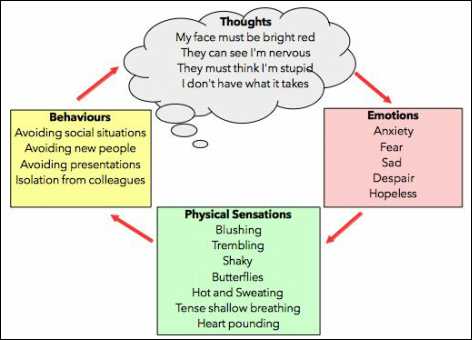
Social anxiety is a psychological disorder characterized by intense fear and avoidance of social situations. People with social anxiety often experience symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, and a strong desire to escape from social interactions. The Covid-19 pandemic has brought about significant changes in social dynamics, leading to a potential connection between the virus and the cycle of avoidance in social anxiety.
One of the primary factors contributing to the cycle of avoidance in social anxiety is the fear of negative evaluation from others. Individuals with social anxiety are often preoccupied with thoughts of being scrutinized or judged by others, leading them to avoid social situations altogether. The Covid-19 pandemic has exacerbated this fear by introducing the concept of public health safety measures, such as social distancing and wearing masks, which further amplify the fear of negative evaluation.
Moreover, the pandemic has also created a sense of uncertainty and unpredictability in social situations. Social anxiety is often associated with a fear of the unknown, and the pandemic has heightened this fear by introducing new rules and regulations that constantly change. This uncertainty leads to increased avoidance as individuals with social anxiety struggle to adapt to the new social norms brought about by the virus.
In conclusion, the Covid-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on individuals with social anxiety, further perpetuating the cycle of avoidance in social situations. The fear of negative evaluation and the heightened sense of uncertainty have contributed to increased avoidance behaviors. It is crucial to acknowledge and address these challenges to provide support and effective interventions for individuals with social anxiety during these unprecedented times.
The Impact of Covid-19 Lockdowns on Social Anxiety
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on people’s mental health, including those who experience social anxiety. The implementation of lockdowns and social distancing measures has changed the way we interact with others, and this change can exacerbate feelings of social anxiety and isolation.
One of the main challenges faced by individuals with social anxiety during the Covid-19 lockdowns is the lack of social contact. Social interactions, such as attending social events or spending time with friends, have become limited or prohibited in many places. This reduction in social contact can lead to feelings of loneliness and isolation, which can further fuel social anxiety.
In addition to the lack of social contact, the Covid-19 lockdowns have also increased the reliance on digital communication platforms for social interactions. While these platforms have allowed people to stay connected in some way, they may not be as effective in reducing social anxiety as face-to-face interactions. The inability to read non-verbal cues and the fear of being judged or misunderstood through digital communication can heighten social anxiety symptoms.
Another factor contributing to the impact of Covid-19 lockdowns on social anxiety is the uncertainty surrounding the pandemic. The constant changes in guidelines and restrictions can create anxiety and stress for individuals with social anxiety. The fear of unknowingly violating social norms or contracting the virus can lead to heightened anxiety levels, making social situations even more challenging.
Furthermore, the Covid-19 lockdowns have disrupted routines and daily activities for many individuals. For individuals with social anxiety, routine can provide a sense of comfort and predictability. The disruption of routines and the lack of structure can increase anxiety levels and make it difficult to engage in social situations, even when restrictions are lifted.
In conclusion, the Covid-19 lockdowns have had a significant impact on social anxiety. The lack of social contact, increased reliance on digital communication, uncertainty, and disruption of routines have all contributed to heightened social anxiety symptoms. It is important for individuals with social anxiety to seek support and engage in self-care strategies to manage these challenges effectively.
Understanding the Cycle of Avoidance in Social Anxiety
Social anxiety is a common mental health disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by an intense fear of social situations, such as parties, public speaking, or even simple conversations. Individuals with social anxiety often go to great lengths to avoid these situations, which can have a significant impact on their daily lives and overall well-being.
The cycle of avoidance in social anxiety is a self-perpetuating pattern that can be difficult to break. It typically starts with a fear or apprehension of social situations, which can be triggered by a variety of factors, including past negative experiences, low self-esteem, or a fear of judgment and rejection.
