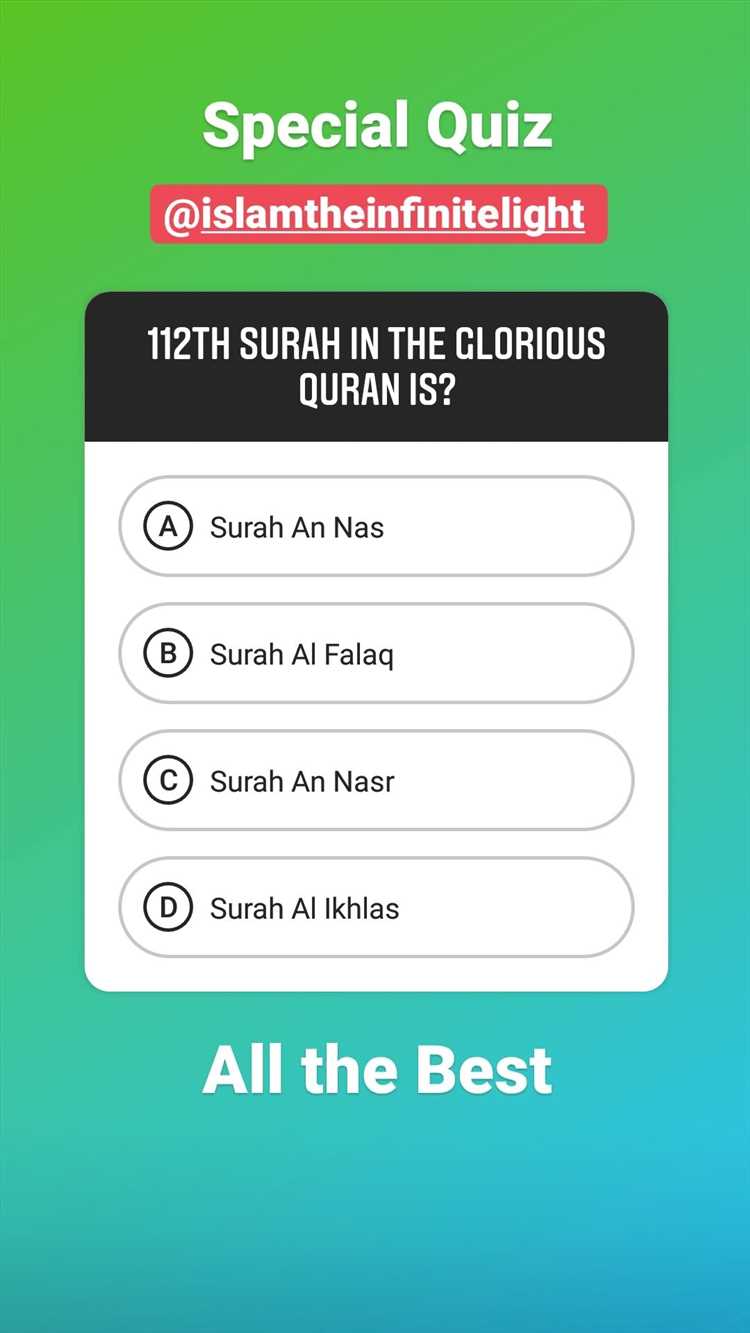
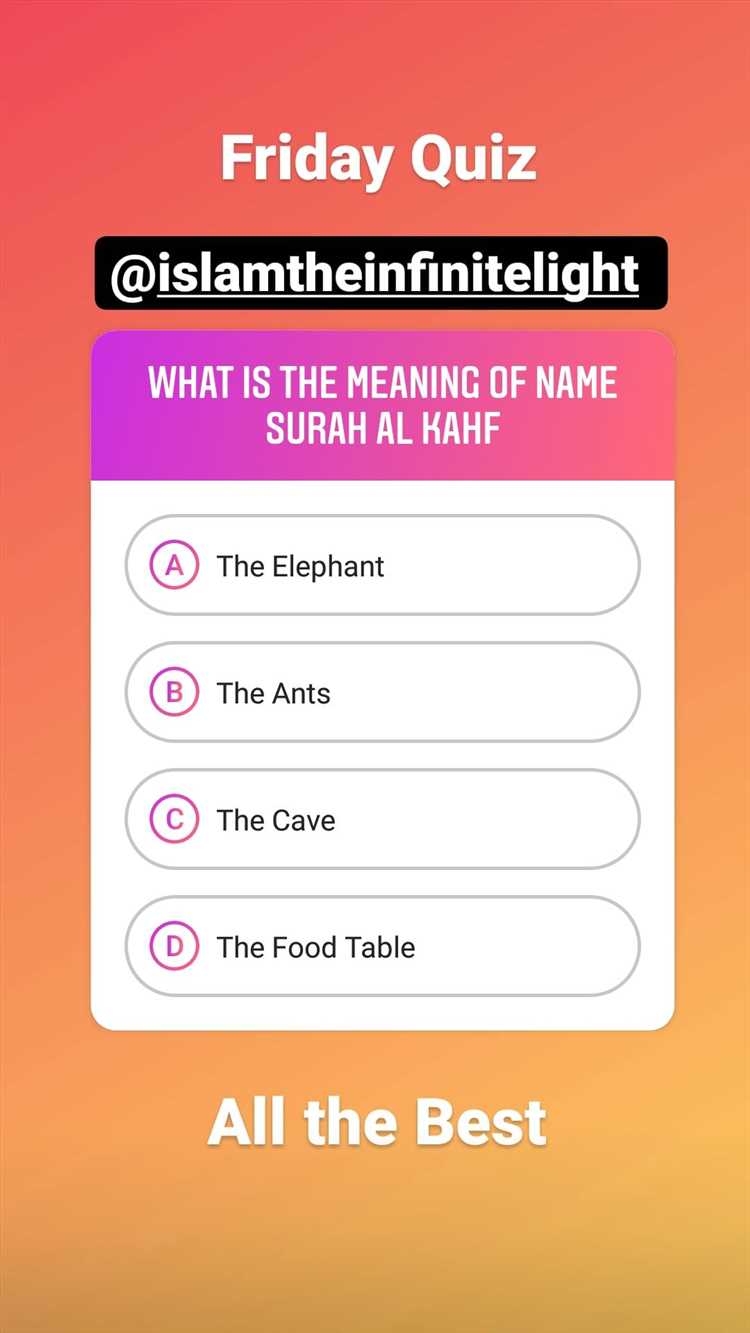
Are you curious about the Islamic faith and its rich history? Do you want to test your knowledge about Islam? Look no further! Our Islamic Quiz is designed to educate and entertain, offering you a unique opportunity to explore the fascinating world of Islam.
