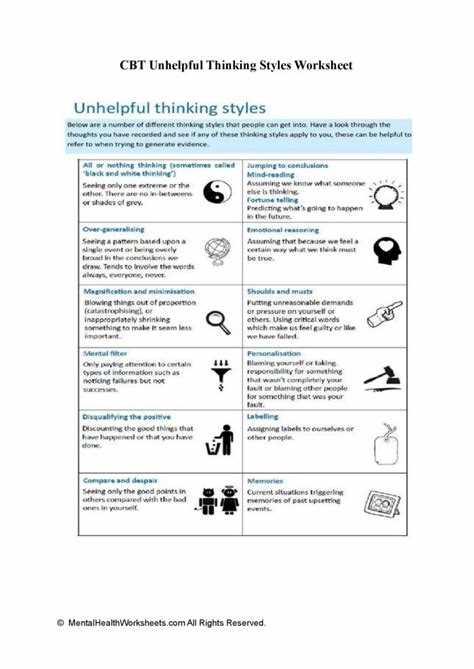
Unhelpful thinking styles can often hinder our ability to cope with challenges and enjoy life to the fullest. Whether it’s negative self-talk, catastrophizing, or excessive worry, these thinking patterns can contribute to feelings of anxiety, depression, and overall dissatisfaction.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) are two evidence-based approaches that offer effective techniques for managing unhelpful thinking styles. CBT focuses on identifying and challenging negative thoughts, while ACT emphasizes acceptance and mindfulness.
One technique used in CBT is cognitive restructuring, where individuals learn to identify and replace irrational thoughts with more rational ones. This process involves examining the evidence for and against a particular thought, considering alternative explanations, and challenging cognitive distortions such as black-and-white thinking or overgeneralization.
ACT, on the other hand, encourages individuals to accept their thoughts and feelings without judgment and to focus on taking action towards their values. Mindfulness exercises, such as meditation and breathing techniques, help individuals become more aware of their thoughts and better able to observe them without getting caught up in them.
In summary, CBT and ACT provide effective techniques for managing unhelpful thinking styles. Through cognitive restructuring and acceptance, individuals can learn to challenge negative thoughts and embrace a more balanced perspective. By incorporating these techniques into their daily lives, individuals can experience improved mental well-being and a greater sense of fulfillment.
Use of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a psychological treatment that focuses on identifying and changing unhelpful thinking patterns and behaviors. It is an evidence-based therapy that has been used to effectively manage a wide range of mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, and various other psychological disorders.
CBT operates on the principle that our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors are interconnected and influence each other. It aims to help individuals become aware of their negative or unhelpful thoughts and beliefs, and replace them with more realistic and positive ones.
One technique commonly used in CBT is cognitive restructuring, which involves identifying and challenging negative thought patterns. This technique encourages individuals to examine the evidence for and against their negative thoughts, consider alternative explanations or interpretations, and develop more balanced and realistic thinking patterns.
Another technique used in CBT is behavioral activation, which aims to help individuals engage in positive and fulfilling activities, even when they do not feel motivated. By gradually increasing engagement in pleasurable activities and setting achievable goals, individuals can break free from a cycle of negative thinking and low motivation.
CBT also emphasizes the importance of learning and practicing new coping skills. These skills may include relaxation techniques, problem-solving strategies, and assertiveness training. By acquiring these new skills, individuals can better manage stressful situations and effectively cope with challenging emotions.
In summary, CBT is a highly effective therapy that helps individuals recognize and change unhelpful thinking patterns and behaviors. It provides practical tools and techniques to manage psychological distress and improve overall mental well-being.
Impact of Unhelpful Thinking Styles on Mental Health
Unhelpful thinking styles can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental health. These thinking patterns, commonly associated with cognitive distortions, can exacerbate symptoms of anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders.
One of the most common unhelpful thinking styles is known as “catastrophizing.” This involves blowing things out of proportion and expecting the worst possible outcomes. For example, when faced with a minor setback, a person might start to believe that their entire life is falling apart. This type of thinking can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and a sense of hopelessness.
