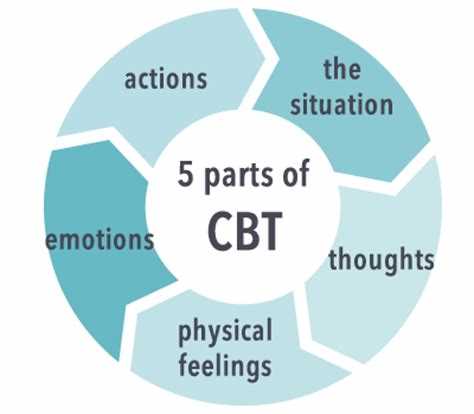
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is a widely-used and evidence-based form of therapy that focuses on the thoughts and beliefs that influence our emotions and behaviors. It is based on the idea that our thoughts can have a powerful impact on our emotions and actions, and that by changing our thought patterns, we can also change how we feel and behave. CBT is a short-term, goal-oriented therapy that aims to help individuals identify and challenge their negative thought patterns and replace them with more positive and realistic ones.
One of the key principles of CBT is that our thoughts are not always accurate or helpful. Sometimes, we may have negative or distorted thoughts that can fuel feelings of anxiety, depression, or low self-esteem. CBT helps individuals recognize these negative thoughts, and teaches them strategies to challenge and replace them with more rational and balanced thoughts.
CBT is often used to treat a wide range of mental health conditions, including anxiety disorders, depression, phobias, and post-traumatic stress disorder. It can also be helpful in managing chronic pain, insomnia, and relationship problems. CBT can be conducted in individual therapy sessions or in group settings, and often involves homework assignments and exercises to practice the skills learned in therapy.
In summary, Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is a therapeutic approach that focuses on the connection between our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. By challenging and replacing negative and distorted thoughts with more positive and realistic ones, CBT can help individuals improve their mental health and well-being. CBT is a widely-used and effective form of therapy that can be applied to a variety of mental health conditions and life challenges.
The Basics of Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is a therapeutic approach that focuses on how thoughts, beliefs, and attitudes influence our feelings and behavior. It is commonly used to treat a variety of mental health issues, including anxiety and depression. Here are the key principles and techniques of CBT:
- Identifying Negative Thought Patterns: CBT helps individuals become aware of their negative thought patterns, such as irrational beliefs or distorted thinking. By recognizing these patterns, they can challenge and reframe them in a more realistic and positive way.
- Setting Realistic Goals: CBT emphasizes the importance of setting achievable goals that are specific and measurable. This helps individuals focus on making small, incremental changes in their behavior and thought processes.
- Breaking the Cycle: CBT aims to break the cycle of negative thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. By identifying triggers and developing coping strategies, individuals can interrupt the pattern and replace it with healthier responses.
- Learning and Practicing New Skills: CBT teaches individuals new skills and techniques to manage their thoughts and emotions effectively. This may include relaxation exercises, problem-solving strategies, or communication skills.
- Maintaining Progress: CBT emphasizes the importance of ongoing practice and maintenance of skills learned in therapy. Individuals are encouraged to continue using the techniques they have learned to ensure long-term progress and prevent relapse.
- Thoughts influence emotions: CBT recognizes that our thoughts have a significant impact on our emotions and behaviors. Negative or irrational thoughts can contribute to feelings of anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues.
- The cognitive model: CBT is based on the cognitive model, which suggests that our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors are interconnected. By identifying and challenging negative thoughts, individuals can break free from unhelpful patterns and develop healthier coping strategies.
- Automatic thoughts: Automatic thoughts are spontaneous and often unconscious thoughts that occur in response to certain situations. These thoughts can be distorted or biased, leading to negative emotions. In CBT, individuals learn to identify and replace automatic thoughts with more realistic and positive ones.
- Behavioral experiments: CBT often incorporates behavioral experiments, which involve testing the accuracy of negative thoughts or beliefs. Through these experiments, individuals can gather evidence to challenge and modify their cognitive patterns.
- Homework and practice: CBT is an active therapy approach that encourages clients to engage in homework assignments and practice new skills outside of therapy sessions. This allows individuals to apply what they have learned in real-life situations and reinforce positive changes.
- Collaborative therapist-client relationship: CBT emphasizes a collaborative working relationship between the therapist and the client. The therapist acts as a guide, helping the client to identify and address their challenges while providing support and guidance throughout the therapy process.