Islam is one of the world’s major religions, with a following of over 1.8 billion people. It originated in the 7th century in the Arabian Peninsula and spread across the globe through preaching and conquest. Islam is not only a religion but also a way of life, encompassing various aspects such as faith, prayer, charity, and pilgrimage.
Our Islamic Quiz covers a wide range of topics, including the life of Prophet Muhammad, the Five Pillars of Islam, Islamic art and architecture, and the contributions of Muslim scientists and scholars. With multiple choice questions and interesting facts, this quiz will challenge your knowledge and keep you engaged.
So, whether you are a Muslim looking to deepen your understanding of your faith or a non-Muslim eager to learn more about Islam, our Islamic Quiz is the perfect opportunity for you. Sharpen your mind, broaden your horizons, and embark on a journey of discovery with our Islamic Quiz!
What is Islam?
Islam is a monotheistic religion that originated in the 7th century CE in the Arabian Peninsula. It is based on the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad, who is believed to have received revelations from Allah, the Arabic name for God. Islam is one of the largest religions in the world, with over 1.8 billion followers, known as Muslims.
The foundation of Islam is the Quran, which Muslims believe to be the word of God as revealed to Muhammad. The Quran serves as a guide for moral and ethical living and provides Muslims with principles and teachings to follow in their daily lives.
The core beliefs of Islam are known as the Five Pillars of Islam. These include:
- Shahada: The declaration of faith, which states, “There is no god but Allah, and Muhammad is his prophet.”
- Salat: The obligation to pray five times a day facing the Kaaba in Mecca.
- Zakat: The giving of alms to the poor and those in need.
- Sawm: Fasting during the holy month of Ramadan from sunrise to sunset.
- Hajj: The pilgrimage to Mecca that all Muslims are required to make at least once in their lifetime, if physically and financially able.
Islam is not just a religion, but also a way of life. It encompasses all aspects of life, including social, economic, and political systems. Muslims strive to follow the teachings of Islam in all aspects of their lives, seeking to achieve spiritual, moral, and ethical growth.
Islam promotes peace, justice, and compassion. Muslims are encouraged to be kind, generous, and respectful towards others, regardless of their religion or background. It emphasizes the importance of unity, brotherhood, and equality among all believers.
Overall, Islam is a rich and diverse religion with a long history and a strong influence on societies and cultures around the world. It continues to be a source of guidance, comfort, and inspiration for millions of people worldwide.
The Five Pillars of Islam
The Five Pillars of Islam are the five basic acts of worship that are the foundation of Muslims’ faith. These pillars serve as a guide for practicing Muslims and are considered obligatory.
-
Shahada: The first pillar is the declaration of faith, known as the Shahada. It is the belief and affirmation that there is no god but Allah, and Muhammad is his prophet. This statement is considered the core of Islam and is recited by Muslims daily.
-
Salat: The second pillar is the act of prayer, known as Salat. It is the ritual prayer performed five times a day facing the Kaaba in Mecca. Muslims are required to pray at specific times throughout the day and night as a way to connect with Allah and seek his guidance.
-
Zakat: The third pillar is the act of giving, known as Zakat. It is the obligation for Muslims to give a portion of their wealth to those in need. The purpose of Zakat is to purify one’s wealth and to ensure the well-being of the less fortunate in society. It is usually given annually and is calculated based on a certain percentage of a person’s wealth or income.
-
Sawm: The fourth pillar is the act of fasting, known as Sawm. It is the practice of abstaining from food, drink, and other physical needs from dawn until sunset during the month of Ramadan. Fasting is an essential part of Islamic faith and is seen as a means of self-discipline, self-control, and an opportunity to purify the soul.
