The Islamic calendar is based on the moon’s cycle and consists of 12 lunar months, each lasting approximately 29 to 30 days. Unlike the Gregorian calendar, which is widely used across the world, the Islamic calendar does not follow a fixed number of days for each month. This means that the start and end dates of Islamic months can vary each year.
It is important for Muslims to know which Islamic month is currently being observed because it has implications for various religious practices and events. For example, the Islamic month of Ramadan is a holy month of fasting and prayer, during which Muslims abstain from food, drink, and other physical needs from dawn until sunset. Knowing that Ramadan is approaching allows individuals to make preparations and participate fully in the spiritual aspects of the month.
The Islamic months are also significant because they mark important historical events in the Islamic calendar. For example, the month of Muharram is the first month of the Islamic year and is considered a sacred month. It commemorates the migration of the Prophet Muhammad from Mecca to Medina and is marked by various religious observances.
With a deep understanding of the Islamic calendar and its significance, Muslims can actively engage in the various religious and cultural traditions associated with each month. By knowing which Islamic month is going on, individuals can ensure that they participate fully in the observances and events that are a part of their faith.
The Importance of Knowing the Current Islamic Month
Knowing the current Islamic month is of great importance for Muslims around the world. It helps them in carrying out their religious obligations, observing important events, and staying connected to the Islamic calendar.
1. Religious Obligations:
Islam is a religion that places great emphasis on following a lunar calendar. Many religious obligations, such as fasting during the month of Ramadan or performing the Hajj pilgrimage, are tied to specific Islamic months. By knowing the current Islamic month, Muslims can ensure that they are fulfilling their religious obligations at the appropriate time.
2. Observance of Important Events:
Islamic history is rich with important events that are associated with specific Islamic months. For example, the month of Ramadan is marked by the revelation of the Quran to Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him). The month of Muharram is significant for its association with the martyrdom of Imam Husayn (may Allah be pleased with him). By knowing the current Islamic month, Muslims can observe these important events and gain a deeper understanding of their faith.
3. Connection to the Islamic Calendar:
The Islamic calendar is different from the Gregorian calendar that is commonly used worldwide. It follows a lunar cycle and is composed of twelve months. Knowing the current Islamic month allows Muslims to stay connected to the Islamic calendar and its unique system of timekeeping.
Conclusion:
Being aware of the current Islamic month is important for Muslims as it helps them fulfill their religious obligations, observe important events, and stay connected to the Islamic calendar. It allows them to live their lives in accordance with their faith and strengthens their connection to the wider Muslim community.
Understanding the Islamic Calendar
The Islamic calendar, also known as the Hijri calendar, is a lunar calendar used by Muslims around the world to determine the dates for religious observances and events. It is based on the cycles of the moon and consists of 12 lunar months in a year, totaling 354 or 355 days.
The Islamic calendar begins with the migration of the Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) from Mecca to Medina, known as the Hijra, which occurred in 622 CE. This event is considered significant in Islamic history and serves as the starting point for the Islamic calendar.
Unlike the Gregorian calendar, which is a solar calendar, the Islamic calendar follows the lunar cycle. Each month begins with the sighting of the new moon, which marks the start of a new Islamic month. The length of each month varies depending on the sighting of the moon, so the Islamic calendar is not fixed and can differ from year to year.
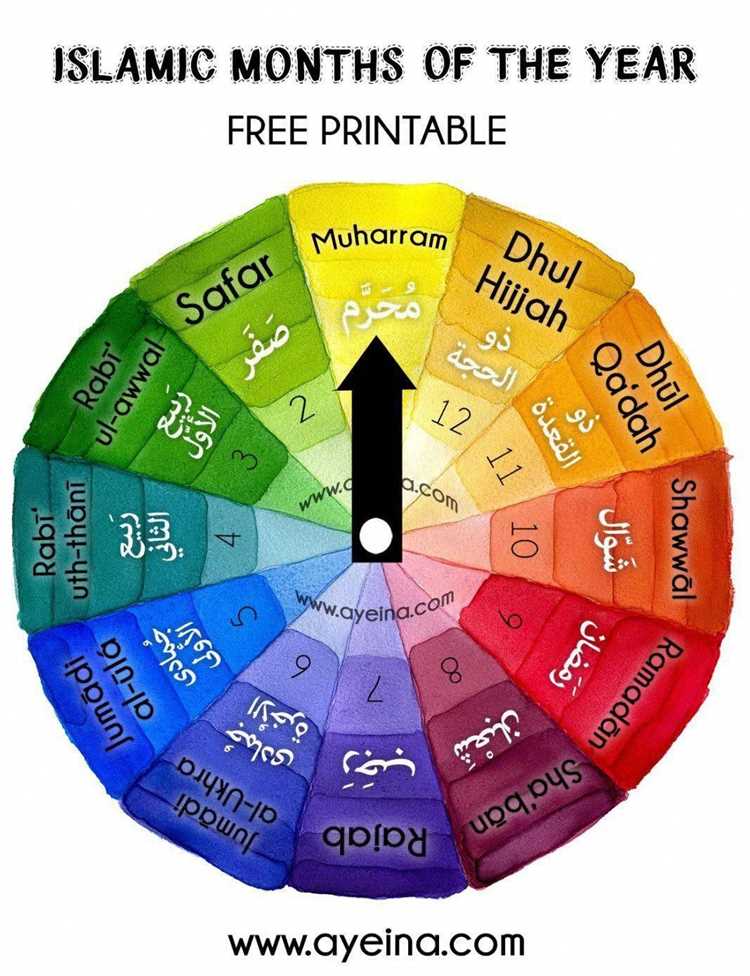
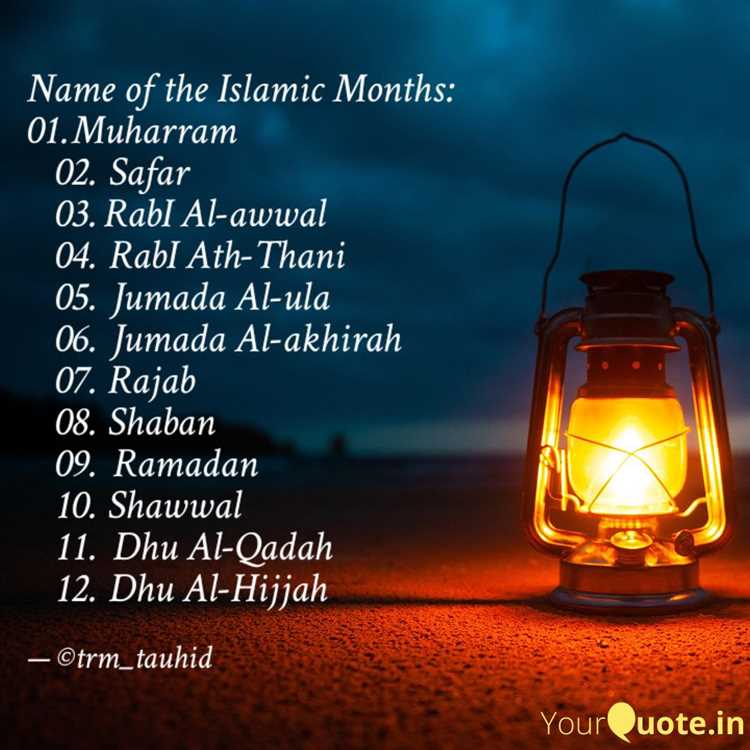
The Islamic calendar consists of 12 months, with each month having either 29 or 30 days. The names of the Islamic months are as follows:
- Muharram
- Safar
- Rabi’ al-Awwal
- Rabi’ al-Thani
- Jumada al-Awwal
- Jumada al-Thani
- Rajab
- Sha’ban
- Ramadan
- Shawwal
- Dhu al-Qidah
