The Islamic calendar, also known as the Hijri calendar, is a lunar calendar used by Muslims around the world to determine the dates of important religious events and observances. Unlike the Gregorian calendar, which is based on the solar cycle, the Islamic calendar follows the phases of the moon.
Today, many Muslims rely on various online platforms and apps to find out the current Islamic date. These platforms provide an easy and convenient way to keep track of the Islamic calendar and stay connected to their religious traditions.
The Islamic calendar consists of 12 lunar months, each lasting either 29 or 30 days, depending on the sighting of the moon. This means that the Islamic date changes every day, according to the lunar cycle. The date begins at sunset, so it is common for Muslims to wait until after sunset to determine the start of a new day in the Islamic calendar.
In Islamic tradition, the day begins at Maghrib, the evening prayer, and ends at Maghrib the following day.
The Islamic date is important for Muslims as it helps them plan their religious activities, such as fasting during Ramadan, celebrating Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha, and observing other significant events in the Islamic calendar. It also serves as a reminder of the lunar nature of time in Islam and the importance of following the moon’s cycles.
In conclusion, finding out today’s date in the Islamic calendar is essential for Muslims to stay connected to their faith and fulfill their religious obligations. With the help of modern technology, it has become easier than ever to determine the Islamic date and stay in touch with the rich traditions of Islam.
What Islamic Date is Today?
The Islamic calendar, also known as the Hijri calendar, is a lunar calendar used by Muslims to determine the dates for Islamic religious observances. It is based on the observation of the moon and follows a 12-month lunar year.
Today’s Islamic date can be found by referring to a Hijri calendar or by using online Islamic date converters. These converters provide the current Islamic date based on the Gregorian calendar.
The Islamic date consists of the day, month, and year. The day starts at sunset and ends at the following sunset in the Islamic calendar. The months in the Islamic calendar are based on the lunar cycle, which means they can be 29 or 30 days long.
It’s important to note that the Islamic calendar is not synchronized with the solar calendar used in the Gregorian calendar. As a result, the Islamic date advances approximately 11 days each year compared to the Gregorian calendar.
To determine today’s Islamic date, you can use an online Islamic date converter or refer to a reliable Hijri calendar. These resources will provide you with the accurate Islamic date for today.
Knowing the Islamic date is significant for Muslims as it helps them keep track of important religious observances, such as fasting during Ramadan, performing the Hajj pilgrimage, and celebrating Islamic holidays.
Islamic Calendar
The Islamic calendar, also known as the Hijri calendar, is a lunar calendar used by Muslims around the world to determine the dates of Islamic events and religious observances. It is based on the moon’s motion relative to the Earth, with each month starting and ending with the sighting of the new moon.
The Islamic calendar has 12 lunar months and is about 10 to 11 days shorter than the Gregorian calendar, which is based on the solar year. This means that Islamic dates do not align with the same dates on the Gregorian calendar and vary from year to year.
The beginning of the Islamic calendar is marked by the migration of the Prophet Muhammad from Mecca to Medina in 622 CE, known as the Hijra. This event is considered significant in Islamic history and serves as the starting point of the Islamic calendar.
Each month in the Islamic calendar can have either 29 or 30 days, depending on the sighting of the moon. The calendar follows a 30-year cycle, with 11 leap years of 355 days and 19 common years of 354 days. The leap years help align the lunar calendar with the solar year.
Islamic months are not named after specific events, but rather the changes in the moon’s appearance. The first month is Muharram, followed by Safar, Rabi al-Awwal, Rabi al-Thani, Jumada al-Awwal, Jumada al-Thani, Rajab, Sha’ban, Ramadan, Shawwal, Dhu al-Qadah, and Dhu al-Hijjah.
The Islamic calendar is primarily used for determining the dates of religious observations, such as the start and end of Ramadan, the month of fasting. It is also used for scheduling Islamic holidays, such as Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha, which mark the end of Ramadan and the Hajj pilgrimage, respectively.
It is important to note that Islamic dates may vary based on regional moon sightings and different interpretations. Therefore, it is advisable to consult with local religious authorities or Islamic organizations for accurate dates and observances.
In summary, the Islamic calendar is a lunar calendar used by Muslims worldwide to determine the dates of Islamic events and religious observances. It follows a 30-year cycle and is based on the sighting of the new moon. The calendar is important for Muslims to schedule their religious practices and celebrations accurately.
Finding Out Today’s Date
To find out today’s date in the Islamic Calendar, you can refer to the following sources:
1. Hijri Date Conversion Websites
There are several online platforms that provide a conversion tool to convert the Gregorian date to the Islamic date. Some popular websites include:
These websites allow you to enter the current Gregorian date and will provide you with the corresponding Islamic date.
2. Islamic Calendar Apps
If you prefer using mobile applications, there are various Islamic calendar apps available for both Android and iOS devices. These apps not only provide the current Islamic date but also offer additional features like prayer times and Qibla direction. Some popular apps include:
- Islamic Calendar (iOS)
- Islamic Calendar (Android)
- IslamicFinder: Prayer Times, Quran, Qibla & Azan (Android)
These apps provide a convenient way to access the Islamic date and other essential Islamic information on your smartphone.
3. Local Mosque or Islamic Center
You can also inquire at your local mosque or Islamic center to find out the current Islamic date. They may have a calendar or provide you with the required information directly.
