Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) is a highly effective treatment approach that combines elements of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) with mindfulness techniques. It was originally developed in the late 1980s by psychologist Marsha M. Linehan, with the aim of treating individuals with borderline personality disorder (BPD). However, DBT has since been found to be helpful for a range of mental health issues, including depression, anxiety, and substance abuse.
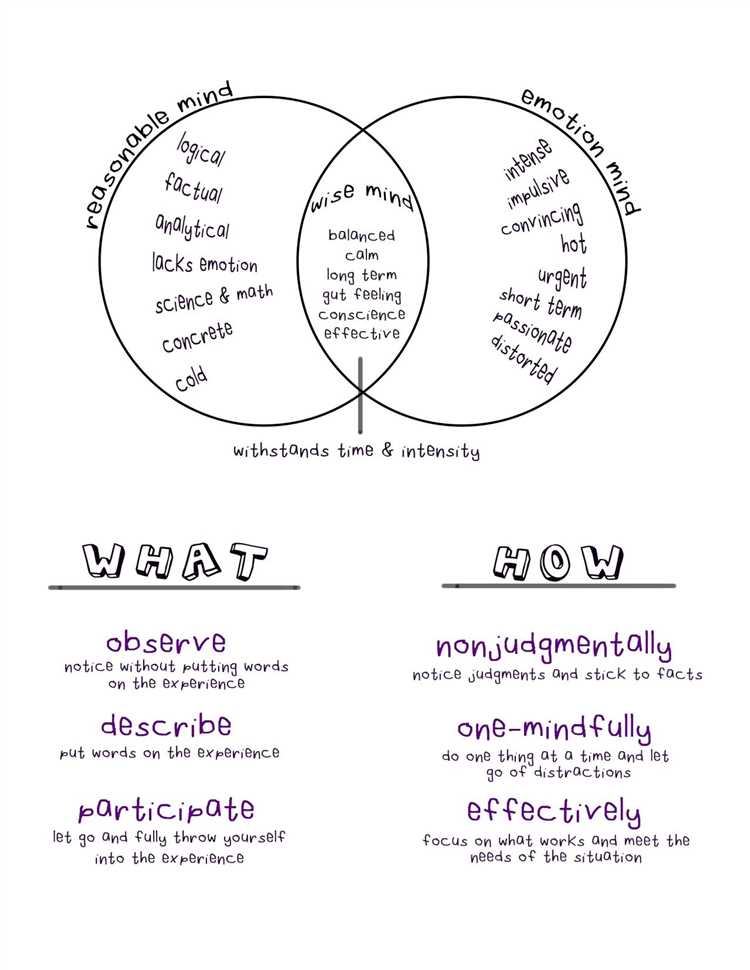
DBT is based on the concept of dialectics, which refers to the idea that two seemingly contradictory truths can coexist. In DBT, this is applied to the idea that individuals can simultaneously accept themselves as they are, while also acknowledging the need for change. This approach is particularly valuable for individuals with difficulty regulating their emotions, as it helps them develop skills to tolerate distress, manage their emotions, and improve interpersonal relationships.
One of the key components of DBT is its focus on mindfulness. Mindfulness involves bringing one’s attention to the present moment without judgment. By practicing mindfulness, individuals can learn to better observe and regulate their thoughts, emotions, and bodily sensations. This can help them become more aware of their automatic reactions and develop the ability to respond more effectively in difficult situations.
Furthermore, DBT incorporates various skill-building exercises to help individuals develop coping strategies. These skills include emotion regulation, interpersonal effectiveness, distress tolerance, and mindfulness. Through regular practice, individuals can learn to identify their emotional triggers, develop healthier ways of coping, and improve their overall well-being.
Overall, DBT offers a comprehensive approach to therapy that addresses the multifaceted nature of mental health issues. By combining elements of CBT, mindfulness, and skill-building exercises, DBT provides individuals with the tools they need to manage their emotions, improve their relationships, and lead more fulfilling lives.
Understanding Dialectical Behaviour Therapy
Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) is a form of therapy that was initially developed by psychologist Marsha M. Linehan to treat individuals with borderline personality disorder (BPD). However, it has since been used to effectively treat a range of mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and substance abuse.