Another unhelpful thinking style is “black-and-white thinking” or “dichotomous thinking.” This involves seeing situations as extremes, with no room for nuance or middle ground. For example, a person might believe that they are either a complete success or an absolute failure, with no acknowledgement of their achievements or strengths. This type of thinking can contribute to feelings of low self-esteem and a distorted perception of reality.
Unhelpful thinking styles can also include “personalization,” where individuals blame themselves for negative events that are beyond their control, and “filtering,” where they solely focus on negative aspects of a situation while ignoring any positive aspects. These thinking patterns can lead to feelings of guilt, shame, and a distorted sense of self-worth.
Moreover, unhelpful thinking styles can reinforce and perpetuate symptoms of mental health disorders. When individuals consistently engage in these negative thinking patterns, it becomes difficult for them to challenge their thoughts and find healthier alternative perspectives. This can create a cycle of negativity and emotional distress.
Overall, the impact of unhelpful thinking styles on mental health cannot be underestimated. Recognizing and addressing these patterns through therapies such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) can be instrumental in improving mental well-being and promoting more positive thought patterns.
Key Techniques in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized and effective form of therapy that aims to help individuals identify and change unhelpful thinking patterns and behaviors. CBT is based on the idea that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected and that by changing our thoughts, we can change our feelings and behaviors for the better.
There are several key techniques that are commonly used in CBT to help individuals manage their unhelpful thinking styles. These techniques include:
- Thought challenging: This technique involves identifying the negative or unhelpful thoughts that contribute to a person’s distress and challenging their accuracy and validity. It encourages individuals to examine the evidence for and against these thoughts and to develop more realistic and positive alternatives.
- Behavioral experiments: This technique involves testing out new behaviors or ways of thinking to see if they lead to different outcomes. By conducting experiments, individuals can gather evidence to support or refute their existing beliefs and assumptions.
- Graded exposure: This technique is commonly used for individuals with anxiety disorders. It involves gradually exposing individuals to the feared situation or stimulus in a controlled and supportive manner. This helps individuals to confront their fears and develop coping strategies to manage their anxiety.
- Activity scheduling: This technique involves planning and scheduling activities that bring a sense of enjoyment or achievement to a person’s life. By setting specific goals and engaging in meaningful activities, individuals can improve their mood and sense of well-being.
- Imagery rescripting: This technique is commonly used to address traumatic or distressing memories. It involves creating new, positive images or scenarios that replace the negative or distressing ones. By repeatedly visualizing these positive images, individuals can change the way they perceive and respond to the original memory.
- Relaxation techniques: These techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or progressive muscle relaxation, help individuals to manage physical symptoms of anxiety or stress. By practicing these techniques regularly, individuals can promote a sense of calm and relaxation.
These are just a few of the key techniques that are commonly used in CBT. The specific techniques used will vary depending on the individual’s needs and goals. By working with a trained therapist, individuals can learn and apply these techniques to effectively manage their unhelpful thinking styles and improve their overall well-being.
Understanding Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is a form of psychotherapy that aims to help individuals develop psychological flexibility and live a meaningful life. Unlike traditional cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) approaches that focus on changing unhelpful thoughts and feelings, ACT emphasizes acceptance of thoughts and emotions, and taking committed action aligned with one’s values.
Core Principles of ACT:
- Acceptance: ACT emphasizes the acceptance of unpleasant thoughts and emotions rather than attempting to eliminate or suppress them. It involves acknowledging and making room for these experiences without judgment.
- Cognitive Defusion: ACT teaches individuals to view thoughts as mere mental events rather than accurate representations of reality. Through various techniques, individuals learn to detach from unhelpful thoughts and avoid getting caught up in them.
- Being Present: ACT encourages individuals to be fully present in the current moment rather than getting caught up in past regrets or future worries. This mindfulness aspect helps individuals tune into their inner experiences and stay connected with the present.