The cycle of avoidance often follows these steps:
- Anxiety and anticipation: The individual begins to feel anxious as they anticipate an upcoming social situation. They may experience physical symptoms such as a racing heart, sweaty palms, or shortness of breath.
- Avoidance behavior: To cope with their anxiety, the individual starts to avoid the triggering social situations. They may cancel plans, make excuses, or isolate themselves from others. This avoidance behavior provides temporary relief from the anxiety, reinforcing the cycle.
- Short-term relief: By avoiding social situations, the individual experiences temporary relief from their anxiety. They may feel a sense of comfort and safety in their isolation. However, this relief is short-lived and does not address the underlying causes of their social anxiety.
- Increased long-term anxiety: Over time, avoiding social situations can actually increase long-term anxiety. The individual’s world becomes smaller as they limit their interactions and experiences. This can lead to a loss of confidence and a further reinforcement of their social anxiety.
- Impact on daily life: The cycle of avoidance can have a significant impact on the individual’s daily life. It can affect their relationships, career opportunities, and overall quality of life. They may miss out on important social events or feel isolated and lonely.
Breaking the cycle of avoidance in social anxiety can be challenging, but it is possible with the right support and treatment. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, and medication are common approaches used to address social anxiety and help individuals gradually confront their fears. By facing their fears and learning coping strategies, individuals can gradually break the cycle of avoidance and regain control over their social lives.
| Social anxiety is characterized by an intense fear of social situations. |
| The cycle of avoidance in social anxiety is a self-perpetuating pattern. |
| The cycle typically involves anxiety and anticipation, avoidance behavior, short-term relief, increased long-term anxiety, and an impact on daily life. |
| Breaking the cycle of avoidance is possible with the right support and treatment. |
How Covid-19 Exacerbates Social Anxiety Symptoms
Social anxiety disorder, often referred to as social phobia, is a common mental health condition characterized by intense fear and avoidance of social situations. Individuals with social anxiety often anticipate negative judgments or embarrassment in social interactions and may experience physical symptoms such as sweating, trembling, or rapid heartbeat.
The Covid-19 pandemic has presented unique challenges for individuals with social anxiety, exacerbating their symptoms and making it even more difficult for them to engage in social situations. Here are some reasons why Covid-19 has had a significant impact on social anxiety:
- The fear of contracting the virus: Individuals with social anxiety may already have heightened levels of fear and worry about their health. The uncertain nature of Covid-19 and the fear of contracting the virus in social situations can amplify their anxieties and make them even more hesitant to interact with others.
- Physical distancing and isolation: The implementation of physical distancing measures and isolation protocols has forced individuals with social anxiety to spend even more time alone and away from social situations. While this may initially seem like a relief for individuals with social anxiety, prolonged isolation can actually increase their feelings of loneliness and exacerbate their symptoms.
- Limited opportunities for exposure therapy: Exposure therapy is a common treatment for social anxiety, where individuals gradually expose themselves to fear-inducing situations in order to reduce their anxiety over time. However, the restrictions and limitations imposed by Covid-19 have made it challenging for individuals to engage in exposure therapy effectively, limiting their opportunities for growth and improvement.
- Increased reliance on virtual communication: With the shift towards remote work and online gatherings, individuals with social anxiety have had to adapt to increased virtual communication. While this may seem like a more comfortable alternative for individuals with social anxiety, it can actually be overwhelming, as virtual interactions can still trigger anxiety and self-consciousness.
- Disruption of routines and support systems: Many individuals with social anxiety rely on routines and support systems to manage their symptoms. The disruption caused by Covid-19, such as changes in work or school environments, the loss of social support networks, and the overall uncertainty, can destabilize these coping mechanisms and increase anxiety levels.
In conclusion, Covid-19 has had a significant impact on individuals with social anxiety, exacerbating their symptoms and making it even more challenging for them to navigate social interactions. It is important to recognize the unique challenges that individuals with social anxiety face in the midst of the pandemic and to provide them with appropriate support and resources to manage their mental health effectively.
