Islamic banking refers to a financial system that operates in accordance with the principles of Islamic law, also known as Shariah. In Islamic banking, the concept of interest, or Riba, is strictly prohibited, as it is considered exploitative and unfair. Instead, Islamic banks provide financial products and services that are based on profit-sharing and risk-sharing principles.
One of the key principles of Islamic banking is that it must be Halal, meaning permissible, under Shariah law. Islamic scholars and experts evaluate the commercial transactions and financial practices of Islamic banks to ensure that they comply with the principles of Shariah. This involves assessing the nature of the transactions, the sources of income, and the risk-sharing arrangements.
In Islamic banking, there are several types of transactions and financial instruments that are considered Halal. For example, mudarabah is a partnership-based contract, where one party provides the capital and the other party manages the business. The profits generated are shared between the parties based on a pre-agreed ratio. This form of financing is considered Halal, as it promotes risk-sharing and fairness.
Similarly, murabahah is a cost-plus financing arrangement, where the bank purchases an asset on behalf of the customer and resells it to the customer at a higher price, which includes a profit margin. This form of financing is also considered Halal, as it does not involve the payment or receipt of interest.
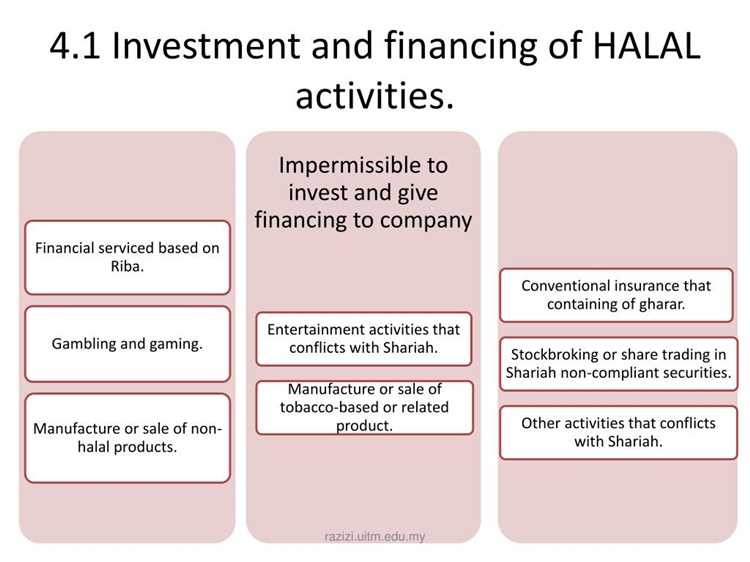
However, not all financial practices in Islamic banking are considered Halal. For example, some scholars argue that certain forms of Islamic bonds, known as sukuk, may involve elements of Riba and are therefore not permissible. Furthermore, some scholars argue that Islamic banks should not engage in speculative activities or invest in industries that are considered haram, such as alcohol, gambling, or pork.
In conclusion, Islamic banking aims to provide financial services that are in line with the principles of Shariah. It operates on the basis of profit-sharing and risk-sharing, and prohibits interest-based transactions. However, the evaluation of whether a particular financial practice is Halal or not can vary among scholars and experts. Therefore, it is important for individuals interested in Islamic banking to consult with knowledgeable scholars or experts to ensure that the financial products and services they are considering are in compliance with Shariah principles.
What is Islamic Banking?
Islamic banking refers to a banking system that operates in accordance with the principles of Islamic law, also known as Shariah law. Shariah law is derived from the religious texts of Islam, including the Quran and the Hadith (teachings and practices of the Prophet Muhammad).
Islamic banking aims to provide financial services that are ethical, fair, and in line with Islamic principles. It prohibits the charging of interest or usury, as well as engaging in speculative or excessive risk-taking activities. Instead, Islamic banks offer financial products and services that are based on profit-sharing, risk-sharing, and asset-backing.
One of the key principles of Islamic banking is the concept of Riba, which refers to the charging or payment of interest. Riba is considered unjust and exploitative in Islam, as it creates an unequal distribution of wealth and can lead to financial hardship for borrowers. Islamic banking seeks to eliminate interest and instead promotes shared risk and reward through participation in legitimate and productive economic activities.
Islamic banks operate on the basis of several key principles, including:
- Mudarabah: This is a form of partnership where one party provides the capital (Rab al-Maal) and the other party provides expertise and labor (Mudarib). Profit earned is shared between the parties according to an agreed-upon ratio.
- Musharakah: This is a form of joint venture or partnership where all parties contribute capital and share both profits and losses based on their respective investment ratios.
- Wakalah: This is a form of agency agreement where one party (Wakil) acts as an agent on behalf of another party (Principle) to manage and invest funds.
- Murabaha: This is a cost-plus financing arrangement where the bank purchases an asset requested by a customer and resells it to the customer at an agreed-upon price, which includes a markup to cover the bank’s costs and profit.
