The Islamic world is often seen as a place of mystery and intrigue, filled with exotic customs and ancient traditions. But beyond the stereotypes, the Islamic world has made significant contributions to human civilization that have had a lasting impact on our daily lives.
One of the most important contributions of the Islamic world is in the field of science and mathematics. During the Golden Age of Islam, scholars in the Islamic world made great advancements in astronomy, mathematics, and medicine. They developed the concept of zero, made significant contributions to algebra, and made groundbreaking discoveries in the field of optics.
Another significant contribution of the Islamic world is in the field of architecture. Islamic architecture is known for its intricate designs, geometric patterns, and elaborate calligraphy. The beauty and grandeur of Islamic architecture can be seen in famous structures such as the Alhambra in Spain, the Hagia Sophia in Turkey, and the Great Mosque of Cordoba in Spain.
The Islamic world also made important contributions to literature and philosophy. Islamic scholars preserved and translated ancient Greek texts, making them accessible to a wider audience. They also made their own contributions to philosophy, with thinkers such as Avicenna and Averroes making significant advancements in the field.
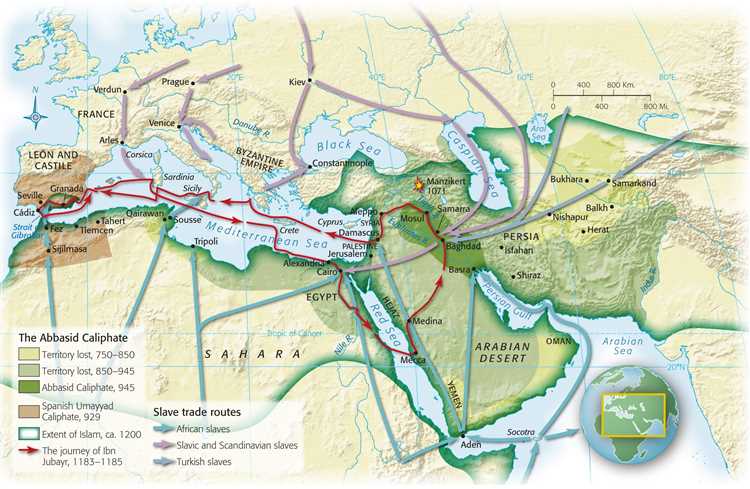
Trade and commerce were also greatly influenced by the Islamic world. Islamic traders established a vast network of trade routes that connected Europe, Africa, and Asia. They introduced new goods and products, such as spices, textiles, and ceramics, to different parts of the world. This exchange of goods and ideas greatly influenced the development of global trade.
The Islamic world also played a crucial role in the preservation and transmission of knowledge. Islamic scholars established centers of learning, known as madrasas, where students could study a wide range of subjects. These centers of learning helped to preserve and transmit ancient texts and knowledge, ensuring that it would not be lost to history.
Art and music also flourished in the Islamic world. Islamic art is characterized by its intricate geometric patterns and calligraphy, which can be seen in everything from pottery to textiles. Islamic music, with its rich melodic and rhythmic traditions, has influenced music around the world.
These are just a few examples of the contributions that the Islamic world has made to human civilization. The achievements of the ancients continue to shape the world we live in today, reminding us of the rich cultural and intellectual heritage of the Islamic world.
Islamic Contributions: An Ancient Legacy
The Islamic world has a rich and diverse cultural heritage that has left an indelible mark on human civilization. From mathematics and astronomy to medicine and architecture, Islamic scholars and scientists made significant contributions that shaped the modern world.
1. Mathematics: The Arabic numeral system, which includes the concept of zero and decimal fractions, was developed by Islamic mathematicians. They also introduced algebra and trigonometry to the world, revolutionizing the field of mathematics.
2. Astronomy: Islamic astronomers made groundbreaking advancements in the field of astronomy. They accurately calculated the movements of celestial bodies, developed astrolabes and celestial globes, and created star charts still used today.
3. Medicine: Islamic physicians were pioneers in the field of medicine. They established the first hospitals, conducted extensive research, and developed advanced surgical techniques. Their knowledge greatly influenced the development of modern medicine.
4. Architecture: Islamic architecture is renowned for its intricate geometric designs and stunning mosques. Islamic architects introduced innovative construction techniques, such as the use of pointed arches and domes, which greatly influenced the architecture of the Western world.
5. Philosophy and Scholarship: Islamic scholars played a crucial role in preserving and translating ancient Greek and Roman texts. Their translations helped preserve the knowledge of the ancient world, which later sparked the European Renaissance.
6. Literature and Poetry: The Islamic world produced exquisite works of literature and poetry. The Thousand and One Nights, an iconic collection of Middle Eastern folk tales, is just one example of the rich literary tradition of the Islamic world.
7. Trade and Commerce: Islamic merchants were pioneers in long-distance trade, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas between different regions of the world. Their trading networks spanned from Africa to Asia, contributing to the growth of global commerce.
In conclusion, the contributions of the Islamic world are vast and far-reaching. From scientific advancements to cultural achievements, the legacy of the Islamic civilization continues to shape our modern world. It is important to recognize and appreciate these contributions, as they have played a significant role in shaping the world as we know it today.
The Golden Age of Islamic Civilization
The Golden Age of Islamic Civilization refers to a period of cultural, intellectual, and scientific advancements that took place in the Islamic world from the 8th century to the 14th century. During this time, the Islamic world saw significant progress in various fields including mathematics, astronomy, medicine, literature, and architecture.
