Welcome to [Website Name], your source for comprehensive information on Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) 2. CBT is a widely used psychotherapeutic approach that focuses on understanding the connection between thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. This approach has been proven effective in treating a range of mental health conditions, including anxiety, depression, and substance abuse.
In our articles, you will find detailed explanations of the principles and techniques of CBT. We provide practical tips and strategies for applying these techniques in everyday life, as well as insights into the theoretical underpinnings of CBT. Whether you are a mental health professional looking to enhance your understanding of CBT or an individual seeking self-help resources, [Website Name] aims to be your go-to resource.
Our team of experts, including licensed therapists and psychologists, contribute to the content on [Website Name]. We strive to bring you the latest research findings and evidence-based practices in CBT. We also feature real-life stories of individuals who have benefited from CBT, providing inspiration and hope for those seeking help.
So, whether you are curious about CBT, looking to start therapy, or simply interested in learning more about mental health, [Website Name] is here to support you. Explore our articles, resources, and tools to empower yourself with knowledge and improve your mental well-being. Let the journey to a healthier mind and outlook begin!
What is Cognitive Behaviour Therapy?
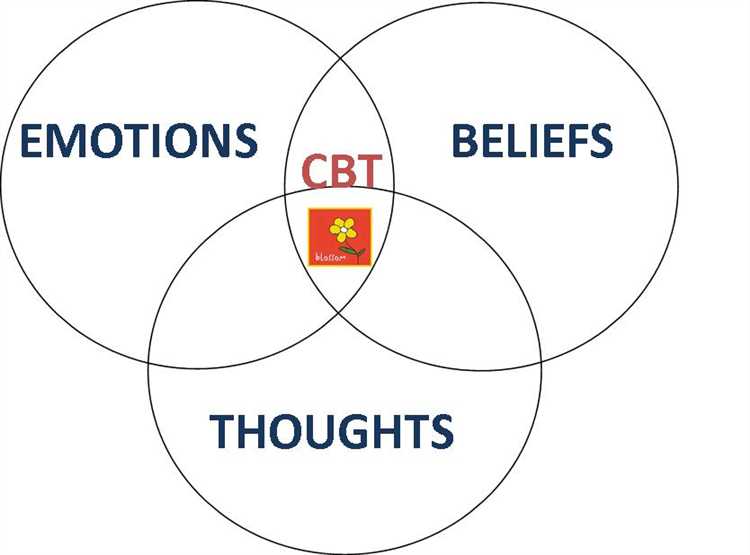
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on the relationship between our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It is based on the idea that our thoughts play a fundamental role in shaping our emotions and actions.
CBT aims to help individuals identify negative or unhelpful thought patterns and replace them with more adaptive and positive ones. It is a structured and goal-oriented therapy that is often used to treat a variety of mental health conditions, such as anxiety disorders, depression, and addiction.
During CBT sessions, the therapist works collaboratively with the client to help them understand how their thoughts are contributing to their emotions and behaviors. The therapist may use various techniques, such as cognitive restructuring, behavioral experiments, and homework assignments, to challenge and change problematic thoughts and behaviors.
CBT also involves teaching individuals practical skills and strategies that they can use to manage their emotions and cope with challenging situations. These skills may include relaxation techniques, problem-solving skills, and communication skills.
CBT is typically delivered over a specific number of sessions, ranging from 6 to 20, depending on the individual’s needs and goals. It is considered to be a brief and time-limited therapy compared to other forms of psychotherapy.
Research has shown that CBT is an effective treatment for a wide range of mental health conditions and can produce long-lasting positive outcomes. It has become one of the most widely used and evidence-based forms of psychotherapy.
Overall, CBT helps individuals develop a deeper understanding of the connections between their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, and provides them with the tools to make positive changes in their lives.
The Principles of Cognitive Behaviour Therapy
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on the connection between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It is based on the principle that our thoughts shape our emotions and actions, and by changing negative or unhelpful thoughts, we can improve our mental well-being.