These principles guide the design and operation of Islamic financial products and services, such as Islamic savings accounts, Islamic mortgages, Islamic bonds (sukuk), and Islamic investment funds. Islamic banks also adhere to ethical investment criteria, avoiding investments in sectors that are deemed forbidden by Shariah law, such as gambling, alcohol, pork, and conventional financial institutions.
In conclusion, Islamic banking is a financial system that operates in accordance with Islamic principles, providing ethical and Shariah-compliant financial products and services. It aims to create a just and equitable financial system that promotes shared risk and reward, and prohibits interest-based transactions and speculative activities.
Key Principles of Islamic Banking
Islamic banking is guided by a set of key principles that distinguish it from conventional banking practices. These principles are derived from Islamic law, known as Shariah, and aim to promote fairness, transparency, and ethical behavior in financial transactions. The following are some of the key principles of Islamic banking:
- Prohibition of Interest: Islamic banking prohibits the charging or receiving of interest (riba). Instead, it promotes the concept of profit-sharing and risk-sharing between the bank and its customers. This ensures that both parties bear the risks and rewards of a financial transaction.
- Prohibition of Speculation: Islamic banking discourages speculative activities that involve excessive uncertainty and risk. Transactions involving gambling, speculation, or contracts with uncertain outcomes (gharar) are prohibited.
- Asset-Backed Financing: Islamic banking focuses on asset-backed financing, where the funds are used for investment in tangible assets or productive economic activities. This ensures that the banking system supports real economic growth and development.
- Ethical Investments: Islamic banking promotes ethical investments that comply with Shariah principles. Investments in industries such as alcohol, gambling, pork, and tobacco are prohibited. Instead, Islamic banks focus on socially responsible sectors such as renewable energy, healthcare, and education.
- Partnership-Based Contracts: Islamic banking encourages partnership-based contracts, such as mudarabah (profit-sharing) and musharakah (joint venture). In these arrangements, the bank and the customer share profits and losses based on agreed-upon terms.
- Prohibition of Uncertainty: Islamic banking requires transparency and certainty in financial transactions. Contracts should clearly define the rights and obligations of all parties involved, avoiding ambiguity or excessive uncertainty (gharar).
- Prohibition of Exploitation: Islamic banking emphasizes ethical behavior and prohibits any form of exploitation or unfair practices. This includes usury, insider trading, excessive fees, and dishonesty in financial transactions.
By adhering to these principles, Islamic banking aims to provide financial services that are compatible with Islamic values and promote economic stability, fairness, and social welfare.
Importance of Halal in Islamic Banking
Halal, meaning “permissible” or “lawful” in Arabic, plays a crucial role in Islamic banking. In Islamic finance, all transactions and investments must comply with the principles of Shariah law, which includes the concept of halal.
Halal is not just limited to the food and beverage industry; it also extends to all aspects of a Muslim’s life, including their financial dealings. Islamic banking adheres to the principles of halal, ensuring that all financial activities are conducted in a permissible manner.
Here are some reasons why the concept of halal is important in Islamic banking:
- Compliance with Shariah law: Islamic banking operates based on the principles of Shariah law. The concept of halal ensures that all financial transactions and investments are in accordance with the ethical and moral principles outlined in the Quran and Sunnah. It prohibits any involvement in activities that are considered haram (forbidden), such as usury (riba), gambling, and investing in businesses that deal with alcohol or pork.
- Ethical and responsible banking: Islamic banking emphasizes ethical and responsible banking practices. The concept of halal ensures that banking activities are conducted in a transparent and equitable manner, promoting fairness and justice. It prohibits any form of exploitation or injustice in financial transactions.
- Preservation of wealth: Islamic banking aims to preserve and grow wealth in a halal manner. By adhering to the principles of halal, Islamic banks provide financial products and services that are free from any usury or speculative elements. This helps in safeguarding the wealth of individuals and the society as a whole.
- Ensuring social welfare: Halal investments in Islamic banking prioritize socially responsible projects that contribute to the well-being of society. Islamic banks avoid investments in industries such as alcohol, gambling, or tobacco, which may have negative impacts on individuals and communities. They promote investments in sectors such as healthcare, education, and renewable energy, which can have a positive social impact.
In conclusion, the concept of halal is of utmost importance in Islamic banking. It ensures that all financial transactions and investments are conducted in compliance with the principles of Shariah law, promoting ethical, responsible, and socially beneficial banking practices.
The Shariah Board and its Role
In Islamic banking, the Shariah Board plays a crucial role in ensuring that all financial activities and products offered by Islamic banks comply with Islamic principles and are therefore considered halal (permissible) under Islamic law.
