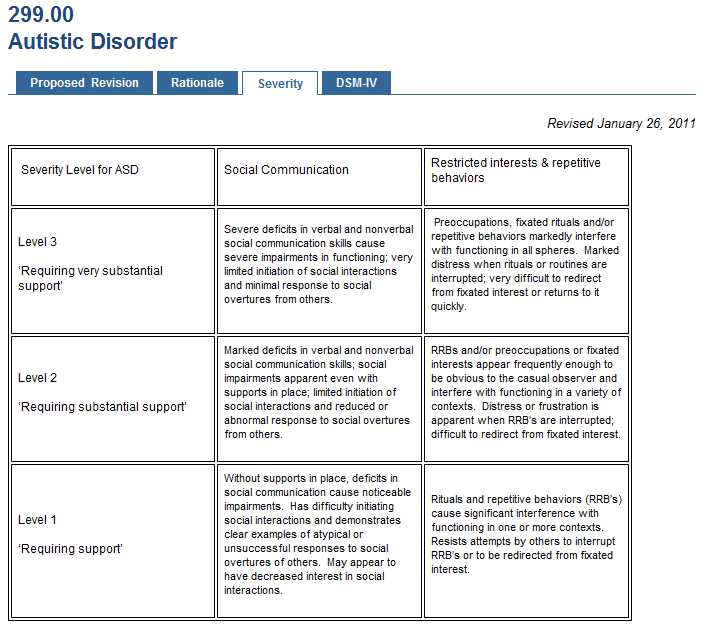
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects individuals’ ability to communicate and interact with others. Meggy Delaunay, a renowned psychologist and expert in the field of autism research, has dedicated her career to understanding the intricacies of ASD and improving the lives of individuals with this condition.
Through her extensive research and clinical work, Delaunay has gained a deep understanding of the challenges faced by individuals with ASD and their families. She has published numerous studies and papers on various aspects of autism, including its causes, early detection, and interventions. Her work has shed light on the diverse range of symptoms and behaviors associated with ASD, and she has played a crucial role in dispelling myths and misconceptions surrounding the condition.
One of the key contributions of Delaunay’s work has been her emphasis on early intervention and personalized treatment plans for individuals with ASD. She believes that it is essential to recognize the unique strengths and needs of each person on the autism spectrum and tailor interventions accordingly. This person-centered approach has proven to be effective in enhancing communication skills, social interactions, and overall quality of life for individuals with ASD.
Delaunay’s passion for improving the lives of individuals with ASD extends beyond her research. She actively works with advocacy groups and organizations to raise awareness about autism, address the stigma associated with the condition, and promote inclusion and acceptance. Her expertise and compassionate approach have made her a trusted resource for families, educators, and professionals seeking guidance in understanding and supporting individuals with autism spectrum disorder.
In conclusion, Meggy Delaunay’s invaluable contributions to the field of autism research have greatly enhanced our understanding of autism spectrum disorder. Her dedication, compassion, and commitment to making a difference in the lives of individuals with ASD are truly inspiring. Through her work, Delaunay continues to pave the way for better diagnosis, support, and interventions for individuals on the autism spectrum.
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects how a person interacts with others, communicates, and experiences the world around them. It is a lifelong condition that typically begins in early childhood and continues into adulthood.
ASD is characterized by a wide range of symptoms and behaviors that can vary greatly from person to person. Some individuals with ASD may have difficulty with social interactions, while others may have difficulty with communication or repetitive behaviors. Sensory sensitivities and restricted interests are also common among individuals with ASD.
It is important to note that ASD is a spectrum disorder, meaning that each individual may experience a unique combination of symptoms and levels of severity. Some individuals may be highly functioning, while others may require more support in their daily lives.
The exact cause of ASD is still unknown, but researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors may contribute to its development. There is currently no cure for ASD, but early intervention and support can greatly improve the quality of life for individuals with the disorder.
Causes of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder that affects a person’s social interaction, communication skills, and behavior. While the exact causes of ASD are still not fully understood, researchers have identified several factors that may contribute to its development.