- Self-as-Context: ACT challenges individuals to observe themselves from a larger perspective, understanding that they are more than their thoughts and experiences. This helps create a sense of psychological flexibility and distance from unhelpful thinking patterns.
- Values Clarification: ACT involves identifying and clarifying personal values to guide one’s actions and goals. This process helps individuals align their actions with what truly matters to them, leading to a more meaningful and fulfilling life.
- Committed Action: ACT emphasizes the importance of taking action in alignment with one’s values. This involves setting realistic goals and actively engaging in behaviors that move individuals closer to their values, despite the presence of uncomfortable thoughts and emotions.
Applications of ACT:
ACT has been successfully used in the treatment of various psychological conditions, including:
- Depression
- Anxiety disorders
- Substance abuse
- Chronic pain
- Eating disorders
- Relationship problems
Effectiveness of ACT:
Research has shown that ACT can be effective in reducing psychological distress and improving overall well-being. It has been found to be particularly helpful for individuals who are resistant to change and have struggled with traditional CBT approaches. ACT’s focus on acceptance and values-based action provides a powerful framework for individuals to navigate challenging thoughts and emotions while moving towards a more fulfilling life.
Utilizing ACT to Manage Unhelpful Thinking Styles
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is a therapeutic approach that focuses on accepting and embracing all experiences, including thoughts and emotions, without judgment or attempts to control or change them. By utilizing ACT techniques, individuals can effectively manage unhelpful thinking styles and cultivate psychological flexibility.
1. Defusion: Defusion involves creating distance from unhelpful thoughts and recognizing them as just thoughts, rather than as factual or accurate reflections of reality. This is done through techniques such as labeling thoughts as “just thoughts” or imagining thoughts as clouds passing by in the sky.
2. Mindfulness: Mindfulness is a core component of ACT and involves paying attention to the present moment non-judgmentally. By cultivating mindfulness, individuals can observe unhelpful thoughts without being consumed by them. Mindfulness can be practiced through meditation, breathing exercises, or simply bringing attention to the present moment throughout the day.
3. Values clarification: Identifying and clarifying personal values can provide a compass for guiding behavior and decision-making. By aligning actions with values, individuals can focus on what truly matters to them, rather than getting caught up in unhelpful thoughts. Engaging in values-based activities can also create a sense of meaning and purpose.
4. Committed action: Committed action involves taking intentional steps towards valued goals and engaging in behaviors that align with personal values. This can help individuals break free from unhelpful thinking patterns by focusing on the actions they take rather than getting caught up in thoughts and rumination. Breaking down goals into small, manageable steps can make them more achievable.
5. Self-as-context: Recognizing that thoughts and emotions are transient experiences that do not define one’s identity can help individuals detach from unhelpful thinking patterns. By cultivating an understanding of the self as an observer rather than an identifier with thoughts, individuals can gain a broader perspective and reduce the impact of unhelpful thoughts on their well-being.
6. Acceptance: ACT emphasizes accepting and making room for all emotions, including uncomfortable or distressing ones. By acknowledging and accepting these emotions as natural and valid, individuals can reduce the struggle and resistance to them, potentially minimizing the impact of unhelpful thoughts associated with these emotions.
By incorporating these ACT techniques into daily life, individuals can effectively manage unhelpful thinking styles and cultivate psychological flexibility, which can contribute to improved well-being and overall mental health.
Advantages of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) are two widely recognized and effective approaches used in psychotherapy. Both CBT and ACT are based on the principles of cognitive psychology and have been proven to be beneficial in managing various mental health concerns. Here are some of the advantages of using CBT and ACT:
1. Empowerment and Self-Help
Both CBT and ACT focus on empowering individuals to identify and challenge unhelpful thoughts and behaviors. By recognizing the connection between thoughts, feelings, and actions, individuals gain a sense of control over their own mental well-being. Through self-help techniques, individuals acquire skills that can be used outside of therapy sessions to cope with everyday challenges.