The Shariah Board is an independent body of religious scholars with expertise in Islamic law and finance. It is responsible for providing guidance and reviewing the operations of Islamic banks to ensure compliance with Shariah principles. The board members are typically appointed by the bank’s management or shareholders, and they are selected based on their knowledge and qualifications in Islamic jurisprudence.
The primary role of the Shariah Board is to issue fatwas (legal opinions) on the permissibility of various financial transactions and products. These fatwas serve as guidelines for Islamic banks, helping them develop Shariah-compliant products and services. The board also reviews and approves the bank’s financial contracts, investment activities, and business operations to ensure they are in line with Islamic principles.
The Shariah Board also plays an important role in monitoring the bank’s operations to ensure ongoing compliance with Islamic principles. It may conduct periodic audits and inspections to assess the bank’s adherence to Shariah guidelines. If any violations or non-compliance are identified, the board may recommend corrective actions or sanctions to ensure the bank rectifies the situation and remains compliant.
In addition to its oversight role, the Shariah Board also has an educational function. It provides training and guidance to the bank’s employees on Islamic finance principles, ensuring that they have a thorough understanding of the Shariah requirements and can implement them effectively in their day-to-day activities.
The Shariah Board’s role is of utmost importance in Islamic banking, as it ensures the integrity and authenticity of Islamic financial transactions and products. By providing expert guidance and oversight, the board ensures that Islamic banks operate in a manner that aligns with the ethical and moral values of Islam.
Is Interest (Riba) Allowed in Islamic Banking?
One of the fundamental principles of Islamic banking is the prohibition of interest, also known as riba. Riba is considered haram (forbidden) according to Islamic law, as it is seen as exploitative and unethical.
In Islamic banking, the concept of profit-sharing is used instead of interest. This means that banks and their customers enter into partnerships or profit-sharing agreements, where both parties share in the profits and losses of the investment or transaction.
Islamic banking operates on the principles of fairness, ethics, and mutual benefit. It aims to provide financial services that align with Islamic principles and values.
By prohibiting interest, Islamic banking aims to promote social justice and avoid the exploitation of borrowers. Instead of charging interest on loans, Islamic banks offer financing through profit-sharing arrangements, leasing, or other Shariah-compliant methods.
While interest is not allowed in Islamic banking, some financial products may still resemble conventional interest-based products in their structure. Islamic scholars evaluate these products to ensure they comply with Shariah principles.
It’s important to note that different scholars and Islamic banking institutions may have varying interpretations of what is considered riba or interest. This can lead to differences in the specific products and practices offered by different Islamic banks.
| Product | Description |
|---|---|
| Murabaha | A financing arrangement where the bank purchases an asset on behalf of the customer and sells it to them at a higher price, allowing the customer to pay in installments. |
| Profit-sharing Investment Accounts | Accounts where customers deposit their money, and the bank invests it in Shariah-compliant ventures. Profits are shared between the bank and the account holders. |
| Ijara | A leasing arrangement where the bank purchases an asset and leases it to the customer for a set period. The customer pays rent instead of interest. |
Islamic banking aims to provide financial services that are in line with Islamic principles and values. By avoiding interest and promoting profit sharing, Islamic banks strive to create a more equitable and ethical banking system.
How Islamic Banks Make Profit
Islamic banks operate on the principles of Shariah law, which prohibits the charging or paying of interest. Instead, Islamic banks rely on a variety of other mechanisms to make a profit.
One of the main ways Islamic banks make profit is through profit-sharing agreements. Instead of charging interest on loans, Islamic banks enter into partnerships with their customers. For example, in a financing partnership called Mudarabah, the bank provides the funds and the customer provides the skills and labor. The bank shares in the profit generated from the partnership according to a pre-agreed-upon ratio, while the customer receives a share as well.
Another method used by Islamic banks is the sale of goods or assets on a deferred payment basis. This is known as Murabaha. In this arrangement, the bank purchases an item on behalf of the customer and then sells it to them at a higher price, allowing the customer to pay in installments over an agreed period of time. While this resembles a traditional loan with interest, the difference lies in the fact that the bank assumes the risk of ownership during the deferred payment period.
Islamic banks also engage in leasing contracts, known as Ijarah, where they purchase an asset and lease it to the customer for a specified period of time. The customer makes regular lease payments to the bank, and at the end of the lease term, the customer has the option to purchase the asset at its fair market value.
In addition, Islamic banks may also provide investment opportunities through equity-based financing. This involves the bank investing in a project or business, sharing in the profits and losses according to an agreed-upon ratio. This allows the bank to participate in the success of the investment without charging interest.
Overall, Islamic banks use a variety of methods to make a profit while adhering to the principles of Shariah law. These methods include profit-sharing agreements, deferred payment sales, leasing contracts, and equity-based financing. By avoiding interest-based transactions, Islamic banks aim to provide financial services that are both ethical and compliant with Islamic principles.