The central philosophy behind DBT is that individuals who struggle with emotional regulation and impulse control need to learn skills that allow them to balance acceptance and change. This balance is referred to as “dialectics,” and it forms the foundation of DBT.
DBT consists of four primary components:
- Individual therapy: This involves one-on-one sessions between the therapist and the client. The therapist helps the client identify and work through specific challenges and develop strategies for coping with intense emotions and self-destructive behaviors.
- Group skills training: In this component, individuals participate in a group setting where they learn and practice skills related to emotional regulation, distress tolerance, interpersonal effectiveness, and mindfulness. These skills are taught using various educational techniques and experiential exercises.
- Phone coaching: Clients have the opportunity to contact their therapist between sessions for support and guidance. This aspect of DBT helps individuals apply the skills they have learned in real-life situations as they arise.
- Consultation team: DBT therapists often meet regularly with a consultation team to receive supervision and support in delivering DBT effectively. This ensures that therapists stay on track and receive guidance in working with difficult cases.
DBT utilizes a variety of therapeutic strategies, including validation, problem-solving, cognitive restructuring, and behavior modification. Additionally, it incorporates the use of mindfulness practices to help individuals become more aware of the present moment and cultivate non-judgmental acceptance of their experiences.
Research has consistently shown that DBT is highly effective in reducing self-destructive behaviors, improving overall functioning, and enhancing quality of life for individuals with a range of mental health conditions. It provides individuals with the tools they need to regulate their emotions, improve relationships, and develop a greater sense of self-acceptance and resilience.
What is DBT?
Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) is a type of therapy that combines elements of cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) with Eastern philosophies and mindfulness practices. Originally developed by psychologist Marsha M. Linehan in the late 1980s, DBT was initially created to treat individuals with borderline personality disorder (BPD), who often struggle with intense emotions, self-destructive behaviours, and difficulties in relationships.
DBT has since been adapted and proven effective for treating a range of mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, substance abuse, eating disorders, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The therapy is typically delivered in a combination of individual therapy sessions, group skills training, phone coaching, and therapist consultation meetings.
The main goals of DBT are:
- To enhance individuals’ capabilities to effectively manage their emotions and behaviours.
- To improve individuals’ skills in navigating interpersonal relationships and maintaining healthy boundaries.
- To increase individuals’ ability to tolerate distress and cope with intense emotions without resorting to self-destructive behaviours or unhealthy coping mechanisms.
- To promote mindfulness and acceptance of the present moment, helping individuals to develop a non-judgmental and non-reactive stance towards their thoughts and feelings.
The key components of DBT include:
- Individual therapy: One-on-one sessions between the therapist and the individual to address specific problems, set goals, and work on developing new coping strategies.
- Group skills training: Weekly group sessions that focus on teaching individuals skills in mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness.
- Phone coaching: Access to the therapist outside of scheduled sessions for additional support and guidance during crises or challenging situations.
- Therapist consultation meetings: Regular meetings where therapists can receive support and guidance from their supervisors to ensure they are providing the best care to their clients.
DBT has been extensively researched and has shown strong evidence of effectiveness in reducing self-harming behaviours, suicidal tendencies, and improving overall quality of life for individuals with a variety of mental health challenges. It provides a comprehensive and multi-faceted approach to therapy, addressing both immediate crisis management and long-term skill development and personal growth.
Note: this article is based on the principles and practices of DBT, but it is not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you or someone you know is struggling with mental health issues, please seek help from a qualified healthcare provider.
How does DBT work?
Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) is a form of therapy that combines elements from cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) and mindfulness practices. It was originally developed by psychologist Marsha M. Linehan to treat individuals with borderline personality disorder, but has since been adapted to help a wide range of individuals struggling with emotional regulation and self-destructive behaviours.
DBT works by helping individuals learn new skills and techniques to better manage their emotions, increase self-awareness, and improve their relationships with others. It focuses on four key areas:
- Mindfulness: DBT emphasizes the practice of mindfulness, which involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment. This helps individuals become more aware of their thoughts, emotions, and sensations, and learn to tolerate distressing experiences.
- Emotion Regulation: DBT teaches individuals how to identify and regulate their emotions in healthy ways. This includes learning strategies for managing intense emotions, reducing emotional vulnerability, and increasing positive emotions.