- Dhu al-Hijjah
One of the most important months in the Islamic calendar is Ramadan, which is the month of fasting. During Ramadan, Muslims abstain from food, drink, and other physical needs from sunrise to sunset. It is a time of spiritual reflection, increased devotion, and worship.
In addition to Ramadan, other significant months in the Islamic calendar include the month of Muharram, which is considered a sacred month, and the month of Dhu al-Hijjah, during which the Hajj pilgrimage to Mecca takes place.
| Islamic Month | Number of Days |
|---|---|
| Muharram | 29 or 30 |
| Safar | 29 or 30 |
| Rabi’ al-Awwal | 29 or 30 |
| Rabi’ al-Thani | 29 or 30 |
| Jumada al-Awwal | 29 or 30 |
| Jumada al-Thani | 29 or 30 |
| Rajab | 29 or 30 |
| Sha’ban | 29 or 30 |
| Ramadan | 29 or 30 |
| Shawwal | 29 or 30 |
| Dhu al-Qidah | 29 or 30 |
| Dhu al-Hijjah | 29 or 30 |
The Islamic calendar holds great importance for Muslims as it not only helps in organizing religious observances but also serves as a reminder of key events in Islamic history. It is a unique calendar that follows a different pattern from the widely used Gregorian calendar.
Significance of the Islamic Months
The Islamic calendar is based on the lunar cycle and consists of twelve months. Each Islamic month holds its own significance and importance for Muslims around the world. Here are the significance of the Islamic months:
- Muharram: The first month of the Islamic calendar, Muharram is considered a sacred month. It is a time for reflection and remembrance, particularly of the martyrdom of Imam Hussain (RA) and his companions in the Battle of Karbala. Muslims often observe fasting and engage in acts of charity during this month.
- Safar: Known as the month of difficulties, Safar is believed to be a month of trials and tribulations. However, Muslims still seek blessings and protection from Allah during this month.
- Rabi ul-Awwal: This month is significant as it marks the birth and prophecy of the Prophet Muhammad (SAW). Muslims celebrate the occasion of Eid Milad-un-Nabi during this month.
- Rabi ul-Aakhir: During this month, Muslims remember the migration of the Prophet Muhammad (SAW) from Makkah to Madinah. This migration, known as the Hijrah, is a crucial event in Islamic history.
- Jumada al-Ula: This month holds no particular significance in terms of Islamic events, but Muslims continue to observe their regular acts of worship and seek blessings.
- Jumada al-Aakhirah: Like its preceding month, Jumada al-Aakhirah has no specific events or significance but is still considered a month of blessings and opportunities for Muslims.
- Rajab: Rajab is regarded as one of the sacred months in Islam. It is a time for spiritual reflection and preparation for the holy month of Ramadan.
- Shaban: Shaban is the month before Ramadan and is often referred to as the preparatory month. Muslims engage in additional acts of worship during this month to spiritually prepare for the upcoming month of fasting.
- Ramadan: Ramadan is the ninth month of the Islamic calendar and is the holiest month for Muslims. It is a time of fasting, prayer, self-reflection, and increased devotion to Allah.
- Shawwal: The month of Shawwal follows Ramadan and is significant because it marks the celebration of Eid al-Fitr, the festival that marks the end of Ramadan.
- Dhul-Qadah: This month is considered a holy month, and it is believed that performing good deeds during this time brings great rewards.
- Dhul-Hijjah: The final month of the Islamic calendar, Dhul-Hijjah is particularly significant for Muslims performing the Hajj pilgrimage to Makkah. It culminates with the celebration of Eid al-Adha, which commemorates the willingness of Ibrahim (AS) to sacrifice his son as an act of obedience to Allah.
Each Islamic month has its own significance and provides Muslims with the opportunity to engage in specific acts of worship, to remember important events in Islamic history, and to seek spiritual growth and blessings from Allah.
Current Islamic Month: Why it Matters
The current Islamic month holds significant importance in the lives of Muslims around the world. It not only impacts their religious practices but also acts as a reminder of important historical events and traditions.
Here are a few reasons why the current Islamic month matters:
- Religious Observances: Each Islamic month has specific religious practices associated with it. For example, during the month of Ramadan, Muslims observe fasting from dawn to sunset. It is a time of self-reflection, increased worship, and an opportunity to seek forgiveness and spiritual growth.