Types of Islamic Banking Products
Islamic banking offers a range of financial products and services that comply with Shariah law principles. These products are designed to provide banking services without the use of interest, or riba, which is prohibited in Islam.
Here are some of the common types of Islamic banking products:
- Murabaha: This is a type of financing where the bank purchases a specific asset, such as a property or a car, and sells it to the customer at a higher price, allowing the customer to pay in installments.
- Mudarabah: Mudarabah is a partnership agreement between the bank and the customer, where the bank provides the capital and the customer provides the expertise. Any profit generated is shared between the bank and the customer according to pre-determined ratios.
- Musharakah: This is a joint venture financing arrangement, where both the bank and the customer contribute capital to a business or investment project. Any profit or loss is shared between them based on their respective capital contributions.
- Ijarah: Ijarah is a type of leasing arrangement, where the bank purchases an asset and leases it to the customer for a specified period. The customer pays regular lease payments, and at the end of the lease term, the asset may be sold to the customer or the lease agreement may be renewed.
- Sukuk: Sukuk are Islamic bonds that represent ownership in a tangible asset or a specific project. Investors earn returns based on the profit generated by the underlying asset or project, rather than receiving fixed interest payments.
Takaful: Takaful is an Islamic alternative to conventional insurance, where participants contribute premiums into a risk-sharing pool. In the event of a loss, the pool provides financial compensation to the affected participants.
These are just a few examples of the types of products offered by Islamic banks. Each product is structured in accordance with Shariah law principles to ensure compliance with Islamic teachings.
It’s important to note that the availability of Islamic banking products and services may vary from country to country, depending on the regulatory environment and the demand for Islamic finance.
Islamic Banking vs Conventional Banking
Islamic banking and conventional banking are two distinct approaches to banking that differ in their principles and practices. Here, we will explore the main differences between Islamic banking and conventional banking.
1. Principles:
Islamic banking operates on the principles of Shariah law, which prohibits earning interest (riba) and engaging in unethical practices. On the other hand, conventional banking is based on interest-based transactions and does not follow Shariah principles.
2. Interest:
In Islamic banking, interest-based transactions are prohibited. Instead, profit-sharing (mudarabah) or cost-plus financing (murabahah) methods are used. In conventional banking, interest is the core element, and banks charge and pay interest on loans and deposits.
3. Risk-sharing:
In Islamic banking, there is a concept of risk-sharing where both the bank and the customer share profits and losses. This promotes a sense of partnership and fairness. Conventional banking does not emphasize risk-sharing as interest is fixed and does not depend on the performance of the financed project or investment.
4. Ethical considerations:
Islamic banking follows ethical guidelines and avoids investments in industries such as alcohol, gambling, or pork. Conventional banking does not have strict ethical restrictions and may invest in any industry as long as it is financially viable.
5. Asset-backed financing:
In Islamic banking, all transactions must be backed by tangible assets. This ensures that investments are real and productive. Conventional banking does not require this level of asset backing and may rely on creditworthiness or future cash flows.
6. Supervision and regulation:
Islamic banking institutions are supervised by Shariah boards, which ensure that their activities adhere to Islamic principles. Conventional banking institutions are regulated by central banks and follow standard banking regulations.
7. Social justice:
Islamic banking aims to promote social justice and reduce wealth inequality. It prohibits predatory practices and exploitative interest charges. Conventional banking may not have a specific focus on social justice and may prioritize profit maximization.
8. Financial products:
Islamic banks offer a range of financial products that are compliant with Shariah principles, such as Islamic mortgages, Islamic bonds (sukuk), and Islamic mutual funds. Conventional banks offer a wide range of financial products including interest-based loans, bonds, and mutual funds.
Conclusion:
The main difference between Islamic banking and conventional banking lies in their underlying principles and practices. While Islamic banking adheres to Shariah principles and promotes ethical finance, conventional banking operates on interest-based transactions and may not have strict ethical guidelines. Both types of banking have their advantages and disadvantages, and individuals and businesses may choose the one that aligns with their beliefs and financial needs.
Islamic Financing: An Alternative to Interest-Based Loans
Islamic financing is a system of financial transactions that is based on the principles of Islamic law, or Shariah. In Islamic finance, the concept of riba (interest) is prohibited, as it is considered exploitative and unfair. Instead, Islamic financing offers alternative methods of financing that are based on shared risk and profit-sharing.
One of the fundamental principles of Islamic finance is the prohibition of riba, or interest. According to Islamic teachings, earning and paying interest is considered usury, and it is seen as a form of exploitation that is harmful to the community. Instead, Islamic financing promotes the concept of profit-sharing, where the financier and the client share the risk and the profit of a venture.
Islamic financing provides several alternatives to interest-based loans. One common method is the concept of murabaha, which is a type of profit-sharing contract. In a murabaha transaction, the financier purchases an asset on behalf of the client and sells it to the client at a higher price, allowing the financier to earn a profit without charging interest. The client then pays the higher price in installments over a predetermined period.
