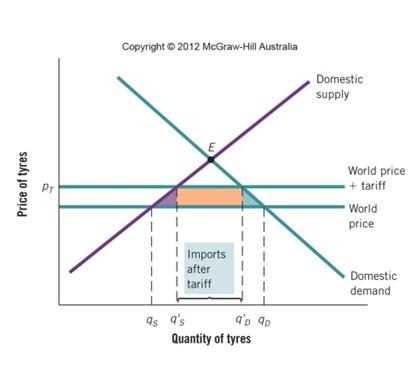
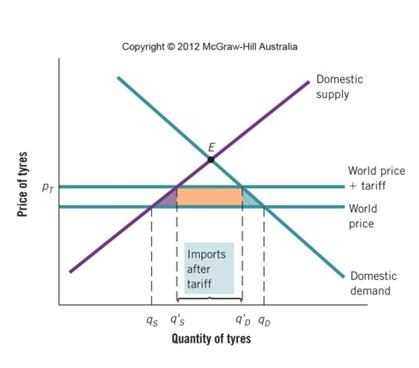
Quotas are a trade policy tool that countries use to limit the quantity or value of goods and services that can be imported or exported. They are often implemented to protect domestic industries from foreign competition. Quotas work as a form of trade restriction, allowing countries to control the influx of foreign goods and ensure that the local industries have a fair chance to compete.
One of the key benefits of quotas is their ability to boost domestic industries. By limiting the quantity or value of imported goods, quotas create a scarcity in the domestic market. This scarcity can lead to increased demand and higher prices for domestic products. As a result, domestic producers are able to expand their production and capture a larger share of the market. This, in turn, can lead to increased investment, job creation, and economic growth.
Quotas also provide domestic industries with a level playing field. By limiting the amount of foreign competition, quotas help to reduce the pressure on local producers to lower their prices or improve their products. This allows domestic producers to focus on innovation and quality improvement, which can make them more competitive in the long run. Additionally, quotas can help to protect industries that are vital for national security or strategic reasons, such as defense or agriculture.
However, it is important to note that quotas can also have negative consequences. They can lead to higher prices for consumers, restrict consumer choice, and create inefficiencies in the market. Moreover, quotas can provoke retaliatory actions from other countries, triggering trade disputes and damaging international relations. Therefore, the use of quotas should be carefully considered and balanced with other trade policy tools to ensure that the benefits outweigh the costs.
The Importance of Quotas in Boosting Local Industries
Quotas play a significant role in boosting local industries by protecting them from foreign competition and promoting domestic production. They are a form of trade restriction that sets a limit on the quantity or value of certain goods that can be imported or exported within a specified time frame.
Promoting Economic Growth
One of the primary reasons why quotas are important in boosting local industries is their ability to promote economic growth. By limiting the imports of specific products, quotas encourage domestic producers to meet the demand for those goods, leading to increased production and employment opportunities. This, in turn, stimulates economic growth and contributes to the overall development of the country.
Protecting Domestic Industries
Quotas help protect domestic industries from foreign competition by limiting the quantity of imported goods. This protection ensures that local producers have a fair chance to compete in the marketplace, preventing them from being overwhelmed by cheap or subsidized foreign products. By maintaining a level playing field, quotas provide domestic industries with the breathing space needed to grow, innovate, and become more competitive.
Preserving National Security
Quotas also play a crucial role in preserving national security. By setting limits on the importation of certain goods, countries can ensure the availability of essential products within their borders. This prevents overdependence on foreign suppliers for crucial goods, reducing the vulnerability of local industries to disruptions in the global supply chain. Additionally, quotas can also be used as a tool to protect specific industries deemed strategic for national security reasons.
Promoting Infant Industries
Quotas can be particularly beneficial for promoting infant industries, which are newly established or emerging sectors with low production capabilities. By restricting imports of competing products, quotas give these industries time to develop and become self-sufficient. This protection allows them to establish economies of scale, access financing, and invest in research and development, ultimately increasing their competitiveness in the long run.
Ensuring Economic Stability
Quotas also contribute to economic stability by reducing the impact of unpredictable market fluctuations. By controlling the flow of trade, quotas can prevent sudden surges or declines in imports that could destabilize local industries. This stability allows domestic producers to plan their production more effectively, maintain consistent employment levels, and ensure a reliable supply of goods for the domestic market.
In conclusion, quotas play a crucial role in boosting local industries by promoting economic growth, protecting domestic industries from foreign competition, preserving national security, promoting infant industries, and ensuring economic stability. By implementing quotas strategically, countries can create an environment that fosters the growth and development of their domestic industries while safeguarding their overall economic well-being.
Balancing Domestic and International Trade
Quotas play a crucial role in the balancing of domestic and international trade. They help protect domestic industries by limiting the amount of goods that can be imported from other countries. By restricting the quantity of imports, quotas allow domestic producers to compete more effectively in the market and maintain their market share.