- Distress Tolerance: DBT helps individuals develop skills to tolerate and cope with distressing situations without resorting to self-destructive behaviours. This involves learning techniques such as distraction, self-soothing, and crisis survival strategies.
- Interpersonal Effectiveness: DBT focuses on improving communication and relationship skills. It helps individuals develop assertiveness, set boundaries, and navigate conflicts in a healthy and effective manner.
DBT utilizes a variety of therapeutic techniques, such as individual therapy sessions, group skills training, phone coaching, and consultation meetings for therapists. It is an evidence-based approach that has been shown to be effective in reducing self-harm, suicidal behaviours, and improving overall well-being.
Overall, DBT provides individuals with the tools and support they need to better manage their emotions, build healthier relationships, and live a more fulfilling life.
The Core Principles of DBT
Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) is a comprehensive and evidence-based treatment approach originally developed by Marsha M. Linehan for individuals with borderline personality disorder (BPD). It has since been expanded and applied to other mental health disorders as well.
DBT is grounded in several core principles that guide its implementation and effectiveness:
- Dialectics: DBT embraces the concept of dialectics, which recognizes the coexistence of opposing forces and the importance of balancing acceptance and change. It encourages individuals to find a middle ground between acceptance of themselves as they are and the need to make changes in their behavior.
- Mindfulness: Mindfulness is a key component of DBT and involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment. It helps individuals become more aware of their thoughts, feelings, and sensations, allowing them to observe and accept them without becoming overwhelmed or reactive.
- Distress Tolerance: This principle focuses on developing skills to tolerate and survive distressing situations without resorting to harmful behaviors. It involves learning techniques to soothe oneself, distract from emotional pain, and ride out intense emotions until they naturally subside.
- Emotion Regulation: Emotion regulation skills teach individuals how to identify, understand, and effectively manage their emotions. This includes learning to recognize and label emotions, increase positive emotions, decrease negative emotions, and change emotional responses that are problematic or unhelpful.
- Interpersonal Effectiveness: Interpersonal effectiveness skills focus on enhancing individuals’ abilities to initiate and maintain healthy relationships, set boundaries, and communicate their needs effectively. It involves strategies to assert oneself, negotiate conflicts, and balance priorities and needs.
These core principles of DBT work together to provide individuals with the tools and strategies they need to navigate challenging situations, regulate their emotions, develop healthy relationships, and ultimately improve their overall well-being.
Mindfulness
Mindfulness is a crucial element in Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) and plays a significant role in helping individuals develop emotional regulation skills. It is the practice of intentionally focusing one’s attention on the present moment, accepting it without judgment.
The Importance of Mindfulness in DBT:
- Mindfulness helps individuals to develop awareness of their thoughts, emotions, and sensations in the present moment, which is the first step towards change.
- It allows individuals to observe their experiences non-judgmentally, cultivating a sense of acceptance and compassion towards themselves, others, and the world around them.
- Mindfulness encourages the development of mindful coping strategies, which can be used when faced with stressors or triggers.
Practicing Mindfulness:
DBT incorporates various mindfulness exercises and techniques to help individuals cultivate mindfulness skills:
- Mindful Breathing: This involves focusing one’s attention on the breath, observing and following the sensation of inhalation and exhalation.
- Body Scan: Individuals systematically bring their attention to different parts of the body, observing sensations without judgment.
- Sensory Awareness: This involves paying attention to the present moment using all senses, such as noticing the taste, smell, or texture of something.
- Mindful Walking: Individuals focus on the physical sensations and movements involved in walking, paying attention to each step taken.
Benefits of Mindfulness in DBT:
| Benefits of Mindfulness | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Emotional Regulation | Mindfulness helps individuals become aware of their emotions and develop skills to manage and regulate them effectively. |
| Reduced Reactivity | Through mindfulness practice, individuals learn to respond, rather than react impulsively, to challenging situations. |
| Decreased Stress and Anxiety | Mindfulness techniques can help individuals reduce stress and anxiety by focusing on the present moment and letting go of worries about the past or future. |
| Improved Interpersonal Relationships | Mindfulness fosters empathy, compassion, and non-judgment, thereby supporting healthier and more satisfying relationships with others. |
Mindfulness is a foundational aspect of Dialectical Behaviour Therapy, helping individuals develop self-awareness, emotional regulation, and compassionate acceptance. By incorporating mindful practices into daily life, individuals can gain valuable skills for coping with emotional difficulties and living a more fulfilling life.