Another alternative to interest-based loans is ijara, which is a type of lease contract. In an ijara transaction, the financier purchases an asset and leases it to the client for a specified period. The client pays rent to the financier, and at the end of the lease term, the client may have the option to purchase the asset at an agreed-upon price.
Islamic financing also utilizes the concept of musharaka, which is a form of partnership. In a musharaka agreement, two or more parties pool their resources together to finance a venture, with each party sharing in the profits and the losses. This type of financing is commonly used for business ventures and projects.
In addition to these methods, Islamic financing also promotes the use of waqf, which is a form of endowment. In a waqf arrangement, a person dedicates an asset, such as property or funds, for a specific charitable purpose. The income generated from the asset can be used to fund various social projects, such as education, healthcare, and poverty alleviation.
Overall, Islamic financing offers a viable alternative to interest-based loans, promoting ethical financial practices based on shared risk and profit-sharing. It provides Muslims with a way to engage in financial transactions that are in line with their religious beliefs and values.
Islamic Banking and Risk Management
Risk management plays a crucial role in Islamic banking, just like in conventional banking. However, the approach to risk management in Islamic banking is slightly different due to the prohibition of interest and the requirement to comply with Sharia principles.
In Islamic banking, risks are managed through various mechanisms and principles that are compliant with Sharia law. Some of the key risk management principles in Islamic banking include:
- Prohibition of Riba: Islamic banking strictly prohibits the charging or payment of interest, as it is considered exploitative. This prohibition helps mitigate the risk of excessive debt burdens and promotes fair and ethical lending practices.
- Profit and Loss Sharing: Islamic banking promotes the concept of profit and loss sharing (PLS) contracts, such as Mudarabah (partnership) and Musharakah (joint venture). These contracts allow risk-sharing between the bank and its clients, reducing the risk for both parties.
- Asset-Backed Financing: Islamic banks typically engage in asset-backed financing, where the bank provides funds against tangible assets or participates in the purchase of real assets. This helps mitigate the risk of default by ensuring that the bank has collateral for the financing provided.
- Due Diligence: Islamic banks are required to conduct thorough due diligence on their clients and potential investment opportunities. This helps identify and assess the risks associated with the transactions and ensure compliance with Sharia principles.
- Risk-Sharing Contracts: Islamic banking encourages the use of risk-sharing contracts, such as Mudarabah and Musharakah, where profits and losses are shared between the bank and its clients. This aligns the interests of both parties and helps manage risks effectively.
Additionally, Islamic banks also use conventional risk management techniques, such as diversification, capital adequacy, and risk assessment models to ensure the soundness and stability of their operations.
Overall, Islamic banking incorporates specific risk management principles and mechanisms to ensure compliance with Sharia law while effectively managing risks. These principles promote fairness, transparency, and ethical practices in the banking industry, with a focus on risk-sharing and asset-backed financing.
The Growth and Global Reach of Islamic Banking
Islamic banking has experienced significant growth and has spread its reach worldwide in recent decades. This unique banking system, based on Islamic principles and Shariah law, has gained popularity primarily among Muslim populations but has also attracted non-Muslim customers seeking ethical banking alternatives.
One of the main factors contributing to the growth of Islamic banking is the increasing demand for financial products that conform to Islamic principles. In Islamic banking, interest (riba) is prohibited, and transactions must be conducted in a halal (permissible) manner. This appeals to individuals and businesses who prioritize ethical and responsible financial practices.
The global reach of Islamic banking can be seen in the establishment of Islamic financial institutions and the growing number of countries offering Shariah-compliant products and services. Islamic banks, such as the Islamic Development Bank (IDB) and Qatar Islamic Bank, have expanded their operations to cater to the needs of Muslim communities across the globe.
Today, Islamic banking operates in various countries, including those with significant Muslim populations, such as Saudi Arabia, Malaysia, and Indonesia. Additionally, many non-Muslim majority countries, including the United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia, have also embraced Islamic banking to cater to the needs of their Muslim citizens and attract investments from the Islamic finance sector.
The growth of Islamic banking has been supported by government initiatives and regulatory frameworks that promote and facilitate Islamic finance. Countries like Malaysia and Bahrain, for example, have established dedicated regulatory bodies to oversee and support the development of Islamic banking within their jurisdictions.
Moreover, international financial institutions, such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank, have recognized the importance of Islamic banking and have started to collaborate with Islamic financial institutions to develop Islamic finance frameworks and promote financial inclusion.
Overall, the growth and global reach of Islamic banking reflect the increasing demand for ethical financial solutions and the principles of Islamic finance. As more countries and individuals embrace this alternative banking system, Islamic banking is poised to continue expanding and becoming an integral part of the global financial landscape.