Key principles of CBT include:
- Thought Awareness: CBT emphasizes the importance of recognizing and identifying negative or distorted thoughts. By becoming aware of these thoughts, individuals can start to challenge and reframe them in a more positive and realistic way.
- Belief Evaluation: CBT helps individuals evaluate their beliefs and assumptions. Many times, negative thoughts and beliefs are based on unrealistic or unhelpful assumptions. Through CBT, individuals can examine these beliefs and replace them with more accurate ones.
- Behavioral Activation: CBT encourages individuals to engage in activities that bring them joy and fulfillment. By increasing positive behaviors and decreasing negative behaviors, individuals can improve their mood and overall well-being.
- Problem-Solving: CBT teaches individuals practical problem-solving skills. By identifying problems and finding effective solutions, individuals can reduce stress and improve their ability to cope with challenges.
Other important principles of CBT include:
- Collaborative Approach: CBT is a collaborative process between the therapist and the individual. It involves setting goals, discussing treatment options, and working together to develop effective strategies for change.
- Focus on the Present: CBT primarily focuses on the present moment and how current thoughts and behaviors impact emotions and well-being. While past experiences are acknowledged, the emphasis is on understanding and changing present patterns.
- Homework Assignments: CBT often involves assigning homework activities to reinforce therapy sessions. These assignments may include thought records, behavioral experiments, or other exercises to practice new skills and reinforce learning.
- Empirical Support: CBT is an evidence-based therapy supported by extensive research. It has been proven effective in the treatment of various mental health conditions, including anxiety disorders, depression, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
In summary, Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is a therapeutic approach that focuses on changing negative thoughts and behaviors to improve mental well-being. Its principles include thought awareness, belief evaluation, behavioral activation, and problem-solving. CBT is a collaborative process and emphasizes the present moment, with the use of homework assignments and empirical support.
Benefits of Cognitive Behaviour Therapy
1. Increased self-awareness: Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) helps individuals become more aware of their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. By understanding the connection between these three factors, individuals can gain insight into how their thoughts and beliefs contribute to their actions and reactions.
2. Improved problem-solving skills: CBT teaches individuals effective problem-solving techniques. It encourages them to identify and challenge negative thoughts and replace them with more positive and constructive ones. This improved ability to solve problems can lead to a reduction in stress and an overall improvement in well-being.
3. Enhanced coping mechanisms: Cognitive Behaviour Therapy equips individuals with healthy coping mechanisms to deal with stress, anxiety, and other challenging emotions. It teaches them skills like relaxation techniques, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness practices to manage their emotions more effectively.
4. Targeted approach: CBT is a goal-oriented therapy that focuses on specific issues and symptoms. It helps individuals develop personalized strategies to overcome their challenges. This targeted approach allows for efficient and effective treatment, leading to positive outcomes in a relatively short period.
5. Long-lasting results: Cognitive Behaviour Therapy is known to produce long-lasting results, even after the therapy sessions have ended. The skills and techniques learned during CBT can continue to be applied in various situations, providing ongoing support and assistance in managing day-to-day challenges.
6. Versatility: CBT can be used to treat a wide range of mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, phobias, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), eating disorders, and substance abuse. It is also effective in addressing relationship issues, improving self-esteem, and enhancing overall well-being.
7. Collaborative approach: Cognitive Behaviour Therapy involves active participation from both the therapist and the individual. It encourages a collaborative and supportive relationship, where the therapist works alongside the individual to identify and overcome their challenges. This partnership creates a safe and non-judgmental space for personal growth and healing.
