Egypt, located in the northeastern corner of Africa, has a rich and diverse history that spans over thousands of years. One significant period that had a profound impact on the country was the Islamic conquest, which led to the eventual conversion of Egypt to Islam.
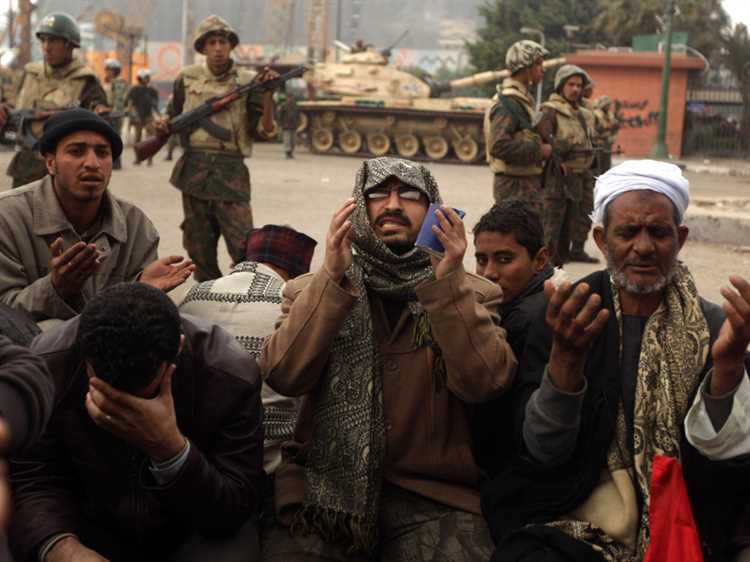
In the 7th century, the Arab Muslim armies, under the leadership of Amr ibn al-As, invaded Egypt and successfully conquered the land. The Egyptians, who were predominantly Christian at the time, faced a choice between converting to Islam or paying a special tax known as jizya.
Many Egyptians embraced Islam willingly, attracted by its teachings and the advantages that came with conversion, such as social and economic opportunities. Over time, the population gradually shifted from Christianity to Islam, and Egypt became an Islamic majority society.
The spread of Islam in Egypt was not solely due to military conquest. Islamic scholars and missionaries also played a significant role in introducing and promoting the religion. They established schools, mosques, and religious centers, which helped facilitate the conversion process and the assimilation of Islamic practices and beliefs into Egyptian society.
Today, Egypt remains one of the most populous Muslim countries in the world, with Islam deeply ingrained in its culture, politics, and daily life. However, the country’s Islamic identity is not without its complexities and challenges, as Egypt continues to navigate its historical legacy while facing modernization and globalization.
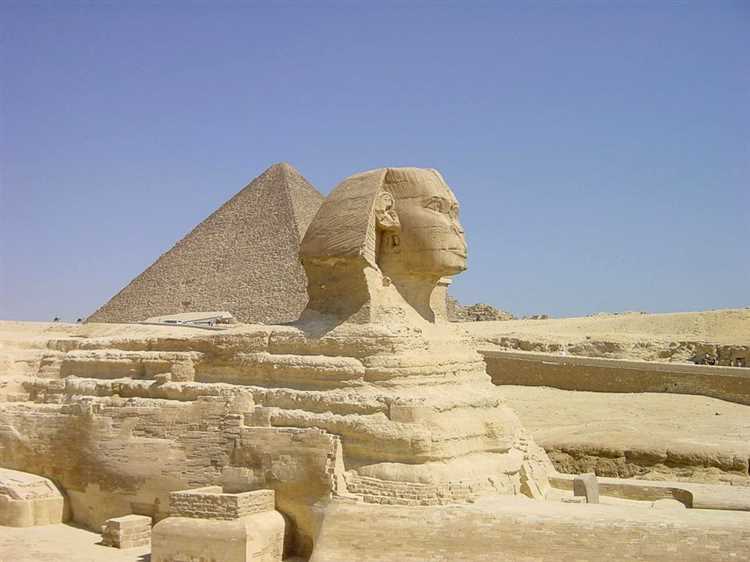
Ancient Egypt and its Religious Beliefs
Ancient Egypt was known for its rich and complex religious beliefs. The Egyptians had a pantheon of gods and goddesses, with each deity representing different aspects of nature, society, and the afterlife. Religion played a central role in every aspect of Egyptian life, influencing their culture, art, and daily rituals.
The Role of Pharaoh: The pharaoh of Egypt was seen as a divine ruler and was believed to be the intermediary between the gods and the people. The pharaoh was not only the political leader but also the religious leader of Egypt. It was believed that their actions and decisions could affect the gods’ favor and the prosperity of the land.
The Sun God: The most significant deity in Ancient Egypt was Ra, the sun god. Ra was considered the creator of the world and the ruler of the sky. He was depicted as a falcon-headed man and was worshipped as the bringer of light and life. His cult had temples throughout Egypt and his worship was widely spread among the Egyptian population.
Animal Worship: Ancient Egyptians also worshipped animals, believing that animals had a connection to the divine. Sacred animals, such as cats, lions, and crocodiles, were believed to embody certain gods or goddesses and were revered. They were often mummified and buried in special animal cemeteries.
Afterlife Beliefs: The Egyptians believed in an afterlife and the importance of preserving the physical body. They believed that the soul would live on after death and would need its physical form to navigate the afterlife. The process of mummification was developed to preserve the body, while elaborate tomb structures, such as the pyramids, were built to house the pharaohs and provide them with everything they would need in the afterlife.
Rituals and Worship: The ancient Egyptians held regular rituals and ceremonies to honor their gods and goddesses. These rituals included offerings of food, drink, and incense. Temples were built as sacred spaces where the gods could reside, and priests played a crucial role in conducting the rituals and maintaining the temples.
Conclusion: The religious beliefs of ancient Egypt were deeply ingrained in their society and had a significant influence on their daily lives. The worship of deities, the role of the pharaoh, and the importance of the afterlife all played key roles in shaping their culture and traditions. Understanding these beliefs is crucial to understanding how Egypt became an Islamic society centuries later.
Arab Conquest of Egypt
The Arab conquest of Egypt can be understood as a turning point in the history of the region, as it marked the beginning of the Arab Muslim rule in Egypt. The conquest occurred in the 7th century CE, during the early expansion of the Islamic empire.
At the time of the Arab conquest, Egypt was part of the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantines had ruled Egypt for over two centuries, and their control over the region was weakening. This provided an opportunity for the Arabs, who were motivated by religious, political, and economic factors, to conquer Egypt.