Emotion Regulation
Emotion regulation plays a crucial role in Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT). It helps individuals to understand, manage, and change their emotions effectively. DBT offers several skills and strategies for emotion regulation, which are essential for individuals who struggle with intense and overwhelming emotions.
1. Mindfulness
- Practicing mindfulness helps individuals to observe and describe their emotions without judgment. It enhances their awareness of emotions and the present moment.
- Through mindfulness exercises, individuals learn to accept and tolerate their emotions rather than reacting impulsively.
2. Emotion Awareness
- DBT helps individuals to identify and label their emotions accurately. This skill enables them to recognize different emotions and differentiate between similar feelings.
- By developing emotion awareness, individuals can gain a better understanding of their emotional experiences and react appropriately.
3. Opposite Action
- Opposite action is a DBT skill that encourages individuals to act opposite to their current emotions when it is ineffective or inappropriate.
- By practicing opposite action, individuals can change their emotional state, reduce negative emotions, and increase positive emotions.
4. Problem-Solving
- Problem-solving skills help individuals to cope with challenging situations that trigger intense emotions. They learn effective strategies to address and resolve problems rather than getting overwhelmed by emotions.
- This skill involves breaking down challenges into smaller manageable parts, generating potential solutions, and evaluating the outcomes.
5. Self-Soothing
- Self-soothing techniques provide individuals with ways to comfort themselves when experiencing distressing emotions. It involves engaging in activities or practices that bring a sense of calm and relaxation.
- Through self-soothing, individuals can reduce emotional intensity and increase positive emotions, promoting emotional well-being.
6. Build Positive Experiences
- A key aspect of emotion regulation in DBT is to increase positive experiences and emotions in daily life.
- Individuals are encouraged to engage in activities that bring joy, satisfaction, and positive emotions. This helps in balancing emotional experiences and enhancing overall well-being.
7. Maintain Physical Health
- Physical health plays a significant role in emotional well-being. DBT highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, balanced diet, and enough sleep.
- By focusing on physical health, individuals can regulate their emotions better and reduce emotional dysregulation.
Overall, emotion regulation skills taught in DBT focus on increasing emotional awareness, accepting emotions, and implementing effective strategies to regulate and manage emotions. These skills empower individuals to have a healthier relationship with their emotions, leading to improved overall well-being.
Distress Tolerance
Distress tolerance is a core component of Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) that focuses on helping individuals manage and tolerate distressing emotions and situations. It is especially useful for individuals who struggle with intense emotions and have difficulty coping effectively.
The goals of distress tolerance skills in DBT are:
- To increase an individual’s ability to tolerate distress without resorting to harmful behaviours or self-destructive actions.
- To encourage individuals to accept distress as a normal part of life and develop strategies to effectively cope in difficult situations.
- To decrease impulsive and self-destructive behaviours that may provide short-term relief but worsen long-term distress.
- To help individuals build resilience and emotional strength in the face of distressing situations.
Distress tolerance skills are divided into four categories:
- Self-Soothing: These skills involve engaging in activities that promote comfort, relaxation, and self-care. Examples include taking a warm bath, listening to soothing music, or practicing deep breathing exercises.
- Distracting: Distracting skills involve shifting attention away from distressing thoughts or situations. This could involve engaging in activities such as reading a book, watching a movie, or going for a walk.
- Improving the Moment: These skills aim to improve the individual’s current experience and help them focus on the positive aspects of the present moment. Examples include using positive affirmations, counting blessings, or engaging in gratitude exercises.
- Pros and Cons: Pros and Cons skills involve evaluating the potential positive and negative consequences of engaging in self-destructive behaviours. This helps individuals make more informed decisions and weigh the short-term relief against the long-term negative impact.
