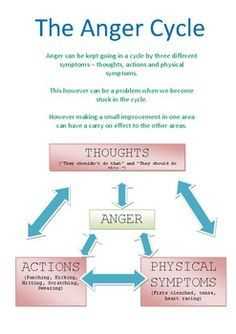
Anger is a natural and normal emotion, but when it becomes uncontrolled and starts to negatively impact your relationships and daily life, it may be time to seek help. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized and effective approach to managing anger and developing healthier coping mechanisms.
CBT focuses on the link between our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, and aims to identify and change irrational or negative thought patterns that contribute to anger. By challenging these thoughts and replacing them with more realistic and positive ones, individuals can learn to respond to anger-triggering situations in a calmer and more constructive way.
One of the key techniques used in CBT for anger management is cognitive restructuring. This involves identifying and analyzing the thoughts that contribute to angry feelings and behaviors, and replacing them with more rational and balanced thoughts. For example, instead of thinking “Everyone is out to get me,” a person may learn to reframe their thought as “Some people may not understand me, but not everyone is against me.”
Another technique commonly used in CBT for anger management is relaxation training. This involves teaching individuals various relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation. These techniques can help a person to lower their physiological arousal and promote a sense of calmness and control in the face of anger.
Understanding Anger: Causes and Effects
Anger is a powerful emotion that can have various causes and effects on an individual’s mental and physical well-being. It can result from a variety of triggers and can impact relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life.
Causes of Anger:
- Stress: High levels of stress can lead to anger as individuals struggle to cope with the pressures and demands of daily life.
- Unmet Expectations: When individuals have unfulfilled expectations or feel disappointed, they may experience anger as a reaction to their perceived loss or injustice.
- Feeling Threatened: Anger can arise when individuals feel threatened physically, emotionally, or psychologically. This can trigger a fight-or-flight response.
- Perceived Injustice: Witnessing or experiencing unfair treatment, discrimination, or injustice can provoke anger as individuals feel their rights or values are violated.
- Physical Discomfort: Physical discomfort like pain, illness, or exhaustion can contribute to irritability and increased likelihood of experiencing anger.
Effects of Anger:
- Relationship Strain: Frequent or intense anger can strain relationships with friends, family, and colleagues. It may lead to conflicts, misunderstandings, and a breakdown in communication.
- Increased Stress: Anger can contribute to a cycle of increased stress. As anger escalates, stress levels rise, and this can further exacerbate anger and perpetuate the cycle.
- Health Issues: Prolonged or unresolved anger can have negative impacts on physical health, such as increased blood pressure, cardiovascular problems, compromised immune function, and digestive issues.
- Impaired Decision Making: Anger can impair decision-making abilities, leading to impulsive or irrational choices that may have negative consequences.
- Decreased Emotional Well-being: Frequent or intense anger can contribute to feelings of guilt, shame, regret, and lower overall emotional well-being.
Overall, understanding the causes and effects of anger is an essential step in effectively managing and coping with this powerful emotion. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) techniques can provide individuals with the tools to identify triggers, challenge distorted thoughts, and develop healthier coping strategies.
Benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for Anger Management
Anger is a natural emotion that everyone experiences from time to time. However, uncontrolled anger can have negative effects on personal relationships, work performance, and overall well-being. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized and effective treatment for managing anger.
1. Increased self-awareness: CBT helps individuals become more aware of their anger triggers and the thoughts and beliefs that contribute to their anger. Through therapy, individuals learn to identify early warning signs of anger and develop strategies to manage their emotions before they escalate.
2. Improved emotional regulation: CBT teaches individuals skills and techniques to regulate their emotions in healthy ways. This includes identifying and challenging negative thought patterns that contribute to anger, practicing relaxation techniques, and developing effective communication skills.
3. Better problem-solving skills: CBT equips individuals with problem-solving techniques to address the underlying issues that contribute to their anger. By learning how to identify and evaluate different solutions, individuals can find more constructive ways to manage their anger and address the root causes.
4. Enhanced communication skills: CBT focuses on improving communication skills, including assertiveness and active listening. By learning how to express themselves effectively and listen to others with empathy, individuals can reduce frustration and misunderstandings that often lead to anger.
5. Strengthened relationships: With improved emotional regulation and communication skills, individuals undergoing CBT often report better relationships with family, friends, and colleagues. They are better equipped to express their needs and listen to the needs of others, fostering healthier and more fulfilling connections.
6. Development of healthy coping mechanisms: Part of CBT involves identifying and practicing healthy coping mechanisms to manage anger in the long term. This may include engaging in physical activities, journaling, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies that provide stress relief.