Utilizing these resources will help you stay updated with the current Islamic date, enabling you to plan your activities in accordance with the Islamic calendar.
Importance of Islamic Date
The Islamic date holds great significance in the lives of Muslims. It is not just a number or a date, but it represents the religious and cultural heritage of the Islamic faith. The following points highlight the importance of the Islamic date:
- Muslim Festivals and Celebrations: The Islamic date plays a crucial role in determining Muslim festivals and celebrations. Festivals like Eid ul-Fitr and Eid ul-Adha are celebrated based on the sighting of the moon and the Islamic lunar calendar. Muslims rely on the Islamic date to mark the beginning and end of these important religious occasions.
- Prayer Times: Salah, the daily ritual prayers of Islam, are performed at specific times throughout the day. The Islamic date helps Muslims determine the prayer times based on the position of the sun. It serves as a guiding factor in maintaining regularity and discipline in their daily worship.
- Commemorating Historical Events: Islamic history is filled with significant events and milestones. Muslims commemorate events like the birth and death anniversaries of Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) and other important figures through specific rituals and acts of worship. The Islamic date helps in commemorating and remembering these events.
- Observance of Fasting: Muslims observe fasting during the holy month of Ramadan, which is determined by the Islamic date. Fasting from dawn to sunset is an essential pillar of Islam, and the Islamic date plays a crucial role in identifying the exact dates for this religious practice.
- Spiritual Reflection and Self-Growth: The Islamic date serves as a reminder for Muslims to reflect on their spiritual journey and engage in self-growth. It prompts individuals to assess their actions, seek forgiveness, and increase their devotion towards Allah.
In conclusion, the Islamic date holds immense importance in the lives of Muslims. It guides them in various aspects of their religious practices and helps maintain a strong connection with their faith and heritage. Recognizing and understanding the Islamic date facilitates the observance of religious rituals, fosters unity within the Muslim community, and enables Muslims to lead a more fulfilling spiritual life.
Islamic New Year
Islamic New Year, also known as Hijri New Year or Arabic New Year, is the beginning of the Islamic lunar calendar year. The Islamic lunar calendar is based on the sighting of the new moon, and each year consists of 12 lunar months, making the Islamic year shorter than the Gregorian calendar year.
The Islamic New Year is a time for reflection and introspection for Muslims around the world. It is an opportunity to look back on the past year and set goals for the upcoming year. Muslims often use this time to engage in prayer, fasting, and acts of charity.
The first month of the Islamic calendar is called Muharram. It is considered one of the four sacred months in Islam, along with Rajab, Dhul-Qa’dah, and Dhul-Hijjah. The tenth day of Muharram, known as Ashura, holds special significance for Muslims. It commemorates various events in Islamic history, including the day Allah saved the Children of Israel from Pharaoh and the day Prophet Muhammad observed fasting and encouraged Muslims to do the same.
During the Islamic New Year, Muslims may gather for special prayers at mosques, listen to sermons about the importance of the new year, and spend time with family and friends. Some Muslims also take the opportunity to make pilgrimage to holy sites and perform special religious rituals.
It is important to note that the Islamic calendar is different from the Gregorian calendar, which is widely used in the Western world. Therefore, the date of the Islamic New Year varies each year on the Gregorian calendar.
Overall, the Islamic New Year is a time for Muslims to reflect on their faith, seek forgiveness, and strive to become better individuals. It is a time of renewal, growth, and gratitude.
Muharram
Muharram is the first month of the Islamic calendar. It is one of the four sacred months mentioned in the Quran. The word “Muharram” means “forbidden” or “sacred” in Arabic, indicating the sanctity of this month.
Muharram holds special significance for Muslims around the world, particularly for Shi’a Muslims. It is during this month that the event of the Battle of Karbala took place in the year 680. This event is of great importance in Shi’a Islam and is commemorated annually during the first ten days of Muharram.
During Muharram, Muslims engage in various activities to commemorate the martyrdom of Imam Husayn, the grandson of Prophet Muhammad. These activities include mourning processions, recitation of elegiac poetry, and reenactments of the Battle of Karbala. Many Muslims also fast on the tenth day of Muharram, known as Ashura, to remember the sacrifices made by Imam Husayn and his companions.
It is important to note that while Muharram is a month of mourning and reflection for Shi’a Muslims, it is not a month of celebration or joy for them. It is a time to remember and grieve the tragedy of Karbala.
Overall, Muharram is a significant month in the Islamic calendar, marked by remembrance, reflection, and mourning for the events of Karbala. It is a time for Muslims to honor the sacrifices made by Imam Husayn and his companions and to reaffirm their faith and commitment to the teachings of Islam.
Safar
Safar is the second month in the Islamic calendar. It is one of the four sacred months in Islam, along with Muharram, Rajab, and Dhu al-Qa’dah. In Arabic, the word “safar” means “to travel” or “journey”.
According to Islamic tradition, the month of Safar is believed to be an unlucky month, associated with trials and tribulations. However, it is important to note that Islamic beliefs and practices vary among different cultures and communities.
Some Muslims may observe certain practices during the month of Safar as a way to seek protection and blessings. This could include performing extra prayers, reciting specific verses from the Quran, or seeking refuge in God.
However, it is important to remember that Islam does not encourage superstitions or attributing negative events to specific times or dates. Muslims are encouraged to put their trust in God and to rely on their faith and good deeds to protect them from harm.