The conquest was led by the Arab general Amr ibn al-As, who had been appointed by the Islamic caliphate to lead the military campaign. Amr ibn al-As and his army faced initial resistance from the Byzantines, but they were able to defeat them in a series of battles.
One of the key factors that contributed to the success of the Arab conquest was the support they received from the local population, particularly the Coptic Christians. The Copts, who were marginalized under Byzantine rule, saw the Arab conquest as an opportunity for greater religious freedom and protection.
After the conquest, Egypt became a province of the Islamic caliphate. The Arab Muslims introduced Arabic as the official language and Islam as the dominant religion. Over time, the Arab conquerors intermingled with the local population, leading to the Arabization of Egyptian society.
It is important to note that the Arab conquest of Egypt had a profound impact on the region’s culture, language, and religion. Islam became deeply ingrained in Egyptian society and played a significant role in shaping its identity. Additionally, Egypt became a center for learning and scholarship, attracting scholars from across the Islamic world.
| Key Points | |
|---|---|
| The Arab conquest of Egypt occurred in the 7th century CE. | |
| The conquest was led by the Arab general Amr ibn al-As. | |
| The support of the local population, particularly the Coptic Christians, contributed to the success of the conquest. | |
| After the conquest, Egypt became a province of the Islamic caliphate. | |
| The Arab conquest had a profound impact on Egypt’s culture, language, and religion. |
Spread of Islam in Egypt
The spread of Islam in Egypt can be traced back to the 7th century CE when Muslim armies, led by Amr ibn al-As, conquered the region as part of the Arab conquests. The Arab conquest of Egypt marked a significant turning point in the history of the country and had a profound impact on its religious, cultural, and political landscape.
Once Egypt was under Muslim rule, the local population gradually converted to Islam. The teachings of Islam spread through various means, including the establishment of mosques, religious education, and the influence of Muslim rulers. The process of conversion was not always peaceful, with some resistance from the Christian and Jewish communities in Egypt. However, over time, Islam became the dominant religion in the region.
One of the factors that facilitated the spread of Islam in Egypt was its integration with the existing religious and cultural practices of the people. The Muslim rulers allowed the Coptic Christian population to retain their religious autonomy and practice their faith, which helped to ease the transition. Additionally, the concept of the dhimmi system, which provided protected status to non-Muslims in exchange for certain obligations, allowed for coexistence and religious diversity within the Islamic state.
The spread of Islam in Egypt also brought about significant changes in the political and administrative systems of the country. The introduction of Islamic law, or Sharia, replaced the previously existing legal systems. This had a profound impact on various aspects of Egyptian society, including family law, criminal justice, and economic practices.
Over time, the Islamic influence in Egypt became deeply ingrained, shaping the country’s religious and cultural identity. Egypt became a center of Islamic learning and scholarship, attracting scholars from across the Muslim world. The city of Cairo, in particular, emerged as a major intellectual and cultural hub.
The spread of Islam in Egypt is a complex and multifaceted process that continues to shape the country’s religious, cultural, and political landscape to this day. The legacy of the Arab conquests and the subsequent Islamic rule can be seen in the architecture, art, and traditions of Egypt, making it an integral part of the Islamic world.
Conversion of Egyptian Population
With the Arab conquest of Egypt in the 7th century, the population of the region underwent a gradual shift towards the Islamic faith. The process of conversion was multi-faceted and occurred over several centuries, resulting in the majority of Egyptians embracing Islam as their religion.
One of the main factors that contributed to the conversion of the Egyptian population was the appeal of the newly introduced religion. Islam offered a sense of unity and equality among its followers, transcending social and tribal divisions. It provided a clear code of conduct and a set of values that resonated with many Egyptians.
The Arab conquerors of Egypt also played a significant role in promoting the adoption of Islam. They established Islamic institutions and appointed officials to administer Islamic law and spread the teachings of the faith. Mosques were built and religious scholars were brought in to educate the local population about the principles and practices of Islam.
Furthermore, the implementation of a religious tax known as the jizya incentivized conversion to Islam. Non-Muslims were required to pay the jizya, creating a financial burden that made conversion an attractive alternative for many Egyptians. Over time, the jizya served as a catalyst for the spread of Islam in Egypt.
Intermarriage between Arab conquerors and local Egyptians also contributed to the conversion of the population. As mixed families formed, the offspring often adopted the religion of their Arab parent, leading to a gradual assimilation of the Egyptian population into the Islamic faith.
The conversion process was not without resistance, however. A significant portion of the Egyptian population initially clung to their traditional beliefs and customs, resisting the spread of Islam. However, over time, the influence of Islamic institutions, religious scholars, and societal pressures gradually eroded these resistance efforts.
| Century | Events |
|---|---|
| 7th | Arab conquest of Egypt |
| 8th | Establishment of Islamic institutions |
| 9th | Introduction of the jizya |
| 10th | Increasing intermarriage between Arabs and Egyptians |
| 11th – 14th | Gradual assimilation of Egyptian population into Islam |
In conclusion, the conversion of the Egyptian population to Islam was a gradual process influenced by various factors, including the appeal of the religion, the establishment of Islamic institutions, the implementation of the jizya, intermarriage, and social pressures. Over time, the majority of Egyptians embraced Islam as their religion, shaping the course of Egyptian history.
Cultural Changes under Islamic Rule
Under Islamic rule, Egypt experienced significant cultural changes that shaped its society. These changes were influenced by the introduction of Islam and its principles, as well as the integration of Arab culture into Egyptian society. Some key cultural changes under Islamic rule include:
- Religious Influence: Islam became the dominant religion in Egypt, bringing with it new religious practices, beliefs, and values. Mosques were built across the country, and Islamic scholars and theologians played a significant role in shaping religious life.
- Language: Arabic replaced Coptic as the primary language of administration, literature, and daily life. The Arabic language became the vehicle for spreading Islamic ideas and served to unify the diverse population of Egypt.
- Education: Islamic education became widespread, with the establishment of schools and madrasas (educational institutions). These institutions not only taught religious knowledge but also subjects such as mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy.
- Architecture: The introduction of Islamic architecture influenced the design and construction of buildings in Egypt. Mosques, with their unique domes and intricate tilework, became prominent symbols of Islamic rule and served as centers of worship and community gathering.
- Art and Literature: Islamic art and literature thrived in Egypt, incorporating elements of Arabic calligraphy, geometric patterns, and intricate designs. Poetry, storytelling, and music were also important cultural expressions during this period.
- Legal System: Islamic law, known as Sharia, became the basis for Egypt’s legal system. The introduction of Sharia influenced social customs, family law, and criminal justice, bringing new norms and practices to Egyptian society.