Islamic Banking and Sustainable Development
Sustainable development is a concept that has gained significant attention in recent years. It refers to the idea of meeting the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Islamic banking, with its focus on ethical and socially responsible practices, aligns closely with the principles of sustainable development.
One of the key aspects of Islamic banking that contributes to sustainable development is the prohibition of interest (riba). Riba is seen as exploitative and unjust, as it allows for the accumulation of wealth without any productive contribution to society. Islamic banking operates on the basis of profit sharing and risk sharing, where both the bank and the customer share the profits and losses of a venture. This promotes a more equitable distribution of wealth and ensures that resources are used in a socially responsible manner.
In addition to the prohibition of interest, Islamic banking also promotes ethical investments that are in line with Islamic principles. This means that investments in industries such as alcohol, gambling, and tobacco are prohibited. Instead, Islamic banks focus on investing in sectors that have a positive impact on society, such as renewable energy, healthcare, and education. By directing funds towards sustainable and socially responsible projects, Islamic banking contributes to the long-term well-being of society and the environment.
Furthermore, Islamic banking encourages transparency and accountability in financial transactions. This is achieved through the use of contracts that clearly define the rights and responsibilities of all parties involved. This ensures that all transactions are conducted in a fair and ethical manner, minimizing the risk of fraud and corruption. By promoting transparency and accountability, Islamic banking contributes to a more stable and sustainable financial system.
In conclusion, Islamic banking and sustainable development go hand in hand. The principles and practices of Islamic banking promote ethical and socially responsible behavior, which is essential for achieving sustainable development. By prohibiting interest, promoting ethical investments, and encouraging transparency and accountability, Islamic banking contributes to a more equitable and sustainable future.
The Challenges Faced by Islamic Banks
Islamic banks face several challenges that are unique to their operations and principles. These challenges can make it difficult for Islamic banks to compete with conventional banks and hinder their growth in the global financial market. Some of the key challenges faced by Islamic banks are:
- Limited investment opportunities: Islamic banks have to comply with Shariah principles, which restrict certain types of investments such as those involving interest, gambling, or uncertainty. This limits their investment opportunities and may result in lower returns compared to conventional banks.
- Lack of Shariah scholars: Islamic banks require the expertise of Shariah scholars to ensure that their operations comply with Islamic principles. However, there is a shortage of qualified scholars, which can delay decision-making and hinder the growth of Islamic banks.
- Legal and regulatory framework: Islamic banking operates within the legal and regulatory framework of conventional banking systems. This can create challenges as the regulatory environment may not fully support or understand the unique nature of Islamic banking operations. Islamic banks often have to work closely with regulators to develop appropriate frameworks.
- Profit-and-loss sharing: Islamic banks follow the principle of profit-and-loss sharing, which means they share both profits and losses with their clients. While this promotes fairness, it also exposes Islamic banks to higher risks. They need to carefully manage their investments to ensure the stability and profitability of their operations.
- Higher transaction costs: Islamic banks may face higher transaction costs compared to conventional banks. This is due to the need for additional monitoring, compliance, and documentation related to Shariah compliance. These additional costs can impact the overall profitability of Islamic banks.
- Limited product offerings: Islamic banks may have limited product offerings compared to conventional banks. This is because they need to develop products and services that are in line with Islamic principles. The limited product range can make it challenging to attract a wider range of customers and compete with conventional banks.
Despite these challenges, Islamic banks have been growing steadily in recent years and gaining recognition in the global financial industry. Efforts are being made to overcome these challenges through innovation, collaboration, and the development of supportive regulatory frameworks.
The Role of Islamic Banking in Poverty Alleviation
Islamic banking, with its unique principles and ethical framework, has the potential to play a significant role in poverty alleviation. It offers an alternative financial system that promotes economic justice and societal welfare.
One of the key features of Islamic banking is its emphasis on social responsibility and fairness. It prohibits the charging of interest (riba) and promotes risk-sharing, which aligns with the principles of Islamic economics and the welfare of society.
Islamic banks offer various financial products and services designed to support individuals and businesses in need, particularly those who are economically disadvantaged. These products include interest-free loans, microfinance, and investment opportunities in sectors that promote social development.
One of the main ways in which Islamic banking contributes to poverty alleviation is through microfinance. Islamic microfinance provides small loans to entrepreneurs, including those in rural areas and informal sectors, who lack access to traditional financial services. These loans help individuals start or expand their businesses, generate income, and improve their living standards.
Moreover, Islamic banking promotes ethical investment practices by encouraging investments in socially responsible sectors, such as renewable energy, healthcare, and affordable housing. By directing funds towards these sectors, Islamic banks contribute to the development of infrastructure, job creation, and the provision of essential services in underserved communities, thereby reducing poverty.
Islamic banking also encourages the concept of waqf, which involves endowments for public welfare. Waqf funds can be used to finance education, healthcare, and other social projects aimed at improving the quality of life for the underprivileged.