- In the Islamic calendar, Safar lasts for 30 days.
- Safar is preceded by the month of Muharram and followed by the month of Rabi’ al-Awwal.
- During Safar, Muslims commemorate the martyrdom of Imam Hussein, the grandson of Prophet Muhammad, which occurred on the 10th of Muharram.
It is important to approach the month of Safar with respect and a spirit of understanding. While some may consider it an unlucky month, it is also a time for reflection, gratitude, and seeking God’s guidance.
Rabi al-Awwal
Rabi al-Awwal is the third month in the Islamic lunar calendar. It is considered an important month in Islamic history and culture.
The word “Rabi” in Arabic means “spring”, and “Awwal” means “first”. Therefore, Rabi al-Awwal can be translated to “the first spring”. It is believed that this month brings spiritual rejuvenation and growth.
Rabi al-Awwal holds significance for Muslims as it is the month in which the Prophet Muhammad was born. Many Muslims commemorate the birth of the Prophet during this month by organizing special events, lectures, and gatherings.
During Rabi al-Awwal, Muslims also reflect upon the life and teachings of the Prophet Muhammad. They study his sayings and actions in order to gain a deeper understanding of Islam and to strengthen their faith.
In addition, Rabi al-Awwal is a month of gratitude and generosity for many Muslims. They engage in charitable acts, give donations, and help those in need as a way to express their gratitude for the blessings they have received.
It is important to note that the precise date of the Prophet’s birth is a subject of debate among scholars. Different sects within Islam may celebrate the birth of the Prophet on different days within Rabi al-Awwal.
Overall, Rabi al-Awwal is a month of reflection, celebration, and gratitude for Muslims around the world.
Rabi al-Thani
Rabi al-Thani is the fourth month of the Islamic lunar calendar. It follows the month of Rabi al-Awwal and precedes the month of Jumada al-Awwal.
The name “Rabi al-Thani” translates to “the second spring” in English. It is called so because it falls during the spring season in many parts of the world. During this month, the weather becomes milder, and the days start to get longer.
In Rabi al-Thani, Muslims commemorate several important events in Islamic history, including the birth anniversary of Imam Hasan ibn Ali, the grandson of Prophet Muhammad, and the martyrdom anniversary of Lady Fatimah, the daughter of Prophet Muhammad. These occasions are observed by Muslims through special prayers, lectures, and gatherings.
It is recommended for Muslims to increase their acts of worship and seek spiritual growth during the month of Rabi al-Thani. Muslims may engage in additional prayers, recitation of the Quran, and acts of charity to earn rewards and draw closer to Allah.
Like other months in the Islamic calendar, the exact beginning of Rabi al-Thani is determined by the sighting of the moon. Islamic scholars and religious authorities make the announcement based on the moon sighting reports from trustworthy sources.
Overall, Rabi al-Thani holds significance in the Islamic calendar as a time for reflection, celebration, and spiritual growth for Muslims around the world.
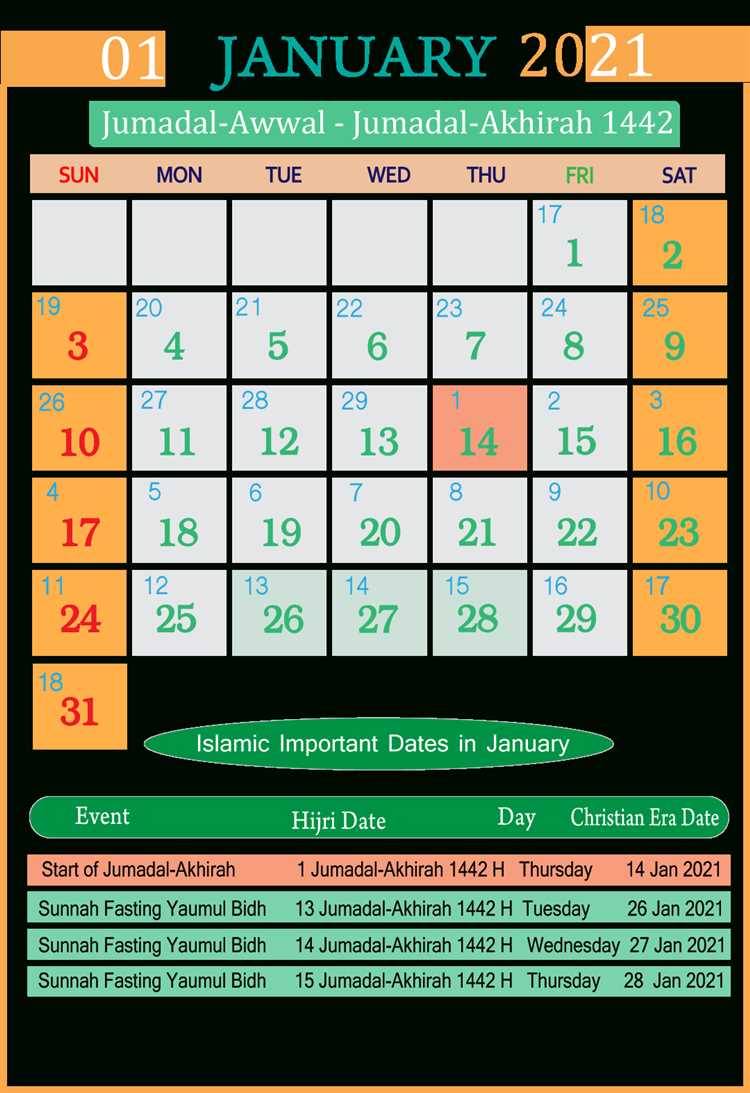
Jumada al-Ula
Jumada al-Ula is the fifth month of the Islamic lunar calendar. It follows the month of Rabi al-Thani and is followed by the month of Jumada al-Akhirah. Jumada al-Ula is also known as Jumada al-Awwal or Jumada al-Ula. It is a sacred month for Muslims, and it holds significance in Islamic history and traditions.