7. Long-lasting results: CBT is designed to provide individuals with long-lasting skills and techniques for managing anger. Once individuals have completed therapy, they are equipped with the tools they need to continue managing their anger independently and effectively.
In conclusion, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers numerous benefits for individuals seeking to manage their anger. By increasing self-awareness, improving emotional regulation, enhancing communication skills, and providing long-lasting coping mechanisms, CBT empowers individuals to take control of their anger and live healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Recognizing Anger Triggers: Identifying Personal Patterns
One of the first steps in effectively managing anger is becoming aware of what triggers your anger. By recognizing the specific situations, events, or thoughts that lead to your anger, you can begin to understand your personal patterns and develop strategies to cope with them.
Here are some important techniques to help you recognize your anger triggers:
- Keep a journal: Start keeping a journal to track your anger episodes. Record what happened, how you felt, and what thoughts were going through your mind at the time. Over time, patterns may emerge that can help you identify common triggers.
- Observe your physical sensations: Pay attention to your body when you start to feel angry. Notice any changes in your breathing, heart rate, muscle tension, or body temperature. These physical sensations can act as early warning signs of anger and help you identify triggers before your anger escalates.
- Identify recurring thoughts or beliefs: Notice the thoughts or beliefs that commonly arise when you become angry. Do you tend to make assumptions or jump to conclusions? Are there specific triggers that consistently lead to negative thoughts? Identifying these cognitive patterns can help you challenge and reframe your thinking.
- Recognize patterns in your environment: Take note of the people, places, or situations that consistently provoke anger in you. Are there certain individuals or settings that always seem to trigger your anger? Recognizing these external triggers can help you avoid or better prepare for these situations.
By consistently practicing these techniques, you can develop a greater understanding of your anger triggers and how they affect you. This self-awareness is a crucial step in managing your anger more effectively and developing healthier coping mechanisms.
Learning Effective Communication: Expressing Anger Appropriately
When it comes to managing anger, effective communication is an essential skill to learn. Expressing anger in an appropriate and healthy way allows individuals to express their feelings without causing harm to themselves or others. Here are some techniques to help you learn how to communicate your anger effectively:
- Take a pause: Before expressing your anger, take a moment to pause and reflect on your emotions. This will help you avoid reacting impulsively and saying or doing something you may later regret.
- Use “I” statements: When expressing your anger, try to use “I” statements instead of blaming or criticizing others. This helps to take responsibility for your feelings and avoids putting others on the defensive. For example, instead of saying “You always make me so mad,” say “I feel angry when…”.
- Be specific: Clearly communicate the specific behavior or action that triggered your anger. This helps the other person understand what they did and allows for a constructive conversation about the issue.
- Listen actively: Effective communication involves listening as well as speaking. Make sure to actively listen to the other person’s perspective, allowing them to express their feelings and thoughts without interrupting or getting defensive.
- Use assertive body language: Your body language can play a significant role in how your anger is perceived. Maintain good posture, make eye contact, and use a calm and steady tone of voice to express your anger assertively.
- Seek compromise or resolution: Instead of just venting your anger, strive for a resolution or compromise that addresses the underlying issue. This can help prevent future conflicts and foster a healthier relationship.
- Practice active problem-solving: As part of effective communication, engage in problem-solving to address the root cause of your anger. Collaborate with the other person to find mutually satisfactory solutions and implement them.
- Consider professional help: If you find it challenging to express your anger appropriately, consider seeking professional help, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). A therapist can teach you additional techniques and provide support along your journey.
Learning effective communication skills takes practice and patience. By incorporating these techniques into your anger management toolkit, you can improve your relationships and reduce the negative impact of anger on your life.
Developing Emotional Regulation Skills: Managing Anger in the Moment
Anger is a natural emotion that everyone experiences from time to time. However, when anger is not managed properly, it can lead to negative consequences and damage relationships. Developing emotional regulation skills can help individuals manage their anger in the moment and prevent it from escalating.
1. Recognize the signs of anger: Before you can effectively manage your anger, it’s important to recognize the physical and emotional signs of anger. This could include increased heart rate, tense muscles, clenched fists, or feelings of irritability and frustration.
2. Take a deep breath: When you start to feel angry, take a moment to pause and take a deep breath. Deep breathing can help calm the body and mind, allowing you to think more clearly and make rational decisions.
3. Identify the trigger: Try to identify the specific event or situation that triggered your anger. Understanding the trigger can help you better understand your emotional response and find ways to address it.
4. Challenge negative thoughts: Anger often arises from negative thoughts or interpretations of a situation. Challenge those negative thoughts by asking yourself if they are rational or if there are alternative explanations for what happened.
5. Use relaxation techniques: Engaging in relaxation techniques can help reduce anger and promote a sense of calm. This could include deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or visual imagery.
