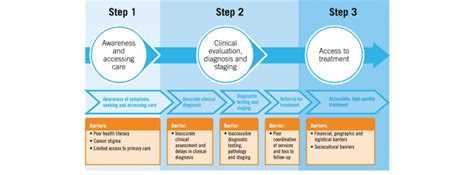
Accurate diagnosis is a crucial aspect of healthcare. It plays a vital role in determining the appropriate treatment and management plan for patients. However, there are several common barriers that healthcare professionals face when trying to make an accurate diagnosis. These barriers can range from limited access to diagnostic tools and resources to the complexity of certain medical conditions.
One major barrier to accurate diagnosis is the lack of access to advanced diagnostic tools and technologies. Many healthcare facilities, especially in developing countries or rural areas, may not have the necessary equipment to perform complex diagnostic tests. This can result in healthcare professionals relying on less accurate or outdated methods, leading to a higher likelihood of misdiagnosis.
Another significant barrier is the complexity of certain medical conditions. Some illnesses have symptoms that mimic other diseases or present differently in different individuals. This can make it challenging for healthcare professionals to pinpoint the exact cause of a patient’s symptoms. In some cases, patients may have multiple conditions that are overlapping, making it even more difficult to make an accurate diagnosis.
Furthermore, limited time and resources can also hinder accurate diagnosis. In busy healthcare settings, healthcare professionals may have limited time to spend with each patient, which can result in rushed assessments or overlooking important details. Additionally, a shortage of healthcare professionals or high patient volumes can lead to delays in receiving test results or consultations with specialists, further delaying an accurate diagnosis.
In conclusion, accurate diagnosis is essential for effective healthcare. However, several barriers, such as limited access to diagnostic tools, complex medical conditions, and limited time and resources, can hinder the accuracy of diagnosis. It is crucial for healthcare systems to address these barriers and provide healthcare professionals with the necessary tools and support to make accurate diagnoses.
Common Barriers to Accurate Diagnosis in Healthcare
Accurate diagnosis is a critical aspect of healthcare that allows healthcare providers to develop appropriate treatment plans and improve patient outcomes. However, there are several barriers that can hinder the process of diagnosis, leading to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis. These barriers can occur at various stages of the diagnostic process and can be categorized into several key areas:
1. Communication:
- Lack of effective communication between healthcare providers and patients can lead to misunderstandings and incomplete information. Language barriers, cultural differences, and limited health literacy can further complicate communication.
- Inadequate communication between healthcare providers can result in a lack of information transfer, leading to incomplete patient histories, missed test results, and other critical information that is necessary for accurate diagnosis.
2. Cognitive biases:
- Cognitive biases, such as confirmation bias and anchoring bias, can influence healthcare providers’ decision-making process and lead to diagnostic errors. These biases can result in premature closure, where providers settle on a diagnosis without considering other possibilities.
- Availability bias, where providers rely on easily accessible information, can also impact the accuracy of diagnosis by overshadowing less common but important diagnoses.
3. Time constraints:
- Time constraints in healthcare settings can limit the amount of time healthcare providers have to spend with each patient. This can result in rushed assessments, inadequate patient histories, and a limited consideration of differential diagnoses.
- Busy schedules and high patient volumes can contribute to increased workload and stress, which may negatively impact healthcare providers’ cognitive abilities and decision-making processes.
4. Diagnostic uncertainty:
- Diagnoses that present with nonspecific symptoms or are rare and complex can pose challenges for healthcare providers. The lack of clear diagnostic criteria and guidelines for such cases can lead to diagnostic uncertainty and difficulty in reaching an accurate diagnosis.
- Limited access to advanced diagnostic tests and technologies can also hinder accurate diagnosis, particularly in resource-limited healthcare settings.
5. Suboptimal collaboration:
- Lack of interdisciplinary collaboration and teamwork among healthcare providers can hinder accurate diagnosis. The failure to share relevant information and collaborate effectively can lead to missed opportunities for accurate diagnosis.
- Fragmented healthcare systems and inadequate coordination between different healthcare settings, such as primary care and specialty care, can also contribute to diagnostic errors and delays.
6. Patient-related factors:
- Patients’ reluctance to disclose sensitive information, lack of understanding about their symptoms, or failure to report previous medical history can impede accurate diagnosis.
