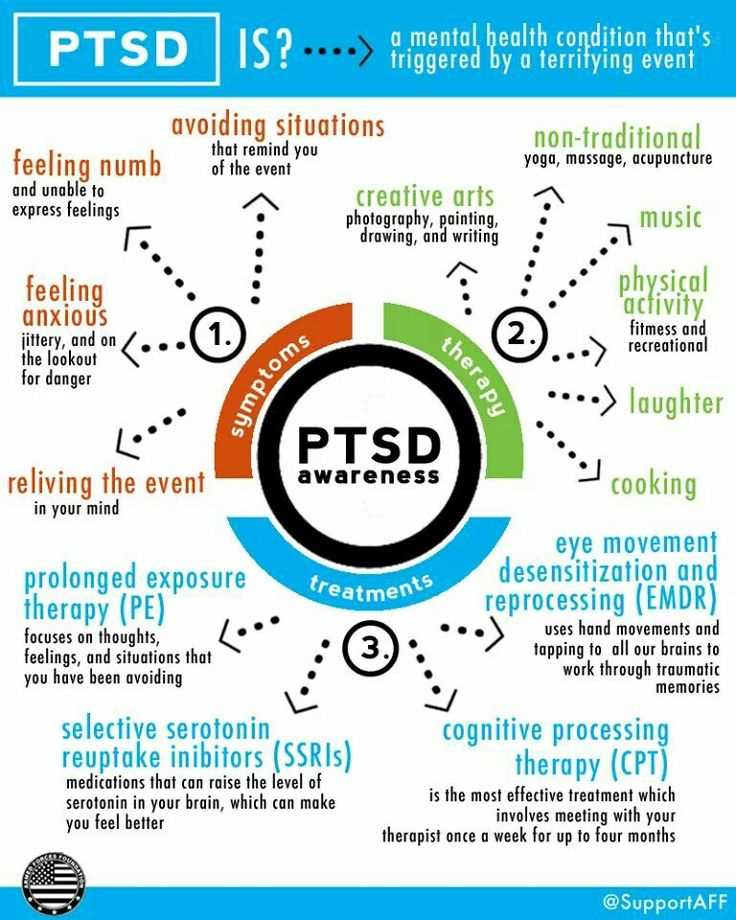
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop after experiencing a traumatic event. It is a serious and debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. However, many individuals may not even realize that they are suffering from PTSD, as the symptoms can often be confusing and easily mistaken for other conditions.
Recognizing the signs of PTSD is the first step towards getting help and starting the healing process. Common symptoms include intrusive thoughts or memories of the traumatic event, flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety or panic attacks. Individuals with PTSD may also experience emotional numbing, avoiding triggers or situations that remind them of the trauma, and hypervigilance.
If you suspect that you may have PTSD, it is crucial to seek professional help. A mental health professional, such as a therapist or psychiatrist, can properly diagnose PTSD and develop an individualized treatment plan. Treatment options may include talk therapy, medication, and various coping techniques.
Remember, seeking help is not a sign of weakness, but rather a courageous step towards healing. With the right support and treatment, it is possible to manage PTSD symptoms and regain control of your life. Don’t suffer in silence – reach out for help and start your journey towards recovery today.
Understanding Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that occurs after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. It can affect individuals of any age and can develop immediately after the traumatic event or take months or even years to appear.
PTSD is often associated with military service, as soldiers commonly experience traumatic events during combat. However, PTSD can also arise from other sources such as sexual assault, car accidents, natural disasters, or other life-threatening experiences. It is estimated that about 8% of the population will develop PTSD at some point in their lives.
Some common symptoms of PTSD can include:
- Recurrent and intrusive thoughts or memories of the traumatic event
- Nightmares or flashbacks
- Feeling detached or emotionally numb
- Difficulty sleeping or concentration
- Hyperarousal or feeling constantly on edge
- Avoiding situations or places that remind them of the traumatic event
It is important to remember that everyone may experience PTSD differently, and not all individuals who experience a traumatic event will develop the disorder. Factors such as the severity of the trauma, previous mental health history, and the individual’s support system can all contribute to the development of PTSD.
If you suspect that you or someone you know may be suffering from PTSD, it is crucial to seek help from a mental health professional. They can provide an accurate diagnosis and develop a treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs. Treatment for PTSD may involve therapy, medication, or a combination of both.