- Identifying and challenging negative thought patterns: CBT helps individuals become aware of their negative thoughts and beliefs and teaches them strategies to challenge and change these patterns. By changing negative thinking, individuals can experience improved mood and reduced anxiety.
- Developing coping skills: CBT equips individuals with practical skills and techniques to manage and cope with difficult emotions, situations, and stressors. These skills can be applied across various areas of life and can help individuals build resilience.
- Improving problem-solving abilities: CBT helps individuals develop problem-solving skills by breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. This can lead to increased confidence in one’s ability to find solutions and make effective decisions.
- Enhancing self-awareness: CBT encourages individuals to explore and understand their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. This increased self-awareness can lead to a better understanding of oneself and improved self-esteem.
- Addressing specific concerns: CBT can be tailored to address specific concerns or challenges, such as anxiety disorders, depression, phobias, insomnia, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). This targeted approach allows individuals to focus on their specific needs and goals.
- Promoting long-term positive change: CBT aims to promote lasting changes by teaching individuals skills and strategies they can continue to use even after therapy has ended. This empowers individuals to manage their mental health and maintain their well-being in the long term.
- Understanding the thoughts and beliefs that contribute to anxiety
- Identifying triggers and patterns of anxious thoughts and behaviors
- Learning and practicing relaxation techniques
- Challenging and reframing negative thoughts
- Developing coping skills and strategies to manage anxiety
- Psychoeducation: The therapist provides information about anxiety disorders, their symptoms, and how CBT can help. This helps the individual understand their condition and the rationale behind the treatment.
- Cognitive restructuring: This involves identifying and challenging negative or irrational thoughts that contribute to anxiety. The individual learns to replace these thoughts with more realistic and helpful ones.
- Exposure therapy: Individuals gradually face their fears or anxiety-provoking situations in a controlled and supportive environment. This helps them learn that their fears are not as threatening as they initially believed.
- Relaxation techniques: Learning and practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness, can help reduce anxiety symptoms.
- Homework assignments: Individuals are often assigned homework exercises to practice the skills and techniques learned in therapy sessions. This helps reinforce the learning and generalization of skills to real-life situations.
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- Panic Disorder
- Social Anxiety Disorder (Social Phobia)
- Specific Phobias
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Empowers individuals to take an active role in their treatment
- Provides practical and effective strategies to manage anxiety
- Addresses the underlying thoughts and beliefs contributing to anxiety
- Can be used in conjunction with medication
- Has long-term benefits and reduces the risk of relapse
- Requires active participation and commitment from the individual
- May initially increase anxiety levels during exposure therapy
- May not be suitable for individuals with severe mental health conditions or complex needs
- May take time to see significant improvements
- May require ongoing maintenance and follow-up sessions
- Assessment: The therapist and client work together to gain an understanding of the individual’s specific symptoms, triggers, and patterns of thinking and behaving.
- Psychoeducation: The therapist provides information about depression, its causes, and how negative thought patterns and behaviours can contribute to and maintain depressive symptoms.
- Thought challenging: The individual is encouraged to identify negative thoughts and beliefs related to their depression and challenge them by examining the evidence for and against these thoughts.
- Behavioural activation: The therapist helps the individual identify and engage in activities that bring them pleasure or a sense of accomplishment, even if they don’t feel like doing them initially.
- Problem-solving: The individual is taught effective problem-solving skills to address difficulties and stressors that may contribute to their depression.
- CBT helps individuals learn to identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to their mental health issues.
- By recognizing and questioning these negative thoughts, individuals can develop more balanced and realistic thinking patterns.
- CBT teaches individuals practical skills and techniques to cope with stressful situations, such as relaxation exercises and problem-solving strategies.
- These coping strategies can help individuals manage their symptoms and prevent them from escalating.
- CBT helps individuals develop better problem-solving skills, enabling them to approach challenges in a more logical and effective way.
- By breaking down problems into manageable steps, individuals can find solutions and overcome obstacles more easily.
- CBT encourages individuals to become more aware of their thoughts, emotions, and behaviours.
- This increased self-awareness can help individuals recognize patterns and triggers for their mental health issues.
- By understanding the underlying causes of their symptoms, individuals can make changes and improve their mental well-being.
- CBT can help individuals improve their communication skills, allowing them to express their needs and emotions effectively.