- Non-adherence to recommended diagnostic tests or follow-up appointments can also contribute to diagnostic errors and delays.
Identifying and addressing these barriers is crucial for improving the accuracy of diagnosis in healthcare. Strategies such as enhancing communication skills, implementing decision support tools, promoting interdisciplinary collaboration, and improving patient education and engagement can help mitigate these barriers and improve diagnostic accuracy.
Limited Access to Healthcare Services
Limited access to healthcare services is one of the common barriers to accurate diagnosis in healthcare. This barrier refers to the challenges individuals face in receiving timely and appropriate medical care due to various factors such as geographical location, lack of healthcare facilities, and inadequate financial resources.
Geographical Location: Many individuals, especially those living in remote or rural areas, may face limited access to healthcare services due to the lack of healthcare facilities in their vicinity. These areas may have a shortage of healthcare professionals, hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic centers, making it difficult for individuals to receive the necessary medical attention. Geographical barriers can result in delayed diagnoses and inadequate treatment.
Lack of Healthcare Facilities: In some regions, there may be a lack of healthcare infrastructure, including hospitals, clinics, and specialized medical centers. This leads to limited availability of medical professionals and diagnostic equipment, making it challenging for individuals to access the healthcare services needed for an accurate diagnosis.
Inadequate Financial Resources: Limited access to healthcare services can also be attributed to financial constraints. The cost of healthcare services, including consultations, diagnostic tests, and treatments, can be unaffordable for many individuals, especially those without health insurance or low-income individuals. As a result, they may delay seeking medical help or avoid necessary diagnostic tests, leading to delayed or inaccurate diagnoses.
Overcoming the limited access to healthcare services barrier requires addressing the underlying factors contributing to it. Efforts should be made to improve healthcare infrastructure in underserved areas, ensure the availability of healthcare professionals, and establish financial support programs for individuals who cannot afford the cost of healthcare services. By addressing these challenges, individuals can receive timely and accurate diagnoses, leading to better health outcomes.
Lack of Medical Knowledge and Training
One of the common barriers to accurate diagnosis in healthcare is the lack of medical knowledge and training among healthcare professionals. Medical knowledge is constantly evolving, with new research and advancements being made in various fields of medicine. However, healthcare professionals may not always have access to the latest information or may lack the necessary training to interpret and apply this knowledge effectively.
The lack of medical knowledge and training can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis, as healthcare professionals may not be aware of the latest diagnostic criteria or may not have the skills to correctly interpret symptoms and test results. This can result in patients receiving inappropriate or ineffective treatments, or their condition may worsen due to delayed or incorrect diagnosis.
To address this barrier, healthcare professionals should prioritize continuing education and training to stay updated with the latest medical advancements and diagnostic techniques. This can be done through attending conferences, participating in workshops, and engaging in online learning platforms that provide access to the latest research and guidelines.
Additionally, healthcare organizations can play a role in ensuring that their staff receives comprehensive and ongoing training. This can include mandatory training programs, regular performance evaluations, and opportunities for professional development. By investing in the knowledge and skills of their workforce, healthcare organizations can improve the accuracy and quality of diagnoses.
Furthermore, collaboration and interdisciplinary communication among healthcare professionals can also help overcome this barrier. By working together, healthcare professionals from different specialties can combine their knowledge and expertise to reach accurate diagnoses. This can be facilitated through regular team meetings, case discussions, and consultations.
Overall, the lack of medical knowledge and training is a significant barrier to accurate diagnosis in healthcare. It is essential for healthcare professionals to continuously update their knowledge and skills to provide the best possible care for their patients.
Miscommunication and Language Barriers
Miscommunication and language barriers are major challenges in healthcare settings that can significantly impact the accuracy of diagnosis. Healthcare providers, patients, and their families may come from diverse cultural and linguistic backgrounds, leading to difficulties in understanding and conveying information effectively.
1. Language Barriers:
Language barriers occur when the patient and healthcare provider do not speak the same language fluently or have limited proficiency in a shared language. This can lead to misunderstandings, misinterpretations, and difficulties in accurately conveying symptoms, medical history, and other important information.
Efforts to overcome language barriers include the use of professional interpreters, translation services, and multilingual healthcare staff. However, these resources may not always be readily available, leading to compromised communication and potential errors in diagnosis.