Genetic Factors:
- Hereditary: Studies have shown that autism tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic component. Certain gene mutations and chromosomal abnormalities have been associated with an increased risk of developing ASD.
- Genetic Variations: Research has identified specific gene variations that are more common in individuals with ASD. These variations may disrupt normal brain development and contribute to the development of ASD.
Environmental Factors:
- Prenatal Factors: Some prenatal factors have been linked to an increased risk of ASD, including maternal use of certain medications during pregnancy, exposure to certain infections, and complications during pregnancy or childbirth.
- Postnatal Factors: Exposure to certain environmental toxins, such as air pollution or heavy metals, may increase the risk of ASD. Additionally, factors such as advanced parental age and low birth weight have also been associated with a higher likelihood of developing ASD.
Neurological Factors:
- Brain Structure and Function: Studies have found differences in the structure and functioning of the brain in individuals with ASD. These differences may affect the way individuals with ASD process information and interact with their environment.
- Neurotransmitters: Imbalances in certain neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, have been observed in individuals with ASD. These neurotransmitters play a crucial role in regulating mood, behavior, and communication.
It’s important to note that ASD is a complex disorder, and no single factor can fully explain its development. Rather, it is likely that a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors interact to contribute to the development of ASD.
Understanding the causes of ASD is crucial for developing effective interventions and support strategies for individuals with ASD. Continued research in this field will help shed more light on the underlying mechanisms of ASD and lead to improved diagnosis and treatment options.
Signs and Symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental disorder that affects social interaction, communication, and behavior. It is a spectrum disorder, which means that individuals with ASD can experience a wide range of symptoms and varying degrees of severity.
Here are some common signs and symptoms of ASD:
- Delayed or lack of speech: Children with ASD may have delayed speech development or may not speak at all.
- Difficulty with social interaction: People with ASD may have difficulty understanding social cues and may struggle with making and maintaining eye contact, understanding others’ emotions, and forming relationships.
- Repetitive behaviors: Individuals with ASD often engage in repetitive behaviors such as hand flapping, rocking back and forth, or lining up objects.
- Difficulty with transitions: People with ASD may have difficulty transitioning from one activity to another and may become upset or agitated when routines are disrupted.
- Sensitivity to sensory stimuli: Individuals with ASD may be hypersensitive or hyposensitive to sensory input, such as bright lights, loud noises, or certain textures.
- Fixation on specific interests: Many individuals with ASD develop intense interests in specific topics or objects and may have a deep knowledge or expertise in those areas.
It is important to remember that not all individuals with ASD will exhibit all of these signs and symptoms. Each person with ASD is unique, and the severity and combination of symptoms can vary widely.
| Signs and Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Delayed or lack of speech | Children with ASD may have delayed speech development or may not speak at all. |
| Difficulty with social interaction | People with ASD may have difficulty understanding social cues and may struggle with making and maintaining eye contact, understanding others’ emotions, and forming relationships. |
| Repetitive behaviors | Individuals with ASD often engage in repetitive behaviors such as hand flapping, rocking back and forth, or lining up objects. |
| Difficulty with transitions | People with ASD may have difficulty transitioning from one activity to another and may become upset or agitated when routines are disrupted. |
| Sensitivity to sensory stimuli | Individuals with ASD may be hypersensitive or hyposensitive to sensory input, such as bright lights, loud noises, or certain textures. |
| Fixation on specific interests | Many individuals with ASD develop intense interests in specific topics or objects and may have a deep knowledge or expertise in those areas. |
If you suspect that you or someone you know may have ASD, it is important to seek a professional evaluation. Early diagnosis and intervention can greatly improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals with ASD.
Diagnosis and Assessment of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Diagnosing autism spectrum disorder (ASD) can be a complex process that involves multiple steps and assessments. ASD is typically diagnosed in childhood, although some individuals may not receive a diagnosis until later in life.
One of the first steps in diagnosing ASD is a comprehensive evaluation by a multidisciplinary team, including a psychologist, pediatrician, and speech and language therapist. This evaluation may involve direct observation of the individual’s behavior and communication skills, as well as interviews with parents and caregivers.