- Effective communication can lead to healthier relationships and a reduction in interpersonal conflicts that can contribute to mental health issues.
- CBT equips individuals with tools and strategies to prevent relapse and maintain their mental health gains.
- Through ongoing practice and reinforcement of learned skills, individuals can reduce the likelihood of their symptoms returning.
- Qualifications: Look for a therapist who has received formal training in CBT. They may have a degree in psychology or a related field, and should have completed additional training or certification in CBT.
- Experience: It can be helpful to find a therapist with experience treating the specific issue or condition you are seeking help for. For example, if you are struggling with anxiety, look for a CBT therapist who specializes in anxiety disorders.
- Approach: Each therapist may have a slightly different approach to CBT. Some therapists may incorporate other therapeutic techniques, such as mindfulness or acceptance and commitment therapy, into their CBT practice. Consider what approach feels most comfortable and effective for you.
- Compatibility: It is important to feel comfortable and supported by your therapist. CBT requires a close working relationship, so it’s essential to find a therapist with whom you feel a positive connection.
- Location and Accessibility: Consider the location and accessibility of the therapist’s office. It may be more convenient to find a therapist who is close to your home or workplace.
- Your primary care physician or healthcare provider may be able to provide a referral to a qualified CBT therapist.
- Mental health organizations or associations may have directories or lists of CBT therapists in your area.
- Online directories, such as Psychology Today or the Association for Behavioral and Cognitive Therapies (ABCT) website, can help you search for CBT therapists based on location and specialization.
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy can be delivered in various formats, including individual therapy sessions, group therapy, or self-help materials. It is a collaborative and goal-oriented approach that empowers individuals to take an active role in their own therapy and develop effective strategies for managing their mental health.
Understanding the Fundamentals of CBT
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is a widely used form of psychotherapy that focuses on the connection between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. By understanding and altering cognitive patterns, individuals can learn to manage their emotions and improve their overall mental well-being. Here are some key fundamentals of CBT:
Overall, CBT provides individuals with practical tools and strategies to address their negative thoughts and behaviors, leading to improved mental well-being and a more positive outlook on life.
Benefits of Cognitive Behaviour Therapy
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized and researched therapeutic approach that has been shown to be effective in treating a variety of mental health issues. Some of the main benefits of CBT include:
Overall, Cognitive Behaviour Therapy offers a range of benefits that can help individuals improve their mental health, build resilience, and achieve their goals. It is a collaborative and evidence-based approach that provides individuals with practical tools to overcome challenges and lead a more fulfilling life.
The Role of Thoughts and Behavior
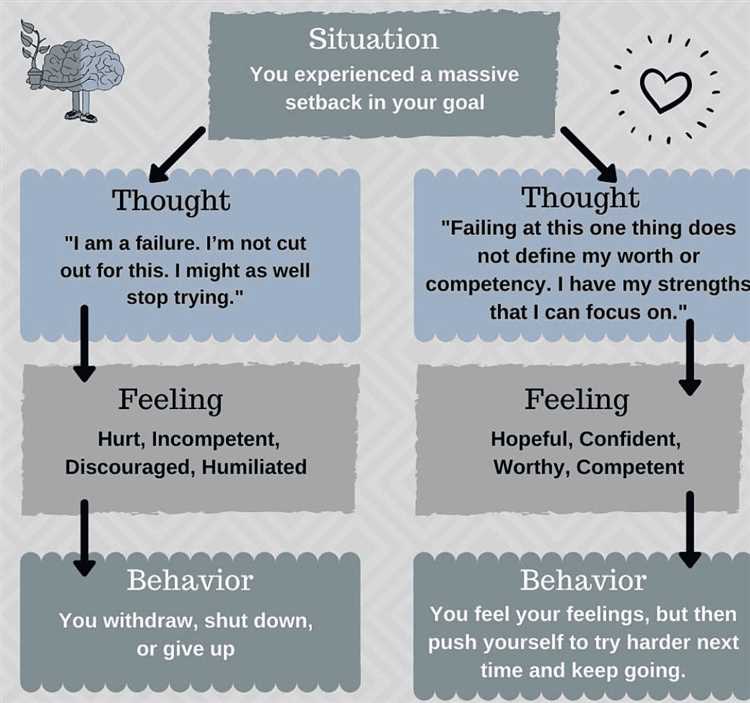
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is based on the idea that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected. It suggests that the way we think about situations and events influences how we feel and how we behave.