1. Preservation and Translation of Classical Knowledge: Islamic scholars played a crucial role in preserving and translating the works of ancient Greek, Roman, Persian, Indian, and Egyptian scholars. These translations helped to preserve the knowledge of the ancient world and facilitated further advancements in various scientific and intellectual disciplines.
2. Advancements in Mathematics: Islamic mathematicians made significant contributions to the field of mathematics. They introduced the decimal system and the concept of zero, which revolutionized the field of mathematics and laid the foundation for modern arithmetic and algebra.
3. Advancements in Astronomy: Islamic astronomers made major contributions to the field of astronomy. They developed sophisticated instruments for astronomical observations and made significant advancements in the understanding of celestial bodies and the movement of the planets.
4. Advancements in Medicine: Islamic physicians made groundbreaking advancements in the field of medicine. They established the first hospitals, developed a comprehensive understanding of anatomy, and made significant progress in the fields of pharmacology and surgery.
5. Advancements in Literature: The Islamic world experienced a renaissance in literature during the Golden Age. Poets and writers produced remarkable works of literature, including epic poems, philosophical treatises, and scientific texts.
6. Architectural Marvels: Islamic architecture flourished during this period, with the construction of iconic structures such as the Great Mosque of Cordoba, the Alhambra Palace, and the Dome of the Rock. These structures showcased the ingenuity and artistic skills of Islamic architects.
7. Spread of Knowledge: Islamic scholars ensured the spread of knowledge by establishing centers of learning, such as the House of Wisdom in Baghdad, which served as a hub for scholars from different cultures and backgrounds to exchange ideas and knowledge.
Overall, the Golden Age of Islamic Civilization was a time of immense progress and intellectual curiosity. The contributions made by Islamic scholars during this period laid the foundation for many of the advancements that we continue to benefit from in the modern world.
Mathematics and Algebra
The Islamic world made significant contributions to the field of mathematics and algebra. Many mathematical concepts and techniques that are still widely used today were developed by Muslim mathematicians during the Islamic Golden Age.
One of the most famous contributions of the Islamic world to mathematics is the development of algebra. The word “algebra” itself comes from the Arabic word “al-jabr,” which means “reunion of broken parts.” The Persian mathematician Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi is often credited with the invention of algebra.
Al-Khwarizmi’s book, known as “Kitab al-Jabr wal-Muqabala” (The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing), introduced the systematic solution of linear and quadratic equations. It also outlined methods for manipulating algebraic expressions and solving geometric problems. This seminal work became the foundation for algebraic studies in the Islamic world and had a profound influence on the development of mathematics in Europe.
In addition to algebra, Muslim mathematicians made numerous other contributions to the field of mathematics. They helped introduce the decimal numeral system to the Western world, which replaced Roman numerals with the Hindu-Arabic numerals we use today. This system also included the concept of zero, which is crucial for modern mathematics.
Muslim mathematicians also made advances in trigonometry and developed many of the trigonometric functions and tables used today. They contributed to the study of geometry, including the development of spherical trigonometry, which was important for astronomy and navigation.
Moreover, Muslim mathematicians expanded on the works of ancient Greek mathematicians, such as Euclid and Archimedes, by studying and translating their texts. These translations helped preserve and transmit ancient knowledge to future generations and played a vital role in the revival of mathematics in Europe during the Renaissance.
Overall, the Islamic world’s contributions to mathematics and algebra were transformative. They laid the foundation for many of the mathematical principles and techniques that are still used today, and their work had a significant impact on the development of mathematics in Europe and the wider world.
Medicine and Pharmacology
The Islamic world made numerous contributions to the field of medicine and pharmacology, building on the knowledge and techniques inherited from the Greeks, Romans, and Persians. During the Islamic Golden Age, scholars and physicians made significant advancements in the understanding of human anatomy, diagnosis, treatment, and pharmacy.
1. Preservation of Greek and Roman Medical Texts
The Islamic world played a vital role in preserving and translating ancient Greek and Roman medical texts into Arabic. These translations enabled further study and dissemination of ancient medical knowledge, laying the foundation for future discoveries.
2. Hospitals and Healthcare Centers
Islamic societies established the earliest hospitals and healthcare centers, known as bimaristans, which provided medical care to both the rich and the poor. These facilities pioneered the idea of specialized wards, skilled staff, and separate sections for various diseases.
3. Medical Education
The Islamic world established some of the first medical schools and universities, offering rigorous medical education to students. These institutions emphasized practical training and clinical observation, paving the way for the development of modern medical education.
4. Systematic Observation and Diagnosis
Islamic physicians introduced systematic observation and diagnosis as essential components of medical practice. They developed detailed case histories, recorded symptoms, collected data, and utilized anatomical knowledge for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
5. Pharmacology and Drug Development
Islamic scholars advanced the field of pharmacology, compiling and expanding the knowledge of medicinal plants and drugs. They created comprehensive drug formularies, documented drug interactions and side effects, and developed sophisticated techniques for drug preparation and administration.
6. Surgical Techniques
Islamic surgeons made significant advancements in surgical techniques. They introduced innovative instruments, developed new procedures, and established principles of asepsis, anesthesia, and wound care. Their surgical knowledge greatly influenced the practice of surgery in Europe.
7. Public Health and Preventive Medicine
The Islamic world emphasized public health and preventive medicine, recognizing the importance of hygiene, sanitation, and disease prevention. They implemented measures such as clean water supply, waste disposal systems, and quarantine to control the spread of diseases.