6. Express yourself assertively: Instead of allowing anger to escalate and lead to aggressive behavior, express yourself assertively. Use “I” statements to communicate your feelings and needs, while also listening and validating the other person’s perspective.
7. Practice empathy: Try to put yourself in the other person’s shoes and understand their perspective. Practicing empathy can help deescalate anger and promote more effective communication and problem-solving.
8. Take a time-out: If you feel overwhelmed by anger, it may be helpful to take a time-out. Step away from the situation temporarily to cool down and regain control of your emotions.
9. Seek support: If anger continues to be a significant challenge, consider seeking support from a therapist or counselor trained in cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). They can provide guidance and teach you additional techniques to manage your anger.
10. Practice self-care: Taking care of your physical and emotional well-being is essential for managing anger. Make sure you are getting enough sleep, eating nutritious meals, and engaging in activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
By developing emotional regulation skills and implementing effective techniques, individuals can learn to manage their anger in the moment and prevent it from causing harm to themselves and others.
Challenging Negative Thoughts: Changing Anger-Inducing Beliefs
One of the core principles of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is that our thoughts and beliefs have a significant impact on our emotions and behaviors. When it comes to managing anger, it is crucial to identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to anger-inducing reactions.
Here are some techniques to help you challenge and change your anger-inducing beliefs:
- Identify your anger triggers: Take note of situations or events that consistently trigger your anger. This will help you recognize patterns and identify the negative thoughts or beliefs associated with these triggers.
- Recognize automatic negative thoughts: Pay attention to the thoughts that automatically arise when you encounter these anger triggers. These thoughts are often irrational and exaggerated, contributing to the intensity of your anger.
- Question the evidence: Challenge the accuracy of your negative thoughts by asking yourself for evidence. Is there concrete evidence to support your belief? Are there alternative explanations for the situation?
- Consider alternative perspectives: Try to see the situation from different angles. Can you look at it from the perspective of another person involved? Are there any positive aspects or potential alternative interpretations?
- Reframe your thoughts: Replace negative thoughts with more realistic and positive ones. Use evidence and alternative perspectives to support this reframing. For example, instead of thinking “They always disrespect me,” reframe it as “They sometimes disregard my opinions, but overall, they do value my input.”
- Practice positive self-talk: Use positive affirmations and self-talk to reinforce your new beliefs. Remind yourself of your progress and achievements in managing anger, and encourage yourself to continue challenging and changing negative thoughts.
- Seek support: Discuss your thoughts and beliefs with a therapist, counselor, or trusted friend who can help you gain perspective and provide guidance in challenging negative thoughts.
Remember, changing deeply ingrained beliefs takes time and practice. However, with consistent effort and the help of CBT techniques, you can develop healthier thought patterns and effectively manage your anger.
Stress Reduction Techniques: Relaxation Methods to Calm Anger
Managing anger can be challenging, but with the help of stress reduction techniques, you can effectively calm your anger. By incorporating relaxation methods into your daily routine, you can learn to respond to challenging situations in a more calm and composed manner. Here are some relaxation techniques that can help you reduce stress and manage anger:
- Deep Breathing: Practice deep breathing exercises to relax your body and mind. Breathe in slowly through your nose, hold your breath for a few seconds, and then release it slowly through your mouth. Repeat this process several times until you feel more relaxed.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: This technique involves tensing and relaxing different muscle groups in your body. Start by tensing the muscles in your feet, then gradually work your way up to your legs, abdomen, arms, and face. Release the tension and focus on the feeling of relaxation in each muscle group.
- Meditation: Meditating regularly can help reduce stress and promote a sense of calm. Find a quiet place, sit in a comfortable position, and focus on your breath or a calming mantra. Allow any thoughts or emotions to come and go without judgment.
- Visualization: Use your imagination to create a peaceful and calming mental image. Imagine yourself in a serene environment, such as a beach or a forest. Visualize the details of the scene and immerse yourself in the feeling of relaxation and tranquility.
- Yoga: Practice yoga poses and deep stretching exercises to release tension in your body. Yoga combines physical movements with controlled breathing, promoting relaxation and reducing stress levels.
- Self-Care: Take care of your physical and mental well-being by engaging in activities that you enjoy. This can include hobbies, spending time with loved ones, or engaging in relaxation techniques. Prioritizing self-care can help reduce stress and prevent anger from building up.
- Journaling: Write down your thoughts, feelings, and experiences in a journal. This can be a therapeutic way to release pent-up emotions and gain clarity on your triggers. Reflecting on your journal entries can also help you identify patterns and develop strategies for managing anger.
- Listening to Calming Music: Play soothing music that promotes relaxation and calmness. Listening to calming music can help shift your mood and reduce stress levels.