2. Cultural Differences:
Cultural differences can also contribute to miscommunication in healthcare settings. Different cultures may have diverse perspectives on illness, symptoms, and treatment, affecting how patients describe their symptoms or understand medical explanations.
For example, some cultures may be more reluctant to discuss certain health issues due to cultural taboos or stigmas. This can lead to incomplete or inaccurate information being shared with healthcare providers, making it challenging to reach an accurate diagnosis.
3. Nonverbal Communication:
Nonverbal communication, including body language and facial expressions, plays a significant role in effective communication. However, cultural differences in nonverbal cues can lead to misinterpretation or misunderstanding.
Healthcare providers may also unintentionally convey mixed messages through their nonverbal communication, creating confusion for patients. This can impede accurate diagnosis and understanding of the patient’s concerns and needs.
4. Health Literacy:
Health literacy refers to a person’s ability to understand and use health information to make appropriate decisions about their healthcare. Low health literacy can contribute to miscommunication and may prevent patients from accurately describing their symptoms or following treatment plans.
Healthcare providers should make efforts to communicate in plain language, avoiding complex medical terminology and jargon. Using visual aids, written instructions, and educational materials in appropriate languages can also help overcome health literacy barriers.
In conclusion, miscommunication and language barriers pose significant challenges to accurate diagnosis in healthcare. By recognizing these barriers and implementing strategies to overcome them, healthcare providers can improve communication and ensure better diagnostic outcomes for their patients.
Diagnostic Errors
In the field of healthcare, diagnostic errors play a significant role in the challenges faced by healthcare professionals. Diagnostic errors refer to mistakes or failures in the diagnostic process, which can lead to incorrect or delayed diagnoses and subsequent adverse outcomes for patients.
There are several factors that contribute to diagnostic errors:
- Cognitive biases: Healthcare providers, like any other humans, are prone to cognitive biases that can affect their judgment and decision-making. These biases, such as confirmation bias or anchoring bias, can lead to errors in information processing and interpretation, making it challenging to arrive at an accurate diagnosis.
- Limited time and resources: In many healthcare settings, healthcare providers are under time constraints and have limited resources. This can lead to rushed assessments and a reduced ability to thoroughly evaluate patients, increasing the likelihood of diagnostic errors.
- Communication breakdown: Effective communication between healthcare providers is crucial for accurate diagnosis. However, breakdowns in communication, such as inadequate information transfer during handoffs or insufficient collaboration between different specialists, can contribute to diagnostic errors.
- Complex and rare conditions: Some conditions can be challenging to diagnose due to their complexity or rarity. Healthcare providers may lack experience or knowledge in identifying these conditions, leading to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis.
- Lack of feedback and learning culture: A culture that does not prioritize learning from diagnostic errors can hinder improvement in diagnostic accuracy. Without feedback mechanisms and a culture of continuous learning, healthcare providers may not have the opportunity to reflect on errors and improve their diagnostic skills.
Addressing diagnostic errors requires a multifaceted approach. It involves implementing strategies to mitigate cognitive biases, improving communication and teamwork among healthcare providers, providing additional time and resources for thorough assessments, and fostering a culture of learning and feedback.
Additionally, the use of technology, such as decision support systems or artificial intelligence, may aid in reducing diagnostic errors by providing healthcare providers with additional information and guidance during the diagnostic process.
By recognizing the barriers that contribute to diagnostic errors and implementing strategies to overcome them, healthcare professionals can strive towards improving diagnostic accuracy and ultimately provide better patient care.
Bias and Stereotyping
Bias and stereotyping can pose significant challenges in accurate diagnosis within the healthcare system. These are cognitive processes that can influence how healthcare providers perceive and interpret information about patients, leading to potential errors in diagnosis and treatment.
Bias:
Bias refers to the tendency of individuals to favor certain beliefs or opinions over others, which can lead to unfair judgments or decisions. In the context of diagnosis, healthcare providers may have preconceived notions or biases about certain patient populations based on factors such as race, age, gender, or socioeconomic status.
For example, a healthcare provider may subconsciously assume that a patient from a lower socioeconomic background is less educated or less likely to adhere to medical recommendations. This bias can result in an inaccurate diagnosis or inadequate treatment plan.
To overcome bias, healthcare providers need to be aware of their own biases and actively work to challenge and correct them. This can be achieved by engaging in cultural competency training and fostering a mindset of empathy and open-mindedness.