-
Hajj: The fifth and final pillar is the pilgrimage to Mecca, known as Hajj. It is an obligatory journey that Muslims must undertake at least once in their lifetime, if physically and financially able. During Hajj, Muslims perform a series of rituals that commemorate the actions of Prophet Muhammad and the prophets before him. It is a time of unity, self-reflection, and spiritual growth.
These Five Pillars of Islam provide Muslims with a framework for practicing their faith, ensuring spiritual growth, and strengthening their relationship with Allah. They form the basis of Islamic belief and serve as a guide for Muslims in their everyday lives.
Islamic Beliefs and Practices
Islam is a religion that holds a set of beliefs and practices that are followed by its followers, known as Muslims. These beliefs and practices shape the way Muslims lead their lives and interact with the world around them.
Beliefs
- Tawhid: Muslims believe in the concept of Tawhid, which means the oneness and unity of Allah (God). They believe that Allah is the one and only God and has no partners or associates.
- Prophets: Muslims believe that Allah has sent Prophets, including Adam, Abraham, Moses, Jesus, and Muhammad, among others, to guide humanity and deliver His message.
- Quran: Muslims believe that the Quran is the word of Allah, as revealed to the Prophet Muhammad through the angel Gabriel. The Quran is considered the ultimate source of guidance for Muslims.
- Angels: Muslims believe in the existence of angels, who are created by Allah and carry out His commands.
- Judgment Day: Muslims believe in the Day of Judgment, when all individuals will be held accountable for their actions in this world and will be rewarded or punished accordingly.
- Predestination: Muslims believe in the concept of predestination, or divine decree, which means that everything that happens is part of Allah’s plan.
Practices
Muslims are required to follow certain practices as part of their faith. These practices include:
- Prayer (Salah): Muslims are obligated to perform five daily prayers, which involve reciting specific prayers and physical movements, such as standing, bowing, and prostrating towards the Kaaba in Mecca.
- Charity (Zakat): Muslims are required to give a portion of their wealth to those in need as an act of worship and to purify their wealth.
- Fasting (Sawm): Muslims fast from dawn to sunset during the holy month of Ramadan as a way to purify their souls and gain self-discipline.
- Pilgrimage (Hajj): Muslims who are physically and financially capable are required to make a pilgrimage to the Kaaba in Mecca at least once in their lifetime.
- Islamic Morals and Ethics: Muslims are encouraged to practice good morals and ethics, such as honesty, kindness, compassion, and justice, in their daily lives.
The Quran
The Quran is the holy book of Islam. It is believed to be the word of God as revealed to the Prophet Muhammad over a period of 23 years. The Quran consists of 114 chapters, or Surahs, which are divided into verses, or Ayahs.
The Quran covers a wide range of topics, including guidance for personal conduct, moral values, social principles, and laws. It emphasizes the importance of monotheism, submission to God, and the brotherhood of mankind.
The Quran is written in Arabic and is considered to be a literary masterpiece. Its verses are often recited during prayer and are also studied for their spiritual and intellectual guidance. Muslims believe that the Quran is the final and most complete revelation from God, superseding all previous scriptures.
Within the Quran, there are various stories about prophets and messengers, including Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, and Jesus. These stories serve as moral and spiritual lessons for believers.
It is believed that the Quran was compiled into book form during the Caliphate of Uthman ibn Affan, the third caliph of Islam. The text has remained unchanged since then, and it is considered to be a preserved and authentic record of God’s message.
The Quran is regarded as a source of guidance and enlightenment for Muslims around the world. It is a book that is studied and revered, and its teachings form the basis of Islamic beliefs and practices.
Prophets in Islam
The Islamic faith recognizes many prophets throughout history who were sent by Allah to guide and teach humanity. These prophets played a crucial role in spreading the message of Islam and guiding people towards righteousness. Among the most prominent prophets in Islam are:
- Adam (A.S): The first human being created by Allah.
- Noah (Nuh) (A.S): Built the Ark to save his followers from the Great Flood.
- Abraham (Ibrahim) (A.S): Known for his unwavering faith in Allah and the sacrifice he was willing to make.
- Moses (Musa) (A.S): Received the Ten Commandments from Allah and led the Israelites out of Egypt.
- Jesus (Isa) (A.S): Highly respected as a prophet, born miraculously to the Virgin Mary.
- Muhammad (S.A.W): The final and most important prophet in Islam, received the Qur’an from Allah.
These prophets were chosen by Allah to convey His message and establish a connection between Him and humanity. They were known for their righteousness, wisdom, and moral conduct, and their teachings form the foundation of Islamic beliefs and practices.
A key belief in Islam is the prophethood of Muhammad (peace be upon him). Muslims believe that Muhammad (S.A.W) received revelations from Allah over a period of 23 years, which were compiled into the holy book of Islam, the Qur’an. He is considered the last and final prophet, sent to guide humanity until the Day of Judgment.
Islamic Holidays and Festivals
Islam has several important holidays and festivals that are celebrated by Muslims around the world. These occasions hold religious and cultural significance for Muslims, and are a time for prayer, reflection, and community gatherings.
Eid al-Fitr: This is one of the most significant holidays in Islam, marking the end of the holy month of Ramadan. It is a time of great joy and celebration, as Muslims break their fast and come together with family and friends. Special prayers are performed at the mosque, and people exchange gifts and visit each other’s homes to share meals.