The word “Jumada” means “dry” or “parched” in Arabic. The month is named Jumada al-Ula because it falls during the dry season in the Arabian Peninsula. It is a time when the land is parched and water is scarce, making it a month of reflection and appreciation for the blessings of water and sustenance.
During Jumada al-Ula, Muslims are encouraged to engage in acts of worship, such as fasting, prayer, and recitation of the Quran. It is also a time for self-reflection, seeking forgiveness, and strengthening one’s faith.
Jumada al-Ula is also associated with significant events in Islamic history. For example, it was during this month that the Battle of Mu’tah took place in the year 8 AH (629 CE). The battle involved a confrontation between the Muslim forces and the Byzantine Empire, and it is remembered for the bravery and sacrifice of the Muslim soldiers.
To commemorate the significance of Jumada al-Ula, Muslims may engage in additional prayers and remembrance of Allah. They may also participate in reciting specific prayers or seeking blessings during this month.
Overall, Jumada al-Ula is a time for Muslims to deepen their faith and seek closeness to Allah. It is a month of reflection, gratitude, and spiritual growth.
Jumada al-Thani
Jumada al-Thani is the sixth month in the Islamic lunar calendar. It follows Jumada al-Ula and precedes Rajab. Jumada al-Thani is also known as Jumada al-Akhir or Jumada al-Sani.
The word “Jumada” in Arabic means “dry” or “parched”, which signifies the dry season in the Arabian Peninsula during this month. The weather is usually hot and dry during Jumada al-Thani.
Jumada al-Thani is considered a sacred month in Islam, along with three other months which are Rajab, Dhu al-Qi’dah, and Dhu al-Hijjah. These months are believed to be months of peace and a time to focus on spiritual growth and reflection.
There are no specific religious observances or holidays associated with Jumada al-Thani. However, Muslims are encouraged to engage in acts of worship, such as fasting, charity, and increased prayers during this month.
It is important to note that the Islamic calendar is a lunar calendar, which means the dates of the months vary each year in relation to the Gregorian calendar. Therefore, it is necessary to consult an Islamic calendar or a reliable source to determine the exact dates of Jumada al-Thani for a particular year.
Key Dates in Jumada al-Thani
- The first day of Jumada al-Thani: This marks the beginning of the month and is determined by the sighting of the new moon.
- Mid-Jumada al-Thani: This is the middle of the month, which falls approximately on the 15th day of the lunar month.
- The last day of Jumada al-Thani: This marks the end of the month and is followed by the start of the next Islamic month, Rajab.
During Jumada al-Thani, Muslims may engage in additional prayers, recitation of the Quran, and other acts of worship to seek blessings and closeness to Allah. It is also a time to reflect on the passing of time and the importance of utilizing it wisely in the pursuit of righteousness.
Rajab
Rajab is the seventh month of the Islamic calendar. It is one of the four sacred months in Islam, along with Muharram, Dhu al-Qidah, and Dhu al-Hijjah. Rajab is a time for Muslims to increase their devotion and engage in acts of worship.
During Rajab, Muslims may choose to observe fasting on specific days, such as the first Thursday of the month or the 27th day of Rajab. This fasting is considered to be a way of seeking forgiveness and drawing closer to Allah.
Some Muslims also perform Umrah, a lesser pilgrimage, during Rajab. Umrah can be performed at any time of the year, but many choose to do it in the sacred month of Rajab as a way of gaining additional rewards.
The Night of Ascension, known as Isra and Mi’raj, is believed to have occurred in Rajab. It is said that the Prophet Muhammad was taken on a miraculous journey from Mecca to Jerusalem and then ascended to the heavens. This event is commemorated by some Muslims during Rajab by participating in special prayers and gatherings.
Overall, Rajab is a month of reflection, worship, and seeking spiritual growth for Muslims. It is a time to increase acts of devotion and strive for a deeper connection with Allah.
Sha’ban
Sha’ban is the eighth month of the Islamic calendar. It is the month that comes before the holy month of Ramadan. The name “Sha’ban” is derived from the Arabic word “sha’b,” which means “to separate” or “distinguish.” This is because the month of Sha’ban separates between Rajab and Ramadan, two significant months in the Islamic calendar.
Sha’ban holds religious significance for Muslims, as it is a time for spiritual preparation for the coming month of Ramadan. Many Muslims engage in voluntary fasting during this month, especially on the 15th day called “Laylat al-Bara’ah” or “Night of Forgiveness.” It is believed that on this night, Allah determines the destiny of individuals for the coming year.
During Sha’ban, Muslims also increase their recitation of the Qur’an, engage in extra prayers, and reflect on their actions and intentions. They seek forgiveness for their past sins and make sincere efforts to improve themselves spiritually.