- Talking to a Therapist: Consider seeking the help of a therapist who specializes in anger management and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). A therapist can provide you with effective techniques to manage your anger and guide you through the process of stress reduction.
Remember, practicing these relaxation techniques regularly and incorporating them into your daily routine can help you better manage your anger and reduce stress. It may take time and practice, but with persistence, you can develop healthier coping mechanisms and live a more balanced and peaceful life.
Anger Control Plans: Creating Personal Strategies for Long-Term Management
Anger can be a challenging emotion to manage, but with the help of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), individuals can develop effective strategies for long-term anger management. One of the key components of CBT is creating an anger control plan, which is a personalized set of techniques and strategies to manage anger in a healthy and constructive way.
To create an effective anger control plan, it is important to first understand the triggers and underlying beliefs that contribute to anger. This self-awareness can help individuals identify situations and thoughts that often lead to anger and allow them to develop specific strategies to address these triggers.
Identifying Triggers
An essential step in creating an anger control plan is identifying the specific triggers that cause anger to arise. Triggers can vary from person to person, but common ones include criticism, feeling overwhelmed, or being in a high-stress environment. By recognizing these triggers, individuals can proactively prepare for potential anger-inducing situations.
Challenging Negative Beliefs
Once triggers have been identified, it is crucial to challenge the negative beliefs that often accompany anger. These beliefs might include thoughts like, “I must always be in control,” or “People should always agree with me.” By challenging and replacing these negative beliefs with more rational and positive thoughts, individuals can reduce the intensity of their anger reactions.
Relaxation Techniques
Another important component of an anger control plan is incorporating relaxation techniques into daily life. The goal is to develop a repertoire of calming strategies that can be used in anger-provoking situations. These techniques may include deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or engaging in physical activities like yoga or meditation.
Communicating Effectively
Effective communication is key in managing anger. The anger control plan should include strategies for expressing anger in a healthy and constructive way, such as using “I” statements, active listening, and assertiveness skills. Learning to express anger assertively rather than aggressively can help prevent tense confrontations and promote better understanding and resolution of conflicts.
Seeking Support
It is important to remember that managing anger is a journey and may require support from others. Including a support system in the anger control plan can provide individuals with a network of friends, family, or therapists who can offer guidance, encouragement, and accountability during challenging times.
Regular Self-Reflection
Lastly, it is important to regularly reflect on progress and adjust the anger control plan as necessary. Self-reflection can help individuals identify patterns, strengths, and areas for improvement in managing anger. By continuously evaluating and updating the plan, individuals can ensure its effectiveness in the long-term.
| Identify triggers | Recognize specific situations that lead to anger |
| Challenge negative beliefs | Replace irrational thoughts with rational ones |
| Incorporate relaxation techniques | Practice calming strategies like deep breathing or meditation |
| Communicate effectively | Express anger assertively and use active listening skills |
| Seek support | Build a support system to provide guidance and accountability |
| Engage in regular self-reflection | Evaluate progress and adjust the plan as needed |
By following these guidelines and developing an anger control plan, individuals can achieve long-term success in managing their anger and lead more fulfilling and balanced lives.
Questions and answers
How can CBT help with anger management?
CBT, or Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, can help with anger management by encouraging individuals to identify and challenge their negative thought patterns and beliefs. Through this process, individuals can gain a better understanding of why they get angry and develop more positive and effective ways of dealing with anger.
What are some effective techniques of CBT for managing anger?
Some effective techniques of CBT for managing anger include identifying and challenging negative thoughts, developing coping strategies and problem-solving skills, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation, and improving communication and assertiveness skills.
How long does it take to see results from CBT for anger management?
The length of time it takes to see results from CBT for anger management can vary depending on the individual and the severity of their anger issues. However, many people report improvements within a few weeks or months of starting therapy.
Is CBT the best approach for anger management?
CBT is one of several approaches that can be effective for managing anger. The best approach may vary depending on the individual and their specific needs and circumstances. It is recommended to consult with a mental health professional to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Can CBT be used in conjunction with medication for anger management?
Yes, CBT can be used in conjunction with medication for anger management. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage underlying causes of anger, such as depression or anxiety. CBT can then be used to address the cognitive and behavioral aspects of anger.
Is anger management through CBT covered by insurance?
The coverage for anger management through CBT can vary depending on the individual’s insurance plan. It is recommended to check with the insurance provider to determine the specific coverage and any requirements for reimbursement.
Can CBT help with anger issues in children?
Yes, CBT can be effective in helping children with anger issues. Children can learn to identify and challenge negative thoughts, develop coping skills, and improve their emotional regulation through CBT techniques tailored to their age and developmental level.