- Commemorating Events: Some Islamic months are linked to significant historical events in the life of Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) and the early Muslim community. For instance, the month of Muharram is a time to remember the martyrdom of Imam Hussein (the grandson of Prophet Muhammad) and his companions in the Battle of Karbala.
- Cultural Traditions: Different regions and countries may have cultural traditions associated with specific Islamic months. For instance, the month of Rabi’ al-Awwal is often celebrated as the birth month of Prophet Muhammad, with communities organizing processions, lectures, and gatherings to honor his life and teachings.
- Seasonal Changes: The Islamic calendar is lunar-based, which means that the months rotate throughout the year. This rotation helps Muslims stay connected to natural cycles and appreciate the changes in the environment. For example, during the month of Dhu al-Hijjah, Muslims perform Hajj (pilgrimage) in Mecca, which marks the end of the lunar year and signifies the changing seasons.
- Community Unity: The current Islamic month often brings Muslims together, as they collectively engage in religious activities and celebrate important occasions. It fosters a sense of unity and belonging within the Muslim community, regardless of geographical boundaries.
Overall, the current Islamic month serves as a reminder for Muslims to engage in spiritual growth, connect with their religious heritage, and strengthen their sense of community. It holds immense value in shaping a Muslim’s personal, social, and cultural life.
Importance of Staying Updated
In Islam, it is important to stay updated with the current Islamic month for several reasons:
- Observance of religious events: Knowing the current Islamic month helps in observing religious events and worshipping accordingly. For example, the month of Ramadan requires Muslims to fast from dawn to sunset, and staying updated ensures that one can start and end the fast at the correct times.
- Planning religious activities: Staying updated with the Islamic month allows individuals and communities to plan religious activities and events. This includes organizing gatherings, lectures, and other spiritual practices that are specific to a particular month. For example, the month of Muharram is significant for mourning the martyrdom of Imam Husayn (AS) and organizing Majlis gatherings.
- Understanding the lunar calendar system: The Islamic calendar follows a lunar calendar system, which is different from the Gregorian calendar. Staying updated with the Islamic month helps in understanding and appreciating this lunar calendar system, which is based on the sighting of the crescent moon.
- Spiritual growth and mindfulness: Being aware of the current Islamic month fosters spiritual growth and mindfulness. It reminds individuals of the passage of time and the importance of making the most of each month in terms of worship, self-reflection, and personal development.
Overall, staying updated with the current Islamic month is crucial for practicing Muslims as it ensures the observance of religious obligations, facilitates planning of religious activities, helps in understanding the lunar calendar system, and encourages spiritual growth and mindfulness.
Benefits of Knowing the Current Islamic Month
Knowing the current Islamic month is of great importance for Muslims around the world. It helps individuals in various aspects of their religious and daily lives. Here are some benefits of being aware of the current Islamic month:
- Observance of religious obligations: By knowing the current Islamic month, Muslims can ensure that they fulfill their religious obligations at the right time. This includes performing the five daily prayers, fasting during Ramadan, and giving Zakat, among other things.
- Celebration of special occasions: The Islamic calendar is filled with special occasions and religious holidays such as Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha. Knowing the current Islamic month allows Muslims to properly prepare for these celebrations and participate in them with enthusiasm.
- Planning events and gatherings: Being aware of the current Islamic month helps Muslims plan events and gatherings in accordance with religious customs and traditions. For example, weddings, birthdays, and other social gatherings can be scheduled in a way that respects the religious significance of the month.
- Increased spiritual awareness: Knowing the current Islamic month helps Muslims stay connected to their spiritual journey. It reminds them of the passage of time and the importance of utilizing each month to grow spiritually and strengthen their relationship with Allah.
- Staying connected with the global Muslim community: By knowing the current Islamic month, Muslims can connect with the global Muslim community. They can participate in collective prayers, charitable activities, and other initiatives that are often organized based on the specific month of the Islamic calendar.
In conclusion, being aware of the current Islamic month is crucial for Muslims as it helps them fulfill their religious obligations, celebrate special occasions, plan events, increase spiritual awareness, and stay connected with the global Muslim community.
How to Determine the Current Islamic Month?
Knowing the current Islamic month is important for Muslims as it helps them plan their religious activities and follow the lunar calendar. Here are the different ways to determine the current Islamic month:
- Moon sighting: The most traditional way to determine the start of a new Islamic month is through moon sighting. Muslims look for the crescent moon in the sky after sunset on the 29th day of the current month. If the moon is sighted, the new month begins; otherwise, the current month completes its full duration of 30 days.
- Lunar calendar: Many Islamic organizations and Islamic centers around the world follow the lunar calendar to determine the start of the Islamic month. They have a pre-determined calendar that specifies the start of each month based on the sighting or calculation of the moon.
- Astronomical calculations: Some Muslims rely on astronomical calculations to determine the new Islamic month. These calculations are based on the astronomical data for the sighting of the moon, such as its age and altitude. However, there is a difference of opinion among scholars regarding the reliability of astronomical calculations.
It’s important to note that different Muslim communities or regions may have variations in determining the start of the Islamic month. Therefore, it is always recommended to follow the guidance of local Islamic authorities or scholars to determine the current Islamic month accurately.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as religious or legal advice. Seek guidance from qualified Islamic scholars for accurate information.
Resources for Updating Yourself
In order to stay updated with the current Islamic month and important dates, you can refer to the following resources:
- Islamic Calendar: The Islamic calendar is based on the lunar cycle and is used to determine the start and end of each Islamic month. You can refer to an Islamic calendar to know which month is currently going on.
- Islamic Websites and Apps: There are several websites and mobile applications dedicated to providing information about Islamic months and important dates. These platforms often have features like daily prayer times, Qibla direction, and comprehensive Islamic calendars.
- Islamic Scholars and Leaders: Islamic scholars and respected religious leaders often share updates about the current Islamic month and important dates during their sermons, lectures, or through other forms of communication. Following them can help you stay updated.