The 15th day of Sha’ban, known as “Mid-Sha’ban” or “Nisf Sha’ban,” is considered a special night of prayer and devotion. Many Muslims spend the night in worship and engage in acts of charity and kindness. It is also a time for family gatherings and reconnecting with loved ones.
- Sha’ban is the month that comes before Ramadan.
- The name “Sha’ban” means “to separate” or “distinguish.”
- Many Muslims engage in voluntary fasting during Sha’ban.
- The 15th day of Sha’ban is known as “Laylat al-Bara’ah” or “Night of Forgiveness.”
- Mid-Sha’ban (Nisf Sha’ban) holds special significance in the Islamic calendar.
Ramadan
Ramadan is the ninth month of the Islamic lunar calendar and is considered one of the holiest months for Muslims around the world. During this month, Muslims observe fasting from dawn until sunset.
The start and end of Ramadan are determined by the sighting of the new moon, making it a highly anticipated time for Muslims to come together in worship and reflection. This month is not only a time of self-discipline and increased devotion, but also a time of community and togetherness.
During Ramadan, Muslims focus on fasting, prayer, and acts of charity. They abstain from food, drink, smoking, and other physical needs during daylight hours, to cleanse their souls and refocus their attention on spirituality. Fasting during Ramadan is one of the Five Pillars of Islam and is obligatory for all adult Muslims, with exceptions for certain groups such as the elderly, pregnant women, or those with health conditions.
In addition to fasting, Muslims increase their recitation of the Quran and engage in additional prayers called Taraweeh, which are performed collectively in the mosque after Isha prayers. It is believed that during Ramadan, the rewards for good deeds are multiplied, and Muslims strive to increase their acts of worship and seek forgiveness.
The end of Ramadan is marked by the celebration of Eid al-Fitr, a joyous festival that brings Muslims together to share meals, exchange gifts, and give thanks for completing the month of fasting. It is a time of family gatherings, generosity, and spreading happiness.
Overall, Ramadan is a special and meaningful month in the Islamic calendar, serving as a time for reflection, self-discipline, and renewal of faith. It is an opportunity for Muslims to strengthen their connection with Allah and with each other, fostering a sense of unity and spiritual growth within the community.
Eid al-Fitr
Eid al-Fitr, also known as the “Festival of Breaking the Fast,” is an important religious holiday celebrated by Muslims worldwide. It marks the end of Ramadan, the Islamic holy month of fasting.
Significance:
- Eid al-Fitr is a time of joyful celebration for Muslims, as it signifies the successful completion of Ramadan and the achievement of spiritual growth and self-discipline.
- It is a time for Muslims to come together as a community, strengthen their bonds, and express gratitude for the blessings received during the month of Ramadan.
Traditions and Customs:
- On the day of Eid al-Fitr, Muslims attend special congregational prayers at mosques or open prayer grounds. These prayers are usually followed by a sermon.
- After the prayers, Muslims exchange greetings of “Eid Mubarak,” meaning “Blessed Eid,” and embrace each other as a sign of unity and love.
- It is customary for Muslims to give charity, known as “Zakat al-Fitr,” to the less fortunate before the Eid prayers. This acts as a purification of their wealth and ensures that those in need can also partake in the festivities.
- Family and friends gather to celebrate Eid al-Fitr by eating special meals and sweets, visiting each other’s homes, and exchanging gifts.
Special Foods:
- During Eid al-Fitr, Muslims prepare and enjoy a variety of delicious dishes that vary from region to region. Some traditional foods include sweet vermicelli, biryani, samosas, and date-filled pastries.
- Sweets and desserts, such as baklava and sheer khurma, are also an integral part of the Eid al-Fitr celebrations.
Date:
The date of Eid al-Fitr is determined by the sighting of the new moon, which marks the beginning of the month of Shawwal in the Islamic calendar. As the Islamic calendar is lunar-based, the date of Eid al-Fitr changes each year and varies from country to country.
Eid al-Fitr is a time of joy, gratitude, and reflection for Muslims worldwide. It is an occasion to celebrate the completion of Ramadan and to spread love and goodwill among family, friends, and the community.
Shawwal
Shawwal is the tenth month in the Islamic calendar. It follows the month of Ramadan and is considered a month of celebration and joy for Muslims around the world. The name Shawwal comes from the word “shawaal” which means “to raise” or “to elevate”, indicating the elevated status and importance of this month.
One of the most important events in Shawwal is the celebration of Eid al-Fitr. This marks the end of Ramadan and the fasting period, and is a time for Muslims to come together with family and friends to celebrate the completion of this spiritual month. It is a day of gratitude, feasting, and giving back to the community.
In addition to Eid al-Fitr, Shawwal also holds significance because it is the month in which the Prophet Muhammad peace be upon him performed the first voluntary fasting after Ramadan. This fasting is known as the “six days of Shawwal” and is recommended for Muslims who are physically capable to observe it.
The Islamic calendar follows a lunar cycle, so each month begins with the sighting of the new moon. The exact start and end dates of Shawwal can vary depending on the moon sighting, so it is important for Muslims to rely on local or regional moon sighting announcements to determine the beginning and end of the month.
During Shawwal, Muslims are encouraged to continue their good deeds, acts of worship, and charity. It is a time to reflect on the blessings and spiritual growth achieved during Ramadan and to carry those virtues forward into the rest of the year.