8. Evidence-based practice: CBT is a well-researched and evidence-based therapeutic approach. It has been extensively studied and proven to be effective in numerous clinical trials. The evidence-based nature of CBT provides individuals with confidence in its efficacy and increases the likelihood of successful outcomes.
| Increased self-awareness | Improved problem-solving skills | Enhanced coping mechanisms |
| Targeted approach | Long-lasting results | Versatility |
| Collaborative approach | Evidence-based practice |
How Cognitive Behaviour Therapy Works
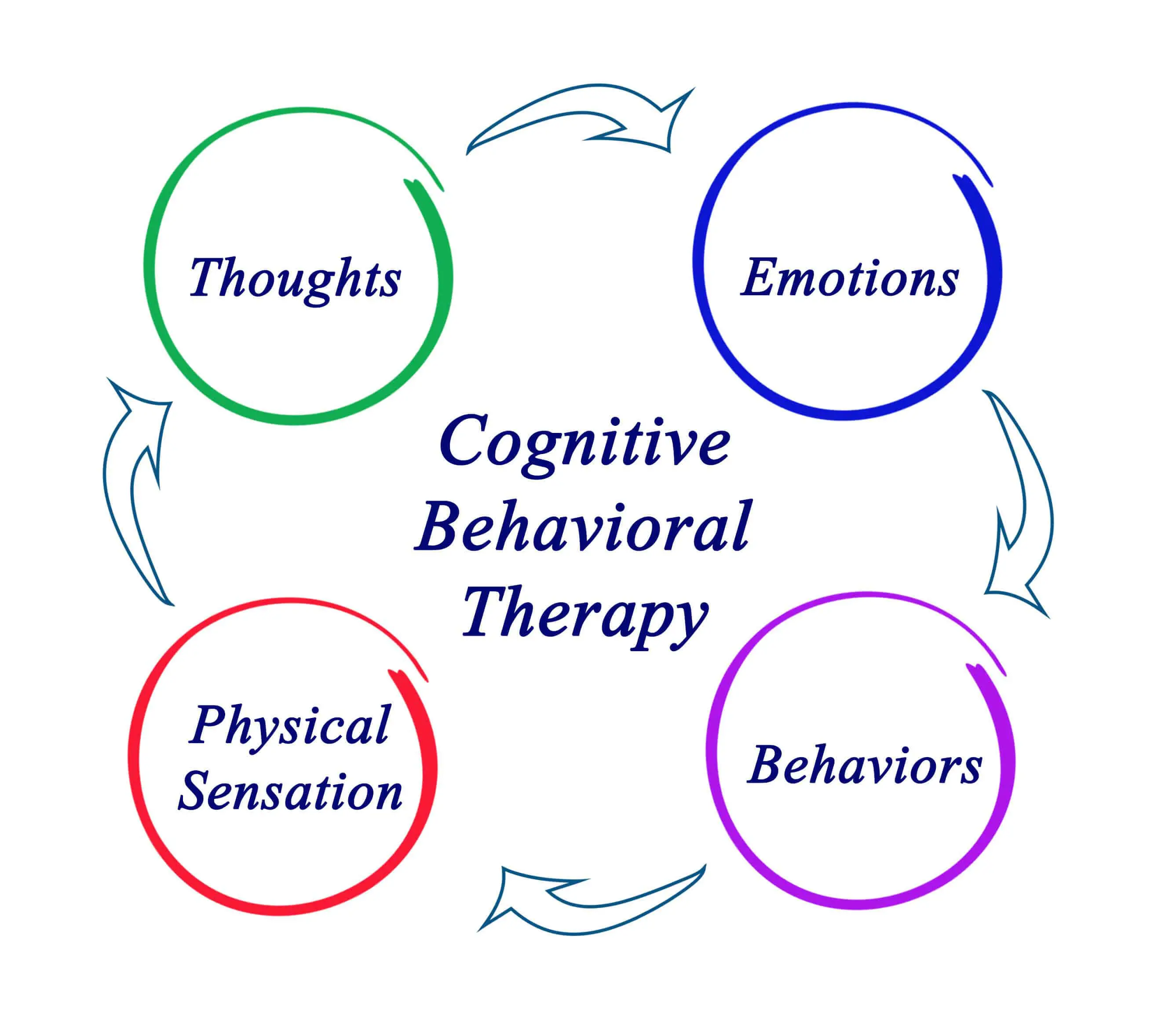
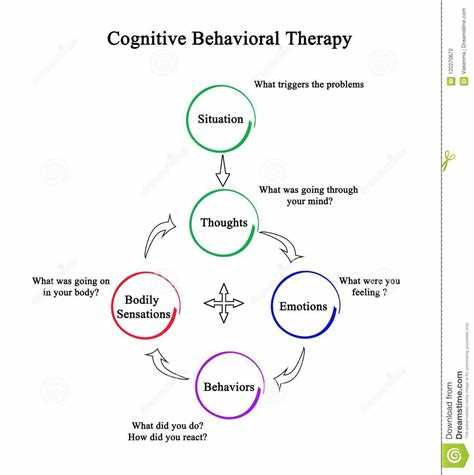
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on changing negative thoughts and behaviours to improve mental health and well-being. It is based on the idea that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviours are interconnected.