- Social Structure: Islamic rule brought changes to the social structure of Egypt. The Arab conquerors and the ruling elite held positions of power, while the local population, including Christians, Jews, and non-Arab Muslims, occupied different social roles.
Overall, the cultural changes under Islamic rule in Egypt were far-reaching and had a lasting impact on the country’s identity. Islam became an integral part of Egyptian society, influencing all aspects of life, from religion to language, education to architecture, and law to social structure.
Islamic Dynasties in Egypt
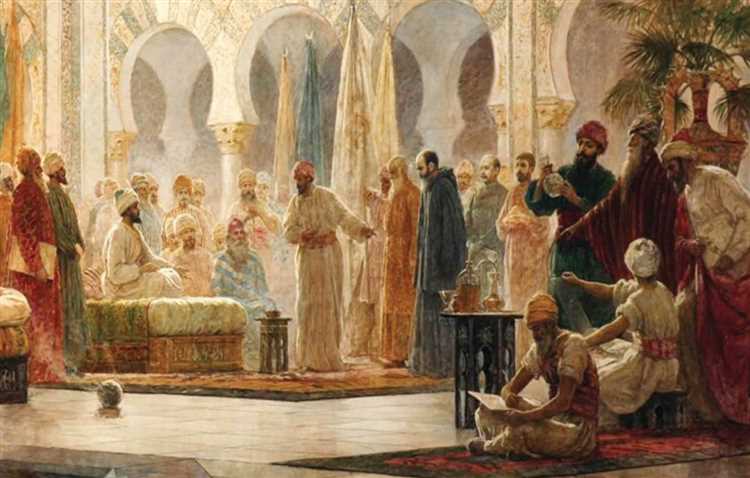
Egypt has a long and rich history of Islamic rule, with various dynasties and sultanates leaving their mark on the country. These dynasties played a significant role in shaping Egypt’s cultural, political, and religious landscape.
- The Umayyad Dynasty (661-750): The Umayyads were the first Islamic dynasty to rule over Egypt after the Islamic conquest of the region. Under their reign, Egypt became an important center of administration and trade, particularly for the expanding Muslim empire.
- The Abbasid Dynasty (750-868): Following the fall of the Umayyads, the Abbasids took control of Egypt. This period marked a time of relative stability and prosperity. Egypt experienced significant economic growth and witnessed the establishment of the world-famous city of Cairo.
- The Tulunid Dynasty (868-905): The Tulunids were a Turkish dynasty that ruled over Egypt during the ninth century. They established their own capital city, Fustat, and introduced various reforms, including improvements to agriculture and infrastructure.
- The Fatimid Dynasty (969-1171): The Fatimids were a Shia Muslim dynasty that originated from modern-day Tunisia and extended their rule to Egypt. They founded the city of Cairo and promoted Ismailism as the state religion. The Fatimids left a lasting legacy in architecture, arts, and education.
- The Ayyubid Dynasty (1171-1250): Founded by Saladin, the Ayyubids became prominent after overthrowing Fatimid rule in Egypt. They were known for their military prowess and successful campaigns against the Crusaders. The Ayyubids also contributed to the development of Islamic architecture.
- The Mamluk Sultanate (1250-1517): The Mamluks were a group of Turkish and Circassian slave soldiers who rose to power and established their own sultanate in Egypt. They successfully defended Egypt against Mongol invasions and also played a role in the expulsion of the Crusaders from the region.
- The Ottoman Empire (1517-1798): The Ottoman Empire conquered Egypt and incorporated it into their vast empire. The Ottomans introduced various reforms and modernization efforts, particularly during the reign of Muhammad Ali Pasha in the 19th century.
- The Muhammad Ali Dynasty (1805-1952): Muhammad Ali Pasha, an Albanian commander, established his own dynasty in Egypt. Under his rule, Egypt embarked on a period of modernization and development. However, this dynasty eventually gave way to widespread dissatisfaction and the rise of nationalist movements, leading to the eventual end of monarchy in Egypt.
These Islamic dynasties played a crucial role in shaping Egypt’s history, politics, and culture. Their legacies can be seen in the country’s architectural wonders, impressive mosques, and diverse cultural traditions that have persisted to this day.
Importance of Cairo as a Center of Islamic Culture
Cairo, the capital city of Egypt, has played a pivotal role in the development and preservation of Islamic culture throughout history. It is widely regarded as one of the most important Islamic cultural centers in the world.
The historical significance of Cairo as a center of Islamic culture can be traced back to the founding of the city in 969 CE by the Fatimid dynasty. The Fatimids, who were Shiite Muslims, established Cairo as their capital and developed it into a flourishing political, economic, and cultural hub.
One of the most notable contributions of Cairo to Islamic culture is its architectural heritage. The city is home to numerous mosques, madrasas (Islamic schools), and other religious and cultural institutions that showcase diverse architectural styles, such as Fatimid, Mamluk, and Ottoman. These structures not only serve as places of worship but also as important centers for religious education and intellectual discourse.
Cairo also became a prominent center for Islamic scholarship and learning. The city houses the Al-Azhar University, one of the oldest universities in the world, founded in 970 CE. Al-Azhar has been a renowned institution for Islamic studies and has attracted scholars from across the Muslim world. It has played a crucial role in preserving and disseminating Islamic knowledge, including Islamic law, theology, and philosophy.
Additionally, Cairo has been home to a vibrant artistic and literary scene. The city has nurtured and inspired many talented poets, writers, and artists throughout history. It has been a center for calligraphy, miniature painting, ceramics, and other forms of Islamic art. Many famous works of Islamic literature, such as the Thousand and One Nights, have been associated with Cairo.
Furthermore, Cairo has served as a melting pot of different Islamic cultures and traditions. It has been a destination for scholars, philosophers, and traders from various parts of the Muslim world, leading to the exchange of ideas and the enrichment of Islamic cultural heritage. The city’s vibrant markets, known as souks, have facilitated this cultural cross-pollination by offering goods from different regions.
In conclusion, Cairo’s significance as a center of Islamic culture cannot be overstated. Its architectural, intellectual, artistic, and cultural achievements have left a lasting impact on the Islamic world. The city continues to serve as a beacon of Islamic heritage, attracting visitors and scholars who seek to explore and appreciate its rich cultural legacy.
Islamic Education and Scholarship in Egypt
Egypt has a rich history of Islamic education and scholarship that dates back centuries. Education has always been highly valued in Islamic culture, and this is reflected in the development of educational institutions in Egypt.
During the early centuries of Islam, education was primarily conducted in private homes, where students would study under the supervision of a learned scholar. This form of education, known as traditional or classical education, emphasized the study of the Quran, Hadith, Arabic grammar, and Islamic law.