Understanding PTSD and its symptoms is the first step towards seeking help and managing the disorder. With the right support and treatment, individuals with PTSD can find relief and regain control of their lives.
What is Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)?
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. This can include situations such as physical or sexual assault, combat exposure, accidents, natural disasters, or the sudden death of a loved one.
PTSD can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background. It is estimated that about 8 million adults in the United States experience PTSD in a given year. Symptoms of PTSD can vary in severity and can affect different aspects of a person’s life, including their thoughts, emotions, behaviors, and relationships.
Some common symptoms of PTSD include:
- Recurrent intrusive memories or flashbacks of the traumatic event
- Nightmares related to the event
- Avoidance of reminders or triggers associated with the trauma
- Negative changes in thoughts and moods
- Increased arousal and reactivity, including feeling constantly on edge or being easily startled
These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s daily functioning and quality of life. It’s important to note that while some people may experience these symptoms shortly after a traumatic event, others may not develop PTSD until months or even years later.
If you suspect that you or someone you know may have PTSD, it is important to seek help from a qualified mental health professional. They can provide a proper diagnosis and develop an individualized treatment plan, which may include therapy, medication, or a combination of both.
Remember, seeking help is not a sign of weakness, but rather a proactive step towards healing and recovery. There is support available, and with the right treatment, individuals with PTSD can learn to manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.
Risk Factors for Developing PTSD
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can develop in anyone who has experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. However, certain risk factors can increase a person’s vulnerability to developing PTSD. It’s important to recognize these risk factors and take appropriate steps to seek help and support.
1. Previous trauma or stressful experiences: Individuals who have previously experienced trauma or highly stressful situations may be more susceptible to developing PTSD.
2. Family history: There may be a genetic component to PTSD, as individuals with a family history of the disorder may be more likely to develop it themselves.
3. Childhood adversity: Childhood experiences of abuse, neglect, or other forms of adversity can increase the risk of developing PTSD later in life.
4. Lack of social support: Having a strong support system can help individuals cope with traumatic events and reduce the risk of developing PTSD. Those who lack social support may be more at risk.
5. Severity of trauma: The severity of the traumatic event can influence the likelihood of developing PTSD. More severe or prolonged traumas may increase the risk.
6. Co-occurring mental health disorders: Having a pre-existing mental health condition, such as depression or anxiety, can increase the risk of developing PTSD after a traumatic event.
7. Gender: Women may be more likely than men to develop PTSD, although the reasons for this are not yet fully understood.
8. Age: While PTSD can affect people of all ages, studies have shown that younger individuals may be at a higher risk, particularly those exposed to traumas during childhood or adolescence.
9. Occupation: Certain occupations, such as military personnel, first responders, and healthcare workers, may increase the risk of experiencing traumatic events and subsequently developing PTSD.
10. Lack of coping skills: Individuals who lack effective coping skills or have difficulty managing stress may be more vulnerable to developing PTSD after a traumatic event.
It’s important to remember that having one or more risk factors does not guarantee the development of PTSD. However, recognizing these risk factors and seeking appropriate professional help and support can be crucial in preventing or effectively managing the disorder.
Recognizing the Signs of PTSD
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can occur after experiencing a traumatic event. It is important to recognize the signs of PTSD so that individuals can seek help and support. The following are some common signs and symptoms of PTSD:
- Flashbacks: People with PTSD may experience vivid and distressing memories of the traumatic event. These flashbacks can occur unexpectedly and may make the individual feel as if they are reliving the event.
- Nightmares: Another common symptom of PTSD is recurrent nightmares related to the traumatic event. These nightmares can be extremely distressing and disrupt sleep patterns.
- Avoidance: Individuals with PTSD often try to avoid reminders or triggers of the traumatic event. This can include avoiding certain places, people, or activities that may remind them of the trauma.
- Anxiety or hypervigilance: PTSD can cause individuals to be constantly on edge or hypervigilant. They may have a heightened sense of danger and may be easily startled.
- Irritability and anger: People with PTSD may experience frequent irritability and have difficulty controlling their anger. They may have outbursts of anger that seem disproportionate to the situation.
- Sleep disturbances: PTSD can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to difficulties falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing restful sleep.