Eid al-Adha: Also known as the Feast of Sacrifice, this holiday commemorates the willingness of Prophet Ibrahim (Abraham) to sacrifice his son Ismail (Ishmael) as an act of obedience to God. Muslims celebrate Eid al-Adha by attending prayers at the mosque and sacrificing an animal, usually a sheep or goat, as a symbol of Ibrahim’s sacrifice. The meat is then distributed to the needy and shared with family and friends.
Mawlid al-Nabi: This is the celebration of the birth of the Prophet Muhammad. It is a time for Muslims to express gratitude for the Prophet’s teachings and reflect on his life. Special prayers are offered at the mosque, and people gather to listen to sermons and participate in processions. The celebrations vary from country to country, with some places organizing parades and distributing sweets to children.
Ashura: Ashura is observed on the 10th day of Muharram, the first month of the Islamic lunar calendar. It has significant historical and religious importance for both Sunni and Shia Muslims. For Shia Muslims, it commemorates the martyrdom of Imam Hussain, the grandson of Prophet Muhammad, in the Battle of Karbala. For Sunni Muslims, it marks the day when Moses and the Israelites were saved from Pharaoh. It is a time for fasting, prayer, and self-reflection.
Ramadan: Although not a holiday or festival in the traditional sense, Ramadan is a month-long period of fasting and spiritual reflection observed by Muslims worldwide. During daylight hours, Muslims abstain from eating, drinking, and other physical needs. The purpose of Ramadan is to purify the soul, increase self-discipline, and empathize with those who are less fortunate. The end of Ramadan is celebrated with the joyous holiday of Eid al-Fitr.
These holidays and festivals are important occasions for Muslims to strengthen their faith, connect with their community, and engage in acts of charity and kindness. They help foster unity and promote understanding among Muslims, while also providing an opportunity for non-Muslims to learn more about the Islamic faith and its traditions.
Islamic Art and Architecture
Islamic art encompasses a wide range of artistic expressions influenced by the teachings of Islam. It emerged in the 7th century and encompasses various forms such as calligraphy, painting, ceramics, textiles, and architecture. Islamic art is known for its intricate designs, rich colors, and geometric patterns.
Calligraphy holds a significant place in Islamic art. It is the art of writing beautifully, particularly the Quranic verses. Arabic calligraphy is often used to decorate mosques, manuscripts, and other Islamic artifacts. The flowing lines and curves in calligraphy reflect the importance of the written word in Islam.
Painting in Islamic art is heavily influenced by the prohibition of depicting living beings, particularly humans, in religious contexts. Instead, Islamic painting focuses on geometric patterns, floral motifs, and landscapes. These paintings often feature intricate designs and vibrant colors.
Ceramics are another important aspect of Islamic art. Islamic pottery is characterized by its unique glazes, intricate patterns, and vibrant colors. Persian pottery, in particular, is highly revered for its delicate craftsmanship and beautiful designs.
Textiles play a significant role in Islamic art, with intricate patterns and designs adorning various fabrics. Textiles are used for clothing, tapestries, carpets, and prayer mats. Many different techniques are employed to create these textiles, including weaving, embroidery, and block printing.
Islamic architecture is perhaps the most visible form of Islamic art. It is characterized by its distinctive features such as domes, arches, and minarets. Islamic architecture is known for its grandeur and intricacy, with geometric patterns and calligraphic decorations adorning mosques and other Islamic buildings.
The Great Mosque of Mecca, the Alhambra in Spain, and the Taj Mahal in India are some famous examples of Islamic architecture. These structures are not only places of worship but also showcase the beauty and sophistication of Islamic art.
In summary, Islamic art and architecture are rich and diverse, reflecting a deep spiritual and cultural significance. From calligraphy and painting to ceramics and textiles, Islamic art encompasses various forms that continue to inspire and captivate people around the world.
Women in Islam
Islam recognizes the fundamental equality of men and women in their rights and responsibilities. Women have a special place in Islam and are considered equal in terms of their spiritual worth and potential.
Here are some key points about the role and status of women in Islam:
- Equality: Islam emphasizes the equal worth and dignity of both men and women. Both are created by Allah and have equal opportunities to seek knowledge, attain spiritual growth, and contribute to society.
- Modesty: Modesty is a virtue both for men and women in Islam. Women are encouraged to dress modestly and cover their bodies in loose-fitting clothing. This is to protect their chastity and maintain societal harmony.
- Education: Islam encourages women to seek knowledge and education. Women have the right and responsibility to gain knowledge in various fields and contribute to society through their intellect and skills.
- Marriage: Marriage is highly encouraged in Islam and is considered a sacred union. Women have the right to consent to marriage and cannot be forced into it. Islam values the role of women as wives and mothers, and emphasizes the importance of family life.
- Legal rights: Islamic law provides women with various rights, including the right to own property, the right to inheritance, the right to initiate divorce, and the right to be financially supported by their husbands.
It is important to note that cultural practices and customs may sometimes deviate from the true teachings of Islam. However, Islam itself promotes the empowerment and upliftment of women, and encourages them to actively participate in society while maintaining their dignity and modesty.
It is crucial to approach women’s issues in Islam with a balanced and contextual understanding, taking into account the principles and teachings of the religion.