In addition to these direct approaches, Islamic banks also engage in corporate social responsibility activities by supporting initiatives that address poverty and inequality. They fund educational programs, vocational training, and community development projects, helping individuals acquire the skills and resources necessary to uplift themselves from poverty.
Overall, Islamic banking serves as a catalyst for poverty alleviation by providing inclusive financial services, promoting ethical investment practices, and actively engaging in social and community development activities. Its principles and practices offer an alternative model that seeks to address economic disparities and enhance the welfare of all members of society.
Islamic Banking and Economic Stability
Economic stability is a crucial factor in the overall well-being and development of any society. It ensures a steady and sustainable economic growth, protects against inflation and financial crises, and promotes investment and employment opportunities. In the context of Islamic banking, this stability is pursued through various principles and practices that adhere to Islamic ethics and values.
One of the key features of Islamic banking is the prohibition of interest, or Riba. This prohibition aims to eliminate unfair and exploitative practices in financial transactions, promoting a more equitable distribution of wealth and resources within the society. By eliminating interest, Islamic banking promotes a system where profit and loss sharing, as well as risk sharing, are emphasized.
Profit and loss sharing is a fundamental principle in Islamic banking. It encourages transparency, fairness, and accountability in financial transactions. In an Islamic banking system, both the banks and the customers share the risks and rewards of investments. This not only promotes a more equitable distribution of profits but also encourages responsible and prudent investment decisions by both parties.
Stability through diversification is another important aspect of Islamic banking. Islamic financial institutions are encouraged to diversify their investment portfolios to spread risk and reduce exposure to any individual asset or sector. This helps in stabilizing the economy and protecting against market fluctuations and potential losses.
Islamic banking and ethical investments go hand in hand. Islamic principles prohibit investments in businesses that are considered unethical or harmful to society, such as gambling, alcohol, or weapons. This focus on ethical investments promotes stability by ensuring that financial resources are directed towards socially responsible and sustainable economic activities.
Regulatory framework and governance play a crucial role in maintaining economic stability in Islamic banking systems. Islamic financial institutions are required to comply with Shariah principles and guidelines set by regulatory bodies. This ensures that the operations of these institutions are transparent, accountable, and aligned with the ethical principles of Islamic finance.
In conclusion, Islamic banking promotes economic stability by emphasizing principles such as profit and loss sharing, diversification, ethical investments, and a strong regulatory framework. These principles help in creating a financial system that is more resilient, equitable, and responsible, ultimately contributing to the overall stability and development of the economy.
Islamic Banking and Ethical Investments
Islamic banking operates under the principles of Shariah, which prohibits usury, speculation, and investments in businesses that are considered unethical or harmful to society. As a result, Islamic banks are required to make ethical investments that align with Islamic principles.
One of the main ethical considerations in Islamic banking is the prohibition of interest (riba). Islamic banks offer interest-free financing options, such as profit-sharing arrangements, leasing, or fee-based services. This ensures that the banks do not profit from charging interest, which is seen as exploitative in Islamic finance.
In addition to avoiding interest, Islamic banking also focuses on investing in businesses that are halal, meaning they are permissible according to Islamic law. This includes avoiding investments in industries related to alcohol, gambling, pork products, and other activities that are considered sinful in Islam.
Islamic banks also prioritize socially responsible investments that have a positive impact on society. This can include investments in renewable energy, healthcare, education, and other sectors that contribute to the well-being and development of communities.
Furthermore, Islamic banks follow the principles of risk-sharing and asset-backing. They are not allowed to engage in speculative activities or invest in complex financial instruments that involve excessive risk. Instead, they focus on investments that are backed by tangible assets and promote fairness and stability in the economy.
Overall, Islamic banking combines financial services with ethical considerations, making it an attractive option for individuals and businesses looking to align their financial activities with their religious beliefs and values. By following Shariah principles, Islamic banks strive to create a financial system that promotes fairness, justice, and social responsibility.
The Future of Islamic Banking Industry
The Islamic banking industry is experiencing significant growth and is expected to continue its expansion in the future. As the global Muslim population grows and there is an increasing demand for financial products and services that align with Islamic principles, the Islamic banking industry is poised to play a key role in the global economy.
1. Market Potential:
The potential market for Islamic banking is vast. With a Muslim population of over 1.8 billion worldwide, there is a large and growing customer base that is seeking Sharia-compliant banking options. This presents an opportunity for Islamic banks to attract customers who may have previously been underserved by traditional banking institutions.
2. Innovation:
The Islamic banking industry has shown a willingness to innovate and adapt to changing market dynamics. As technology continues to advance, Islamic banks have the opportunity to leverage digital platforms and fintech solutions to enhance their services and reach a broader customer base.