Additional distress tolerance techniques include:
| TIPP Skill: | TIPP stands for Temperature, Intense exercise, Paced breathing, and Paired muscle relaxation. These techniques help bring down the intensity of emotional arousal and distressing emotions. |
| Acceptance: | Accepting the reality of distressing situations and learning to be nonjudgmental towards oneself. This helps individuals build resilience and develop a more balanced perspective. |
| Radical Acceptance: | Radical acceptance involves fully accepting a distressing situation without judgment or resistance. It helps individuals let go of futile efforts to change the unchangeable and find peace in acceptance. |
| Urge Surfing: | Urge surfing is a skill that involves riding out intense urges and cravings without giving in to self-destructive behaviours. By observing and accepting the urges, individuals learn that the intensity is temporary and will eventually pass. |
Developing distress tolerance skills takes practice and patience. Through DBT treatment, individuals can learn to effectively manage distressing emotions and situations, leading to improved overall well-being.
The Benefits of DBT
DBT, or Dialectical Behaviour Therapy, offers several benefits for individuals experiencing various mental health conditions. Some of these benefits include:
- Improved Emotional Regulation: DBT teaches individuals techniques and skills to cope with overwhelming emotions and regulate their emotional responses. This helps them manage stress, anxiety, and other intense emotions effectively.
- Enhanced Interpersonal Relationships: DBT focuses on improving communication and relationship skills, helping individuals develop healthier and more satisfying relationships with others. It teaches them to express their needs, set boundaries, and resolve conflicts effectively.
- Reduced Self-Destructive Behaviours: DBT provides strategies to address self-destructive behaviours, such as self-harm and suicidal ideation. It helps individuals identify the triggers behind these behaviours and develop alternative, healthier coping mechanisms.
- Increased Mindfulness: DBT emphasizes the practice of mindfulness, which involves being fully present in the moment and non-judgmentally observing one’s thoughts, feelings, and sensations. This enhances self-awareness and helps individuals develop a balanced perspective.
- Effective Problem-Solving Skills: DBT equips individuals with problem-solving skills, enabling them to identify and address life’s challenges in a constructive manner. It helps them break down problems into manageable tasks and develop effective solutions.
- Reduced Risk of Relapse: DBT has shown to be effective in reducing the risk of relapse for individuals with conditions such as borderline personality disorder and substance abuse. It provides them with ongoing support and skills to prevent regression.
Overall, DBT offers a comprehensive approach to treating various mental health conditions, helping individuals lead more fulfilling and balanced lives.
Why is DBT effective?
DBT, or Dialectical Behaviour Therapy, has been proven to be highly effective in treating various mental health conditions. There are several key reasons why DBT is considered effective:
- Comprehensive approach: DBT incorporates multiple therapeutic techniques and strategies to address different aspects of mental health, including emotion regulation, distress tolerance, interpersonal effectiveness, and mindfulness. This comprehensive approach ensures that individuals receive holistic and well-rounded treatment.
- Validation: DBT emphasizes the importance of validating individuals’ experiences and emotions. This validation helps to build trust between the therapist and the client, and creates a safe and non-judgmental environment for exploring challenges and making progress.
- Skills training: DBT places a strong emphasis on teaching practical skills that individuals can use in their daily lives to manage and cope with difficult emotions and situations. These skills are taught in a structured and systematic manner, empowering individuals to take control of their mental health.
- Individualized treatment: DBT recognizes that everyone’s experiences and needs are unique. Treatment plans are tailored to the individual, taking into account their specific challenges, strengths, and goals. This individualized approach ensures that therapy is relevant and meaningful to each person.
- Focus on motivation and commitment: DBT incorporates motivational techniques to help individuals stay engaged and committed to the therapy process. By fostering motivation and commitment, individuals are more likely to actively participate in therapy and make sustainable changes in their lives.
- Supportive relationship: The therapeutic relationship between the client and the therapist is a fundamental component of DBT. The therapist provides a supportive and empathetic presence, and serves as a guide and mentor throughout the therapy journey. This supportive relationship helps individuals feel heard and understood, facilitating the therapeutic process.
- Evidence-based: DBT is a well-established and evidence-based therapy. Numerous studies have shown its effectiveness in treating conditions such as borderline personality disorder, self-harm behaviours, suicidal ideation, substance use disorders, and eating disorders. The evidence base for DBT gives individuals confidence in the effectiveness of the therapy.