In conclusion, the Islamic world made immense contributions to medicine and pharmacology, revolutionizing the understanding and practice of healthcare. Their advancements continue to shape modern medicine and serve as a testament to the ingenuity and intellect of Islamic scholars.
Astronomy and Navigation
The Islamic world has made significant contributions to the fields of astronomy and navigation. During the Golden Age of Islam, Muslim scholars built on the knowledge of ancient civilizations and made groundbreaking discoveries of their own. Here are some key contributions made by the Islamic world in the field of astronomy and navigation:
-
Development of celestial globes: Islamic astronomers were the first to create celestial globes, which were three-dimensional models of the celestial sphere. These globes helped in understanding the positions and movements of celestial objects.
-
Refinement of the astrolabe: Islamic astronomers improved upon the astrolabe, an instrument used for measuring the angles of celestial bodies. They developed more accurate and portable astrolabes, which were widely used for navigation and determining prayer times.
-
Advancement in trigonometry: Muslim mathematicians developed trigonometry as a separate field of study, making significant contributions to the understanding of angles and measurements. This knowledge was crucial in astronomy and navigation.
-
Introduction of astronomical observatories: Islamic astronomers built observatories to conduct systematic observations of celestial bodies. The most famous example is the Maragheh Observatory in Persia, which was equipped with advanced instruments and employed a large team of astronomers.
-
Compilation and translation of ancient texts: Muslim scholars translated and compiled ancient Greek, Indian, and Persian texts on astronomy and navigation. These translations preserved and disseminated valuable knowledge, allowing further advancements to take place.
-
Study of celestial motion: Islamic astronomers made significant progress in understanding the motion of celestial bodies. They developed accurate models and calculations to predict the positions of the sun, moon, planets, and stars, which greatly aided navigation and timekeeping.
-
Development of navigational instruments: Muslim sailors and navigators invented various instruments for navigation, such as the kamal, quadrant, and the magnetic compass. These instruments improved accuracy and made long-distance sea voyages possible.
The contributions of the Islamic world in the fields of astronomy and navigation laid the foundation for later scientific advancements in these areas. The knowledge and techniques developed by Islamic scholars were disseminated to Europe, influencing the Renaissance and shaping our understanding of the universe.
Architecture and Urban Planning
During the Islamic Golden Age, Muslims made significant contributions to architecture and urban planning, leaving a lasting impact on the world. These contributions brought forth innovations in the design and construction of buildings, as well as the planning and layout of cities.
Mosques:
- The construction of mosques became one of the most important architectural developments during this period. Mosques were designed to reflect the spiritual and communal nature of Islamic worship. They incorporated unique elements such as minarets, domes, and prayer halls.
- Notable examples include the Great Mosque of Cordoba in Spain, the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem, and the Alhambra in Granada.
Palaces and Fortresses:
- Islamic architecture also flourished in the construction of palaces and fortresses. These structures showcased intricate designs, innovative building techniques, and beautiful decorative elements.
- One well-known example is the Alhambra palace complex in Granada, Spain, which features stunning Islamic architecture and design.
Water Management:
- Islamic societies excelled in the field of water management, developing advanced systems for irrigation, water storage, and distribution.
- Examples of their water management achievements include the qanat system, which brought underground water to the surface for agricultural purposes, and the construction of elaborate fountains and pools in urban areas.
Urban Planning:
- Islamic cities were meticulously planned, with a focus on creating functional and aesthetic urban spaces. Streets were laid out in a grid pattern, providing easy access to markets, mosques, and other public spaces.
- The city of Baghdad, founded in the 8th century, is a prime example of Islamic urban planning.
Influence on Western Architecture:
- The architectural and urban planning contributions of the Islamic world had a profound influence on Western architecture, particularly during the Renaissance. Islamic motifs, arches, and decorative elements found their way into European buildings.
- One example is the Alhambra-inspired architecture of the Generalife Gardens in Granada, which influenced European garden design.
Scientific Contributions:
- Islamic scholars and engineers conducted extensive research on architectural techniques and materials, which led to advancements in geometry, structural engineering, and construction methods.
- Their scientific contributions paved the way for future architectural developments worldwide.
Literature and Poetry
One of the most significant contributions of the Islamic world to global culture is in the field of literature and poetry. Islamic scholars and poets made significant advancements in various literary genres, leaving a lasting impact on the world of literature.
1. Arabic Language
One of the most outstanding achievements of Islamic literature is the development and refinement of the Arabic language. Arabic became the language of literature, science, and culture during the Islamic Golden Age. Islamic scholars worked diligently to standardize and develop the language, making it more refined and suitable for literary expression.
2. Arabic poetry
Islamic civilization gave birth to a rich tradition of Arabic poetry. Arabic poetry during this era was characterized by its eloquence, complex rhyme schemes, and detailed descriptions of nature and love. This tradition greatly influenced subsequent literary movements in Europe and other parts of the world.
3. One Thousand and One Nights
The One Thousand and One Nights, also known as Arabian Nights, is a collection of folk tales and stories that have captured the imagination of readers worldwide. These stories, including famous tales such as Aladdin and Ali Baba, originated from the Islamic world and have been translated into numerous languages.
4. Historical works
Islamic scholars wrote extensive historical works that documented the events and achievements of their time. Prominent examples include Ibn Khaldun’s “Muqaddimah,” a comprehensive historical and sociological work, and Al-Tabari’s “History of the Prophets and Kings,” which chronicles the history of the Islamic world from its beginnings.
5. Philosophical and scientific literature
Islamic scholars made significant contributions to the fields of philosophy and science, and their works became foundational texts for future generations. Avicenna’s “The Canon of Medicine” and Al-Kindi’s “On First Philosophy” are just two examples of influential Islamic texts that shaped the development of these fields.