In the 10th century, the establishment of the Al-Azhar mosque and university in Cairo brought a new era in Islamic education in Egypt. Al-Azhar became a center of learning and attracted scholars, students, and intellectuals from all over the Muslim world. The university offered a wide range of subjects, including theology, jurisprudence, Arabic literature, mathematics, and astronomy.
Over the centuries, Al-Azhar has maintained its prestigious status and continues to be a leading institution of Islamic education. It has played a crucial role in shaping the religious and intellectual landscape of Egypt and the broader Islamic world. The university has produced many renowned scholars and theologians who have contributed significantly to Islamic thought and scholarship.
In addition to Al-Azhar, Egypt is also home to several other prominent Islamic educational institutions. These institutions cater to various educational needs, ranging from primary schools to higher education. They provide both religious and secular education, offering a well-rounded approach to learning.
Islamic education in Egypt extends beyond formal institutions. Many mosques throughout the country serve as centers of learning, where people can attend lectures, study circles, and religious classes. These mosques play a vital role in promoting religious literacy and providing opportunities for individuals to deepen their understanding of Islam.
The tradition of Islamic scholarship in Egypt is characterized by a strong emphasis on intellectual exchange and dialogue. Scholars engage in rigorous debates and discussions on various theological and legal issues, fostering intellectual growth and the development of new ideas.
In recent years, there has been a renewed focus on Islamic education in Egypt as the country seeks to promote a more comprehensive understanding of Islam and counter extremist ideologies. Efforts have been made to modernize Islamic curricula, incorporate critical thinking, and emphasize the importance of tolerance and dialogue.
The continued commitment to Islamic education and scholarship in Egypt reflects the nation’s deep-rooted Islamic heritage and its recognition of the importance of knowledge in the pursuit of a well-rounded society.
Influence of Sufism on Egyptian Islam
Sufism, a mystical branch of Islam, has had a significant impact on Egyptian Islam throughout history. This spiritual tradition emphasizes the pursuit of a direct personal experience of God and seeks to attain inner spiritual awareness and enlightenment.
One of the key aspects of Sufism is its emphasis on the concept of “oneness” or unity with God. Sufis believe in the unity of all existence and strive to cultivate a deeper connection with the divine through practices such as meditation, prayer, and chanting. This emphasis on spirituality and inner experience has influenced the beliefs and practices of Egyptian Muslims.
Sufism also emphasizes the importance of the spiritual guide or teacher, known as a “sheikh” or “pir”. These spiritual guides play a central role in guiding individuals on their spiritual journey and helping them attain a direct experience of God. In Egypt, Sufi sheikhs have been highly respected figures and have often acted as intermediaries between the people and the divine.
Another significant contribution of Sufism to Egyptian Islam is the rich tradition of Sufi poetry and music. Sufi poets, such as Rumi and Ibn Arabi, have left a lasting impact on Egyptian culture through their profound mystical verses. Sufi music, known as “Sama”, is often characterized by its repetitive rhythmic patterns and melodic chants, which aim to induce a state of spiritual ecstasy. These artistic expressions have played a crucial role in shaping the religious and cultural landscape of Egypt.
Sufi orders, or “tariqas,” have also played a vital role in the development and dissemination of Islam in Egypt. These orders, which function as spiritual communities, provide a supportive environment for individuals seeking spiritual growth and enlightenment. They have often been involved in charitable works, education, and spreading the teachings of Islam to both Muslims and non-Muslims.
In conclusion, Sufism has had a profound influence on Egyptian Islam through its emphasis on spirituality, the importance of the spiritual guide, the tradition of Sufi poetry and music, and the establishment of Sufi orders. The teachings and practices of Sufism have left an indelible mark on the religious and cultural fabric of Egypt.
Islamic Art and Architecture in Egypt
Islamic art and architecture in Egypt are a testament to the rich cultural heritage of the country. With a mix of influences from various Islamic dynasties and local Egyptian traditions, the art and architecture of Egypt reflect the historical and religious significance of the region.
One of the most prominent architectural styles in Egypt is the Islamic mosque. These places of worship are known for their intricate designs, geometric patterns, and ornate calligraphy. The mosques often feature large domes, minarets, and courtyards, creating a striking visual impact.
The use of geometric patterns is a key characteristic of Islamic art in Egypt. These patterns are created using mathematical principles and are often seen in tiling, woodwork, and calligraphy. The repetition and precision of these patterns reflect the Islamic belief in the perfection of God’s creation.
Calligraphy also plays a significant role in Islamic art in Egypt. Arabic script is used to write verses from the Quran and other religious texts, often adorned with decorative elements. Calligraphic works can be found in various forms, such as manuscripts, wall decorations, and even on textiles.
In addition to mosques, other architectural structures also showcase Islamic influences. Palaces, madrasas (Islamic schools), and mausoleums are examples of buildings that feature Islamic architectural styles. These structures often exhibit intricate detailing, such as beautifully carved doors and windows, to reflect the wealth and status of the people who commissioned them.
The use of materials in Islamic art and architecture in Egypt is also noteworthy. Stone, wood, and ceramics are commonly used, with intricate designs and patterns carved or painted onto these surfaces. These beautifully crafted materials are not only visually appealing but also serve as a means of expressing artistic and religious devotion.
The influence of Islamic art and architecture in Egypt can also be seen in the decoration of everyday objects. Items such as ceramic bowls, textiles, and metalwork are often adorned with Islamic motifs and patterns, showcasing the integration of art and design into everyday life.
Overall, Islamic art and architecture in Egypt reflect the country’s rich history and cultural heritage. The diverse influences and meticulous craftsmanship seen in mosques, palaces, and everyday objects highlight the importance of Islamic aesthetics in Egyptian society.
Impact of Islamic Law on Egyptian Society
The introduction and implementation of Islamic law, also known as Sharia, in Egypt has had a profound impact on the country’s society. Islamic law, derived from the teachings of the Quran and the Hadith (sayings and actions of the Prophet Muhammad), has influenced various aspects of Egyptian life, including family law, criminal law, and moral values.
Family Law: Islamic law has significantly shaped the family structure and relationships in Egyptian society. It governs marriage, divorce, inheritance, and child custody. Under Islamic law, marriage is considered a sacred contract and is intended to be a lifelong commitment. Divorce is permissible but discouraged, with strict conditions and procedures to be followed. Inheritance laws ensure the fair distribution of wealth among family members, with male heirs generally receiving a larger share than females.