Dhu al-Qidah
Dhu al-Qidah is the eleventh month in the Islamic calendar. It is one of the four sacred months in Islam, along with Dhu al-Hijjah, Muharram, and Rajab. The name “Dhu al-Qidah” means “the month of truce” or “the month of sitting.”
Dhu al-Qidah is significant because it precedes the month of Hajj, which begins on the first day of Dhu al-Hijjah. During Dhu al-Qidah, it is recommended for Muslims to perform voluntary acts of worship and prepare themselves spiritually for the upcoming month of Hajj.
There are no specific rituals or practices unique to Dhu al-Qidah. However, it is encouraged to engage in good deeds, such as giving charity, reciting the Quran, and seeking forgiveness. Muslims may also participate in optional fasting during this month.
It is important to note that the Islamic calendar is based on the lunar cycle, so the dates of each month may vary from year to year in comparison to the Gregorian calendar.
Overall, Dhu al-Qidah is a month of spiritual preparation and reflection for Muslims before the holy month of Hajj.
Dhu al-Hijjah
Dhu al-Hijjah is the twelfth and final month in the Islamic lunar calendar. It is a significant month for Muslims around the world, as it includes the Hajj, which is the pilgrimage to the holy city of Mecca. During this month, Muslims from different parts of the world gather in Mecca to perform various rituals and acts of worship.
The name “Dhu al-Hijjah” translates to “the month of the pilgrimage” in Arabic. It is during this month that Muslims who are financially and physically capable make the pilgrimage to Mecca at least once in their lifetime. The Hajj is considered one of the five pillars of Islam and is a deeply spiritual journey for Muslims.
In addition to the Hajj, Dhu al-Hijjah is also a month of fasting and other acts of worship. It is recommended to fast on the first nine days of this month, particularly on the ninth day which is known as the Day of Arafah. This day is considered highly blessed and it is believed that fasting on this day expiates sins of the previous year and the coming year.
During Dhu al-Hijjah, Muslims also perform the ritual sacrifice known as Qurbani. This involves the slaughtering of an animal, such as a sheep or a goat, as an act of obedience to Allah and as a means of giving thanks for His blessings. The meat from the sacrificed animal is distributed among family, friends, and the less fortunate.
Overall, Dhu al-Hijjah is a month of great spiritual significance for Muslims. It is a time for reflection, worship, and unity as Muslims from all corners of the world come together to fulfill their religious obligations and seek closeness to Allah.
Eid al-Adha
Eid al-Adha, also known as the Feast of Sacrifice, is one of the most important festivals in the Islamic calendar. It commemorates the willingness of Ibrahim (Abraham) to sacrifice his son as an act of obedience to God’s command. Just as Ibrahim was about to sacrifice his son, God provided a lamb to be sacrificed instead. This event is seen as a test of faith and is celebrated as a reminder of the importance of obedience and submission to God.
Eid al-Adha is celebrated on the 10th day of the Islamic month of Dhu al-Hijjah, which is the 12th month of the Islamic lunar calendar. The date of Eid al-Adha changes each year as the Islamic lunar calendar is shorter than the Gregorian calendar. It is based on the sighting of the new moon, so the exact date can vary depending on the location.
During Eid al-Adha, Muslims around the world perform special prayers and gather for communal prayers at mosques or open grounds. They also sacrifice an animal, usually a sheep, goat, or cow, in remembrance of Ibrahim’s willingness to sacrifice his son. The meat from the sacrificed animal is divided into three parts: one part for the person who performs the sacrifice, one part for family and friends, and one part for the less fortunate.
After the prayers and the sacrifice, the day is spent in feasting and celebration. Muslims dress in their finest clothes and visit family and friends, exchanging greetings and gifts. It is also a time for acts of charity and giving, with many Muslims donating to those in need.
Eid al-Adha is a time of joy, gratitude, and reflection for Muslims worldwide. It is an opportunity to strengthen family and community bonds and to remember the importance of sacrifice and obedience in one’s faith.
Mohammad’s Birthday
The birthday of Prophet Mohammad, also known as Mawlid al-Nabi or Eid-e-Milad, is an important event for Muslims around the world. It is celebrated on the 12th day of the Islamic month of Rabi’ al-Awwal. This day is considered a significant occasion to reflect on the life and teachings of the Prophet.
Prophet Mohammad was born in the city of Mecca, in what is now Saudi Arabia, on the 12th day of Rabi’ al-Awwal in the year 570 CE. He is regarded as the last prophet and the final messenger of Allah (God) in Islam. Mohammad’s teachings and actions, as recorded in the holy book of Quran and Hadith, form the basis of Islamic beliefs and practices.
On Mohammad’s birthday, Muslims gather in mosques and homes to offer prayers, recite Quran, and listen to sermons that focus on the life and legacy of the Prophet. Many also engage in acts of charity and do good deeds as a way of expressing gratitude for the guidance and teachings of Mohammad.
It is worth noting that the celebration of Mohammad’s birthday varies among different Muslim communities and countries. Some may organize large processions, decorate streets, and hold public lectures, while others may mark the occasion with more subdued gatherings within their homes or local mosques.
Overall, Mohammad’s birthday is a time for Muslims to remember the Prophet, honor his teachings, and strive to follow his example of compassion, justice, and love for humanity.