During the evaluation, professionals will assess various areas of functioning, including social communication, repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities. They will also consider the individual’s developmental history and any specific challenges or difficulties they may be experiencing.
Diagnostic criteria for ASD are outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). These criteria include difficulties in social interaction and communication, as well as restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities. The severity of these symptoms can vary widely among individuals with ASD.
In addition to the DSM-5 criteria, professionals may use standardized assessment tools to further evaluate and diagnose ASD. These tools can include the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) and the Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R). These assessments provide a structured way to gather information about an individual’s behavior and can help confirm or rule out an ASD diagnosis.
It’s important to note that diagnosing ASD can be challenging, as symptoms can vary greatly among individuals and can be influenced by factors such as age, gender, and cognitive abilities. Some individuals may present with more obvious signs of ASD, while others may exhibit more subtle characteristics.
Overall, the diagnosis and assessment of ASD require a thorough evaluation and consideration of multiple factors. Early diagnosis and intervention can greatly improve outcomes for individuals with ASD, allowing for the implementation of tailored interventions and support services.
Treatment and Therapy for Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder that affects communication, behavior, and social interaction. While there is no cure for ASD, there are various treatment and therapy options available to help individuals with ASD manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
1. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA):
ABA is a highly structured, evidence-based therapy that focuses on modifying behavior patterns and teaching new skills. It involves breaking down tasks into smaller steps and using positive reinforcement to encourage desired behaviors. ABA is widely recognized as an effective treatment for individuals with ASD.
2. Speech and Language Therapy:
Many individuals with ASD have difficulties with speech and language, making it challenging for them to communicate effectively. Speech and language therapy can help improve communication skills, such as understanding and using language, articulation, and social communication.
3. Occupational Therapy:
Occupational therapy aims to help individuals with ASD develop the skills they need for everyday life activities, such as dressing, eating, and self-care. It focuses on sensory integration, fine motor skills, and improving coordination and independence.
4. Social Skills Training:
One of the core challenges for individuals with ASD is difficulties in social interactions. Social skills training provides individuals with strategies and practice to improve their social skills, including understanding nonverbal cues, initiating and maintaining conversations, and developing friendships.
5. Medications:
While there are no medications that can treat the core symptoms of ASD, medications may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms such as anxiety, aggression, or sleep disturbances. The use of medication should always be under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional.
6. Alternative Therapies:
Some families may explore alternative therapies such as dietary interventions, melatonin supplements, or alternative medicine modalities. It’s important to note that the evidence for the effectiveness of these therapies is limited, and families should consult with healthcare professionals before trying any alternative treatments.
In conclusion, treatment and therapy options for Autism Spectrum Disorder can help individuals with ASD manage their symptoms, improve their communication and social skills, and enhance their overall quality of life. It is essential for families to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses the specific needs and challenges of each individual with ASD.
Support and Resources for Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Living with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can present unique challenges, but there are numerous support systems and resources available to help individuals with ASD and their families. These resources aim to provide assistance, education, and community support to promote greater understanding and inclusion.
1. Autism Speaks: Autism Speaks is one of the largest autism advocacy organizations in the world. They offer a variety of resources, including educational materials, toolkits, and a 24/7 autism response team for support and guidance.
2. National Autism Association (NAA): NAA provides support, resources, and advocacy for individuals with ASD and their families. They offer a helpline, host conferences and events, and have various programs focused on education and safety.
3. Autism Society: The Autism Society is dedicated to improving the lives of all individuals affected by autism. They provide information about local services, support groups, and educational resources. The organization also promotes awareness through initiatives like National Autism Awareness Month.
4. Local Support Groups: Many communities have local support groups specifically for individuals with ASD and their families. These groups provide a safe space to connect, share experiences, and offer emotional support. Contacting local autism organizations or searching online directories can help find these groups.
5. Specialized Therapies and Interventions: There are numerous evidence-based therapies and interventions available for individuals with ASD. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), speech therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills training are some examples. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine the most appropriate therapies for an individual’s specific needs.
6. Educational Resources: Many schools offer specialized programs and resources for students with ASD. These resources may include individualized education plans (IEPs), assistive technology, and support services. Additionally, there are online platforms and organizations that provide educational materials and resources for individuals with ASD and their families.