3. Regulatory Support:
Governments and regulators in many Muslim-majority countries have recognized the importance of Islamic finance and have implemented supportive regulatory frameworks. This has provided a conducive environment for the growth of the Islamic banking industry.
4. Ethical and Sustainable Finance:
Islamic banking operates on principles that emphasize fairness, transparency, and risk-sharing. As the global financial industry puts increasing emphasis on ethical and sustainable finance, Islamic banks are well-positioned to meet this demand. The principles of Islamic banking, such as avoiding excessive speculation and investing in real assets, align with the principles of sustainable finance.
5. Global Integration:
The Islamic banking industry has gradually become more integrated into the global financial system. International organizations, such as the International Islamic Financial Market (IIFM) and the Accounting and Auditing Organization for Islamic Financial Institutions (AAOIFI), have been established to develop standards and promote harmonization in Islamic finance practices. This integration enables Islamic banks to participate in cross-border transactions and attract international investors.
6. Education and Awareness:
As the awareness of Islamic banking grows, there is a need for greater education and training in this field. Institutions, both academic and industry-focused, are playing a crucial role in building the necessary expertise in Islamic finance. This will help ensure the growth and sustainability of the Islamic banking industry.
Overall, the future of the Islamic banking industry looks promising. With a growing market, innovation, regulatory support, ethical and sustainable finance principles, global integration, and increased education and awareness, Islamic banks are well-positioned to thrive and become a significant player in the global financial system.
Islamic Banking and Financial Inclusion
Financial inclusion refers to the accessibility and usage of financial services by individuals and businesses, especially those who are traditionally underserved or excluded from the formal banking sector. Islamic banking plays a significant role in promoting financial inclusion by offering an alternative banking system that caters to the needs of a broader range of people.
One of the core principles of Islamic banking is the prohibition of interest (riba). Instead of charging and receiving interest, Islamic banks operate on the concept of profit and loss sharing (PLS). This means that the financial institutions share the risk and reward with their clients, creating a more equitable and inclusive system.
The PLS system not only aligns itself with ethical and moral values but also helps to address the issue of financial exclusion. Interest-based banking often excludes individuals and businesses that do not meet the stringent criteria of conventional banks, such as those without collateral or a steady income. On the other hand, Islamic banking focuses on the client’s credibility and the viability of their business idea, making it more accessible and inclusive for entrepreneurs and small businesses.
In addition to the PLS system, Islamic banking also promotes financial inclusion through innovative products and services. For example, Islamic microfinance and micro-takaful (insurance) products specifically target low-income individuals and small businesses, providing them with access to the necessary funds and protection against risks.
Furthermore, Islamic banking institutions prioritize social responsibility and ethical investing. They offer Sharia-compliant investment options that align with Islamic principles, such as avoiding investments in industries like alcohol, gambling, and tobacco. This ensures that individuals and businesses can invest their money in line with their beliefs, which is particularly important for Muslims who may have religious restrictions on certain types of investments.
Islamic banking also promotes financial education and literacy, another crucial aspect of financial inclusion. Through various outreach programs and initiatives, Islamic banks aim to educate individuals and communities about Islamic finance principles and how they can benefit from them. This helps to empower individuals with knowledge and understanding, enabling them to make informed financial decisions and participate fully in the banking system.
| Advantages of Islamic Banking in Promoting Financial Inclusion: |
|---|
|
In conclusion, Islamic banking plays a vital role in promoting financial inclusion by offering an alternative and inclusive banking system. By replacing the interest-based system with profit and loss sharing, focusing on client credibility, offering innovative products, and promoting social responsibility and financial education, Islamic banking ensures that a broader range of individuals and businesses can access and benefit from financial services.
FAQ
What is Islamic banking?
Islamic banking is a financial system that operates in accordance with Islamic principles, which prohibit interest (riba) and promote risk-sharing and ethical business practices.
Why is interest considered haram in Islam?
Interest is considered haram (forbidden) in Islam because it is seen as exploiting the borrower and creating an unequal relationship. Islamic teachings promote fairness and discourage exploitative practices.
How does Islamic banking work?
In Islamic banking, instead of charging interest on loans, financial institutions enter into partnerships or profit-sharing agreements with their clients. They share both the risk and the profit from the investment, creating a more equitable system.
Is Islamic banking halal?
Yes, Islamic banking is considered halal (permissible) according to Islamic law. It operates in compliance with Shariah principles and ethical guidelines, making it a viable option for Muslim individuals and businesses.
What are the key principles of Islamic banking?
The key principles of Islamic banking include prohibition of interest (riba), adherence to ethical business practices, risk-sharing, and the promotion of socio-economic justice and welfare.
Are all financial products in Islamic banking halal?
No, not all financial products in Islamic banking are automatically considered halal. Each product or transaction needs to be evaluated to ensure compliance with Shariah principles. Islamic scholars play a crucial role in providing guidance and certification for halal financial products.