Islamic Contributions to Science
The Islamic civilization made significant contributions to the field of science during the Golden Age of Islam, which spanned from the 8th to the 14th centuries. Islamic scholars and scientists made groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in various scientific disciplines, laying the foundation for modern scientific understanding. Here are some notable contributions:
- Astronomy: Islamic astronomers developed precise observational tools and made significant advances in the field. They built observatories, cataloged stars, and accurately measured the movement of celestial bodies. Their works influenced European astronomers like Nicolaus Copernicus and Galileo Galilei.
- Medicine: Islamic physicians made crucial advancements in medicine, building upon the knowledge of ancient Greek, Roman, and Persian physicians. They developed new surgical techniques, introduced anesthesia, and made significant contributions to pharmacology. One notable Islamic physician was Ibn Sina (Avicenna), whose “Canon of Medicine” became a standard medical textbook in European universities for centuries.
- Mathematics: Islamic mathematicians made important contributions to the field, such as introducing the decimal numeral system and the concept of zero to the Islamic world. They also developed algebra and made advancements in trigonometry and geometry. The works of scholars like Al-Khwarizmi and Omar Khayyam greatly influenced European mathematicians during the Renaissance.
- Chemistry: Islamic chemists made significant contributions to the field, particularly in the areas of alchemy and distillation. They developed new chemical processes and experimental methods that laid the foundation for modern chemistry. Their works influenced later European chemists like Robert Boyle and Antoine Lavoisier.
These are just a few examples of the many contributions Islamic scholars made to the field of science. Their achievements not only advanced scientific knowledge but also preserved and expanded upon the knowledge of ancient civilizations, ensuring that their discoveries could be passed on to future generations.
The contributions of Islamic scholars to science have had a lasting impact, shaping the development of scientific thought throughout history. Recognizing and appreciating these contributions is essential in understanding the rich scientific heritage of Islamic civilization.
Islamic Ethics and Morality
In Islam, ethics and morality play a central role in guiding the behavior of individuals. Islamic ethics are derived from the teachings of the Quran, the holy book of Islam, and the Hadith, the sayings and actions of Prophet Muhammad.
Islamic ethics emphasize the importance of righteousness, justice, honesty, and kindness. Muslims are encouraged to strive for moral excellence in all aspects of their lives and to treat others with respect and compassion.
One of the key principles in Islamic ethics is the concept of “taqwa,” which can be translated as “God-consciousness.” Taqwa entails being constantly aware of God’s presence and seeking to please Him in all actions and decisions. It serves as a guiding principle for Muslims to make ethical choices and avoid actions that are deemed sinful or immoral.
Islamic ethics also emphasize the importance of fulfilling one’s responsibilities and upholding one’s obligations towards others. This includes respecting one’s parents, being just and fair in dealings, and fulfilling one’s promises and contracts.
Islamic ethics also provide guidance on interpersonal relationships. Muslims are encouraged to be respectful, kind, and compassionate towards others, regardless of their religious or cultural backgrounds. They are also advised to avoid gossip, slander, and backbiting, as these actions are considered harmful and unethical.
The concept of Islamic morality extends beyond individual behavior to include societal ethics. Islam promotes social justice and equality, and Muslims are encouraged to work towards creating a just and fair society. This includes addressing issues of poverty, oppression, and discrimination, and advocating for the rights of the less privileged.
In summary, Islamic ethics and morality emphasize the importance of righteousness, justice, honesty, kindness, and compassion. Muslims are encouraged to constantly be aware of God’s presence and strive for moral excellence in all aspects of their lives. Islamic ethics guide not only individual behavior but also societal ethics, with an emphasis on creating a just and fair society.
Islamic Calligraphy
Islamic calligraphy is a form of visual art that is deeply rooted in Islamic culture and has a rich history dating back centuries. It is the artistic practice of handwriting and lettering in the Arabic language using beautiful and intricate designs.
In Islamic calligraphy, words from the Quran, the holy book of Islam, are often depicted in stylized forms. The calligraphers use various scripts and techniques to create aesthetically pleasing and meaningful compositions.
The art of Islamic calligraphy is highly regarded in the Muslim world and is considered a spiritual art form. It is believed that the beauty and harmony of the calligraphy reflect the divine nature of the Quranic verses.
Calligraphy plays a significant role in Islamic architecture, as it is often used to decorate mosque walls, domes, and prayer rugs. It is also used in the creation of illuminated manuscripts and other religious texts.
There are several styles of calligraphy in Islamic art, including Kufic, Naskh, Thuluth, and Diwani. Each style has its own unique characteristics and is used for different purposes.
Islamic calligraphy has influenced other art forms around the world, and many non-Muslim artists have also embraced this exquisite form of expression.
In conclusion, Islamic calligraphy is a revered art form that has deep cultural and religious significance in the Islamic world. It showcases the beauty of Arabic script and serves as a visual representation of the divine words of the Quran.
Islamic Clothing and Modesty
Introduction
Islamic clothing is an important aspect of the religion of Islam. It not only reflects the modesty and humility of its followers, but also serves as a means to differentiate Muslims from followers of other religions.