- Feelings of guilt or shame: Individuals with PTSD may experience intense feelings of guilt or shame related to the traumatic event. They may blame themselves for what happened or feel responsible in some way.
- Emotional numbing: Some individuals with PTSD may experience a sense of emotional numbness or disconnectedness. They may have difficulty experiencing positive emotions or have a general sense of feeling detached from others.
It is important to note that everyone’s experience with PTSD may be different, and not all individuals with PTSD will display the same symptoms. If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms and has recently experienced a traumatic event, it may be helpful to seek professional help and support.
Physical Symptoms of PTSD
While Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is primarily associated with psychological symptoms, it can also manifest in physical ways. These physical symptoms can vary from person to person, but they are often a result of the body’s natural response to trauma. Here are some common physical symptoms of PTSD:
- Insomnia: Many individuals with PTSD struggle with sleep disturbances, such as difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep throughout the night.
- Fatigue: Chronic fatigue is another common physical symptom of PTSD, often attributed to the high levels of stress and anxiety experienced by those with the disorder.
- Headaches: Recurring headaches, including tension headaches and migraines, can be a physical manifestation of the underlying stress and tension caused by PTSD.
- Gastrointestinal issues: PTSD can lead to digestive problems, including stomachaches, constipation, and diarrhea, as the body’s stress response affects the digestive system.
- Increased heart rate: Many individuals with PTSD experience an increase in heart rate, which can manifest as a racing heart or palpitations.
- Hyperventilation: Breathing difficulties, such as rapid breathing or hyperventilation, can occur as a physical response to heightened anxiety and stress.
- Muscle tension: Chronic muscle tension and body aches, including tension headaches, backaches, and jaw pain, are often experienced by individuals with PTSD.
It is important to note that these physical symptoms can also be attributed to other medical conditions, so it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause.
If you are experiencing any of these physical symptoms along with other psychological symptoms such as flashbacks, nightmares, or intrusive thoughts, it may be an indication that you are suffering from PTSD. Seeking help from a mental health professional is crucial in order to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Psychological Symptoms of PTSD
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) can have a profound impact on an individual’s psychological well-being. The psychological symptoms of PTSD can vary in intensity and duration, but they generally fall into several categories:
- Re-experiencing Symptoms
- Avoidance Symptoms
- Negative Mood and Cognition
- Hyperarousal Symptoms
- Emotional and Physical Symptoms
People with PTSD may frequently relive the traumatic event through distressing memories, nightmares, or flashbacks. These intrusive thoughts and memories can be triggered by reminders of the event, causing significant distress and emotional upheaval. Individuals may also experience intense physical and emotional reactions when exposed to reminders of the trauma.
Individuals with PTSD often go to great lengths to avoid reminders of the traumatic event, whether they are people, places, or situations that might trigger distressing memories. They may avoid talking or thinking about the trauma, and may avoid activities or places that remind them of the event. This avoidance behavior can lead to social isolation and difficulty participating in everyday activities.
People with PTSD commonly experience negative changes in their mood and thinking patterns. They may have persistent negative beliefs about themselves, others, or the world, and may have distorted thoughts or memories related to the traumatic event. They may also experience a pervasive sense of guilt, shame, or blame for the event, and may lose interest in activities they once enjoyed. Other common symptoms include difficulty experiencing positive emotions, feelings of detachment from others, and a sense of emotional numbness.
PTSD can also manifest in a heightened state of arousal or vigilance. Individuals may have difficulty sleeping, experience irritability or anger outbursts, and may be easily startled or have an exaggerated startle response. They may have difficulty concentrating or staying focused, and may constantly feel on edge or hypervigilant. This constant state of hyperarousal can be exhausting and make it difficult to relax or feel at ease.
PTSD can also cause a range of emotional and physical symptoms. These can include exaggerated negative emotions, such as fear, anxiety, or sadness, as well as physical symptoms like headaches, stomachaches, and muscle tension. Individuals may also experience changes in appetite or weight, and may engage in self-destructive behaviors such as substance abuse or self-harm as a way to cope with the distressing symptoms of PTSD.
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these psychological symptoms after a traumatic event, it is important to seek help from a mental health professional. PTSD is a treatable condition, and there are effective therapies and interventions available to help individuals manage and overcome the symptoms of PTSD.