It is important to stay informed about the current Islamic month in order to observe and perform religious obligations accurately. Utilize these resources to ensure you are aware of the ongoing Islamic month and can accordingly plan your religious activities and observances.
Islamic Months: A Brief Overview
Islam follows a lunar calendar, which means that its months are based on the phases of the moon. This results in the Islamic calendar being approximately 10 or 11 days shorter than the Gregorian calendar, which is based on the solar cycle. Here is a brief overview of the Islamic months:
- Muharram: The first month of the Islamic calendar. It is considered a sacred month and holds historical significance, particularly for Shia Muslims.
- Safar: The second month. It is believed to be a month of evil omens, and some superstitious beliefs surround it. However, Islam encourages believers to rely on Allah’s guidance rather than superstitions.
- Rabi’al-Awwal: The third month. It is significant because it is the month in which the Prophet Muhammad was born. Many Muslims celebrate his birthday during this month.
- Rabi’ath-Thani: The fourth month. It is not as widely recognized as the previous month, but it still holds importance in Islamic history.
- Jumadal-Ula: The fifth month. It does not hold any significant religious events, but it is still part of the Islamic calendar.
- Jumadal-Akhirah: The sixth month. Like the previous month, it does not have any specific religious events associated with it.
- Rajab: The seventh month. It is one of the sacred months and holds special importance. It is a month of reflection and preparation for the holy month of Ramadan.
- Sha’aban: The eighth month. It is the month before Ramadan and is often considered a month of preparation and anticipation for the fasting month.
- Ramadan: The ninth month. It is the holiest month in the Islamic calendar and is a time of fasting, prayer, and self-reflection for Muslims worldwide.
- Shawwal: The tenth month. It marks the end of Ramadan and is celebrated with the festival of Eid al-Fitr, which signifies the breaking of the fast.
- Dhul-Qi’dah: The eleventh month. It is a month of peace and truce, historically significant for the Arabian tribes.
- Dhul-Hijjah: The twelfth and final month of the Islamic calendar. It is the month of the Hajj pilgrimage to Mecca, the holiest pilgrimage in Islam. It culminates with the festival of Eid al-Adha, which commemorates the sacrifice of Prophet Ibrahim.
These are the twelve months of the Islamic calendar, each holding its own significance and purpose. Muslim communities around the world observe these months in their religious and cultural practices.
Muharram: The First Islamic Month
Muharram is the first month of the Islamic lunar calendar. It holds great significance for Muslims around the world as it marks the beginning of the Islamic year. The word “Muharram” means “forbidden” or “sacred” in Arabic, highlighting its hallowed nature.
One of the most notable events associated with Muharram is the martyrdom of Imam Hussein (AS), the grandson of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH), in the Battle of Karbala in 680 AD. This tragic event is commemorated by Muslims, particularly Shia Muslims, through mourning rituals and processions.
During Muharram, Muslims engage in acts of remembrance, self-reflection, and repentance. They strive to lead spiritual lives and seek forgiveness for any wrongdoings. Many Muslims choose to fast during Muharram, particularly on the 9th and 10th days, known as the Day of Ashura. Fasting on these days is believed to bring blessings and forgiveness.
The Day of Ashura also holds historical significance for different communities within Islam. It is believed that on this day, Allah saved Prophet Musa (Moses) and the Children of Israel by parting the Red Sea, allowing them to escape from the Pharaoh’s army.
In addition to fasting, Muslims may engage in acts of charity and give to the poor and needy during Muharram. This month serves as a reminder of the importance of compassion, empathy, and helping others.
It is important to note that Muharram is a month of mourning for some Muslims, particularly Shia Muslims. They may participate in processions, where they recite poetry and mourn the tragic events of Karbala. These processions often involve flagellation and chest-beating as acts of penance and solidarity with Imam Hussein (AS).
Overall, Muharram holds a special place in the Islamic calendar. It signifies a time of reflection, remembrance, and devotion for Muslims worldwide. It serves as an opportunity to reconnect with one’s spiritual self and to seek forgiveness and blessings.
Safar: The Second Islamic Month
Safar is the second month of the Islamic lunar calendar. It is known as a holy month in Islam, but it is not as significant as the preceding month of Muharram or the following month of Rabi’ al-Awwal.
Here are some key facts about the month of Safar:
- Safar means “empty” or “void” in Arabic, as there were no sacred months or major religious events recorded in this month.
- There are no specific rituals or special prayers prescribed in Islam for the month of Safar.
- Superstitions and myths surrounding the month have no basis in Islamic teachings.
- The month of Safar should not be associated with bad luck or ill omens.
It is important to note that Islam discourages the practice of attributing negative events or misfortunes to specific times or months. Muslims believe that all events occur by the will of Allah and are not influenced by particular times or superstitions.
While Safar may not hold as much religious significance as other months, it is still a time for believers to focus on their faith and reflect on their actions. Muslims are encouraged to seek knowledge, perform good deeds, and be grateful for the blessings bestowed upon them by Allah.
Overall, the month of Safar is a time for Muslims to continue their spiritual journey and strive towards righteousness, seeking the blessings and mercy of Allah in all aspects of their lives.
Rabi-al-Awwal: The Third Islamic Month
Rabi-al-Awwal is the third month of the Islamic calendar. It is a significant month for Muslims around the world as it holds great religious and historical importance.
The word “Rabi” means spring, and “Awwal” means first. Rabi-al-Awwal signifies the beginning of spring, which is a season of growth and renewal. This month is considered auspicious by Muslims, and it is believed to bring blessings and blessings.
One of the most notable events that occurred in Rabi-al-Awwal is the birth of the Prophet Muhammad (pbuh). Muslims celebrate this occasion on the 12th of Rabi-al-Awwal, which is known as Milad-un-Nabi or Eid-e-Milad. It is a time to commemorate the life, teachings, and noble character of the Prophet Muhammad (pbuh).
In addition to the birth of the Prophet Muhammad (pbuh), other significant events also took place in Rabi-al-Awwal. For example, it was in this month that the Prophet Muhammad (pbuh) migrated from Makkah to Madinah, changing the course of Islamic history.