In summary, DBT is effective due to its comprehensive approach, focus on validation, emphasis on skills training, individualized treatment plans, motivation and commitment techniques, supportive therapeutic relationship, and strong evidence base.
Who Can Benefit from DBT?
DBT is a therapeutic approach that can benefit a wide range of individuals who may be experiencing emotional dysregulation, self-destructive behaviors, and interpersonal difficulties. It was originally developed to treat individuals with borderline personality disorder (BPD), but it has proven to be effective for various other mental health conditions as well.
Here are some of the main groups of individuals who can benefit from DBT:
- Individuals with Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD): DBT was initially designed to help individuals with BPD, as they often struggle with intense emotions, self-image issues, and unstable relationships. DBT can provide these individuals with practical skills to cope with their emotions, and improve their ability to regulate their emotions and behavior.
- Individuals with Suicidal Behavior: DBT has been shown to be effective in reducing suicidal behaviors. It helps individuals develop skills to manage crises, regulate emotions, and increase their reasons for living. DBT’s emphasis on building a life worth living can be particularly helpful for individuals struggling with suicidal thoughts.
- Individuals with Self-Harm Behaviors: Self-harm behaviors are often related to difficulties in emotion regulation. DBT provides individuals with alternative skills to manage their emotions and distress, reducing the reliance on self-harming behaviors.
- Individuals with Substance Use Disorders: DBT can be used to address the emotional dysregulation and impulsivity that often underlie substance use disorders. By teaching individuals new coping skills and strategies, DBT can be an effective tool for reducing substance abuse and preventing relapse.
- Individuals with Eating Disorders: DBT has shown promise in helping individuals with eating disorders, particularly those with bulimia nervosa and binge eating disorder. It can help individuals identify and regulate their emotions, and develop healthy coping mechanisms to manage the underlying emotional issues that contribute to their eating disorder.
- Individuals with Mood Disorders: DBT skills can be helpful for individuals with mood disorders such as depression and bipolar disorder. The focus on emotion regulation and distress tolerance can empower individuals to better manage their mood swings and depressive symptoms.
- Individuals with Interpersonal Difficulties: DBT can also benefit individuals who struggle with building and maintaining healthy relationships. It teaches individuals effective communication skills, assertiveness, and emotional regulation, improving their ability to navigate interpersonal conflicts and build more satisfying relationships.
In conclusion, DBT is a versatile and effective therapeutic approach that can benefit individuals with a range of mental health conditions. Whether an individual is struggling with emotion regulation, self-destructive behaviors, or interpersonal difficulties, DBT can provide them with the skills and tools they need to create a more fulfilling and balanced life.
Questions and answers
What is Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT)?
Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) is a type of therapy that combines elements of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) with techniques from Eastern mindfulness practices. It was originally developed to treat individuals with borderline personality disorder, but has since been used to effectively treat a range of mental health conditions.
Who can benefit from Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT)?
Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) can benefit individuals who struggle with emotional regulation, impulsive behaviors, self-harming behaviors, and relationship difficulties. It is particularly effective for individuals with borderline personality disorder, but can also be helpful for those with depression, anxiety, eating disorders, and substance abuse issues.
What are the main components of Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT)?
The main components of Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) include individual therapy, group skills training, phone coaching, and therapist consultation teams. Individual therapy focuses on building a therapeutic relationship and addressing specific issues, while group skills training teaches individuals skills in mindfulness, interpersonal effectiveness, emotion regulation, and distress tolerance. Phone coaching and therapist consultation teams provide additional support and guidance outside of therapy sessions.
How does Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) help with emotional regulation?
Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) helps individuals with emotional regulation by teaching them skills to identify and label emotions, tolerate distress, and effectively manage intense emotions. These skills include mindfulness techniques, emotion regulation strategies, and distress tolerance skills. By learning and practicing these skills, individuals can gain more control over their emotions and reduce impulsive and self-harming behaviors.
Is Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) effective?
Yes, Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) has been shown to be effective in treating a range of mental health conditions. Numerous studies have demonstrated its effectiveness in reducing self-harm behaviors, suicidal ideation, depression, anxiety, and impulsivity. It has also been shown to improve emotion regulation, interpersonal functioning, and overall quality of life.