CBT is typically conducted through structured sessions with a trained therapist, although there are also self-help resources available for individuals who prefer to work on their own. The therapy is usually short-term and goal-oriented, with the aim of helping individuals develop strategies to better manage their problems.
In CBT, the therapist and the individual work together to identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to distressing emotions or problematic behaviours. The therapy often involves teaching individuals new coping skills and strategies, as well as helping them to develop a more realistic and balanced way of thinking.
One of the key techniques used in CBT is cognitive restructuring. This involves identifying and changing negative thought patterns, such as overgeneralizing or catastrophizing, into more positive and realistic thinking. By challenging and replacing irrational thoughts with more rational ones, individuals can change their emotional responses and behaviours.
Another important component of CBT is behavioural activation. This involves helping individuals engage in activities that they may have been avoiding or neglecting due to their mental health difficulties. By gradually increasing their engagement in positive and rewarding activities, individuals can improve their mood and overall well-being.
CBT also emphasizes the importance of homework assignments and practice outside of therapy sessions. The therapist may assign tasks such as keeping thought records, practicing relaxation techniques, or engaging in exposure exercises. These activities help individuals further apply the skills and strategies learned in therapy and reinforce positive changes.
Research has shown that CBT is effective in treating a wide range of mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It is considered to be a evidence-based therapy that is grounded in scientific research and has been shown to produce significant and lasting improvements in mental health outcomes.
In summary, CBT works by helping individuals identify and challenge negative thoughts and behaviours, develop new coping skills and strategies, and engage in positive activities. It is a structured and goal-oriented therapy that has been proven to be effective in improving mental health and well-being.
Who can benefit from Cognitive Behaviour Therapy
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is a highly effective form of therapy that can be helpful for a wide range of individuals dealing with various mental health issues. It is a goal-oriented and practical approach that focuses on changing patterns of thinking and behavior to improve overall well-being.
CBT can benefit:
- Anxiety Disorders: People experiencing symptoms of anxiety disorders such as generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias can benefit from CBT. It helps individuals identify and challenge the irrational thoughts and beliefs that contribute to their anxiety.
- Depression: CBT is an effective treatment for depression. It helps individuals identify and modify negative thinking patterns and develop healthier coping strategies. It focuses on breaking the cycle of negative thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): CBT is proven to be effective in treating PTSD. It helps individuals process the traumatic event and develop skills to manage intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, and other symptoms associated with the disorder.
- Addiction: CBT can be used as a treatment for substance use disorders and addictive behaviors. It helps individuals identify triggers and develop strategies to cope with cravings and prevent relapse.
- Eating Disorders: CBT is widely used in the treatment of eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge eating disorder. It focuses on changing distorted thoughts and beliefs related to body image, food, and weight.
- Insomnia: CBT for insomnia, also known as CBT-I, is a recommended treatment for chronic insomnia. It helps individuals identify and change the thoughts and behaviors that contribute to their sleep difficulties.