During Rabi-al-Awwal, Muslims engage in various religious activities to express their love and gratitude towards the Prophet Muhammad (pbuh). These may include reciting prayers, organizing processions, holding gatherings to remember his teachings, and helping those in need.
Overall, Rabi-al-Awwal is a month of reflection, devotion, and spiritual growth for Muslims. It is a time to deepen their understanding of Islam and strengthen their connection with the Prophet Muhammad (pbuh).
Rabi-al-Thani: The Fourth Islamic Month
Rabi-al-Thani, also known as Rabi-ul-Akhir, is the fourth month of the Islamic calendar. It follows the month of Rabi-al-Awwal and precedes the month of Jumada-al-Awwal.
The word “Rabi-al-Thani” is derived from the Arabic word “Rabi” which means “spring”. It is believed that this month brings positive energy and blessings to the lives of Muslims.
In Islamic history, several important events have taken place during Rabi-al-Thani. For instance, the death of the Prophet Muhammad’s daughter, Fatimah Zahra, occurred in this month. It is also believed to be the month in which the Battle of Khaybar took place, marking a significant victory for the Muslims.
During Rabi-al-Thani, Muslims are encouraged to increase their acts of worship and seek spiritual growth. They are encouraged to follow the teachings of the Quran and the Prophet Muhammad, and to engage in acts of charity and kindness towards others.
Some Muslims may choose to fast during this month, although it is not obligatory. Fasting can be seen as a way to purify the soul and seek forgiveness from Allah.
Overall, Rabi-al-Thani is a month that holds great spiritual significance for Muslims. It is a time for reflection, prayer, and connection with Allah. Muslims strive to make the most of this month by engaging in acts of worship and increasing their devotion to their faith.
Jumada-al-Awwal: The Fifth Islamic Month
Jumada-al-Awwal is the fifth month in the Islamic lunar calendar. It is also known as Jumada I or Jumada al-Ula. This month is considered to be a significant part of the Islamic year, and it holds special religious and historical significance for Muslims around the world.
The origin of the name “Jumada-al-Awwal” comes from the Arabic word “Jumada,” which means “dryness.” The term “al-Awwal” refers to “the first.” Hence, Jumada-al-Awwal can be translated as “the first dry month.” This name reflects the weather conditions prevalent during this time of the year in certain regions.
During Jumada-al-Awwal, Muslims engage in various spiritual activities and reflection. They focus on deepening their connection with Allah and striving to improve themselves as individuals and members of the community. It is also a time for Muslims to learn from the historical events that took place during this month.
Some important events in Islamic history that occurred during Jumada-al-Awwal include the Treaty of Hudaybiyyah, which was signed between the Prophet Muhammad and the Quraysh tribe in the sixth year of Hijrah (622 CE). This treaty played a crucial role in establishing peaceful relations between the Muslims and the Quraysh, paving the way for the eventual conquest of Mecca by the Muslims.
Furthermore, Jumada-al-Awwal is also a time to commemorate the birth of Fatimah bint Muhammad, the beloved daughter of Prophet Muhammad and his wife Khadijah. Fatimah holds a special place in Islamic history and is revered for her piety, wisdom, and devotion to Allah.
Overall, Jumada-al-Awwal is a month of reflection, remembrance, and gratitude for Muslims. It serves as a reminder of the importance of peace, faith, and family values in Islam, and it encourages Muslims to strive for self-improvement and righteousness.
Jumada-al-Thani: The Sixth Islamic Month
Jumada-al-Thani is the sixth month of the Islamic lunar calendar. It follows the month of Jumada-al-Awwal and precedes the month of Rajab. Jumada-al-Thani is also known as Jumada al-Akhir or Jumada al-Thaniyah.
In Arabic, the word “Jumada” means “forbidding” or “prohibiting,” which may refer to the ancient Arab practice of postponing wars during this month. The term “Thani” means “second” in Arabic, indicating that Jumada-al-Thani is the second month of the lunar year.
During Jumada-al-Thani, Muslims observe various religious practices and activities. Here are some significant events associated with this month:
- Birth of Imam Ali – The 13th day of Jumada-al-Thani marks the birth anniversary of Imam Ali, the cousin and son-in-law of Prophet Muhammad. Imam Ali is highly respected and revered by Shia Muslims.
- Birth of Lady Fatimah – The 20th day of Jumada-al-Thani is celebrated as the birth anniversary of Lady Fatimah, the daughter of Prophet Muhammad and the wife of Imam Ali. Lady Fatimah holds a significant place in Islamic history.
During Jumada-al-Thani, Muslims are encouraged to engage in acts of worship, such as prayer, fasting, and recitation of the Quran. It is also a time for reflection and self-improvement.
Understanding the Islamic calendar and the significance of each month allows Muslims to connect with their faith and engage in meaningful practices. Jumada-al-Thani is a month of spiritual growth and devotion, providing Muslims with an opportunity to strengthen their relationship with Allah and seek blessings.
Rajab: The Seventh Islamic Month
Rajab is the seventh month of the Islamic calendar. It is one of the four sacred months in Islam, the other three being Dhul-Qidah, Dhul-Hijjah, and Muharram.
Rajab is a month of great significance for Muslims around the world. It is a time for reflection, self-improvement, and seeking forgiveness from Allah. Many Muslims observe fasting and engage in increased prayers during Rajab.
During Rajab, there are no specific obligatory acts of worship or rituals prescribed in Islam. However, it is encouraged to engage in voluntary acts of worship, such as extra prayers, fasting, giving charity, and reciting the Quran. It is also recommended to perform the Umrah pilgrimage during this month.
Rajab is also associated with the miraculous night journey of Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) known as Isra and Mi’raj. It is believed that the Prophet was transported from Mecca to Jerusalem and then ascended to the heavens to receive guidance from Allah.
It is important to note that the exact dates of Rajab may vary each year as the Islamic calendar follows a lunar cycle. Muslims rely on moon sightings to determine the start and end of each month.