Challenges Faced by Individuals with Social Anxiety During a Pandemic
Individuals with social anxiety face unique challenges during a pandemic such as Covid-19. The fear of social situations and interaction with others can be heightened due to the necessity of following safety protocols and social distancing guidelines. This can further exacerbate feelings of isolation and anxiety, leading to a cycle of avoidance and withdrawal from social activities.
1. Limited social contact:
- Individuals with social anxiety already struggle with initiating and maintaining social interactions.
- The pandemic has limited opportunities for social contact, making it even more difficult for individuals with social anxiety to overcome their fears and engage in social activities.
- Virtual platforms may offer an alternative, but the fear of being judged or misunderstood can still persist.
2. Fear of exposure to the virus:
- Individuals with social anxiety may have heightened health anxiety, leading to an increased fear of contracting the virus.
- This fear can make it challenging for them to leave their homes or engage in activities that involve being in close proximity to others.
- The fear of being judged for adhering to safety protocols or the fear of encountering others who do not follow them can also contribute to heightened anxiety and avoidance behaviors.
3. Increased isolation:
- Social anxiety can already lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
- The pandemic has further increased the need for physical distancing, which can exacerbate these feelings.
- Reduced social support and a lack of opportunities for socialization can intensify the negative impact of social anxiety on mental well-being.
4. Uncertainty and change:
- The constantly evolving nature of the pandemic can lead to uncertainty and fear of the unknown.
- Changes in guidelines and restrictions can trigger additional anxiety, making it challenging for individuals with social anxiety to navigate social situations.
- Adapting to new norms such as wearing masks, avoiding physical contact, and maintaining distance can be particularly challenging for individuals with social anxiety who may already struggle with self-consciousness and fear of criticism.
5. Impact on mental well-being:
- The combination of increased anxiety, isolation, and uncertainty can have a significant impact on the mental well-being of individuals with social anxiety.
- Feelings of sadness, depression, and a heightened sense of vulnerability may arise.
- Access to mental health support may be limited during this time, further compounding the challenges faced by these individuals.
In conclusion, individuals with social anxiety face unique challenges during a pandemic. The fear of social situations, limited social contact, fear of exposure to the virus, increased isolation, uncertainty and change, and the impact on mental well-being are all factors that contribute to the difficulties faced by individuals with social anxiety. It is important to recognize and address these challenges to provide support and assistance to those who need it.
Ways to Break the Cycle of Avoidance in Social Anxiety During Covid-19
Social anxiety can be challenging at any time, but during the Covid-19 pandemic, it can become even more difficult to manage. With social distancing and remote work becoming the new norm, opportunities for social interactions have decreased, leading to an increased cycle of avoidance in individuals with social anxiety. However, there are several strategies that can help break this cycle and improve mental well-being.
- Challenge negative thoughts: Social anxiety is often fueled by negative thoughts and assumptions about oneself and others. It is important to challenge these thoughts and replace them with more realistic and positive ones. Practicing self-compassion and reminding oneself of their strengths can be helpful in this process.
- Gradual exposure: Gradual exposure to social situations can be an effective way to overcome social anxiety. This can be done by starting with small, manageable social interactions, such as joining online support groups or participating in virtual events. Gradually increasing the level of exposure can help build confidence and reduce anxiety.
- Seeking professional help: It is essential to reach out to a mental health professional if social anxiety becomes overwhelming and begins to interfere with daily life. Therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or exposure therapy can provide valuable tools and strategies for managing social anxiety.
- Self-care: Engaging in self-care activities can help reduce anxiety and improve overall well-being. This can include practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or mindfulness, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet, and getting enough sleep.
- Support network: Building a support network of family and friends can provide a sense of belonging and understanding. Sharing experiences and concerns with others who can relate to social anxiety can help alleviate feelings of isolation and provide practical advice and support.
- Embrace virtual connections: Although physical interactions may be limited, virtual connections can still provide opportunities for socializing. Participating in online communities, joining virtual classes or clubs, and engaging in video calls with loved ones can help maintain social connections and combat the cycle of avoidance.
- Focus on personal growth: Instead of solely focusing on the fear of social situations, try to shift the focus towards personal growth and self-improvement. Setting achievable goals and challenging oneself to step out of the comfort zone can lead to increased confidence and a sense of accomplishment.
