are compliant with Shariah, or Islamic law. These mortgages adhere to the principles of riba, or usury, which is prohibited in Islam. Instead of charging interest, Islamic mortgages involve an alternative mechanism, such as leasing or partnership, to facilitate the purchase of a home.
How do Islamic mortgages differ from conventional mortgages?
Islamic mortgages differ from conventional mortgages in that they do not involve the charging or paying of interest. In conventional mortgages, interest, or riba, is a fundamental component of the loan agreement. Islamic mortgages, on the other hand, use alternative arrangements, such as Musharakah (partnership) or Ijara (leasing), to make the purchase of the property Shariah compliant.
What are the benefits of Islamic mortgages?
Islamic mortgages offer several benefits to individuals who wish to abide by Islamic principles. Firstly, since they do not involve interest, they are considered halal and compliant with Shariah law. Secondly, Islamic mortgages often come with flexible payment options, allowing individuals to tailor their payments to their financial situation. Additionally, some Islamic mortgages may offer profit-sharing arrangements, providing individuals with an opportunity to earn returns on their investment.
Are Islamic mortgages widely available?
Yes, Islamic mortgages are becoming increasingly popular and widely available in many countries, especially in regions with a significant Muslim population. Islamic banks and financial institutions offer a variety of Islamic mortgage options, making it easier for individuals to find a halal financing solution for their home purchase.
Are Islamic mortgages more expensive than conventional mortgages?
The cost of an Islamic mortgage can vary depending on various factors, such as the bank or financial institution offering the mortgage and the specific terms of the agreement. In some cases, Islamic mortgages may have slightly higher upfront costs or processing fees compared to conventional mortgages. However, it is important to note that the long-term cost of an Islamic mortgage may be lower, as they do not involve interest payments.