2. Effectiveness
CBT and ACT have a strong evidence base and have been extensively researched and proven to yield positive results. They have been effective in treating a variety of mental health conditions, such as anxiety disorders, depression, substance abuse, and PTSD. The structured nature of CBT and the emphasis on acceptance and mindfulness in ACT contribute to their effectiveness.
3. Focus on the Present
Both CBT and ACT emphasize the importance of focusing on the present moment. CBT helps individuals identify and challenge negative patterns of thinking and develop healthier coping strategies. ACT encourages individuals to accept and embrace their thoughts and feelings, and to take committed action towards their values and goals. By focusing on the present, individuals develop greater awareness and openness to experiences.
4. Flexibility
CBT and ACT can be used in various settings and adapted to different populations. They can be delivered individually or in a group format, and can be integrated with other therapeutic approaches. CBT and ACT can also be tailored to address specific goals and concerns, making them applicable to a wide range of individuals and mental health issues.
5. Long-Term Benefits
CBT and ACT provide individuals with lifelong skills and strategies for managing their mental health. By learning how to identify and challenge unhelpful thinking patterns, individuals can better cope with difficult situations and prevent relapses. The goals and values explored in ACT can create a sense of purpose and meaning that extends beyond the therapy sessions, contributing to long-term happiness and fulfillment.
| Advantages of CBT and ACT |
|---|
| Empowerment and Self-Help |
| Effectiveness |
| Focus on the Present |
| Flexibility |
| Long-Term Benefits |
Questions and answers
What are some effective techniques for managing unhelpful thinking styles?
Some effective techniques for managing unhelpful thinking styles include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT). Both approaches help individuals identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs, and develop more positive and helpful thinking styles. Additionally, techniques like mindfulness and relaxation exercises can help individuals become more aware of their thoughts and emotions, and learn to let go of unhelpful thinking patterns.
How does cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) help in managing unhelpful thinking styles?
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps in managing unhelpful thinking styles by focusing on identifying and challenging negative thoughts and beliefs. Through CBT, individuals learn to recognize cognitive distortions, such as all-or-nothing thinking or overgeneralization, and replace them with more balanced and realistic thoughts. This can lead to a change in behavior and emotions, and help individuals develop healthier and more productive thinking patterns.
What is acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) and how does it help in managing unhelpful thinking styles?
Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) is a mindfulness-based approach that helps individuals accept their thoughts and emotions, rather than trying to suppress or control them. ACT teaches individuals to observe their thoughts and let them pass, without attaching meaning or judgement to them. By practicing acceptance, individuals can learn to distance themselves from unhelpful thinking styles and focus on their values and goals, leading to a more fulfilling and meaningful life.
Can mindfulness and relaxation exercises be effective in managing unhelpful thinking styles?
Yes, mindfulness and relaxation exercises can be effective in managing unhelpful thinking styles. By practicing mindfulness, individuals can develop a greater awareness of their thoughts and emotions, and learn to observe them without getting caught up in them. This can help break the cycle of negative thinking and reduce anxiety and stress. Additionally, relaxation exercises like deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation can help individuals calm their minds and bodies, making it easier to let go of unhelpful thinking patterns.
How long does it take to see results from managing unhelpful thinking styles using CBT and ACT?
The time it takes to see results from managing unhelpful thinking styles using CBT and ACT can vary depending on the individual and the severity of their unhelpful thinking patterns. Some individuals may begin to notice positive changes within a few weeks, while others may require several months of therapy. Consistency and practice are key in making lasting changes, and individuals may continue to use the techniques learned in therapy even after the formal treatment has ended.
Are there any self-help resources available for managing unhelpful thinking styles?
Yes, there are self-help resources available for managing unhelpful thinking styles. Many books, online courses, and mobile apps are available that provide guidance and exercises based on CBT and ACT principles. These resources can be a helpful supplement to therapy or a starting point for individuals who want to learn more about managing their thoughts and emotions. However, it’s important to note that self-help resources may not be as effective as working with a trained therapist in addressing complex or severe unhelpful thinking styles.