In conclusion, Rajab is a sacred month in Islam that encourages Muslims to engage in acts of worship and seek forgiveness. It is a time for reflection, self-improvement, and drawing closer to Allah.
Sha’ban: The Eighth Islamic Month
Sha’ban is the eighth month of the Islamic calendar and is considered one of the significant months for Muslims. It falls between the months of Rajab and Ramadan. The name “Sha’ban” comes from the Arabic word which means to scatter and disperse, signifying that the tribe’s horses would be let loose and would roam freely during this month.
In Islamic tradition, Sha’ban has both religious and cultural significance. It is a time for Muslims to engage in various worship and preparation activities before the arrival of Ramadan, which is the holy month of fasting. Here are some important aspects of Sha’ban:
- Recommended Fasting: Although fasting is not obligatory during Sha’ban, it is highly recommended, especially during the second half of the month. The Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) used to fast frequently during this month, emphasizing its spiritual significance.
- Night Prayers (Tahajjud): Muslims are encouraged to offer voluntary night prayers, known as Tahajjud, during the month of Sha’ban. These prayers are performed after the nightly obligatory prayers and are believed to earn great rewards.
- Preparation for Ramadan: Sha’ban is considered a month of preparation for Ramadan. It is an ideal time to increase devotion and engage in self-reflection to cleanse the soul and body before the arrival of the holy month.
In addition to its religious significance, Sha’ban also holds cultural importance in many Muslim communities. It is a month of celebration and festivities, with people coming together for communal prayers, sharing meals, and exchanging greetings and gifts.
| Important Dates in Sha’ban | Year 2022 (Hijri 1444) |
|---|---|
| First Day of Sha’ban | March 30, 2022 |
| Nisf Sha’ban (Mid-Sha’ban) | April 13, 2022 |
| Last Day of Sha’ban | April 28, 2022 |
Overall, Sha’ban holds great significance in the Islamic calendar. It serves as a bridge between the preceding month of Rajab and the upcoming month of Ramadan, providing an opportunity for Muslims to prepare themselves mentally, physically, and spiritually for the blessed month of fasting and increased devotion.
Ramadan: The Ninth Islamic Month
Ramadan is the ninth month of the Islamic calendar and holds significant importance in the Muslim faith. It is considered the holiest month of the year for Muslims worldwide.
During Ramadan, Muslims observe a period of fasting from sunrise to sunset. This fasting involves abstaining from eating or drinking anything, including water, from dawn until dusk. It is a time of self-reflection, increased devotion, and worship for Muslims.
The fast is broken each evening with the evening meal called Iftar, which is typically shared with family and friends. Muslims also gather for congregational prayers known as Taraweeh, performed after the evening prayer.
The month of Ramadan is believed to be the time when the first verses of the Quran were revealed to the Prophet Muhammad. It is a time of heightened spirituality, where Muslims seek forgiveness for their sins, engage in acts of charity, and deepen their connection with Allah.
During Ramadan, Muslims also strive to practice patience, humility, and gratitude. It is a time when people come together, support each other, and strengthen familial and community bonds.
In addition to fasting, Muslims are encouraged to engage in extra prayers and recitation of the Quran during this blessed month. It is believed that the rewards for good deeds and acts of worship during Ramadan are multiplied.
Overall, Ramadan is a month of purification, self-discipline, and spiritual growth for Muslims around the world. It serves as a reminder to appreciate the blessings in life, seek forgiveness, and strive for righteousness.
Shawwal: The Tenth Islamic Month
The month of Shawwal is the tenth month in the Islamic lunar calendar. It follows the holy month of Ramadan and is significant for Muslims around the world.
During Shawwal, Muslims celebrate the festival of Eid al-Fitr, which marks the end of Ramadan. Eid al-Fitr is a time of joy and celebration, where Muslims come together to offer prayers, exchange gifts, and share meals with family and friends.
Shawwal is also the month when Muslims observe six days of voluntary fasting known as the “Six Days of Shawwal.” These fasts are performed after Eid al-Fitr as a way to earn additional rewards and seek closeness to Allah. Fasting in Shawwal is highly recommended but not obligatory.
In addition, Shawwal holds great significance as it is the month in which the Battle of Badr took place. The Battle of Badr was a major milestone in Islamic history and marked the first victory of the Muslims against the Quraysh tribe in Mecca.
To keep track of the Islamic months, Muslims follow the lunar calendar, which is based on the sighting of the moon. This means that the beginning of Shawwal, like other Islamic months, can vary depending on the moon sighting.
In summary, Shawwal is a month of celebration, fasting, and historical significance for Muslims. It is a time for reflection, gratitude, and strengthening one’s faith.
Dhu al-Qidah: The Eleventh Islamic Month
Dhu al-Qidah is the eleventh month of the Islamic lunar calendar. It is one of the four sacred months in Islam, along with Muharram, Rajab, and Dhu al-Hijjah. The name “Dhu al-Qidah” translates to “the month of truce,” indicating its significance in terms of peace and harmony.
During Dhu al-Qidah, Muslims are encouraged to perform good deeds, seek forgiveness, and engage in acts of worship. It is also a time for reflection and self-improvement.
Here are a few important things to know about Dhu al-Qidah:
- Dhu al-Qidah is preceded by the month of Shawwal and followed by the month of Dhu al-Hijjah.
- It is recommended to fast during the first nine days of Dhu al-Qidah, particularly on the 9th day, known as the Day of Arafah.
- The Day of Arafah is one of the most important days in Islam, as it is the day when the Hajj pilgrimage takes place in the Islamic holy city of Mecca.
- Many Muslims also observe voluntary fasts on the 13th, 14th, and 15th days of Dhu al-Qidah, known as the “white days.”
- During Dhu al-Qidah, Muslims can engage in various acts of worship, such as reciting the Quran, making dua (supplication), giving charity, and performing extra prayers.
It is important for Muslims to make the most of the sacred month of Dhu al-Qidah by increasing their devotion and seeking closeness to Allah. By performing good deeds and seeking forgiveness, Muslims can purify their souls and strengthen their faith.