The Principles of Islamic Clothing
- Modesty: Islamic clothing is designed to cover the body and maintain modesty. It is based on the principle that both men and women should dress in a way that does not attract unnecessary attention.
- Loose-fitting: Islamic clothing is typically loose-fitting to ensure that the shape of the body is not revealed. This includes long and loose pants or skirts for women, and loose shirts or tunics for men.
- Head covering: For women, Islamic clothing often includes a head covering called a hijab. This is worn to cover the hair, neck, and sometimes the shoulders. It symbolizes the protection of a woman’s modesty and is an important part of the Islamic dress code.
Different Types of Islamic Clothing
There are various types of Islamic clothing for both men and women:
- Hijab: The hijab is a headscarf worn by women to cover their hair. It is available in different styles and colors, allowing women to express their individuality while adhering to the principles of modesty.
- Abaya: The abaya is a loose-fitting, full-length garment worn by women, typically in black. It covers the entire body except for the face, hands, and feet.
- Jalabiya: The jalabiya is a loose, robe-like garment worn by both men and women. It is often made of lightweight fabric and is suitable for hot climates.
- Thobe: The thobe is a long, flowing garment worn by men. It is typically white and is often worn with a head covering called a kufi.
Conclusion
Islamic clothing is not just a form of dress, but an expression of faith and devotion. It promotes modesty, humility, and a sense of belonging to the Muslim community. By adhering to the principles of Islamic clothing, Muslims strive to uphold the values and teachings of Islam in their daily lives.
Islamic Education
Islamic education plays a crucial role in the lives of Muslims as it provides them with the knowledge and understanding of Islamic teachings. It encompasses various aspects, including religious studies, Islamic history, and the teachings of the Quran and Hadith.
1. Quranic Studies: Quranic studies form the foundation of Islamic education. Muslims learn to read and memorize the Quran, understand its meaning, and apply its teachings in their daily lives. They also learn about the different chapters (Surahs) and verses (Ayahs) of the Quran and their significance.
2. Hadith Studies: Hadith studies focus on the teachings and practices of the Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him). Muslims learn about the collection and authentication of Hadiths, as well as their interpretation and application in various aspects of life. Hadith studies help Muslims understand the traditions and customs of Prophet Muhammad.
3. Islamic Jurisprudence: Islamic jurisprudence, also known as fiqh, provides guidance on the application of Islamic teachings in practical matters. Students learn about the different schools of Islamic jurisprudence and the principles and rules governing various aspects of life, including worship, transactions, and family matters.
4. Islamic History: Islamic history plays a crucial role in Islamic education as it helps Muslims understand their past and the accomplishments of the early Muslim community. Students learn about the life of Prophet Muhammad, the caliphs, the early Muslim conquests, and the contributions of Muslim scholars and scientists.
5. Arabic Language: Arabic is the language of the Quran, and its study is an integral part of Islamic education. Muslims learn to read, write, and speak Arabic to understand the Quran in its original language and to connect with the Islamic heritage.
6. Moral and Ethical Values: Islamic education emphasizes the development of moral and ethical values. Students learn about the importance of sincerity, honesty, compassion, and justice in Islam. They are encouraged to apply these values in their interactions with others and in their personal conduct.
7. Muslim Civilization: Islamic education also encompasses the study of Muslim civilization and its contributions to various fields, including science, mathematics, philosophy, and literature. Students learn about renowned Muslim scholars and their works, which have had a significant impact on the advancement of knowledge.
8. Tafseer (Quranic Exegesis): Tafseer is the interpretation of the Quranic verses to understand their deeper meanings. Students learn about different methods of tafseer and how to analyze and interpret the Quranic text. This enables them to gain a deeper understanding of the messages and lessons conveyed by the Quran.
In conclusion, Islamic education provides Muslims with a comprehensive understanding of their religion and helps them live a fulfilling and righteous life. It instills moral values, fosters critical thinking, and encourages the pursuit of knowledge, both religious and secular. Islamic education is not limited to formal classrooms but extends to family and community settings, where individuals learn from scholars, elders, and fellow community members.
Islamic Food and Dietary Restrictions
Islam has specific dietary laws and restrictions that are followed by Muslims around the world. These restrictions are based on Islamic teachings and are aimed at promoting good health and spirituality.
Halal and Haram
In Islam, the terms “halal” and “haram” are used to describe food and drinks that are permissible and forbidden, respectively. Halal means “lawful” or “permissible”, while haram means “forbidden” or “prohibited”. Muslims are required to consume only halal food and avoid haram food.
Halal Requirements
To be considered halal, food and drinks must meet certain requirements. The basic requirements are as follows:
- The animal must be slaughtered by a Muslim who is of sound mind and has reached the age of puberty.
- The animal must be slaughtered by cutting the throat, windpipe, and blood vessels in the neck, ensuring a quick and humane death.
- The name of Allah (God) must be invoked at the time of slaughtering.
- The animal must be healthy at the time of slaughter, and it should not have been dead prior to slaughter.
- The animal’s blood should be fully drained from the body.
In addition to these requirements, there are certain haram ingredients that Muslims are prohibited from consuming. Some examples include pork and its by-products, alcohol, and meat from animals that were not slaughtered according to Islamic law.