Criminal Law: Egyptian society has also been influenced by the implementation of Islamic criminal law. Islamic law prohibits certain actions considered sinful in Islam, such as theft, adultery, and consumption of alcohol. These offenses are punishable under Sharia with specific penalties, including fines, imprisonment, or corporal punishment. However, in modern Egypt, the legal system includes elements of both Islamic law and civil law, leading to a complex blend of legal principles.
Moral Values: The presence of Islamic law in Egypt has played a significant role in shaping moral values and societal norms. Islamic teachings promote honesty, integrity, modesty, and compassion. Islamic moral values guide individuals in their everyday lives, impacting their behavior, choices, and interactions with others. These values have become deeply ingrained in Egyptian society and influence various aspects, including social etiquette, clothing choices, and gender relations.
The impact of Islamic law on Egyptian society is also reflected in the country’s legal system, education system, and governance. It has influenced the development of a unique Egyptian cultural identity, blending Islamic traditions with local customs and practices. However, it is important to note that interpretations and implementations of Islamic law can vary among different individuals and communities within Egypt.
Role of Islamic Courts in Egypt
Islamic courts have played a significant role in the legal system of Egypt throughout its history. These courts, also known as Sharia courts, have been responsible for resolving disputes and enforcing Islamic law in various aspects of daily life.
One of the key roles of Islamic courts in Egypt is to ensure the application of Sharia law, which is based on the Quran and the teachings of Prophet Muhammad. These courts interpret and apply Islamic principles to matters such as marriage, divorce, inheritance, and contracts.
Islamic courts in Egypt have the authority to issue judgments and enforce rulings according to Islamic law. They provide individuals and communities with a system of justice that is rooted in religious beliefs and moral values.
Historically, Islamic courts in Egypt have worked alongside secular courts, which are based on civil law principles. However, in recent decades, there has been a renewed emphasis on the role of Islamic courts in the legal system. This has led to debates and discussions regarding the appropriate balance between Islamic law and civil law.
Islamic courts in Egypt operate within a hierarchical structure. At the top is the Grand Mufti, who is responsible for issuing fatwas (religious rulings) on various legal matters. Below the Grand Mufti are the courts of first instance, appeals courts, and the Court of Cassation, which is the highest court in the Egyptian legal system.
In addition to their judicial functions, Islamic courts in Egypt have also played a role in educating the public on Islamic law and promoting Islamic values. They offer courses, seminars, and workshops on various legal issues, which help to enhance the understanding of Islam and its legal framework.
Overall, Islamic courts in Egypt have served as an important institution for maintaining the application of Islamic law and ensuring justice according to religious principles. Their role has evolved over time, reflecting the changing legal landscape and societal needs.
Islamic Holidays and Festivals in Egypt
Egypt, with its rich Islamic heritage, celebrates a number of important Islamic holidays and festivals throughout the year. These occasions hold great significance for Muslims in Egypt, and they are celebrated with enthusiasm and fervor.
Eid al-Fitr
Eid al-Fitr, also known as the Festival of Breaking the Fast, marks the end of Ramadan, the holy month of fasting. It is a joyous occasion that brings families and communities together. In Egypt, people wake up early to perform special prayers at mosques. They then gather with loved ones to enjoy delicious festive meals, exchange gifts, and visit friends and relatives.
Eid al-Adha
Eid al-Adha, or the Festival of Sacrifice, commemorates the willingness of Prophet Ibrahim to sacrifice his son as an act of obedience to God’s command. In Egypt, this holiday is marked by the sacrifice of an animal, most commonly a sheep or a goat, which is then distributed among the poor. Families also gather for prayers, feasts, and celebrations.
Mawlid al-Nabi
Mawlid al-Nabi, also known as the Prophet’s Birthday, is celebrated to honor the birth of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. In Egypt, this holiday is observed with religious processions, recitations of verses from the Quran, and storytelling sessions about the life of the Prophet Muhammad. People also decorate their homes and mosques with lights and green banners.
Ramadan
While not a holiday in itself, Ramadan is a significant month-long period of fasting and spiritual reflection for Muslims. Throughout this month, Muslims in Egypt abstain from food and drink from dawn until sunset. The evenings come alive with special nightly prayers, called Taraweeh, and religious gatherings hosted by mosques. It is a time for deep introspection and increased acts of worship.
Islamic New Year
The Islamic New Year, also known as Hijri New Year, marks the beginning of the lunar Hijri calendar. In Egypt, this holiday is observed with prayers, sermons, and religious lectures that reflect on the importance of the Muslim calendar. People also spend time with their families and loved ones, making resolutions for the year ahead.
Conclusion
Islamic holidays and festivals in Egypt provide an opportunity for Muslims to strengthen their faith, come together as a community, and reflect on the rich Islamic heritage of the country. These celebrations are characterized by spiritual practices, charity, family gatherings, and joyful festivities, creating a vibrant cultural tapestry in Egypt.
Contributions of Egyptian Islamic Scholars
Egypt has a long and rich history of producing influential Islamic scholars who have made significant contributions to the field of Islamic studies. These scholars have played a crucial role in shaping the religious and intellectual landscape of Egypt and the wider Muslim world.
- Al-Maziri: Al-Maziri, a renowned jurist from Egypt, developed a legal methodology known as the Maliki School of Islamic jurisprudence. His comprehensive legal rulings and interpretations have had a lasting impact on the practice of Islamic law not only in Egypt but also in North Africa.
- Al-Ghazali: Al-Ghazali, a philosopher and theologian, greatly influenced the development of Islamic theology. His works, such as “The Incoherence of the Philosophers” and “The Revival of the Religious Sciences,” addressed the compatibility of philosophy and Islamic teachings, and revitalized religious devotion in Egypt and beyond.
- Ibn Hajar al-Asqalani: Ibn Hajar was a prominent Egyptian scholar in the field of hadith (sayings and actions of Prophet Muhammad). His exhaustive compilation of hadith, called “Fath al-Bari,” established him as one of the leading authorities on the subject and is still widely studied by students of Islamic scholarship.
Egyptian scholars have also made significant contributions to other areas of Islamic knowledge, such as tafsir (interpretation of the Qur’an), fiqh (jurisprudence), and Arabic language and literature.
- Abu Hayyan al-Gharnati, an Egyptian scholar, made notable contributions to the field of tafsir with his work “Al-Bahr al-Muhit.” His commentary on the Qur’an provides valuable insights into the linguistic and contextual aspects of the verses.
- Abu Hanifa an-Nu‘man, although not originally from Egypt, settled in the country and established the Hanafi School of Islamic jurisprudence. His legal theories and rulings became influential not only in Egypt but also in other parts of the Muslim world.