Thoughts: Our thoughts are the internal dialogue we have with ourselves. They are the beliefs, assumptions, and interpretations we make about ourselves, others, and the world around us. Our thoughts can be positive or negative, rational or irrational.
CBT recognizes that our thoughts can have a powerful impact on our emotions. For example, if we tend to have negative thoughts about ourselves or our abilities, we are more likely to feel anxious, depressed, or insecure. On the other hand, if we have positive and realistic thoughts, we are more likely to feel confident, motivated, and happy.
Behavior: Our behaviors are the actions we take or the things we do in response to situations. They can be visible or invisible, intentional or unintentional. Behaviors are influenced by our thoughts and emotions.
CBT emphasizes the importance of behavioral changes in overcoming psychological difficulties. By changing our behaviors, we can directly influence our thoughts and emotions. For example, if we tend to avoid social situations because we feel anxious, our anxiety may continue to worsen. However, if we face our fears and gradually expose ourselves to social situations, we can learn that our fears are not as justified as we initially thought, and our anxiety may decrease.
CBT uses various techniques and strategies to help individuals identify and challenge their negative thoughts, and to modify their behaviors in a way that promotes positive change. By understanding the role of thoughts and behaviors in our mental well-being, we can gain greater control over our lives and improve our overall functioning.
Key Techniques and Strategies in CBT
In Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT), there are several key techniques and strategies that therapists use to help individuals address their negative thoughts, emotions, and behaviours. These techniques are based on the idea that our thoughts and beliefs influence our emotions and behaviours, and by changing our thought patterns, we can change how we feel and behave.
Cognitive Restructuring: This technique involves identifying and challenging negative or unhelpful thoughts and beliefs. The therapist helps the individual to examine the evidence for and against their thoughts, and develop more balanced and realistic ways of thinking. By changing negative thinking patterns, individuals can reduce their feelings of anxiety, depression, and other negative emotions.
Behavioural Activation: This strategy involves encouraging individuals to engage in activities that they have been avoiding due to their negative thoughts or emotions. By gradually reintroducing enjoyable or meaningful activities into their lives, individuals can increase their level of happiness and well-being.
Problem Solving: This technique involves helping individuals to identify and solve practical problems in their lives. The therapist guides the individual through a structured problem-solving process, helping them to break down problems into smaller, more manageable steps. By learning effective problem-solving skills, individuals can reduce their feelings of helplessness and improve their ability to cope with challenges.
Exposure Therapy: This technique is often used to treat anxiety disorders, such as phobias or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The individual is gradually exposed to the feared situation or object, while learning and practicing relaxation techniques to manage their anxiety. Over time, individuals become desensitized to the feared stimuli and experience a reduction in their anxiety symptoms.
Relaxation Techniques: Various relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery, are commonly used in CBT to help individuals manage stress and reduce anxiety. These techniques can help individuals to relax their body and mind, which in turn can help to reduce their emotional and physical symptoms of stress and anxiety.
Social Skills Training: This strategy involves teaching individuals effective communication and interpersonal skills. The therapist helps the individual to identify their social skills deficits and provides them with the necessary tools and practice to improve their ability to interact with others. By developing better social skills, individuals can enhance their relationships and overall well-being.
Thought Recording: This technique involves keeping a record of negative thoughts or beliefs, and then challenging and replacing them with more realistic and positive alternatives. By monitoring their thoughts and replacing negative ones with positive ones, individuals can reframe their thinking and reduce their negative emotions.
Mindfulness: Mindfulness is a practice that involves intentionally focusing on the present moment and accepting it without judgment. This technique is often used in CBT to help individuals become more aware of their thoughts, emotions, and sensations, and to develop a non-reactive and accepting attitude towards them. By practicing mindfulness, individuals can learn to observe their thoughts and emotions without becoming overwhelmed by them.
Goal Setting: Setting goals is an important strategy in CBT, as it helps individuals to identify what they want to achieve and develop a plan to work towards it. Goals can be short-term or long-term, and they should be specific, achievable, and measurable. By setting and working towards goals, individuals can experience a sense of purpose and accomplishment, which can improve their overall well-being.
Self-Monitoring: Self-monitoring involves keeping track of one’s thoughts, emotions, and behaviours in order to identify patterns and triggers. By monitoring themselves, individuals can gain a better understanding of their cognitive and behavioural patterns and make more informed decisions about how to change them.