Muslim Dietary Habits
Muslims are encouraged to follow a balanced and healthy diet. Islam promotes the concept of moderation in all aspects of life, including eating. Excessiveness and overindulgence in food and drink are discouraged.
Fasting is also an important part of the Islamic faith, especially during the holy month of Ramadan. Muslims abstain from eating and drinking from dawn until sunset during this period to demonstrate self-discipline and strengthen their spirituality.
Conclusion
Islamic dietary laws play a significant role in the lives of Muslims. Following these laws helps Muslims maintain a healthy and halal lifestyle. By adhering to these restrictions, Muslims not only fulfill their religious obligations but also promote a sense of unity and community among Muslims around the world.
Islamic Finance and Banking
Islamic finance is a financial system that is based on the principles of Islamic law, also known as Shariah. Shariah prohibits certain activities such as charging interest (riba), gambling (maysir), and uncertainty (gharar). Islamic finance promotes ethical and socially responsible investments.
In Islamic finance, banking activities are structured to comply with Shariah principles. Some key components of Islamic banking include:
- Profit-and-loss sharing (PLS): Islamic banks operate on the principle of shared risk and reward. Instead of providing loans with interest, they engage in partnerships and profit-sharing agreements with their clients. This ensures that both parties are invested in the success of the venture.
- Prohibition of interest: Islamic banking strictly prohibits the charging or receiving of interest. Instead, banks earn profit by engaging in legitimate business activities, such as trading, leasing, and asset-based financing.
- Asset-backed financing: Islamic banks focus on asset-based financing rather than lending money. They provide funds for specific assets or projects, sharing the profits and risks associated with the investment.
Islamic finance has gained popularity worldwide, with Islamic banks and financial institutions operating not only in Muslim-majority countries but also in non-Muslim countries. This form of finance appeals to individuals and businesses seeking ethical and responsible financial solutions.
Islamic banking has several advantages, including:
- Ethical principles: Islamic banking follows a strict ethical framework, avoiding activities that are harmful or exploitative.
- Shared risk and reward: The profit-and-loss sharing model ensures that both the bank and its clients are mutually invested in the success of a venture.
- Asset-backed financing: Islamic banks focus on real economic activities and assets, contributing to more stable and sustainable financing.
In conclusion, Islamic finance and banking offer an alternative approach to traditional banking systems. With a focus on ethical principles and shared risk and reward, Islamic finance provides a sustainable and responsible financial solution for individuals and businesses around the world.
Islamic Countries
The Islamic world is vast and diverse, comprising of numerous countries that are home to millions of Muslims. These countries span across different continents and have their unique history, culture, and traditions. Here are some of the prominent Islamic countries:
-
Saudi Arabia: Known as the birthplace of Islam, Saudi Arabia is home to the two holiest cities in Islam, Mecca and Medina. It is a country deeply rooted in Islamic traditions and holds significant importance for Muslims worldwide.
-
Iran: With a rich history and deep Islamic roots, Iran is often referred to as the center of Shiite Islam. It has a unique blend of ancient Persian culture and Islamic traditions, making it a culturally diverse Islamic country.
-
Indonesia: As the country with the largest Muslim population in the world, Indonesia is known for its diverse and vibrant Islamic culture. It has a rich history of Islamic influence, with many beautiful mosques and Islamic traditions.
-
Pakistan: Pakistan is an Islamic country in South Asia with a significant Muslim population. It is known for its strong Islamic identity, with mosques and Islamic institutions spread throughout the country.
-
Egypt: With a long and storied history, Egypt has been home to various Islamic dynasties and has numerous iconic Islamic landmarks. It is known for its Islamic architecture, including mosques such as the Al-Azhar Mosque and the Sultan Hassan Mosque.
-
Turkey: Turkey is an Islamic country with a rich cultural heritage and a blend of Eastern and Western influences. It is known for its Ottoman-era mosques, such as the famous Blue Mosque in Istanbul.
These are just a few examples of the many Islamic countries around the world. Each country has its unique contributions to Islamic culture, history, and traditions, and exploring them can offer a fascinating glimpse into the global Muslim community.
Islamic Music and Poetry
Islamic music and poetry have a rich history and tradition in the Islamic world. They are important forms of expression and have played a significant role in Islamic culture throughout the centuries. They are not only used for entertainment purposes but also serve as a means of spiritual connection and worship.
Islamic Music:
- Nasheeds: Nasheeds are a popular form of Islamic music that involves the singing of religious and spiritual songs. They are usually performed without musical instruments, using only voice, hand clapping, and sometimes drums. Nasheeds can vary in style and language but often focus on themes of faith, love, and devotion to Allah.
- Sufi Music: Sufi music is another important genre in Islamic music. It is associated with the mystical branch of Islam known as Sufism, which emphasizes the inner search for divine love and knowledge. Sufi music often features repetitive chants and melodies that create a trance-like state, allowing the listener to connect with the spiritual realm.
- Classical Music: Islamic classical music has a long history dating back to the medieval period. It is influenced by various musical traditions from the Middle East, North Africa, and Central Asia. This genre often includes instruments such as the oud, ney, and qanun and is appreciated for its intricate melodies and poetic lyrics.