- Practice self-compassion: Remember that it is okay to struggle with social anxiety, especially during these challenging times. Practicing self-compassion and treating oneself with kindness and understanding can help break the cycle of avoidance and foster a more positive mindset.
In conclusion, breaking the cycle of avoidance in social anxiety during Covid-19 requires a combination of challenging negative thoughts, gradual exposure, seeking professional help, engaging in self-care, building a support network, embracing virtual connections, focusing on personal growth, and practicing self-compassion. By implementing these strategies, individuals with social anxiety can find ways to manage their anxiety and thrive despite the limitations imposed by the pandemic.
Seeking Support: The Role of Therapy in Managing Social Anxiety During a Pandemic
Living with social anxiety can be challenging at any time, but the COVID-19 pandemic has brought about additional stressors and uncertainties that can intensify these symptoms. With the restrictions on social gatherings and isolation measures, individuals with social anxiety may find it even more difficult to navigate social interactions and maintain their mental well-being.
Therapy plays a crucial role in helping individuals manage their social anxiety during the pandemic. By providing a safe and non-judgmental space, therapists can help individuals explore their anxieties and develop effective coping strategies. Here are some ways therapy can support individuals with social anxiety:
- Psychoeducation: Therapists can provide valuable information about social anxiety, its causes, and how it can be triggered by the pandemic. Understanding the root causes of their anxiety can help individuals gain a new perspective and find ways to address their fears.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is an evidence-based therapy that focuses on challenging negative thoughts and behaviors. Therapists can guide individuals through structured sessions that help them identify distorted thinking patterns and replace them with more rational and positive thoughts.
- Exposure Therapy: Exposure therapy is often used to treat social anxiety by gradually exposing individuals to feared social situations. During the pandemic, therapists can help individuals adapt this technique to virtual settings, such as participating in online group activities or practicing video calls with trusted individuals.
- Online Support Groups: Therapy sessions can also provide an opportunity for individuals to connect with others who are facing similar challenges. By participating in online support groups, individuals can share their experiences, learn from others, and find a sense of community.
It is important to note that therapy may need to be adapted to the unique challenges of the pandemic. Therapists may need to utilize teletherapy or online platforms to ensure continuity of care and maintain the safety of both clients and therapists. Additionally, therapists can help individuals develop a self-care routine and implement relaxation techniques to manage anxiety symptoms in their daily lives.
Seeking therapy for social anxiety during a pandemic can be a powerful step towards managing and overcoming anxiety. By working with a therapist, individuals can gain the tools and support necessary to navigate social interactions, maintain their mental well-being, and ultimately break the cycle of avoidance that fuels social anxiety.
Coping Strategies for Individuals with Social Anxiety During Covid-19
Living with social anxiety can be challenging, especially during a time when social distancing and isolation have become the new norm. However, there are several coping strategies that individuals with social anxiety can implement to navigate these difficult times. These strategies aim to help manage anxiety and promote overall well-being:
- Practice self-care: Engage in activities that promote relaxation and self-soothing. This can include taking warm baths, practicing deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies that bring joy and distraction.
- Stay informed but limit exposure to news: It is important to stay updated on the latest information about Covid-19, but constant exposure to news can increase anxiety levels. Set specific times to catch up on news and rely on reputable sources.
- Maintain a routine: Establishing a daily routine can provide a sense of structure and control amid uncertainty. Set specific times for waking up, working, exercising, and engaging in leisure activities.
- Connect with others: While physical distancing is necessary, it is crucial to maintain social connections. Use technology to stay connected with friends, family, or support groups through video calls, text messages, or online communities.
- Challenge negative thoughts: Social anxiety often involves negative self-talk and distorted thinking patterns. Identify and challenge these thoughts by questioning their validity and replacing them with more realistic and positive ones.
- Set small, achievable goals: Break large tasks or goals into smaller, manageable steps. Celebrating small achievements can boost self-confidence and provide a sense of accomplishment.
- Engage in exposure exercises: Gradually expose yourself to situations that trigger anxiety. Start with easier situations and gradually move on to more challenging ones. This can help desensitize the anxiety response over time.