6. Sufi Poetry
Sufi poetry emerged as a distinct literary genre within Islamic literature. Sufi poets expressed their mystic experiences and spiritual insights through intricate verses filled with symbolism and metaphors. Their poetry continues to inspire readers and seekers of spiritual enlightenment.
7. Translation and preservation of classical works
Islamic scholars played a crucial role in translating Greek and Roman classical works into Arabic and preserving them for future generations. Without their efforts, many works of ancient literature, philosophy, and science may have been lost to the world.
| Contributions | Description |
|---|---|
| Arabic Language | The development and refinement of the Arabic language. |
| Arabic poetry | A rich tradition of eloquent and intricate Arabic poetry. |
| One Thousand and One Nights | A collection of captivating folk tales and stories. |
| Historical works | Detailed documentation of historical events and achievements. |
| Philosophical and scientific literature | Foundational texts in the fields of philosophy and science. |
| Sufi Poetry | Expressing mystic experiences and spiritual insights through verses. |
| Translation and preservation of classical works | Translating and preserving ancient Greek and Roman texts. |
Music and Musical Instruments
Music played a significant role in the Islamic world, and its influence can still be felt today. Islamic music was diverse and included various genres and styles. It was often performed to accompany various rituals, ceremonies, and celebrations, as well as for entertainment purposes.
Islamic musical instruments also made valuable contributions to the world of music. Some of the notable instruments include:
-
Oud: This stringed instrument, similar to a lute, was widely used in Islamic music. It had a pear-shaped body and a short neck with 11 or 12 strings. The oud had a rich and melodic sound that added depth to the music.
-
Qanun: The qanun was a plucked string instrument, similar to a zither. It had a trapezoidal shape and was played using picks attached to the player’s fingers. The qanun had a bright and resonant sound and was commonly used in both classical and folk music.
-
Rebab: The rebab was a bowed string instrument with a resonating chamber made of coconut or gourd. It had a single string and was played with a bow. The rebab was widely used in Islamic music and added a haunting, melancholic tone.
-
Daf: The daf was a large frame drum with metal rings attached to the inside of the rim. It was played by shaking or striking the drumhead with the hand or a stick. The daf provided a rhythmic and percussive element to Islamic music.
-
Ney: The ney was a flute made of reed or bamboo. It had a distinctive sound that was often associated with spiritual and mystical music. The ney was played by blowing air into the open end and creating different tones by covering and uncovering the finger holes.
These are just a few examples of the many musical instruments that were developed and used in the Islamic world. The creativity and innovation of Islamic musicians and instrument makers have left a lasting impact on the world of music, and their contributions continue to be appreciated and celebrated.
Philosophy and Science
- One of the most notable contributions of the Islamic world to humanity is in the field of philosophy and science.
- The Islamic Golden Age, which lasted from the 8th to the 14th centuries, witnessed remarkable advancements in various scientific disciplines.
- Islamic scholars preserved and translated many ancient Greek texts into Arabic, building upon the knowledge of the ancient philosophers.
- One of the most influential Islamic philosophers was Ibn Sina (Avicenna), who made significant contributions to the fields of medicine, philosophy, and logic.
- His monumental work, “The Canon of Medicine,” was widely used as a medical textbook in Europe for several centuries.
- Islamic scholars also made significant advancements in mathematics. Persian mathematician Al-Khwarizmi is considered the father of algebra, and his book “Al-Kitab al-mukhtasar fi hisab al-jabr wal-muqabala” laid the foundations for modern algebraic equations.
- In addition to algebra, Islamic mathematicians made important contributions to trigonometry, geometry, and the development of the decimal system.
- The Islamic world also played a crucial role in the advancement of astronomy. Scholars such as Al-Battani and Al-Farghani made accurate observations of celestial bodies and developed new theories.
- Their works greatly influenced the development of astronomy in Europe during the Middle Ages.
Calligraphy and Islamic Art
The art of calligraphy holds a special place in Islamic culture and has played a significant role in the development of Islamic art. Calligraphy is the decorative and artistic writing of script, and it is highly regarded in Islamic society for its spiritual and aesthetic value.
Religious Significance:
Calligraphy is highly valued in Islamic art due to its close association with the Quran. The Quran, which is the holy book of Islam, is written in Arabic, and Arabic calligraphy is considered the primary visual expression of Islam. The beautiful calligraphy of the Quranic script serves as a visual representation of the word of God and is highly revered by Muslims worldwide.
Arabesque Style:
In addition to calligraphy, Islamic art also encompasses other forms such as geometric patterns and arabesques. Arabesques are intricate and repetitive designs that are often used to decorate architecture, textiles, and other visual arts. Calligraphy is often incorporated into these designs, creating a harmonious blend of script and pattern.
Expressing Beauty and Spirituality:
Islamic calligraphy is not only a form of visual art but also a means of expressing beauty and spirituality. The calligrapher carefully selects and arranges the letters, emphasizing both their aesthetic qualities and their spiritual meaning. The flowing lines and curves of the script create a sense of tranquility and harmony, inviting contemplation and meditation.
Innovation and Influence:
Islamic calligraphy has had a profound impact on the development of art and design in the Islamic world and beyond. It has inspired artists and designers throughout history and continues to influence contemporary art and typography. The art of calligraphy has also been a catalyst for the development of innovative techniques and styles, pushing the boundaries of what is possible with the written word.