In addition to the conditions mentioned above, CBT can be beneficial for individuals dealing with stress, anger management issues, low self-esteem, relationship problems, and many other mental health concerns. It is a versatile therapy that can be tailored to address each individual’s unique needs and goals.
If you are wondering whether CBT is suitable for your specific situation, it is recommended to consult with a qualified mental health professional who can assess your needs and provide appropriate guidance.
Finding a CBT Therapist
If you’re interested in Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) and think it could be helpful for you, finding a qualified CBT therapist is an important step. Here are some tips on how to find a CBT therapist:
- Ask for Recommendations: Start by asking your primary care physician, friends, or family members if they know of any CBT therapists they can recommend. Personal referrals can be a great way to find a therapist who has experience and a good reputation.
- Research Online: Use online directories or search engines to find CBT therapists in your area. Many therapists have websites where you can learn more about their background, areas of expertise, and treatment approach. Look for therapists who are licensed and affiliated with reputable organizations.
- Check with Insurance: If you have health insurance, contact your insurance company to find out if CBT therapy is covered and if they have a list of therapists you can choose from. This can help narrow down your search and make therapy more affordable.
- Schedule Consultations: Once you have a list of potential therapists, schedule consultations with them. This will allow you to ask questions, discuss your treatment goals, and see if you feel comfortable with the therapist. It’s important to find someone who you trust and feel at ease with.
- Consider Accessibility: Take into account the location and availability of the therapist. It’s important to find someone who is convenient for you to reach and has availability that fits with your schedule.
- Ask about Fees: Discuss the therapist’s fees and payment options upfront. CBT therapy sessions can vary in cost, so it’s important to have a clear understanding of what to expect financially.
Finding the right CBT therapist may take some time and effort, but it’s worth it to find a therapist who can support you in your journey towards better mental health and well-being.
Cognitive Behavior Therapy Techniques
Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on changing negative thoughts and behaviors. It is a goal-oriented and practical approach that helps individuals manage their emotions and improve their mental well-being. Here are some commonly used techniques in CBT:
1. Cognitive Restructuring
This technique involves identifying and challenging negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to negative emotions or behaviors. It helps individuals replace irrational or unhelpful thoughts with more rational and positive ones.
2. Behavioral Activation
This technique encourages individuals to engage in activities that they have been avoiding due to depression or anxiety. By gradually increasing their activity levels and participation in pleasurable activities, individuals can improve their mood and overall well-being.
3. Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy is often used to treat anxiety disorders. It involves gradually exposing individuals to feared situations or objects in a safe and controlled environment. Through repeated exposure, individuals can learn to manage their anxiety and reduce fear responses.
4. Thought Records
Thought records are tools used to analyze and challenge negative thoughts. Individuals are encouraged to write down their negative thoughts, identify the evidence supporting or contradicting those thoughts, and come up with more balanced and rational alternatives.
5. Social Skills Training
This technique is helpful for individuals who struggle with social anxiety or have difficulties in social situations. It involves learning and practicing effective communication skills, assertiveness, and problem-solving techniques to improve interpersonal relationships.
6. Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation, can help individuals reduce stress and anxiety. These techniques are often taught and practiced during therapy sessions and can be used as coping mechanisms in daily life.
7. Goal Setting
Goal setting is an important aspect of CBT. Therapists work with individuals to set specific, achievable, and realistic goals. By breaking down larger goals into smaller, manageable steps, individuals can track their progress, increase motivation, and build a sense of accomplishment.
8. Problem-Solving Skills
This technique focuses on teaching individuals effective problem-solving skills. By identifying the problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating the pros and cons, and implementing the best solution, individuals can improve their ability to cope with challenging situations.
These are just a few examples of the various techniques used in Cognitive Behavior Therapy. The specific techniques used will vary depending on the individual’s needs and goals. CBT is a highly effective therapy that can help individuals develop strategies to manage their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors in a healthy and productive way.