- Al-Jahiz, an Egyptian scholar known for his literary and linguistic expertise, contributed to the development of Arabic language and literature. His works explored various aspects of language and eloquence and had a profound impact on subsequent generations of Arabic scholars.
These are just a few examples of the contributions made by Egyptian Islamic scholars. Their intellectual and scholarly endeavors have not only enriched the Islamic tradition but have also played a vital role in preserving and transmitting knowledge to future generations.
Islamic Influence on Egyptian Language and Literature
The advent of Islam in Egypt had a profound impact on the development of its language and literature. The Arab conquest of Egypt in the 7th century brought with it the Arabic language, which gradually replaced Coptic as the dominant language in the region. As a result, Arabic became the language of administration, religion, and culture, shaping the linguistic landscape of Egypt.
Arabic, being the language of the Quran, also influenced the writing style and content of Egyptian literature. Islamic literature emerged as a prominent genre, with its themes centered around religious teachings, morality, and prophecy. The Quran itself became a major source of inspiration for poets and writers, leading to the creation of numerous works that explored Islamic values and beliefs.
The spread of Islam in Egypt also led to the development of religious and historical texts in Arabic. Scholars and theologians wrote treatises on Islamic theology, jurisprudence, and hadith (the sayings and actions of the Prophet Muhammad). These writings played a crucial role in the establishment and spread of Islamic knowledge in Egypt and beyond.
In addition to religious literature, Arabic also influenced other forms of Egyptian literature, such as fiction, poetry, and storytelling. Egyptian authors incorporated Arabic vocabulary, idioms, and imagery into their works, adding depth and richness to their storytelling. This fusion of Arabic and Egyptian cultural elements created a unique literary tradition that continues to flourish in modern Egypt.
The impact of Islam on Egyptian language and literature can also be seen in the prevalence of Arabic loanwords in the Egyptian dialect. Over time, Arabic words and phrases were integrated into the Egyptian vernacular, resulting in a distinct linguistic blend. Today, Egyptian Arabic reflects this fusion of Arabic and native Egyptian elements, showcasing the enduring influence of Islam on Egyptian language.
| Author | Work | Islamic Theme |
|---|---|---|
| Al-Jahiz | The Book of Misers | Reflections on wealth, generosity, and contentment |
| Rifa’a al-Tahtawi | An Imam in Paris | Comparison of Islamic and Western civilizations |
| Taha Hussein | The Days | Islamic principles and values in modern society |
In conclusion, the Islamic influence on Egyptian language and literature cannot be overstated. Arabic became the dominant language, shaping the linguistic landscape and becoming the medium of religious and literary expression. Islamic themes and values permeated Egyptian literature, and the fusion of Arabic and Egyptian cultural elements created a distinctive literary tradition. The enduring impact of Islam on Egyptian language and literature is a testament to the deep-rooted Islamic heritage in Egypt.
Islamic Influence on Egyptian Music and Dance
The influence of Islam on Egyptian music and dance can be traced back to the Islamic conquest of Egypt in the 7th century. With the arrival of Islam, new religious beliefs and cultural practices were introduced, which significantly impacted the arts and entertainment in Egypt.
Religious Music: Islamic religious music, known as “nashid” or “munshid,” became an integral part of Egyptian music. Nashid are acapella songs praising Allah and Prophet Muhammad, often performed during religious ceremonies and festivals. This form of music is characterized by its spiritual lyrics and melodious tunes.
Sufi Music: Sufism, a mystical branch of Islam, also had a profound influence on Egyptian music. Sufi music is characterized by its emphasis on spiritual experiences and the use of repetitive chanting, drumming, and rhythmic movements. Egyptian Sufi music, known as “zikr,” is often performed by Sufi orders during their gatherings and celebrations.
Instrumentation: Islamic influence on Egyptian music also brought changes in instrumentation. Traditional Arabic musical instruments, such as the oud (a string instrument) and the darbuka (a goblet-shaped drum), became widely used in Egyptian music. These instruments added a distinctive Arabian flavor to Egyptian melodies and rhythms.
Folk Music and Dance: Islamic traditions also influenced Egyptian folk music and dance. Many folk songs and dances incorporate Islamic themes and melodies. For example, the “moulid” is a traditional Egyptian festival celebrating the birth of a Muslim saint, which features lively music, dance, and performances that reflect Islamic beliefs and customs.
Contemporary Trends: Today, Islamic influence on Egyptian music and dance is still evident. Contemporary Egyptian musicians often infuse their music with Islamic elements, creating a unique blend of traditional and modern styles. Islamic-inspired dance forms, such as “raqs sharqi” (belly dancing), have also gained popularity both in Egypt and globally.
In conclusion, the Islamic influence on Egyptian music and dance has shaped the cultural landscape of Egypt. From traditional religious chants to contemporary fusion styles, Islamic elements continue to play a significant role in the artistic expression of Egypt’s rich heritage.
Islamic Influence on Egyptian Cuisine
The Islamic influence on Egyptian cuisine has been significant throughout history. With the spread of Islam in Egypt, new culinary traditions and flavors were introduced, blending with existing Egyptian food practices to create a unique and diverse cuisine.
Halal Meat:
One of the most notable impacts of Islamic influence on Egyptian cuisine is the adherence to halal dietary laws. Halal meat, which is slaughtered in accordance with Islamic principles, is a fundamental component of Egyptian cuisine. This has led to the prevalence of dishes such as kofta (spiced ground meat skewers), shawarma (grilled or roasted meat), and various meat stews.
Spices and Aromatics:
Islamic traders introduced a variety of spices and aromatics to Egypt, bringing an explosion of flavors to the local cuisine. Ingredients such as cinnamon, ginger, cardamom, and saffron became common and were incorporated into both sweet and savory dishes. The use of aromatic spices in Egyptian cuisine can be seen in popular dishes like koshari (a mixed rice and lentil dish), hawawshi (spiced meat-filled pita bread), and basbousa (a sweet semolina cake).
Influence from Other Muslim Cultures:
The Islamic world is diverse, and Egyptian cuisine has been influenced by various Muslim cultures throughout history. Persian, Turkish, and Arab cuisines have all made their mark on Egyptian cooking, contributing unique techniques, flavors, and dishes. For example, Egypt’s national dish, ful medames (fava bean stew), is believed to have originated from ancient Persia and spread throughout the Islamic world.
Vegetarian and Vegan Options:
Islamic dietary guidelines also promote the consumption of plant-based foods. As a result, Egyptian cuisine offers a wide array of vegetarian and vegan options. Dishes like tabbouleh (herb and grain salad), fattoush (vegetable salad), and stuffed vegetables are staples of the Egyptian table.