Preserving Tradition:
Calligraphy is an art form that requires years of practice and dedication to master. In Islamic culture, calligraphers are highly respected and their craft is considered sacred. By preserving and practicing the art of calligraphy, the Islamic world has ensured that this ancient tradition continues to thrive and evolve.
Cultural Exchange:
Islamic calligraphy has also played a significant role in cultural exchange throughout history. As Islamic civilization spread across different regions, calligraphy became a powerful means of visual communication, transcending language barriers. It has facilitated the exchange of ideas, knowledge, and artistic influence between diverse cultures.
Conclusion
Calligraphy holds a special place in Islamic culture and has made significant contributions to the world of art. Its religious significance, intricate designs, expression of beauty and spirituality, innovation and influence, preservation of tradition, and role in cultural exchange all highlight its importance in Islamic art and beyond.
Agriculture and Irrigation
The contributions of the Islamic world to the field of agriculture and irrigation were significant and far-reaching. Islamic civilizations made important advancements in agricultural techniques, crop cultivation, and irrigation systems that greatly expanded agricultural productivity and helped sustain growing populations.
1. Development of irrigation systems:
- The Islamic world pioneered the development of advanced irrigation systems, including the construction of underground channels known as qanats to transport water from distant sources to agricultural fields.
- These qanats utilized the principle of gravity to deliver water efficiently, allowing for the cultivation of crops in arid and semi-arid regions.
- The Islamic engineers also improved the design and efficiency of traditional irrigation systems, such as the shaduf and the saqiya, which were used to lift water from wells and distribute it to fields.
2. Introduction of new crops:
- Through extensive trade networks, Islamic civilizations introduced various crops to different regions, transforming agricultural practices and diets.
- Crops such as rice, citrus fruits, bananas, and sugar cane were introduced to parts of Africa, Europe, and the Americas, greatly diversifying agricultural production.
- The Islamic world also played a crucial role in the diffusion of crops like cotton, saffron, and spices, which became important commodities in global trade.
3. Agricultural manuals and scientific knowledge:
- Islamic scholars and scientists wrote influential agricultural manuals, compiling knowledge about crop cultivation, soil management, and pest control.
- These manuals not only consolidated existing knowledge but also brought new scientific insights and experiment-based approaches to agriculture.
- The Islamic agricultural experts emphasized the importance of sustainable farming practices, crop rotation, and the use of organic fertilizers.
4. Expansion of agricultural education:
- Islamic institutions of higher learning, such as universities and madrasas, played a significant role in the education and training of agriculturalists.
- These institutions offered specialized courses on agriculture, horticulture, and land management, contributing to the spread of agricultural knowledge.
- Islamic scholars also established agricultural experiment stations, where new techniques and crop varieties were tested and disseminated to the farming communities.
5. Adoption and improvement of existing techniques:
- The Islamic world built upon the knowledge of ancient civilizations, including the Greeks, Persians, and Egyptians, to further improve agricultural practices.
- They developed new tools and techniques, such as the multi-tube irrigation system known as a noria, which increased water distribution efficiency.
- Furthermore, Islamic scientists conducted experiments and made observations to enhance understanding of plant anatomy, growth patterns, and breeding techniques.
6. Terraced agriculture:
- In mountainous regions, Islamic civilizations pioneered the practice of terraced agriculture.
- By constructing stepped fields on hillsides, they maximized arable land, prevented soil erosion, and conserved water resources.
- These terraced fields facilitated crop production in challenging terrains and allowed for the cultivation of a wider range of crops.
7. Water management and conservation:
- The Islamic world placed great emphasis on water management and conservation, developing sophisticated systems to ensure efficient use of water resources.
- They introduced the concept of water rights and established legal frameworks for equitable water distribution among farmers.
- Islamic engineers developed complex hydrological structures, such as dams, canals, and reservoirs, to control water flow and store water during periods of surplus for use during droughts.
In conclusion, the contributions of the Islamic world to agriculture and irrigation were instrumental in transforming agricultural practices, expanding crop cultivation, and improving water management. These advancements had a lasting impact on global agriculture and continue to shape agricultural systems to this day.
Banking and Finance
The Islamic world made significant contributions to the field of banking and finance. Islamic finance is based on the principles of Sharia, which prohibits charging or paying interest on loans. Instead, Islamic banking operates on the concept of profit-sharing and risk-sharing.
- Invention of Banking: The Islamic world introduced the concept of modern banking through the establishment of “Hawala” or the money transfer system. Hawala allowed individuals to transfer money without physically moving it, which laid the foundation for modern banking.
- Development of Checks: Muslims also developed the concept of checks, known as “Sakk” in Arabic. Merchants would issue sakk to each other as a form of payment, similar to the modern-day check system.
- Creation of Joint-Stock Companies: Islamic scholars developed the concept of joint-stock companies, known as “Mudarabah” and “Musharakah.” These partnerships allowed individuals to pool their resources and invest in business ventures, similar to modern-day corporations.
- Insurance and Risk Management: Islamic scholars also introduced the concept of insurance, known as “Takaful.” Takaful is based on the principle of mutual cooperation and shared responsibility, where individuals pool their resources to provide coverage against risks and losses.
- Introduction of Financial Contracts: Islamic finance introduced various types of financial contracts, such as “Murabaha” (cost-plus financing), “Ijarah” (leasing), and “Sukuk” (Islamic bonds). These contracts provided alternatives to interest-based financing and facilitated economic activities.
- Encouragement of Entrepreneurship: Islamic finance promotes entrepreneurship by providing access to capital through mechanisms such as “Qard al-Hasan” (interest-free loans) and “Mudarabah” (partnership financing). These mechanisms encouraged innovation and economic development.