Stereotyping:
Stereotyping involves categorizing individuals into groups based on certain characteristics and assuming that everyone within that group shares the same characteristics or traits. These stereotypes can impact how healthcare providers perceive and interpret symptoms, leading to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis.
For instance, a healthcare provider may stereotype older adults as being forgetful or resistant to change, potentially overlooking symptoms of a serious medical condition such as dementia.
To combat stereotyping, healthcare providers should focus on treating each patient as an individual, rather than making assumptions based on stereotypes. Taking the time to listen to the patient’s concerns, conducting a thorough examination, and considering the patient’s unique circumstances can help mitigate the influence of stereotypes on the diagnostic process.
Conclusion:
Bias and stereotyping are common barriers to accurate diagnosis in healthcare. Overcoming these challenges requires healthcare providers to be attentive to their own biases and stereotypes, and actively work to challenge and correct them. By fostering a culture of inclusivity, empathy, and open-mindedness, healthcare professionals can provide more accurate and effective diagnoses, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Fragmented Healthcare Systems
Fragmented healthcare systems are one of the major barriers to accurate diagnosis in healthcare. A fragmented healthcare system refers to a system where there is a lack of coordination and communication between different healthcare providers and institutions.
One of the main reasons for a fragmented healthcare system is the uncoordinated referral process. Patients may visit multiple specialists and healthcare facilities in order to receive a diagnosis and treatment for their condition. However, without proper communication and sharing of medical records between these providers, there is a higher risk of misdiagnosis and incorrect treatment.
Additionally, different healthcare providers may use different diagnostic tests and procedures, further contributing to the fragmentation. For example, a laboratory may use different reference ranges for interpreting test results compared to another laboratory. This can lead to inconsistencies in diagnosis and treatment decisions.
Another aspect of fragmentation in healthcare systems is the lack of a centralized electronic health record (EHR) system. Without a unified EHR system, patient information is often scattered across multiple providers and is inaccessible to other healthcare professionals involved in the patient’s care. This can lead to missed or incomplete information, resulting in inaccurate diagnosis and treatment decisions.
The fragmented healthcare systems also pose a challenge to continuity of care. Patients may receive different diagnoses and treatment plans from different providers, leading to confusion and potential harm. There is a need for better care coordination and integration between healthcare providers to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
In conclusion, fragmented healthcare systems create significant barriers to accurate diagnosis in healthcare. The lack of coordination, communication, and information sharing between different providers and institutions can contribute to misdiagnosis and incorrect treatment decisions. Addressing these challenges requires a focus on improving referral processes, standardizing diagnostic tests and procedures, implementing a centralized EHR system, and promoting better care coordination and integration.
Financial Constraints
Financial constraints are a common barrier to accurate diagnosis in healthcare. Limited financial resources can impact both patients and healthcare providers, leading to challenges in accessing and delivering appropriate diagnostic tests and procedures.
Patient Factors:
- Lack of insurance: Many individuals lack health insurance coverage, which can limit their ability to seek medical care and receive necessary diagnostic tests.
- High deductibles and copayments: Even for individuals with insurance, high deductibles and copayments can be a significant financial burden, dissuading them from pursuing diagnostic evaluations.
- Limited income: Patients with low income may struggle to afford transportation costs to medical facilities or the costs associated with diagnostic tests.
Healthcare Provider Factors:
- Reimbursement limitations: Healthcare providers may face limitations in reimbursement for diagnostic tests and procedures, which can deter them from ordering certain tests or referring patients to specialists.
- Cost of diagnostic equipment: Acquiring and maintaining diagnostic equipment can be expensive for healthcare facilities, leading to a lack of access to state-of-the-art technology and delaying accurate diagnoses.
- Medical supply costs: The cost of medical supplies needed for diagnostic tests, such as laboratory kits or imaging contrast agents, can also limit healthcare providers’ ability to perform certain tests.