One way quotas help in balancing trade is by reducing the trade deficit. When a country imports more than it exports, it results in a trade deficit. By implementing quotas on certain goods, a country can control the amount of imports and reduce its trade deficit. This can have a positive impact on the domestic economy by stimulating domestic production and increasing employment opportunities.
Quotas also help in balancing domestic and international trade by preventing dumping. Dumping occurs when foreign producers sell their goods at significantly lower prices in the domestic market, threatening domestic industries. By imposing quotas, a country can prevent dumping and protect its domestic producers from unfair competition. This allows domestic industries to grow and prosper, contributing to the overall economic development of the country.
Furthermore, quotas promote self-sufficiency and reduce reliance on imported goods. By placing limits on imports, a country can encourage the production of certain goods domestically. This helps to develop local industries and contributes to the growth of the domestic economy. Self-sufficiency also provides a sense of security and stability, as it reduces the dependence on foreign nations for essential goods.
In conclusion, quotas play a critical role in balancing domestic and international trade. They help protect domestic industries, reduce trade deficits, prevent dumping, promote self-sufficiency, and contribute to the overall economic development of a country. While there may be some drawbacks or criticisms of quotas, they remain an effective measure for supporting domestic industries and maintaining a balance in international trade.
Protecting Local Businesses from Unfair Competition
One of the main reasons why quotas are implemented is to protect local businesses from unfair competition. When foreign goods flood the domestic market, local producers often struggle to compete on price and quality. Quotas help to limit the import of these goods, ensuring that local businesses have a fair chance to thrive.
By setting a limit on the quantity of goods that can be imported, quotas prevent foreign producers from flooding the market with cheap goods that undercut domestic prices. This is especially important for industries that rely heavily on labor, such as manufacturing. Without quotas, local businesses might be forced to close down or downsize due to the inability to compete with cheaper imports.
Quotas also support the growth of local industries by encouraging investment in domestic production. When a quota is in place, it creates a predictable and stable market for local producers, giving them the confidence to invest in expanding their operations. This can lead to the creation of more jobs and contribute to overall economic development.
Furthermore, quotas can help protect local businesses from unfair practices such as dumping. Dumping occurs when foreign producers sell their goods at prices below their production costs, with the intention of driving competitors out of the market. By imposing quotas, the government can prevent dumping and ensure a level playing field for local businesses.
However, it’s important to note that quotas should be implemented carefully to avoid negative consequences. For instance, if quotas are set too low, they can lead to shortages and higher prices for consumers. Additionally, they can potentially hinder competition and innovation by shielding local businesses from global market forces.
In conclusion, quotas play a crucial role in protecting local businesses from unfair competition. They limit the import of goods, ensuring that domestic producers have a fair chance to compete. By creating stable market conditions, quotas also encourage investment in local industries. However, it is essential to strike the right balance to avoid unintended consequences and promote fair trade practices.
Encouraging Investment in Local Industries
Quotas play a significant role in encouraging investment in local industries. By imposing limits on the import of certain goods, governments can create a protected market for domestic producers. This protection provides an incentive for businesses to invest in local industries, as they can rely on steady demand and reduced competition from foreign imports.
One way quotas encourage investment is by providing predictability and stability. When businesses know that their products will have a guaranteed market share due to import restrictions, they are more likely to invest in expanding their production capacity or developing new products. This increased investment leads to job creation and economic growth in the local industry.
Another advantage of quotas in encouraging investment is the reduction of competition from foreign producers. Without import limitations, domestic industries often face tough competition from foreign companies that may benefit from lower production costs or other advantages. By implementing quotas, governments can level the playing field and give local producers a chance to compete.
In addition, quotas can also serve as a tool to attract foreign direct investment (FDI). Companies from abroad may be more willing to invest in a country if they see that the government is committed to protecting local industries through import restrictions. This can lead to the establishment of new factories and facilities, further stimulating economic development.
It is important to note that while quotas can be effective in encouraging investment in local industries, they should be used judiciously and with careful consideration of potential negative consequences. Overly restrictive quotas can limit consumer choice and lead to higher prices for goods. Additionally, they may provoke retaliation from other countries, resulting in trade tensions and potential economic repercussions.
In conclusion, quotas can play a crucial role in encouraging investment in local industries. By providing predictability, reducing competition, and attracting foreign investment, quotas create a favorable environment for businesses to invest in and develop domestic industries. However, it is essential for policymakers to strike the right balance and ensure that quotas are implemented in a way that benefits both local producers and consumers.
Promoting Job Creation and Economic Growth
Quotas are a policy tool that domestic governments can use to protect and promote their own industries. By limiting the importation of certain goods, quotas create a market advantage for domestic producers, allowing them to increase production, create new jobs, and stimulate economic growth.