- Ethical and Socially Responsible Finance: Islamic finance emphasizes ethical and socially responsible practices. Investments in sectors such as alcohol, gambling, and pork are prohibited, promoting sustainable and responsible financial activities.
The contributions of the Islamic world to banking and finance have had a profound impact on the global financial system. The principles of Islamic finance continue to shape modern financial practices, promoting fairness, equity, and ethical conduct.
Papermaking and Bookbinding
The process of papermaking was revolutionized by the Islamic world in the 8th century, leading to the spread of knowledge and literacy. Prior to this, writing materials were predominantly made from papyrus, parchment, or silk, which were costly and limited in supply.
The introduction of papermaking techniques took place in the Abbasid Caliphate, specifically in the city of Baghdad. Paper was made from raw materials such as rags, hemp, and flax fibers. These fibers were pounded into a pulp, mixed with water, and then spread onto a flat surface to dry, forming sheets of paper.
The papermaking process quickly spread throughout the Islamic world, reaching North Africa, Spain, and eventually Europe. It significantly increased the availability and accessibility of books, enabling the dissemination of knowledge across regions and cultures.
Along with the development of papermaking, the Islamic world also made important contributions to the art of bookbinding. Bookbinding is the process of assembling, protecting, and decorating books. Islamic bookbinders perfected techniques, such as leather binding, gilt tooling, and the use of decorative motifs.
Islamic bookbindings often featured intricate designs, which included geometric patterns, floral motifs, and calligraphic script. These designs were meticulously crafted using various tools, including stamps, punches, and filigree. The resulting book covers were not only functional but also exquisite works of art.
Islamic bookbinding techniques were eventually adopted by European bookbinders during the Renaissance, spreading the art form across the continent. Many historical Islamic bookbindings can still be found in museums and libraries today, showcasing the skill and craftsmanship of the Islamic bookbinders.
The advancements in papermaking and bookbinding made by the Islamic world played a significant role in the preservation and dissemination of knowledge. Without these contributions, the spread of literacy and the development of printing press technology may not have been possible.
Cuisine and Spices
The Islamic world made significant contributions to the field of cuisine and spices, leaving a lasting impact on global culinary traditions. Here are some key contributions:
- Introduction of spices: Islamic civilizations played a crucial role in introducing a wide variety of spices to the world. These included spices such as cinnamon, cloves, nutmeg, and black pepper. The trade routes established by Muslims allowed for the exchange of spices between different regions, leading to the enrichment of culinary practices in many countries.
- Development of cooking techniques: Islamic scholars and chefs developed innovative cooking techniques that are still used today. They perfected the art of marinating meats, grilling, and frying, which resulted in the creation of delectable dishes with distinct flavors. These techniques spread to different parts of the world through trade and cultural exchange.
- Influence on European cuisine: The Islamic world’s influence extended to European cuisine during the medieval period. Arab cooks introduced various ingredients, recipes, and culinary techniques to Europe. These influences can be seen in dishes such as stews, pastries, and confections, which still bear traces of Islamic culinary traditions.
- Introduction of coffee: Islamic cultures were responsible for introducing coffee to the world. Coffee beans were first cultivated and brewed as a beverage in the Islamic world, and the practice quickly spread to other regions. Today, coffee is consumed worldwide and has become an integral part of many cultures.
- Development of food hygiene: Islamic scholars placed great emphasis on food hygiene and sanitation. They developed strict guidelines for handling, preparing, and storing food to ensure its safety and quality. These principles are still followed in many culinary establishments around the world.
- Advancement in culinary literature: Muslim scholars recorded their culinary knowledge in various manuscripts and books, creating a rich culinary literature. These texts contained detailed recipes, cooking methods, and the use of spices. Many of these writings have been translated and preserved, allowing future generations to explore and learn from Islamic culinary traditions.
- Diversity and fusion of cuisines: Islamic societies had a diverse culinary landscape, influenced by the cultures of different regions. The integration of spices, ingredients, and culinary techniques from various sources resulted in the fusion of cuisines. This culinary cross-pollination led to the development of unique dishes that combined flavors and techniques from different cultures.
The contributions of the Islamic world to cuisine and spices continue to shape global culinary practices and serve as a testament to the rich and diverse culinary heritage of these civilizations.
Textiles and Weaving
Weaving and textile production were highly developed in the Islamic world, contributing greatly to the advancement of this industry globally. The Islamic world introduced various innovative techniques and materials that revolutionized the production of textiles.
Cotton: Islamic civilization played a significant role in the cultivation and spread of cotton across the world. Cotton was a vital crop, and the Islamic world established extensive cotton farms, improving its cultivation and enhancing the quality of the fibers. The production of cotton fabrics flourished, and the Islamic world exported textiles made of cotton to various regions.
Spinning Techniques: The Islamic world introduced the spinning wheel, which greatly improved the efficiency of spinning thread and yarn. This innovation led to the production of finer and stronger threads, making textiles more durable and desirable.
Dyeing: Islamic artisans developed advanced dyeing techniques that allowed for vibrant and long-lasting colors in textiles. They discovered new natural dye sources and perfected methods for dyeing fabrics. The intricate patterns and beautiful colors in Islamic textiles became highly sought after throughout the world.
Patterned Fabrics: Islamic textiles were renowned for their intricate patterns and designs. Islamic artisans used techniques such as brocade, velvet weaving, and silk embroidery to create stunning textiles. These techniques influenced textile production in Europe and other parts of the world.