Impact on Diagnosis:
The financial constraints faced by patients and healthcare providers can result in delayed or inadequate diagnostic evaluations. Patients may postpone seeking medical care due to cost concerns, leading to delayed diagnosis and potentially worsening health outcomes. Healthcare providers, constrained by financial limitations, may resort to less costly diagnostic alternatives that may not be as accurate or comprehensive, leading to potential misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis.
| Scenario | Patient Impact | Provider Impact |
|---|---|---|
| A patient cannot afford the copayment for an MRI scan recommended by a specialist. | The patient may decline to undergo the diagnostic test, potentially delaying the diagnosis of a serious condition. | The provider may need to consider less costly alternatives or advocate for the patient to receive financial assistance, potentially delaying the diagnosis. |
| A healthcare facility cannot afford to purchase a new ultrasound machine. | Patients may have limited access to ultrasounds or may need to travel to another facility, causing inconvenience and potential delays in diagnosis. | Providers may have to rely on older or less advanced equipment, which may result in lower quality imaging and potentially inaccurate diagnoses. |
Addressing financial constraints in healthcare is crucial to ensure accurate and timely diagnoses. Policy measures aimed at improving access to affordable health insurance, reducing out-of-pocket costs for diagnostic tests, and providing financial support for healthcare facilities can help mitigate this barrier. Additionally, innovative healthcare delivery models, such as telemedicine, can help bridge the gap by offering more cost-effective diagnostic options to patients in remote or underserved areas.
Patient Empowerment and Engagement
Patient empowerment and engagement are crucial components of accurate diagnosis and successful healthcare outcomes. When patients are active participants in their own healthcare journey, they are better able to communicate their symptoms, concerns, and preferences with their healthcare providers, ultimately leading to more accurate diagnoses.
1. Education and information: Patient empowerment starts with education and access to accurate information about their conditions and available treatment options. By providing patients with resources and knowledge, they can make informed decisions and engage actively in their own care.
2. Shared decision-making: Patients who are empowered and engaged are encouraged to actively participate in the decision-making process. Healthcare providers should involve patients in the discussion of treatment options, explaining the pros and cons, and considering the patient’s preferences, values, and goals.
3. Open communication: Effective communication between patients and healthcare providers is essential for accurate diagnosis. Patients should feel comfortable expressing their concerns, asking questions, and providing feedback. Healthcare providers, on the other hand, need to actively listen, ask relevant questions, and address any uncertainties or misunderstandings.
4. Patient advocacy: Empowered patients are their own advocates. They are proactive in seeking second opinions, questioning diagnoses, and asserting their rights. When patients play an active role in their healthcare, they can help ensure that their concerns are heard and addressed.
5. Support networks: Empowered patients often surround themselves with support networks, such as family, friends, or online communities. These networks can provide emotional support, advice, and additional information, further enhancing the patient’s empowerment and engagement.
6. Access to medical records: Patients who have access to their medical records can review and understand their own health information. This transparency allows patients to proactively participate in their care, verify the accuracy of their records, and provide important context to their healthcare providers.
7. Continuous learning and self-management: Empowered patients are invested in continuous learning about their conditions and self-management techniques. They take an active role in managing their health, following prescribed treatment plans, and making necessary lifestyle changes.
8. Respect and partnership: Patient empowerment involves establishing a partnership between patients and healthcare providers. When patients feel respected, valued, and involved in their care, they are more likely to engage actively in the diagnosis and treatment process.
By promoting patient empowerment and engagement, healthcare providers can overcome common barriers to accurate diagnosis and improve overall healthcare outcomes.
Questions and answers
What are some common barriers to accurate diagnosis in healthcare?
Some common barriers to accurate diagnosis in healthcare include inadequate communication between healthcare providers, limited access to medical information, time constraints, cognitive biases, and diagnostic errors.
How does inadequate communication between healthcare providers contribute to inaccurate diagnoses?
Inadequate communication between healthcare providers can hinder accurate diagnosis as important information may be missed or not properly conveyed. This can lead to misunderstandings, incorrect assumptions, and incomplete assessments, ultimately affecting the accuracy of the diagnosis.
Why is limited access to medical information a barrier to accurate diagnosis?
Limited access to medical information can make it difficult for healthcare providers to obtain comprehensive patient histories, access previous test results or medical records, and stay up to date with the latest research and guidelines. This lack of information can impede the accuracy of the diagnosis and limit treatment options.
What are some cognitive biases that can affect accurate diagnosis?
Some cognitive biases that can affect accurate diagnosis include confirmation bias, where healthcare providers only seek information that supports their initial hypothesis, and anchoring bias, where they focus too much on one piece of information and fail to consider other possibilities. These biases can lead to premature closure and inaccurate diagnoses.