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 1st-9th Dhu al-Qidah | Recommended fasting |
| 9th Dhu al-Qidah | Day of Arafah |
| 13th, 14th, and 15th Dhu al-Qidah | Recommended fasting (white days) |
By observing the recommended acts of worship and remembering the significance of Dhu al-Qidah, Muslims can deepen their spiritual connection and strengthen their relationship with Allah.
Dhu al-Hijjah: The Twelfth Islamic Month
Dhu al-Hijjah is the twelfth and final month of the Islamic lunar calendar. It is one of the holiest months for Muslims around the world.
The name Dhu al-Hijjah translates to “the month of pilgrimage.” This is because the annual Hajj pilgrimage, one of the five pillars of Islam, takes place during the first ten days of this month.
During Dhu al-Hijjah, Muslims from all over the world travel to the holy city of Mecca in Saudi Arabia to perform the Hajj. It is a time of intense spiritual devotion and a reminder of the unity of the Muslim ummah (community).
Aside from the Hajj, Dhu al-Hijjah is also a month of great significance for other acts of worship and virtuous deeds. Muslims are encouraged to engage in fasting, recitation of the Qur’an, giving charity, and performing additional prayers.
Key Dates and Practices during Dhu al-Hijjah:
- Day 1: The first day of Dhu al-Hijjah marks the beginning of the Hajj pilgrimage. Muslims dress in the simple white garments called Ihram and enter into a state of spiritual purity.
- Day 9: Known as the Day of Arafah, this is the most important day of Hajj. Pilgrims gather at the plain of Arafat and engage in supplication, seeking forgiveness, and reflecting on their faith. For those not on Hajj, fasting on this day is highly recommended.
- Day 10: This day is known as Eid al-Adha, or the Feast of Sacrifice. It commemorates the willingness of Prophet Ibrahim (Abraham) to sacrifice his son. Muslims around the world celebrate by performing the Eid prayer, offering animal sacrifice, distributing meat to the needy, and participating in festive gatherings.
- Last days of Dhu al-Hijjah: Muslims are encouraged to continue their acts of worship and good deeds throughout the remaining days of the month, particularly fasting and voluntary prayers.
Overall, Dhu al-Hijjah is a month of profound spiritual significance for Muslims. It is a time of reflection, self-improvement, and strengthening of faith, as well as a time of unity and brotherhood for the global Muslim community.
The Importance of Observing the Current Islamic Month
The Islamic calendar is based on the lunar year, and it consists of 12 months. Each month holds its own significance and importance for Muslims all around the world. Observing the current Islamic month is not only a religious duty, but it also helps in strengthening one’s faith and deepening their connection with Allah.
Here are some reasons why observing the current Islamic month is important:
- Following the Sunnah: The Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) emphasized the importance of observing and following the Islamic calendar. By observing the current Islamic month, we are following the Sunnah and carrying on the practices of the Prophet.
- Gaining spiritual blessings: Each Islamic month has its own blessings and rewards associated with it. For example, the month of Ramadan is known for its immense spiritual rewards and the opportunity to seek forgiveness and draw closer to Allah. By observing the current Islamic month, we can actively participate in these blessings and seek spiritual growth.
- Staying connected with the Muslim community: Observing the current Islamic month allows Muslims to stay connected with the larger Muslim community. It creates a sense of unity and solidarity, as Muslims all around the world are observing the same month and engaging in similar acts of worship.
- Learning and reflecting: Each Islamic month has its own significance and historical events associated with it. By observing the current Islamic month, we get the opportunity to learn about these events and reflect upon their lessons. It helps in increasing our knowledge and understanding of Islamic history and teachings.
- Planning and preparation: Observing the current Islamic month helps in planning and preparing for upcoming religious events and obligations. For example, knowing that the month of Hajj is approaching allows Muslims to make necessary arrangements and preparations to fulfill this pillar of Islam.
In conclusion, observing the current Islamic month is of great importance for Muslims. It helps in following the Sunnah, gaining spiritual blessings, staying connected with the Muslim community, learning and reflecting, and planning for upcoming religious obligations. By observing the Islamic calendar, Muslims can deepen their faith and strengthen their relationship with Allah.
Rituals and Practices During Each Islamic Month
Islamic months hold great significance in the lives of Muslims around the world. Each month has its own special rituals and practices that Muslims observe. Here are some of the rituals and practices performed during each Islamic month:
- Muharram: The first month of the Islamic calendar is Muharram. It is a month of remembrance and reflection. Muslims commemorate the martyrdom of Imam Hussain, the grandson of Prophet Muhammad, by participating in processions, holding majlis (gathering) to remember his sacrifice, and fasting on the 10th day of Muharram, known as Ashura.
- Safar: Safar is the second month of the Islamic calendar. While it is believed by some to be a month filled with bad luck and misfortune, it is important for Muslims to remember that only Allah has the power to control destiny. Muslims should put their trust in Allah and engage in good deeds during this month.
- Rabi’ al-Awwal: This is the third month of the Islamic calendar and is of great significance for Muslims as it marks the birth month of the Prophet Muhammad. Muslims celebrate the occasion of Prophet Muhammad’s birthday, known as Mawlid, by offering prayers, reciting poetry, and engaging in acts of charity and kindness.
- Rabi’ al-Thani: Rabi’ al-Thani is the fourth month of the Islamic calendar. It is a month of reflection and seeking forgiveness from Allah. Muslims focus on increasing their acts of worship, reciting the Quran, and reflecting on their actions. They also make an effort to seek forgiveness and repent for their sins.
- Jumada al-Awwal: Jumada al-Awwal is the fifth month of the Islamic calendar. Muslims strive to increase their knowledge and understanding of Islam during this month. They engage in studying the teachings of Prophet Muhammad, attending religious lectures, and seeking opportunities for self-improvement.
- Jumada al-Thani: Jumada al-Thani is the sixth month of the Islamic calendar. Muslims focus on building a strong relationship with Allah during this month. They engage in acts of worship, such as offering voluntary prayers and fasting, and seek closeness to Allah through supplication and remembrance.