Trade Routes: The Islamic world played a vital role in the global trade of textiles. The establishment of extensive trade networks allowed for the exchange of textile knowledge, techniques, and materials between different regions. This facilitated the spread and development of the textile industry worldwide.
Textile Centers: Cities such as Damascus, Baghdad, and Cairo became major centers for textile production in the Islamic world. Skilled weavers thrived in these cities, creating a rich textile culture that influenced the global market. These centers also contributed to the development of advanced weaving techniques and the production of high-quality textiles.
Textile Innovations: Islamic artisans introduced various tools and innovations to improve textile production. They enhanced looms, developed new weaving techniques, and created intricate patterns through jacquard weaving. These innovations revolutionized the textile industry and laid the foundation for future advancements.
- The Islamic world played a significant role in the cultivation and spread of cotton worldwide.
- They introduced the spinning wheel, improving the efficiency of spinning thread and yarn.
- Islamic artisans developed advanced dyeing techniques for vibrant and long-lasting colors.
- Islamic textiles were renowned for their intricate patterns and designs.
- The Islamic world facilitated the global trade of textiles through extensive trade networks.
- Cities like Damascus, Baghdad, and Cairo became major centers for textile production.
- Islamic artisans introduced various tools and innovations to improve textile production.
Dental Care and Hygiene
The Islamic world played a significant role in the advancement of dental care and hygiene. Several contributions from ancient Islamic societies have had a lasting impact on dentistry as we know it today.
Development of Dental Tools:
Ancient Islamic scholars and scientists improved upon existing dental tools, introducing new instruments for oral surgery and dental examinations. The invention of the first toothbrush, known as the miswak, is attributed to Islamic civilizations. This natural, plant-based toothbrush was widely used across the Islamic world and is still used in some Muslim cultures today.
Recognition of Gum Disease:
Islamic scholars of the medieval period made significant contributions to the understanding and treatment of gum disease. They recognized the importance of oral health and hygienic practices in preventing dental issues, and their writings on dental hygiene became influential across the world.
Emphasis on Oral Hygiene:
The Islamic world placed great importance on oral hygiene, promoting regular brushing, flossing, and rinsing. Islamic scholars emphasized the importance of maintaining clean teeth and gums as part of overall personal hygiene. Their teachings and practices continue to influence oral hygiene practices today.
Development of Dental Education:
The Islamic world established some of the earliest institutions dedicated to the education and training of dental professionals. Scholars in Muslim civilizations created specialized dental schools and established curriculums that included comprehensive studies of dental care and hygiene.
Advancements in Dental Techniques and Treatments:
Ancient Islamic scholars made significant advancements in dental techniques and treatments. They developed innovative methods for tooth extraction, restoration, and dental prosthetics. These techniques laid the foundation for modern dentistry and influenced dental practices across the globe.
Introduction of Anesthesia:
The Islamic world played a crucial role in the introduction of anesthesia for dental procedures. Ancient Islamic physicians developed techniques for pain management during dental surgeries, including the use of herbal medications and local anesthesia. These methods revolutionized dental care and made procedures more comfortable and efficient.
Promotion of Preventative Dentistry:
Ancient Islamic societies stressed the importance of preventative dentistry, including regular dental check-ups, cleanings, and oral care. Their emphasis on preventive measures has had a lasting impact on modern dentistry, inspiring similar practices and philosophies around the world.
Overall, the Islamic world made significant contributions to dental care and hygiene, revolutionizing the field and promoting oral health practices that are still used today. The advancements made by ancient Islamic scholars have helped shape modern dentistry and continue to improve oral health worldwide.
Public Libraries and Education
One of the most significant contributions of the Islamic world to education was the establishment of public libraries. These libraries played a crucial role in the dissemination of knowledge and the advancement of education.
The Islamic world placed great importance on learning and scholarship, and this led to the creation of numerous libraries. Some of the most famous libraries in the Islamic world included the House of Wisdom in Baghdad and the Library of Alexandria in Egypt.
Public libraries in the Islamic world were open to everyone, regardless of their social status or background. This inclusivity allowed people from all walks of life to access knowledge and engage in intellectual pursuits.
These libraries were not only repositories of books, but they also served as centers of learning. Scholars would gather in these libraries to study, debate, and exchange ideas. This collaborative atmosphere fostered intellectual growth and contributed to the development of various fields of knowledge.
In addition to preserving and transmitting ancient texts, Islamic libraries played a significant role in the translation and interpretation of these works. Arab scholars translated Greek and Roman texts into Arabic, preserving valuable knowledge that would have otherwise been lost.
The establishment of public libraries also had a profound impact on education. Students and scholars had access to a wide range of resources, enabling them to pursue their studies in various disciplines.
The presence of public libraries also promoted literacy and education among the general population. People were encouraged to read and expand their knowledge, leading to a more informed and educated society.
The Islamic world’s emphasis on public libraries and education laid the foundation for the development of modern libraries and educational institutions. Today, the legacy of these libraries can be seen in the widespread availability of information and access to knowledge.
| Name | Location |
|---|---|
| House of Wisdom | Baghdad, Iraq |
| Library of Alexandria | Alexandria, Egypt |
| Dar al-Kutub | Cairo, Egypt |
| Bayt al-Hikma | Baghdad, Iraq |
These public libraries were not only a testament to the Islamic world’s commitment to knowledge but also served as a catalyst for intellectual growth and educational advancements that continue to shape our world today.