In conclusion, Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) employs a variety of techniques and strategies to help individuals change their negative thoughts, emotions, and behaviours. By challenging negative thoughts, engaging in positive activities, solving problems, facing fears, practicing relaxation, improving social skills, reframing thoughts, practicing mindfulness, setting goals, and self-monitoring, individuals can effectively address their mental health concerns and improve their overall well-being.
CBT for Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive and persistent worry, fear, or unease. They can affect a person’s daily life and functioning, making it difficult to cope with everyday tasks and responsibilities.
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is an effective treatment approach for anxiety disorders, as it focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety. CBT aims to help individuals develop healthier ways of thinking and coping with anxiety, leading to better overall mental health.
The goals of CBT for anxiety disorders include:
CBT for anxiety disorders typically involves several components:
CBT for anxiety disorders can be effective for:
It is important to note that CBT is not a one-size-fits-all approach and may be tailored to the individual’s specific needs and preferences. The duration and number of therapy sessions can vary depending on the severity of the anxiety disorder and the individual’s response to treatment.
| Pros of CBT for Anxiety Disorders | Cons of CBT for Anxiety Disorders |
|---|---|
|
|
|
CBT for anxiety disorders can be an effective and evidence-based treatment option for individuals experiencing excessive worry and fear. It provides practical tools and techniques to manage anxiety and improve overall well-being.
CBT for Depression
Depression is a common mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities.
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is an evidence-based treatment that has been found to be effective in helping individuals with depression. CBT for depression aims to identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviours that contribute to and maintain depressive symptoms.
CBT for depression typically involves the following components:
CBT for depression is typically conducted over a series of structured sessions, usually ranging from 12 to 20 sessions, although the exact number may vary depending on the individual’s needs and progress. It is important for the individual to actively participate in therapy and practice the skills learned between sessions.
Research has consistently shown that CBT for depression is an effective treatment. It has been found to be as effective as medication in the short-term and can have lasting effects, reducing the risk of relapse. CBT can also be combined with medication for individuals who may benefit from both approaches.
In summary, CBT is a well-established and effective treatment for depression. It helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviours that contribute to and maintain depressive symptoms. With the help of a trained therapist, individuals can learn new skills to manage their depression and improve their overall well-being.
How CBT Can Improve Your Mental Health
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on changing unhelpful thought patterns and behaviours. It is commonly used to treat a variety of mental health conditions, including anxiety disorders, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder. CBT can be an effective treatment option for individuals looking to improve their mental health.
1. Identify and challenge negative thinking
2. Develop coping strategies
3. Improve problem-solving skills
4. Increase self-awareness
5. Enhance communication skills
6. Prevent relapse
Overall, CBT can be a powerful tool for improving mental health. By challenging negative thinking, developing coping strategies, improving problem-solving skills, increasing self-awareness, enhancing communication skills, and preventing relapse, individuals can take control of their mental well-being and experience lasting positive changes in their lives.
Finding a CBT Therapist
Finding a qualified Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) therapist is an important step in seeking treatment. Here are some factors to consider when looking for a CBT therapist:
You can find CBT therapists through various resources, such as:
When you have found potential therapists, consider scheduling an initial consultation or phone call to discuss your needs and ask any questions you may have. This can help you determine if the therapist is the right fit for you.
Remember, finding a CBT therapist is a personal process, and it may take time to find the right therapist for your needs. Don’t hesitate to seek recommendations and take the time to find a therapist who is experienced, qualified, and with whom you feel comfortable working.
Questions and answers
What is Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT)?
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on the connection between a person’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It aims to help individuals identify and change negative or unhelpful thinking patterns and develop healthier ways of coping with challenges.
How does Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) work?
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) works by helping individuals become aware of their negative or distorted thinking patterns and how these thoughts contribute to their emotional distress and negative behaviors. Therapists use a variety of techniques to challenge and change these negative thoughts, helping individuals develop more positive and realistic thoughts and beliefs.
What conditions can Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) be used to treat?
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) can be used to treat a variety of mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), eating disorders, and substance abuse. It is also sometimes used to help manage chronic pain and improve relationships.
Is Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) effective?
Yes, Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) has been extensively studied and has been shown to be an effective treatment for many mental health conditions. Research has shown that CBT can lead to significant improvements in symptoms and overall functioning, and the effects of CBT can be long-lasting.