Milad un-Nabi
Milad un-Nabi, also known as Mawlid or the Birth of the Prophet, is an Islamic holiday that commemorates the birth of Prophet Muhammad. It is celebrated on the 12th day of Rabi’ al-Awwal, which is the third month of the Islamic lunar calendar.
During Milad un-Nabi, Muslims around the world gather to honor and remember the life, teachings, and contributions of Prophet Muhammad. This holiday is typically observed with various activities and customs, which may vary based on cultural and regional traditions.
One common practice during Milad un-Nabi is the recitation of poems and songs praising the Prophet Muhammad. Many Muslims also organize processions and parades, where people march through the streets singing hymns and displaying banners and flags with religious messages.
Another important aspect of Milad un-Nabi is the sharing of food and meals. People often prepare special dishes and distribute them among family, friends, and the less fortunate. This act of charity is considered a way to honor the Prophet’s teachings of generosity and compassion.
In some countries, Milad un-Nabi is a public holiday, and schools and government offices may be closed. Mosques and Islamic centers often hold special programs and events, including lectures, seminars, and exhibitions, to educate people about the life and message of Prophet Muhammad.
Overall, Milad un-Nabi is a significant occasion for Muslims to express their love and reverence for the Prophet Muhammad and to strengthen their spiritual connection to him and his teachings.
Islamic Holidays
The Islamic calendar is based on the lunar cycle and consists of 12 months. In addition to the regular days, there are several holidays observed by Muslims worldwide. These holidays are significant religious and cultural events that commemorate important moments in Islamic history. Here are some of the major Islamic holidays:
- Eid al-Fitr: This holiday marks the end of Ramadan, the holy month of fasting. Muslims celebrate with prayers, feasts, and giving to charity.
- Eid al-Adha: Also known as the “Festival of Sacrifice,” this holiday commemorates Ibrahim’s willingness to sacrifice his son as an act of obedience to Allah. Muslims celebrate by sacrificing an animal and distributing the meat to the needy.
- Mawlid al-Nabi: This holiday celebrates the birth of the Prophet Muhammad. Muslims gather for prayers, recitations of the Quran, and to learn about the life and teachings of the Prophet.
- Ashura: This day marks the martyrdom of Imam Hussein, the grandson of Prophet Muhammad. It is observed with fasting, special prayers, and mourning.
- Laylat al-Qadr: Also known as the “Night of Power,” it commemorates the night when the first verses of the Quran were revealed to the Prophet Muhammad. Muslims spend the night in prayer and reflection.
- Islamic New Year: Muslims observe the Islamic New Year with fasting, prayers, and reflection on the Hijra, the migration of the Prophet Muhammad from Mecca to Medina.
These holidays are an important part of the Islamic calendar and provide an opportunity for Muslims to come together with family and friends, reflect on their faith, and engage in acts of charity and worship.
Islamic Lunar Calendar
The Islamic lunar calendar follows a different system than the Gregorian calendar commonly used in the Western world. It is based on the cycles of the moon, with each month beginning at the sighting of the new moon.
The Islamic lunar calendar consists of 12 months, each lasting either 29 or 30 days. The months are ordered as follows: Muharram, Safar, Rabi’ al-Awwal, Rabi’ al-Thani, Jumada al-Ula, Jumada al-Thani, Rajab, Sha’ban, Ramadan, Shawwal, Dhu al-Qadah, and Dhu al-Hijjah. The exact length of each month is determined by the sighting of the new moon and may vary from year to year.
The year in the Islamic lunar calendar is shorter than the Gregorian year, as it consists of 354 or 355 days. This means that Islamic dates do not align with the same dates in the Gregorian calendar each year. As a result, Islamic holidays and important dates, such as the start of Ramadan, vary from year to year in the Gregorian calendar.
To keep track of the Islamic lunar calendar, Muslims often refer to a lunar calendar or consult local authorities who determine the start and end of each month based on moon sightings. This ensures that Islamic dates are observed accurately and in accordance with the teachings of Islam.
Understanding the Islamic lunar calendar is important for Muslims worldwide as it dictates the timing of religious events, such as fasting during Ramadan, the Hajj pilgrimage, and the celebration of Eid-ul-Fitr and Eid-ul-Adha.
In conclusion, the Islamic lunar calendar is a unique system based on the cycles of the moon. It consists of 12 months and is shorter than the Gregorian calendar year. Muslims rely on this calendar to determine the timing of important religious dates and events.
Conversion to Gregorian Calendar
The Islamic calendar is a lunar calendar based on the cycles of the moon. Each month begins with the sighting of the new crescent moon. However, when it comes to determining the corresponding date in the Gregorian calendar, it can be a bit more complex.
The Islamic calendar is shorter than the Gregorian calendar with its 365 days. It consists of 12 lunar months, totaling approximately 354 or 355 days, depending on the sighting of the new moon. As a result, the Islamic dates do not align directly with the Gregorian dates and vary every year.
To convert an Islamic date to the Gregorian calendar, several factors need to be considered:
- Moon sighting: The start of each month in the Islamic calendar depends on the sighting of the new crescent moon. This can vary from region to region, so it is important to consider local sightings when making conversions.
- Lunar year: The Islamic calendar follows a lunar year, which is approximately 11 days shorter than the solar year. As a result, the Islamic dates shift approximately 11 days earlier each year in the Gregorian calendar.