Diplomacy and International Relations
The Islamic world has made significant contributions to the development of diplomacy and international relations. These contributions have played a crucial role in shaping the modern concepts and practices of diplomacy that we see today. Here are a few key contributions:
- Treaties and Diplomatic Immunity: Islamic civilization built on the earlier traditions of diplomacy and contributed to the development of treaties as a means of establishing and maintaining peaceful relations between nations. Islamic scholars introduced the concepts of diplomatic immunity and the sanctity of diplomatic envoys, which are now universally recognized principles in international relations.
- The Ambassador System: The Islamic world pioneered the ambassadorial system, which involved sending emissaries to foreign lands to represent the interests of their ruling authorities. This system facilitated communication, negotiation, and the exchange of knowledge and ideas between different civilizations.
- Translation and Interpretation: Islamic scholars played a pivotal role in translating ancient Greek and Roman works into Arabic, preserving and transmitting this knowledge to the Western world. This translation movement not only facilitated intellectual exchange but also acted as a bridge between different cultures, facilitating diplomatic and international engagements.
- International Law and Legal Systems: Islamic civilization developed a comprehensive legal system that addressed various aspects of international relations, including the rights and responsibilities of nations, trade regulations, and conflict resolution mechanisms. These legal frameworks influenced the development of international law and provided a basis for modern legal systems worldwide.
- Mediation and Conflict Resolution: Islamic scholars played a significant role in mediating disputes and conflicts between different nations and tribes. Through their knowledge of Islamic law and principles of justice, they helped resolve conflicts and foster peace among warring parties, promoting stability and harmonious relations.
- Diplomatic Corps and Consular Services: The Islamic world established formal diplomatic corps and consular services to facilitate diplomatic relations and support the needs of foreign visitors and residents. These institutions provided a platform for diplomatic negotiations, trade, and cultural exchange.
- Trade Networks and Diplomatic Missions: Islamic civilizations fostered extensive trade networks that spanned across continents, facilitating diplomatic missions and cultural exchanges. These networks, such as the Silk Road, promoted economic, political, and cultural interactions between various regions and civilizations.
The contributions of the Islamic world to diplomacy and international relations have had a lasting impact on the global stage. They have influenced diplomatic practices, legal frameworks, and the promotion of peace and understanding between nations.
Wind Power and Engineering
The Islamic civilization made significant contributions to the development of wind power and engineering. They not only harnessed the power of wind for various purposes but also made advancements in engineering techniques to improve the efficiency of wind-powered devices.
1. Windmills: The Islamic world pioneered the use of windmills for grinding grains and pumping water. Windmills were ingeniously designed with vertical-axis and horizontal-axis configurations, allowing them to harness the power of wind from any direction. These windmills were widely used in the Middle East, North Africa, and Spain, helping to enhance agricultural productivity and facilitate irrigation systems.
2. Improved Sail Design: Islamic engineers made significant advancements in sail design, which enhanced the efficiency and maneuverability of ships. By using triangular sails, known as lateen sails, ships could optimize their navigation against the wind, enabling long-distance trade and exploration.
3. Windcatchers: Windcatchers, or “badgirs,” were innovative architectural features developed in Iran and used extensively in the Islamic world. These passive ventilation systems captured and directed wind into buildings, providing natural and cool airflow during hot summers. Windcatchers played a crucial role in maintaining comfortable indoor environments without relying on energy-intensive cooling systems.
4. Water Wheels: Islamic engineers utilized wind power to drive water wheels, thus providing a continuous source of energy for various applications such as grinding grains and pumping water. These water wheels were crucial for the development of agriculture and irrigation systems in arid regions.
5. Wind Turbines: The Islamic civilization also experimented with wind turbines, precursor to the modern wind turbines used for electricity generation. These early wind turbines featured lightweight, vertical-axis designs and were used for various industrial applications, including milling, sawing, and pumping.
6. Astrolabe: Wind power played a significant role in the development and use of astrolabes, an astronomical instrument used for determining the time of day, studying celestial bodies, and navigating the seas. Astrolabes relied on accurate wind measurements and calculations to determine the position of stars and planets.
7. Wind Energy Principles: Islamic scholars, such as Abbas ibn Firnas and Al-Jazari, conducted experiments and studies on wind energy principles. They formulated theories on wind power, including the concepts of kinetic energy and the conversion of wind power into mechanical work, which laid the foundation for future advancements in the field of wind power and engineering.
Overall, the Islamic world’s contributions in wind power and engineering not only improved the quality of life but also paved the way for modern developments in harnessing renewable energy sources efficiently.
FAQ
What are some significant contributions of the Islamic world to civilization?
Some significant contributions of the Islamic world to civilization include advancements in mathematics, astronomy, medicine, architecture, agriculture, and literature.
Can you give me examples of advances in mathematics made by the Islamic world?
Of course! The Islamic world made significant advancements in mathematics, including the introduction of Arabic numerals, the concept of zero, algebra, and trigonometry. These contributions greatly impacted the field of mathematics and laid the foundation for many modern mathematical concepts.
What advancements did the Islamic world make in the field of medicine?
The Islamic world made significant contributions to the field of medicine. They translated and preserved ancient Greek and Roman medical texts, developed a system of hospitals, and made advances in surgeries, pharmacology, and ophthalmology. Islamic scholars also developed the concept of quarantine and made important discoveries in the field of anatomy.
What are some notable architectural contributions of the Islamic world?
The Islamic world made significant architectural contributions, including the development of distinctive architectural styles such as the beautiful mosques with intricate geometric designs and domes. They also made advancements in irrigation systems and developed the concept of courtyard housing.