Islamic Poetry:
- Sufi Poetry: Sufi poets have contributed significantly to Islamic literature, expressing deep spiritual insights and emotions through their poetry. Their verses often contain metaphorical language and symbolism, exploring themes of love, unity, and the quest for divine truth. Famous Sufi poets include Rumi, Hafiz, and Ibn Arabi.
- Ghazals: Ghazals are a form of Arabic poetry that originated in the Arabian Peninsula and later spread to other parts of the Islamic world. They consist of rhyming couplets with a specific meter and often express themes of love, loss, and longing. Ghazals are known for their emotional depth and lyrical beauty.
- Nasheed Poetry: Many nasheeds include poetic lyrics that convey religious teachings and moral values. The verses often praise the Prophet Muhammad and his companions, as well as express gratitude to Allah for His blessings. Nasheed poetry is simple yet powerful, resonating with audiences of all ages.
Islamic music and poetry continue to thrive in the modern era, blending traditional elements with contemporary styles and themes. They offer a unique window into the rich cultural heritage of the Islamic world and provide a source of inspiration and reflection for Muslims and non-Muslims alike.
Islam and Modernity
Islam and Modernity is an ongoing dialogue and debate within the Muslim community. As the world continues to rapidly change and technologically advance, Muslims face the challenge of reconciling their faith with the changing times.
Modernization has brought about significant changes in various aspects of life, including technology, politics, economics, and social norms. Muslims have had to navigate these changes while remaining true to their faith and values.
One of the key areas of discussion is the relationship between Islamic teachings and modern science. While some see a harmony between the two, others raise questions about the compatibility of certain scientific discoveries with religious beliefs. This includes topics such as evolution, cloning, and assisted reproductive technologies.
Furthermore, the impact of globalization and Westernization has also been a subject of debate. Some argue that adopting Western values and practices contradicts Islamic ideals, while others emphasize the importance of adapting to the modern world while preserving Islamic values.
An important aspect of the dialogue on Islam and modernity is the role of women in society. Traditional gender roles and practices are being questioned and re-evaluated, as women seek more rights and opportunities. Issues such as education, employment, and gender equality are at the forefront of this discussion.
It is important to note that there is no single, monolithic view on Islam and modernity, as Muslims come from diverse backgrounds and perspectives. There is a wide range of interpretations and approaches, which makes this dialogue dynamic and subject to ongoing evolution.
Overall, the discourse on Islam and modernity reflects the desire of Muslims to navigate the complexities of the modern world while staying grounded in their faith. It is an ongoing attempt to find a balance between tradition and progress, and to ensure that Islamic values are integrated into the changing times.
Islamic Medicine and Healing
The field of Islamic medicine and healing has a rich history that spans centuries. Islamic scholars made significant contributions to various areas of medicine, including anatomy, surgery, pharmacy, and healthcare.
Knowledge Transfer:
During the Islamic Golden Age, which lasted from the 8th to the 14th century, Arabic scholars translated and preserved numerous Greek and Roman medical texts. These texts were further expanded upon and developed by Islamic scholars, integrating ideas from other civilizations such as India and Persia.
Unani Medicine:
One of the prominent branches of Islamic medicine is Unani medicine, derived from the Greek word “Οὐανους” (Unani), which means “Greek.” This system focuses on the balance between the body’s elements, including earth, water, air, and fire. Unani medicine emphasizes herbal remedies, diet, exercise, and cupping therapy.
Treatments and Therapies:
Islamic medicine incorporated various treatments and therapies. For example, Islamic physicians developed advanced surgical techniques, including the use of cauterization and sutures. They also introduced new medicines made from various plants and minerals.
Islamic medicine also emphasized the importance of preventive care and emphasized a holistic approach to health. A healthy lifestyle, proper diet, regular exercise, and mental well-being were all considered essential components of maintaining good health.
Impact and Legacy:
The advancements in Islamic medicine had a profound impact on the development of medical science worldwide. Many Islamic medical texts were translated into Latin and other European languages, influencing the Renaissance and shaping the future of medicine.
Conclusion:
The field of Islamic medicine and healing played a crucial role in the advancement of medical science. The contributions made by Islamic scholars helped shape our understanding of various medical disciplines and laid the foundation for modern medical practices. Today, the legacy of Islamic medicine continues to inspire researchers and healthcare professionals worldwide.
FAQ
What are some basic beliefs of Islam?
Some basic beliefs of Islam include the belief in one God (Allah), the belief in angels, the belief in the prophethood of Muhammad, the belief in the divine books (such as the Quran), and the belief in the Day of Judgment.
What is the significance of Ramadan in Islam?
Ramadan is the holy month of fasting for Muslims. It is a time of spiritual reflection, increased devotion, and worship. Muslims fast from sunrise to sunset during this month to purify their souls and seek forgiveness from Allah.
Can you explain the five pillars of Islam?
The five pillars of Islam are the five basic acts of worship that are considered fundamental to the practice of Islam. They include the Shahada (declaration of faith), Salah (prayer), Zakat (charity), Sawm (fasting during Ramadan), and Hajj (pilgrimage to Mecca).
What is the importance of Mecca in Islam?
Mecca is the holiest city in Islam as it is the birthplace of the Prophet Muhammad and the site of the Kaaba, which is considered the most sacred place in Islam. Muslims around the world face towards Mecca during their daily prayers and the pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj) is one of the five pillars of Islam.