- Leap years: The Gregorian calendar has leap years to account for the extra 0.25 days in a solar year. However, the Islamic calendar does not have leap years, so the annual shift in dates is not consistent.
Given these factors, it can be challenging to convert the Islamic date to the Gregorian calendar without specific astronomical data for the region in question. Therefore, it is recommended to use online resources or consult with a knowledgeable authority for accurate conversions.
Various websites and mobile applications provide automatic conversion tools that can calculate the corresponding Gregorian date for a given Islamic date, taking into account local moon sighting data and leap year adjustments. These tools ensure accurate conversions and simplify the process of determining today’s date in the Islamic calendar.
In conclusion, converting an Islamic date to the Gregorian calendar requires consideration of moon sightings, lunar years, and leap years. Using online conversion tools or consulting with experts in the field can help ensure accurate conversions and facilitate tracking Islamic dates in relation to the Gregorian calendar.
Calculating Islamic Date
Calculating the Islamic date involves a complex lunar calendar system. The Islamic calendar is based on the lunar cycle, which means that the months are determined by the sighting of the new moon. The Islamic calendar consists of 12 months with each month lasting for either 29 or 30 days.
The start of the Islamic calendar is marked by an important event in Islamic history, the Hijra, which refers to the migration of the Prophet Muhammad from Mecca to Medina in 622 AD. The Islamic calendar is also known as the Hijri calendar.
To calculate the Islamic date, the following steps can be followed:
- Determine the current lunar month: The lunar month can be determined by observing the moon and looking for the sighting of the new moon. Once the new moon is seen, the current lunar month is known.
- Determine the current lunar day: The lunar day starts at sunset and lasts until the next sunset. The number of days in a lunar month can vary, so it is important to determine the current lunar day accurately.
- Calculate the Gregorian date: Once the current lunar month and lunar day are known, a conversion can be made to the Gregorian calendar, which is the standard calendar used in most parts of the world. Various conversion tools and online resources are available for this purpose.
It is important to note that the Islamic calendar is based on the lunar cycle, and as a result, the Islamic date is approximately 10 to 12 days shorter than the Gregorian date each year. This means that the Islamic dates will vary each year, and there will be a gradual shift in the Islamic calendar compared to the Gregorian calendar.
Overall, calculating the Islamic date involves a combination of observing the moon, tracking the lunar month, determining the lunar day, and converting it to the Gregorian calendar to obtain the Islamic date.
Online Islamic Date Converters
If you want to find out today’s date in the Islamic calendar or convert a Gregorian date to the equivalent Islamic date, there are several online tools available. These converters can help you easily determine the Islamic date for any given day.
1. IslamicFinder.org
IslamicFinder.org is a popular website that offers a wide range of Islamic tools, including an Islamic date converter. Simply visit their website and navigate to the date converter section. There, you can enter the desired Gregorian date and instantly get the corresponding Islamic calendar date.
2. Al-habib.info
Al-habib.info is another online resource that provides an Islamic date converter. The website offers a user-friendly interface where you can input the Gregorian date and convert it to the Islamic date. Additionally, they offer other helpful Islamic tools like a prayer time calculator.
3. Islamicity.org
Islamicity.org is a comprehensive Islamic website that offers various resources, including an Islamic date converter. You can easily access the date converter tool on their website and convert any Gregorian date to the corresponding Islamic date. Islamicity.org also provides information about upcoming Islamic holidays and important dates.
4. Dawateislami.net
Dawateislami.net is a website operated by a global Islamic organization called Dawat-e-Islami. They offer an Islamic date converter tool that allows you to convert dates between the Gregorian and Islamic calendars. The website also provides access to Islamic books, media, and scholarly resources.
5. Al-Islam.org
Al-Islam.org is a reputable online resource for Islamic knowledge and information. Along with their collection of Islamic books, they offer an Islamic date converter tool as well. You can easily convert dates between the Gregorian and Islamic calendars using their date converter.
These online Islamic date converters provide a convenient way to determine the Islamic date for any given day. Whether you’re planning for an Islamic event or simply want to stay aware of the current Islamic date, these tools can be extremely helpful.
FAQ:
What is the Islamic date today?
The Islamic date today is based on the lunar calendar and may vary depending on the sighting of the moon. To find out the exact Islamic date today, you can check with your local mosque or refer to an online Islamic calendar.
How does the Islamic calendar work?
The Islamic calendar is a lunar calendar consisting of 12 months in a year of 354 or 355 days. The months are determined by the sighting of the new moon, and each month begins with the sighting of the crescent moon. The Islamic calendar follows the Islamic lunar year, which is shorter than the Gregorian solar year.
Why does the Islamic date change every year?
The Islamic date changes every year because the Islamic calendar is based on the lunar cycle. The lunar year is shorter than the solar year, so the dates of the Islamic calendar do not align with the dates of the Gregorian calendar. This is why the Islamic date moves forward approximately 11 days each year.
Is there a difference between the Islamic date and the Gregorian date?
Yes, there is a difference between the Islamic date and the Gregorian date. The Gregorian calendar is a solar calendar, while the Islamic calendar is a lunar calendar. As a result, the dates of the Islamic calendar do not correspond exactly to the dates of the Gregorian calendar. This difference can range from 10 to 12 days, depending on the year.