Seeking Help for PTSD
If you suspect that you may be experiencing post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), it is crucial to seek help from a qualified healthcare professional. Ignoring the symptoms or attempting to self-medicate can worsen the condition and have negative long-term consequences. Here are some steps to take when seeking help for PTSD:
- Reach out to your primary care physician: Start by scheduling an appointment with your primary care physician. They can evaluate your symptoms, provide a preliminary diagnosis, and refer you to specialists if necessary. Be open and honest about your experiences and concerns.
- Find a mental health specialist: Consider seeking help from a mental health specialist who has experience in diagnosing and treating PTSD. This could be a psychiatrist, psychologist, or licensed mental health counselor.
- Ask for recommendations and referrals: Seek recommendations and referrals from friends, family, or your primary care physician. You can also use online directories provided by professional organizations to find qualified specialists in your area.
- Verify insurance coverage: Before making an appointment, verify with your insurance provider to understand what mental health services are covered under your plan. This will help you estimate any out-of-pocket expenses.
- Schedule an appointment: Contact the mental health specialist and schedule an appointment that works for you. Be prepared to provide a brief overview of your symptoms and experiences when making the appointment.
- Attend therapy sessions: Attend therapy sessions as recommended by your mental health specialist. This may involve individual therapy, group therapy, or a combination of both. Be open to trying different treatment approaches to find what works best for you.
- Consider medication: Depending on the severity of your symptoms, your mental health specialist may recommend medication to help manage PTSD. It is essential to follow their guidance and inform them of any side effects or concerns.
- Build a support network: Surround yourself with a supportive network of friends, family, and fellow individuals who have experienced PTSD. Joining support groups or seeking online communities can provide additional guidance and understanding.
- Practice self-care: Incorporate self-care activities into your daily routine to help manage symptoms and promote overall well-being. This can include regular exercise, healthy eating, getting enough sleep, engaging in hobbies, and reducing stress.
- Monitor your progress: Keep track of your symptoms and progress throughout your treatment journey. This will help you and your mental health specialist evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment plan and make any necessary adjustments.
Remember, seeking help for PTSD is a courageous step towards healing and recovery. With proper support and treatment, it is possible to manage PTSD symptoms and live a fulfilling life.
Treatment Options for PTSD
There are various treatment options available for individuals who have been diagnosed with Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). These options can help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. It is important to consult with a mental health professional to determine the best treatment plan for each individual case.
1. Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is a common treatment option for PTSD. It involves working with a therapist to identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with the traumatic event. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) are two types of psychotherapy that have shown effectiveness in treating PTSD.
2. Medications
Medications can be prescribed to help manage the symptoms of PTSD. Antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), are commonly prescribed to alleviate symptoms associated with depression and anxiety. Other medications, such as prazosin, may be used to help reduce nightmares and improve sleep.
3. Group Therapy
Group therapy involves participating in therapy sessions with other individuals who have experienced similar traumatic events. This treatment option can provide a sense of community and support, as well as opportunities to learn from others and share experiences. Group therapy can be a valuable complement to individual therapy.
4. Self-Help Strategies
Self-help strategies can be an important part of managing PTSD symptoms. These strategies may include practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in regular physical exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, and avoiding substances such as alcohol and drugs. Engaging in activities that bring joy and a sense of accomplishment can also be helpful.
5. Alternative Therapies
Some individuals may find relief from PTSD symptoms through alternative therapies such as yoga, acupuncture, or meditation. These therapies can help reduce stress, promote relaxation, and improve overall well-being. It is important to consult with a qualified practitioner to determine the most suitable alternative therapy.
Ultimately, the best treatment plan for PTSD is one that is tailored to the individual’s specific needs and preferences. With the right combination of treatments and support, individuals with PTSD can learn to manage their symptoms and regain control of their lives.
Living with PTSD: Coping Strategies and Support
Living with Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) can be challenging, but with the right coping strategies and support, individuals can manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. Here are some strategies that can help:
1. Seek Therapy
Psychotherapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), can be incredibly beneficial for individuals with PTSD. A therapist can help you process your trauma, challenge negative thoughts and beliefs, and develop healthy coping mechanisms to manage symptoms.
2. Build a Support Network
Having a strong support network is crucial when living with PTSD. Surround yourself with understanding, non-judgmental individuals who can provide emotional support and validation. Consider joining support groups to connect with others who share similar experiences.