Sweet Delights:
Islamic influence can also be seen in the assortment of desserts and sweets in Egyptian cuisine. The use of honey, dates, almonds, and pistachios adds richness and sweetness to many dishes. The popular dessert, baklava, which consists of layers of phyllo dough filled with nuts and soaked in honey syrup, is a classic example of the Islamic influence on Egyptian sweets.
The Role of Hospitality:
Islamic teachings emphasize the importance of hospitality, leading to the widespread practice of sharing food, especially during religious holidays and celebrations. Traditional Egyptian meals are often communal, with large platters of food served for everyone to share. The concept of generosity and sharing has become deeply ingrained in Egyptian culture, making hospitality a significant part of the dining experience.
The Islamic influence on Egyptian cuisine has shaped and enriched the culinary landscape of the country. The blending of traditional Egyptian food practices with Islamic dietary laws, spices, and flavors has produced a diverse and vibrant cuisine that continues to evolve and delight locals and visitors alike.
Islamic Pilgrimage to Mecca: The Hajj
The Hajj, or pilgrimage to Mecca, is one of the Five Pillars of Islam and is considered a sacred duty for every able-bodied Muslim who can afford it. It is a profound spiritual journey that takes place annually during the Islamic month of Dhu al-Hijjah.
During the Hajj, Muslims from all over the world come together in Mecca to perform a series of rituals that commemorate the life and teachings of Prophet Muhammad. The rituals of the Hajj are believed to have been established by the Prophet himself and have been practiced for over 1,400 years.
The pilgrimage begins with the arrival of pilgrims in Mecca, where they enter a state of purity known as Ihram. This involves wearing simple white garments for both men and women, symbolizing equality and the abandonment of worldly possessions. The act of entering Ihram signifies a spiritual transformation and a commitment to focus solely on worship and devotion during the pilgrimage.
One of the central rituals of the Hajj is the Tawaf, in which pilgrims circumambulate the Kaaba, a cube-shaped structure that is considered the holiest site in Islam. The Kaaba is believed to have been built by Prophet Abraham and his son Ishmael, and it serves as the focal point for Muslim prayers around the world. During the Tawaf, pilgrims walk around the Kaaba seven times in a counterclockwise direction while reciting prayers and supplications.
Another important ritual of the Hajj is the Sa’i, which involves walking between the hills of Safa and Marwa seven times. This commemorates the story of Hagar, the wife of Prophet Abraham, who ran between the hills in search of water for her son Ishmael. The Sa’i is a reminder of perseverance and faith in the face of adversity.
The climax of the Hajj is the standing at Arafat, where pilgrims gather on the ninth day of Dhu al-Hijjah. This day is known as the Day of Arafah and is considered the most important day of the Hajj. Pilgrims spend the day in prayer and supplication, seeking forgiveness for their sins and asking for blessings from Allah. It is believed that the supplications made on the Day of Arafah are answered by Allah.
After Arafat, pilgrims proceed to Muzdalifah, where they spend the night in open air, collecting pebbles for the next ritual. The following day, known as Eid al-Adha, pilgrims stone symbolic pillars called Jamarat, representing the devil, as a reminder of Prophet Abraham’s rejection of Satan’s temptations. This ritual symbolizes the rejection of evil and the commitment to a righteous life.
Finally, pilgrims return to Mecca to perform the final Tawaf and say farewell to the Kaaba before ending their Hajj. The Hajj experience is considered a profound spiritual journey that brings Muslims from different backgrounds together in a unique display of unity and devotion.
Overall, the Hajj is an important aspect of Islamic faith and plays a significant role in the lives of Muslims worldwide. It serves as a reminder of the unity of the Muslim community and the shared history and beliefs that bind them together.
Islamic Influence on Egyptian Clothing and Fashion
The spread of Islam in Egypt brought significant changes to the country’s clothing and fashion styles. As Islam became the dominant religion, Islamic principles and cultural practices began to shape the way Egyptians dressed.
Modesty is a fundamental concept in Islam, and it heavily influenced Egyptian clothing. Both men and women were expected to dress modestly and avoid drawing attention to themselves. This led to the popularization of loose-fitting garments that covered the body, such as the jilbab for women and traditional robes and galabiyas for men.
Hijab, or the head covering worn by some Muslim women, also became a prominent feature in Egyptian fashion. Women started wearing various styles of headscarves, such as the hijab and niqab, to abide by religious and cultural norms.
Islamic motifs began to appear in Egyptian clothing and textiles. Islamic calligraphy, geometric patterns, and arabesque designs were incorporated into fabrics, creating visually stunning garments. These motifs not only reflected religious devotion but also added an artistic and cultural dimension to Egyptian fashion.
The influence of Arab and Ottoman cultures on Egyptian fashion also grew stronger with the rise of Islam. Arab and Ottoman styles were adopted and adapted, resulting in the fusion of various cultural elements. This fusion gave rise to unique clothing styles that were distinctively Egyptian while still embracing Islamic principles.
The impact of globalization on Egyptian clothing and fashion cannot be overlooked. As Egypt became more connected to the global community, Western fashion trends started to influence local styles. However, even with the influence of global fashion, Islamic principles and cultural norms continued to shape Egyptian clothing choices.
The significance of identity also played a role in shaping Egyptian fashion under Islamic influence. Clothing became a symbol of religious and cultural identity, and individuals used it to display their devotion to Islam and their affiliation with Egyptian and Arab culture.
In summary, the Islamic influence on Egyptian clothing and fashion has been profound. From promoting modesty to incorporating Islamic motifs and blending regional cultural styles, Islam has left an indelible mark on Egyptian fashion. Today, the fusion of Islamic principles, cultural norms, and global fashion trends continues to shape the ever-evolving world of Egyptian clothing and fashion.
Islamic Influence on Egyptian Traditional Medicine
Islamic civilization has had a profound impact on many aspects of Egyptian society, including traditional medicine. The introduction of Islam to Egypt in the 7th century brought with it new ideas and practices that greatly influenced the development of traditional Egyptian medicine.
One of the most significant contributions of Islamic culture to Egyptian traditional medicine was the translation and preservation of ancient Greek and Roman texts. During the Islamic Golden Age, scholars in the Islamic world translated and studied works by ancient Greek and Roman physicians, such as Hippocrates and Galen. These texts, which had been lost or forgotten in the West, were brought to Egypt and other parts of the Islamic world, where they were translated into Arabic and preserved.