One of the main ways quotas promote job creation is by encouraging domestic producers to expand their operations. When faced with a limited supply of imported goods, consumers have no choice but to turn to domestic alternatives. This increased demand for local products incentivizes domestic producers to increase their output, leading to the creation of new jobs in manufacturing, distribution, and other related sectors.
Furthermore, quotas can also help to address unemployment issues by providing protection for industries that are labor-intensive. By effectively limiting the competition from imported goods, quotas can help to sustain local industries that rely heavily on manual labor. This ensures that jobs are preserved within the domestic economy and provides stability for workers in these industries.
In addition to job creation, quotas also contribute to overall economic growth. When domestic industries experience increased demand and expansion, there is a subsequent increase in economic activity. This growth is not only limited to the specific industry protected by the quota, but also extends to related industries and sectors that support the domestic production process.
Moreover, the economic benefits of quotas can extend beyond the immediate job creation and economic growth. By supporting domestic industries, quotas also enable countries to develop their own capabilities and expertise in certain sectors. This can lead to long-term advantages such as technological advancements, improved productivity, and enhanced competitiveness in the global market.
It is important to note that while quotas can provide short-term benefits for domestic producers, they can also have downsides. Quotas can lead to higher prices for consumers, reduced product choices, and potential trade disputes with exporting countries. Therefore, the implementation of quotas should be carefully balanced and monitored to ensure that the overall benefits outweigh the potential drawbacks.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Increase in domestic production | Quotas create a market advantage for domestic producers, leading to increased production and expansion of their operations. |
| Job creation | Expanded domestic production results in the creation of new jobs in manufacturing and related sectors. |
| Protection of labor-intensive industries | Quotas sustain industries that rely heavily on manual labor, helping to address unemployment issues. |
| Economic growth | Increased demand and expansion in domestic industries contribute to overall economic growth. |
| Development of capabilities and expertise | Quotas support the development of domestic capabilities and expertise in certain sectors, leading to long-term advantages. |
| Consideration of potential drawbacks | Quotas may lead to higher prices for consumers, reduced product choices, and trade disputes. |
Ensuring National Self-Sufficiency
Quotas play a crucial role in ensuring national self-sufficiency by protecting domestic industries and reducing dependency on foreign goods. By limiting the quantity of imports allowed into the country, quotas aim to give local producers a competitive advantage, allowing them to meet the domestic demand and maintain a stable market position.
One of the primary reasons for implementing quotas is to safeguard national security. By reducing dependence on imports, especially for critical goods such as food, energy, or defense-related products, countries can protect themselves from potential disruptions in the global supply chains. This ensures that the country can sustain itself even in times of crisis or conflict, reducing vulnerability to external threats.
Furthermore, quotas can foster the development and growth of domestic industries. By limiting the competition from foreign producers, quotas create opportunities for domestic businesses to expand their operations, employ more workers, and invest in research and development. This can lead to innovation, increased productivity, and the creation of new technologies, which can in turn boost the overall competitiveness of the nation’s industries.
Quotas also help in maintaining a balanced trade relationship between countries. By setting limits on imports, countries can prevent excessive trade deficits and promote a more equal distribution of benefits. This can reduce the risk of economic dependence and ensure a fair competition in both domestic and international markets.
However, it is important to note that while quotas can bring short-term benefits to domestic industries, they can also lead to negative consequences in the long run. Restricting imports may result in higher prices for consumers, limited product choices, and reduced access to international markets. It can also provoke retaliation from other countries, sparking trade tensions and potential trade wars.
Therefore, finding a balance between protecting domestic industries and promoting international trade is crucial. Quotas should be used as a temporary measure to facilitate domestic industry development, while also considering the potential long-term implications and exploring alternative solutions. International cooperation and negotiation are key in addressing the challenges associated with quotas and ensuring a sustainable and mutually beneficial global trade environment.
Safeguarding National Security
Quotas can also play a critical role in safeguarding national security. By implementing quotas on certain goods, countries can protect their own industries and ensure the availability of essential products in times of crisis or conflict.
In times of war or geopolitical tension, relying on imports for essential goods can become a significant security risk. By imposing quotas, countries can ensure that they have a domestic supply of key products, such as food, energy, or military equipment.
Quotas can help prevent overreliance on foreign suppliers and reduce the vulnerability of a country’s economy to disruptions in global trade. By supporting local industries through quotas, countries can maintain a certain level of self-sufficiency and reduce their dependence on other nations.
In addition to safeguarding national security, quotas can also contribute to the development of domestic industries. By protecting local businesses from foreign competition, quotas provide an opportunity for domestic producers to grow, innovate, and become more competitive over time.