Frequently Asked Questions about Cognitive Behaviour Therapy
1. What is Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT)?
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on understanding the connections between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It aims to help individuals identify and change negative or unhelpful patterns of thinking and behavior in order to improve their emotional well-being.
2. What are the goals of CBT?
The goals of CBT are to help individuals develop healthier ways of thinking, coping with stress, and managing emotions. It aims to provide individuals with practical tools and strategies that they can use to overcome challenges and improve their quality of life.
3. What conditions can CBT treat?
CBT is an evidence-based therapy that has been proven effective in treating a range of mental health conditions, including anxiety disorders, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), eating disorders, and substance abuse. It can also be helpful for managing chronic pain and stress-related disorders.
4. How long does CBT treatment typically last?
The duration of CBT treatment can vary depending on the individual and the specific problem being addressed. In general, CBT is a short-term therapy, often lasting between 8 to 20 sessions. However, the number of sessions required may vary depending on the severity of the problem and the individual’s progress.
5. What can I expect during a CBT session?
During a CBT session, you can expect to work collaboratively with a CBT therapist to identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs, develop coping strategies, and set goals for treatment. The therapist will guide you through various exercises and techniques designed to help you change unhelpful patterns of thinking and behavior.
6. Can CBT be combined with other therapies?
Yes, CBT can be combined with other therapies, such as medication management or other forms of psychotherapy. This multidisciplinary approach is often used to provide comprehensive treatment for complex or co-occurring mental health conditions.
7. How effective is CBT?
CBT is a highly effective therapy that has been extensively researched and shown to produce significant and lasting improvements in a wide range of mental health conditions. Studies have consistently demonstrated its effectiveness in reducing symptoms and improving overall well-being.
8. Is CBT suitable for everyone?
CBT can be beneficial for many individuals, but it may not be suitable for everyone. It typically requires active participation and willingness to engage in the therapeutic process. It is important to consult with a mental health professional to determine if CBT is the right approach for your specific needs.
9. Can I learn CBT techniques on my own?
While self-help resources and books on CBT can provide valuable information and techniques, it is generally recommended to work with a trained CBT therapist who can provide personalized guidance and support. A therapist can help you apply CBT techniques to your specific circumstances and ensure that you are using them effectively.
10. How can I find a CBT therapist?
You can find a CBT therapist by asking your primary care physician for a referral, contacting your insurance provider for a list of covered providers, or searching online directories of mental health professionals. It is important to choose a therapist who is qualified, experienced, and with whom you feel comfortable working.
Questions and answers
What is Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) and how does it work?
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is a type of therapy that focuses on the connection between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It helps individuals identify negative patterns of thinking and replace them with more positive and healthy thoughts. CBT works by helping individuals challenge their negative thoughts and beliefs and replace them with more realistic and adaptive ones.
What are the main goals of Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT)?
The main goals of CBT are to help individuals identify and change negative thought patterns, develop healthier coping mechanisms, improve problem-solving skills, and reduce symptoms of mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression.
Can Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) be helpful for anxiety?
Yes, CBT is often used as an effective treatment for anxiety disorders. It can help individuals identify and challenge anxious thoughts, develop relaxation techniques, and learn new coping skills to manage anxiety symptoms.
How long does Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) typically last?
The length of CBT therapy can vary depending on the individual and their specific needs. In general, CBT can range from a few weeks to several months, with regular sessions usually taking place once a week.
Are there any side effects of Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT)?
No, there are typically no side effects of CBT. It is a safe and non-invasive form of therapy that focuses on changing thoughts and behaviors rather than relying on medication.
Is Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) suitable for everyone?
CBT is a widely used and evidence-based therapy, but it may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with severe mental health conditions or those who are not willing to actively participate in therapy may not benefit as much from CBT.
Can Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) be done online?
Yes, CBT can be done online through teletherapy or online therapy platforms. Online CBT can be just as effective as in-person therapy, with the added convenience and accessibility of being able to have sessions from the comfort of one’s own home.