The translation and preservation of these ancient texts played a crucial role in the development of Egyptian traditional medicine. Egyptian physicians were able to access and study the ancient medical knowledge contained in these texts, and incorporate it into their own practices. This led to the emergence of a rich and diverse medical tradition in Egypt that combined elements of ancient Greek and Roman medicine with traditional Egyptian healing practices.
In addition to the translation of ancient texts, Islamic influence on Egyptian traditional medicine can also be seen in the introduction of new medicinal herbs and treatments. Islamic scholars traveled extensively throughout the Islamic world, exchanging knowledge and gathering information about different healing practices. They brought with them new medicinal herbs and treatments, many of which were incorporated into Egyptian traditional medicine.
Furthermore, Islamic teachings on hygiene and cleanliness also had a significant impact on Egyptian traditional medicine. The Islamic tradition emphasized the importance of cleanliness and hygiene for maintaining good health. This led to the development of practices such as regular bathing, handwashing, and the use of clean instruments in medical treatments.
In conclusion, Islamic influence has greatly shaped Egyptian traditional medicine. The translation and preservation of ancient medical texts, the introduction of new medicinal herbs and treatments, and the emphasis on hygiene and cleanliness all played a role in the development of this rich and diverse medical tradition. Today, Egyptian traditional medicine continues to be influenced by Islamic principles and practices, while also incorporating elements from other cultures and medical traditions.
Islamic Influence on Egyptian Sports and Recreation
The Islamic religion has had a profound impact on various aspects of Egyptian culture, including sports and recreation. Throughout its history, Egypt has seen the adoption and adaptation of Islamic principles and values in its sporting activities, creating a unique blend of traditional and Islamic practices.
Sports in Islamic Civilization
The Islamic civilization has a rich tradition of sports and physical activities. The Prophet Muhammad himself encouraged physical fitness and participation in sports, considering it essential for maintaining a healthy body and mind. This emphasis on physical wellness has influenced Egyptian sports and recreation.
Traditional Islamic Sports in Egypt
Egypt has a long history of traditional sports that have been influenced by Islamic values. One prominent example is horse racing and equestrian sports. Horse racing was already popular in pre-Islamic Egypt, but it gained a new significance under Islamic rule, as horses were considered a symbol of power and prestige. It is still a popular sport in Egypt today.
Another traditional Islamic sport in Egypt is archery. Archery has been practiced in the region for centuries and was encouraged by Islamic rulers for military training. Today, archery clubs can still be found in many Egyptian cities, celebrating this ancient sport.
Modern Sports in Egypt
In addition to traditional sports, Egypt has embraced modern sports that involve Islamic principles and values. Football (soccer) is a prime example of a sport that has become deeply ingrained in Egyptian society. It has united people of different social and religious backgrounds, and Islamic principles of fairness and teamwork are often emphasized in the context of the game.
Furthermore, Egypt has been successful in various international sporting events, including the Olympic Games. Islamic values of discipline, perseverance, and dedication have contributed to the achievements of Egyptian athletes in various sports, such as athletics, boxing, and taekwondo.
Islamic Influence on Recreation
Islamic values have also influenced recreational activities in Egypt. Traditional Islamic festivals, such as Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha, are occasions for communal celebrations, where people gather for feasts, music, and traditional folk dances. These events provide opportunities for social interaction and strengthen community ties.
Moreover, Islamic teachings promote moderation in all aspects of life, including recreation. Islamic scholars emphasize the importance of striking a balance between work and leisure activities, encouraging individuals to engage in recreational pursuits that are beneficial and morally acceptable.
Conclusion
The Islamic religion has had a significant influence on Egyptian sports and recreation. Traditional and modern sports in Egypt carry Islamic principles of physical fitness, fairness, teamwork, and discipline. Islamic values also shape the recreational activities of the Egyptian people, promoting social interaction and moderation. The integration of Islamic beliefs and practices into sports and recreation reflects the profound impact of Islam on Egyptian culture and society.
Contemporary Islam in Egypt
In modern Egypt, Islam continues to play a central role in the daily lives of the majority of the population. The country is predominantly Sunni Muslim, with the majority belonging to the Sunni branch of Islam.
Islamic practices and rituals are integrated into various aspects of Egyptian society, including religious festivals, family life, and the legal system. Islamic law, or Sharia, influences family matters, personal status issues, and matters related to inheritance and criminal law.
The Al-Azhar Mosque and University, located in Cairo, is one of the oldest universities in the world and a prominent institution of Islamic learning. It serves as a center for religious education and the dissemination of Islamic knowledge.
Friday prayers, known as Jummah, are an important part of the weekly religious practice for Muslims in Egypt. Mosques across the country are filled with believers gathering for prayers and sermons.
Islamic activism and political movements have also played a significant role in Egypt’s recent history. The Muslim Brotherhood, founded in 1928, has been a major force in Egyptian politics, advocating for the implementation of Islamic principles in the country. However, the group has faced periods of repression and has been banned at times by the government.
In recent years, there has been a rise in more conservative and fundamentalist interpretations of Islam in Egypt. Salafism, a movement that aims to adhere to the practices and teachings of the early Muslim community, has gained popularity. This has led to debates and tensions within Egyptian society regarding the role of religion in public life.
Despite these debates and tensions, Islam remains an integral part of Egypt’s cultural and social fabric. It continues to shape the values, traditions, and everyday practices of the Egyptian people.
FAQ
What was the religion of Egypt before Islam?
Before Islam, the majority of Egyptians practiced various forms of polytheism, with the worship of gods and goddesses such as Ra, Osiris, and Isis.
When did Islam start to spread in Egypt?
Islam started to spread in Egypt in the 7th century AD, after the Arab conquest of Egypt led by Amr ibn al-As.
Who was the first Arab conqueror of Egypt?
The first Arab conqueror of Egypt was Amr ibn al-As, a companion of the Prophet Muhammad.
How was Egypt governed during the early Islamic period?
During the early Islamic period, Egypt was governed by the Rashidun Caliphate, followed by the Umayyad Caliphate and later the Abbasid Caliphate.
What role did the Coptic Christians play in the transition to Islam?
The Coptic Christians of Egypt played a significant role in the transition to Islam as many of them converted to Islam, while others continued to practice Christianity as a religious minority.
What were the effects of Islamic rule on Egyptian society?
The effects of Islamic rule on Egyptian society were profound. Arabic became the dominant language, Islamic law was implemented, and cultural and religious practices were influenced by Islamic traditions.
Did Egypt face any resistance to Islamic rule?
Yes, there were several instances of resistance to Islamic rule in Egypt, including the revolt of the Berber tribes and the revolts led by religious minorities such as the Copts and Shia Muslims.