Example: Quotas on Critical Technologies
One example of how quotas can safeguard national security is the imposition of quotas on critical technologies. Countries may restrict the export of advanced technology products or components to prevent the transfer of sensitive technology to potential adversaries.
By implementing quotas, countries can control the export of certain technologies and prevent them from falling into the wrong hands. This helps protect national security by safeguarding valuable intellectual property and ensuring that sensitive technologies are not misused or exploited by foreign powers.
Conclusion
Quotas can serve as an important tool for safeguarding national security. By implementing quotas on essential goods and critical technologies, countries can protect their own industries, reduce dependency on foreign suppliers, and ensure the availability of key products in times of crisis or conflict.
However, it is important to strike a balance between national security concerns and the benefits of international trade. Quotas should be designed and implemented carefully to avoid unnecessary trade barriers and maintain a healthy global trading environment.
Stimulating Innovation and Technological Advancements
Quotas on imports have been proven to stimulate innovation and technological advancements within domestic industries. When domestic producers are protected from foreign competition through quotas, they have a higher incentive to invest in research and development to improve their products and processes.
With limited competition from foreign producers, domestic companies can focus on developing new technologies and improving efficiency to increase their market share. They can allocate more resources towards innovation without the immediate threat of foreign companies undercutting their prices.
The presence of quotas also incentivizes domestic producers to collaborate with universities, research institutions, and other stakeholders to develop and adopt new technologies. These partnerships can lead to the transfer of knowledge and expertise, further fueling innovation within the domestic industry.
Additionally, quotas create an environment that encourages domestic producers to invest in advanced manufacturing techniques and automation. By implementing these technological advancements, companies can reduce production costs, increase productivity, and improve product quality.
Furthermore, the protection provided by quotas allows domestic industries to nurture and develop niche markets that may have been otherwise overlooked. With reduced competition, companies have the opportunity to specialize in unique products or services and cater to specific customer demands. This specialization can drive innovation by pushing companies to develop new technologies or approaches to meet the needs of their target market.
In summary, quotas on imports serve as a catalyst for innovation and technological advancements within domestic industries. The protection they provide allows companies to invest in research and development, collaborate with other institutions, adopt advanced manufacturing techniques, and nurture niche markets. By stimulating innovation, quotas help domestic producers remain competitive in the global marketplace and contribute to the growth of their local industries.
Fostering a Diversified and Resilient Economy
The implementation of quotas can play a significant role in fostering a diversified and resilient economy. By protecting and promoting domestic industries, quotas contribute to the growth and development of a country’s economy. Here are some ways quotas can help achieve this:
-
Promoting Local Industries: Quotas provide domestic producers with a competitive advantage by limiting the amount of imports entering the market. This stimulates local production and encourages investment in domestic industries, leading to job creation and economic growth.
-
Encouraging Specialization: Quotas can drive domestic producers to specialize in producing certain goods or sectors. As quotas decrease competition from foreign imports, domestic producers have the opportunity to focus on developing their expertise and becoming more efficient in producing specific products. This can enhance competitiveness and support the growth of specialized industries.
-
Reducing Dependency on Imports: By implementing quotas, countries can reduce their dependency on imports for certain goods. This helps in safeguarding national security and maintaining economic stability. Additionally, it provides a level of self-sufficiency, especially in critical sectors, which can become crucial during times of global economic uncertainties or disruptions in supply chains.
-
Developing Technological Advancements: Quotas can encourage domestic industries to invest in research and development, innovation, and technology upgrades. In order to compete with foreign imports, domestic producers may need to improve their products or processes, leading to advancements in technology and overall industrial development.
-
Protecting Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs): Quotas can provide a level playing field for small and medium-sized enterprises by limiting the influx of low-cost imports that may pose a threat to their survival. This protection allows SMEs to grow and thrive, contributing to the diversification of the economy and fostering entrepreneurship.
In conclusion, quotas can be a valuable tool in fostering a diversified and resilient economy. By promoting local industries, encouraging specialization, reducing dependency on imports, fostering technology advancements, and protecting SMEs, quotas contribute to the growth and development of domestic industries, subsequently enhancing the overall economic stability and resilience of a country.
Question and answer:
Why do countries implement quotas?
Countries implement quotas in order to protect their domestic industries and ensure their survival in the face of foreign competition.
How do quotas help domestic producers?
Quotas help domestic producers by limiting the quantity of imported goods, which reduces competition and allows domestic industries to capture a larger share of the market.
Do quotas boost local industries?
Yes, quotas can boost local industries by creating a more level playing field and providing them with a competitive advantage over foreign producers.
What are the advantages of quotas for domestic producers?
The advantages of quotas for domestic producers include increased market share, higher profits, and protection from foreign competition.
Are there any drawbacks to using quotas?
Yes, there are drawbacks to using quotas. They can lead to higher consumer prices, reduced product variety, and retaliation from other countries.