- Rajab: The seventh month of the Islamic calendar is Rajab, which is considered a sacred month. Muslims observe fasting, offer special prayers, and engage in acts of worship to seek the blessings and forgiveness of Allah. It is also recommended to perform Umrah, a pilgrimage to Mecca, during this month.
- Sha’ban: Sha’ban is the eighth month of the Islamic calendar. Muslims engage in increased acts of worship and prepare themselves for the upcoming month of Ramadan. They offer voluntary prayers, recite the Quran, and seek forgiveness from Allah.
- Ramadan: Ramadan is the ninth month of the Islamic calendar and is considered the holiest month for Muslims. Muslims fast from dawn to sunset, abstaining from food, drink, and other physical needs. They engage in increased acts of worship, such as offering additional prayers, reciting the Quran, giving charity, and seeking closeness to Allah.
- Shawwal: Shawwal is the tenth month of the Islamic calendar. It is the month following Ramadan and Muslims celebrate Eid al-Fitr, the festival marking the end of Ramadan. They gather for prayers, give gifts, share meals, and engage in acts of charity and kindness.
- Dhu al-Qidah: Dhu al-Qidah is the eleventh month of the Islamic calendar. Muslims consider it a sacred month and refrain from engaging in acts of warfare or conflict during this time. Muslims focus on acts of worship and seek good deeds to increase their rewards from Allah.
- Dhu al-Hijjah: Dhu al-Hijjah is the twelfth and final month of the Islamic calendar. It is the month of Hajj, the pilgrimage to Mecca. Muslims who are physically and financially able perform Hajj and engage in various rituals, such as circling the Kaaba, standing at Mount Arafat, and sacrificing animals in commemoration of Prophet Ibrahim’s willingness to sacrifice his son.
These rituals and practices during each Islamic month contribute to the spiritual growth and connection of Muslims with Allah and their community. They serve as a means of seeking forgiveness, increasing blessings, and reinforcing the values and teachings of Islam.
Planning Your Religious Activities
When it comes to planning your religious activities during the current Islamic month, it’s important to consider the significance and virtues of the month itself. Here are some tips to help you plan your religious activities:
- Reciting the Quran: Make a commitment to recite the Quran regularly during this Islamic month. Allocate specific time slots in your daily routine to recite the Quran and reflect on its teachings.
- Offering Salah: Ensure you perform your daily prayers on time and strive to pray the recommended prayers and Taraweeh prayers if it is the month of Ramadan.
- Voluntary Fasting: If it is the month of Ramadan, plan to fast the voluntary fasts such as the Sunnah fasts on Mondays and Thursdays, the white days, and fasting on the 13th, 14th, and 15th of each lunar month.
- Giving Charity: Allocate a portion of your income to give in charity during this month. You can donate to Islamic organizations or directly help those in need in your community.
- Attending Religious Gatherings: If there are any religious gatherings, lectures, or workshops happening in your area, make an effort to attend and benefit from the knowledge shared.
- Performing Umrah or Hajj (if applicable): If you have the opportunity and means, plan your pilgrimage to Makkah for Umrah or Hajj during the current Islamic month. These acts of worship hold immense significance in Islam.
Remember, the key to planning your religious activities is to prioritize your spiritual growth and connection with Allah. By incorporating these activities into your routine during the current Islamic month, you can make the most of the blessings and virtues that the month brings.
Staying in Sync with the Islamic Community
Being aware of the Islamic month and staying in sync with the Islamic community is important for Muslims around the world. It helps them in practicing their faith, observing important religious events and participating in community activities. Here are a few ways you can stay updated:
- Islamic Calendar: The Islamic calendar is a lunar calendar that consists of 12 months. Each month begins with the sighting of the new moon. Keep a copy of the Islamic calendar with you or download a digital version on your smartphone or computer to stay updated about the current month.
- Local Mosques: Visit your local mosque and connect with the community. Mosques often announce the beginning of the Islamic month and important events during their Friday congregational prayers. Stay connected with your mosque to know the current month and upcoming events.
- Islamic Organizations: There are several Islamic organizations that provide information about the Islamic month and related events. Subscribe to their newsletters or follow them on social media platforms to stay updated. They often share resources, articles, and reminders about the current month.
- Community Gatherings: Attend community gatherings and events organized by Islamic centers and organizations. These gatherings often take place during significant months or events in the Islamic calendar, providing an opportunity to learn, participate, and connect with the community.
- Educational Resources: There are many online resources, books, and videos available that provide in-depth knowledge about the Islamic calendar, its months, and the significance of important events. Explore these resources to enhance your understanding and stay in sync with the Islamic community.
By staying in sync with the Islamic community and being aware of the current Islamic month, you can actively participate in religious practices, observe important events, and strengthen your connection with the Muslim community.
Question and answer
What is the current Islamic month?
The current Islamic month is Dhu al-Hijjah.
How many Islamic months are there?
There are 12 Islamic months in total.
What are the names of all the Islamic months?
The names of all the Islamic months are: Muharram, Safar, Rabi’ al-Awwal, Rabi’ al-Thani, Jumada al-Awwal, Jumada al-Thani, Rajab, Sha’ban, Ramadan, Shawwal, Dhu al-Qidah, and Dhu al-Hijjah.
What significance does the current Islamic month hold?
The current Islamic month, Dhu al-Hijjah, holds immense significance as it is the month of Hajj, the pilgrimage to Mecca.
What is the significance of the Islamic month of Ramadan?
The Islamic month of Ramadan is of great significance as it is the month of fasting for Muslims around the world. It is considered a time of spiritual reflection, increased devotion, and worship.
How long is the Islamic calendar compared to the Gregorian calendar?
The Islamic calendar is shorter than the Gregorian calendar by about 11 days. It is a lunar calendar and is based on the cycles of the moon.
Can you explain the process of determining the start of a new Islamic month?
The start of a new Islamic month is determined by the sighting of the new moon. Islamic scholars and local religious authorities look for the crescent moon after sunset, and if it is sighted, the new month begins.