- Practice mindfulness: Mindfulness exercises, such as meditation or body scan techniques, can help individuals with social anxiety stay present and grounded. These techniques can also promote relaxation and reduce stress levels.
- Seek professional help: If social anxiety symptoms become overwhelming or interfere with daily functioning, consider seeking help from a mental health professional. They can provide effective treatments, such as therapy or medication, tailored to individual needs.
Overall, individuals with social anxiety have a unique set of challenges to navigate during the Covid-19 pandemic. By implementing these coping strategies, it is possible to manage anxiety, improve well-being, and maintain social connections in a time of physical distancing and isolation.
The Long-Term Effects of Covid-19 on Social Anxiety and the Importance of Seeking Help
Social anxiety is a common mental health condition that affects individuals in social situations, causing intense fear and discomfort. The ongoing Covid-19 pandemic has significantly impacted people’s lives, leading to various psychological and emotional effects. One area that has seen a notable increase is the connection between Covid-19 and the cycle of avoidance in social anxiety.
Although social distancing measures and lockdowns have been necessary to control the spread of the virus, they have also created a breeding ground for social anxiety. The isolation and lack of social interaction have exacerbated existing social anxiety symptoms and triggered the development of new cases.
One of the long-term effects of Covid-19 on social anxiety is the reinforcement of avoidance behaviors. Individuals with social anxiety tend to avoid social situations due to the fear of judgment and embarrassment. The pandemic has provided a valid reason for individuals to continue avoiding social interactions, leading to a reinforcement of avoidance behaviors. This perpetuates the cycle of anxiety and further increases the social anxiety symptoms.
Another long-term effect of Covid-19 on social anxiety is the erosion of social skills. Social skills are crucial for building and maintaining relationships, and the lack of social interaction during lockdowns has resulted in the decline of these skills. Individuals with social anxiety may find it even more challenging to re-engage in social situations post-pandemic, as the lack of practice and exposure has weakened their social skills.
It is important for individuals experiencing social anxiety to seek help, especially in the context of the long-term effects of Covid-19. Professional therapists and mental health services can provide the necessary support and guidance in managing social anxiety symptoms. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective treatments for social anxiety, helping individuals challenge and reframe their negative thoughts and behaviors.
In addition to seeking professional help, individuals with social anxiety can also benefit from connecting with support groups or participating in online therapy sessions. These platforms provide a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, learn coping strategies, and gain a sense of community.
In conclusion, the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic has had significant long-term effects on social anxiety. The reinforcement of avoidance behaviors and the erosion of social skills are among the key impacts. Seeking help from mental health professionals and engaging in support communities can play a crucial role in managing social anxiety symptoms and reducing the negative effects of the pandemic on individuals’ mental well-being.
Questions and answers
What is social anxiety?
Social anxiety is a psychological condition characterized by a fear of social situations and a strong desire to avoid them. People with social anxiety often feel anxious or intimidated when they are around others, especially in situations where they may be the center of attention.
How does social anxiety affect people’s lives?
Social anxiety can have a significant impact on a person’s life. It can make it difficult for them to form and maintain relationships, perform well in school or at work, and participate in social activities. It can also lead to feelings of isolation, low self-esteem, and depression.
Is social anxiety a common condition?
Yes, social anxiety is a common condition. It is estimated that around 7% of the population suffers from social anxiety disorder at some point in their lives. However, many people with social anxiety do not seek treatment and may try to cope with their symptoms by avoiding social situations.
What is the cycle of avoidance in social anxiety?
The cycle of avoidance in social anxiety is a pattern of behavior where individuals with social anxiety avoid social situations that trigger their anxiety. This avoidance provides temporary relief from anxiety, reinforcing the behavior and leading to further avoidance in the future. This cycle can perpetuate social anxiety and make it difficult for individuals to overcome their fears.
How does the Covid-19 pandemic relate to social anxiety and the cycle of avoidance?
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on social anxiety and the cycle of avoidance. With social distancing measures and lockdowns in place, many individuals with social anxiety have had their usual avoidance behaviors reinforced and reinforced again. This can make it even more challenging for them to re-engage in social activities and overcome their anxiety once the pandemic is over.