3. Practice Self-Care
Engaging in self-care activities can help reduce stress and promote well-being. Make time for activities you enjoy, such as exercising, practicing mindfulness or meditation, engaging in hobbies, or spending quality time with loved ones.
4. Establish a Routine
Creating a structured daily routine can provide a sense of stability and control, which can be comforting for individuals with PTSD. Try to establish regular sleep patterns, meal times, and engage in activities that promote relaxation and self-care.
5. Practice Stress Management Techniques
Learning and implementing stress management techniques can be beneficial for managing PTSD symptoms. Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery are a few techniques that can help reduce anxiety and promote relaxation.
6. Avoid Triggers
Avoiding triggers that activate traumatic memories or worsen your symptoms is essential for managing PTSD. Identify your triggers and develop strategies to avoid or minimize exposure to them. This may involve avoiding certain places, situations, or people.
7. Educate Yourself
Take the time to educate yourself about PTSD and its symptoms. Understanding the disorder can help you feel more empowered and in control of your situation. It can also help you communicate effectively with loved ones and healthcare professionals.
8. Be Patient with Yourself
Recovery from PTSD takes time, and healing is a gradual process. Be patient with yourself and acknowledge that it’s normal to have ups and downs. Celebrate small victories and give yourself credit for the progress you make, no matter how small it may seem.
9. Communicate with Loved Ones
Openly communicating with your loved ones about your experiences and needs can help them better understand and support you. Explain your triggers, symptoms, and any specific ways they can assist you. Having their support can make a significant difference in your recovery.
10. Stay Positive and Hopeful
Living with PTSD can be challenging, but maintaining a positive and hopeful outlook can make a significant difference. Surround yourself with positive influences, practice gratitude, and remind yourself that healing is possible.
Remember, everyone’s journey with PTSD is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. It’s important to find coping strategies and support that align with your individual needs and preferences. Don’t hesitate to reach out to mental health professionals for guidance and support along the way.
Questions and answers
What are the signs and symptoms of post traumatic stress disorder?
Some common signs and symptoms of post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) include recurrent nightmares, flashbacks, and intrusive thoughts related to the traumatic event. Other symptoms may include avoidance of triggers related to the trauma, emotional numbing, difficulty concentrating, and changes in mood and sleep patterns.
How is post traumatic stress disorder diagnosed?
Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is typically diagnosed by a mental health professional through a comprehensive evaluation. This evaluation includes a discussion of symptoms, a review of medical and trauma history, and an assessment of the impact of symptoms on daily functioning. In some cases, the mental health professional may use validated assessment tools to assist in the diagnosis of PTSD.
Can anyone develop post traumatic stress disorder?
While anyone can experience a traumatic event, not everyone who experiences trauma will develop post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The development of PTSD is influenced by various factors, including the severity and duration of the trauma, the individual’s previous exposure to trauma, and their level of social support. Additionally, individuals with certain pre-existing mental health conditions, such as anxiety or depression, may be more susceptible to developing PTSD.
What are the treatment options for post traumatic stress disorder?
Treatment options for post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) typically include a combination of therapy and medication. Therapeutic interventions, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), can help individuals process and cope with the traumatic event. Medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), may also be prescribed to help manage symptoms of PTSD.
Is it possible for post traumatic stress disorder to go away on its own?
While post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms can naturally decrease over time for some individuals, it is not guaranteed that the disorder will go away on its own. Without treatment, PTSD symptoms can persist and may negatively impact an individual’s quality of life. Seeking professional help and engaging in appropriate treatment interventions can greatly increase the likelihood of symptom reduction and recovery from PTSD.
What should I do if I think I have post traumatic stress disorder?
If you suspect that you may have post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), it is important to reach out to a mental health professional for a thorough evaluation. They can assess your symptoms, provide a diagnosis, and discuss appropriate treatment options with you. Additionally, sharing your concerns with someone you trust, such as a family member or close friend, can also provide support and guidance as you seek help.
How long does treatment for post traumatic stress disorder usually last?
The duration of treatment for post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can vary depending on the individual and their specific needs. Some individuals may see improvement within a few months of treatment, while others may require longer-term therapy. The length of treatment can also be influenced by the severity of symptoms, the presence of comorbid conditions, and the individual’s response to therapy and medication.