7. Financial Assistance: Financial assistance programs can help individuals with ASD and their families cover the costs associated with therapies, interventions, and educational support. These programs may be offered by government agencies, non-profit organizations, or through private foundations.
8. Employment Support: Several organizations provide employment support for individuals with ASD, including job training programs, vocational rehabilitation services, and assistance with job placement. These resources aim to promote independence and self-sufficiency in the workplace.
9. Community Resources: Many communities offer recreational programs, social skills groups, and inclusive activities for individuals with ASD. These resources provide opportunities for social interaction, skill development, and community integration.
10. Research and Advocacy: Contributing to autism research and advocacy efforts can help advance the understanding and support for individuals with ASD. Supporting organizations that fund research, participating in clinical trials, and advocating for policy changes can have a significant impact on improving the lives of individuals with ASD.
It is essential for individuals with ASD and their families to explore and utilize the available support systems and resources. These resources can help enhance quality of life, promote inclusion, and empower individuals with ASD to reach their full potential.
Strategies for Managing Autism Spectrum Disorder
1. Establish a Routine: Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) thrive on predictability and structure. Creating a consistent daily routine can help reduce anxiety and provide a sense of stability. It is important to follow the same schedule as much as possible, including mealtimes, bedtime, and activities.
2. Use Visual Supports: Visual supports, such as visual schedules, charts, and cue cards, can help individuals with ASD understand and follow instructions. They provide a visual representation of tasks and expectations, which can aid in communication and reduce confusion and frustration.
3. Provide Clear Instructions: When giving instructions to individuals with ASD, it is crucial to use clear and concise language. Break down tasks into smaller steps and provide visual aids, if necessary. Repeat and reinforce instructions to ensure understanding.
4. Create a Calming Environment: Sensory sensitivities are common in individuals with ASD. Create a calming environment by minimizing noise, bright lights, and clutter. Provide sensory experiences, such as a weighted blanket or fidget toys, to help regulate sensory input and promote relaxation.
5. Encourage Social Skills Development: Many individuals with ASD struggle with social skills. Encourage social skills development by providing opportunities for social interaction and teaching specific social skills through visual supports and role-playing. Social stories can also be helpful in explaining social situations and appropriate behaviors.
6. Implement Behavior Management Strategies: Develop and implement behavior management strategies to address challenging behaviors. These may include positive reinforcement, token systems, and visual cues. Consistency and clear expectations are key in managing behaviors effectively.
7. Collaborate with Professionals: Work closely with professionals, such as therapists, educators, and doctors, to develop and implement an individualized treatment plan. They can provide guidance, support, and specialized interventions to address the unique needs of individuals with ASD.
8. Foster a Supportive Environment: Create a supportive and understanding environment for individuals with ASD. Educate family members, friends, and classmates about ASD and promote acceptance and inclusion. Encourage open communication and provide opportunities for individuals with ASD to express their thoughts and feelings.
9. Prioritize Self-Care: Caring for an individual with ASD can be demanding. It is important to prioritize self-care to avoid burnout. Take time for yourself, seek support from others, and engage in activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
10. Stay Informed: Stay informed about the latest research, therapies, and strategies for managing ASD. Attend workshops, conferences, and support groups to learn from experts and connect with other individuals and families affected by ASD.
By implementing these strategies, individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder can lead fulfilling and successful lives, while their loved ones and caregivers can provide the necessary support and understanding.
The Importance of Awareness and Acceptance of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects individuals’ social interaction, communication, and behavior. While it is a lifelong condition, early intervention and support can greatly improve the quality of life for individuals with ASD. However, one of the biggest challenges faced by individuals with ASD is the lack of awareness and acceptance from society.
Awareness of ASD is crucial because it helps people understand the challenges faced by individuals with ASD and how to support them better. Many individuals with ASD have unique strengths and talents that can contribute positively to society if given the opportunity. By raising awareness, we can create a more inclusive and accepting environment for individuals with ASD and promote their participation in various aspects of life.
Acceptance is equally important as it paves the way for individuals with ASD to be treated with respect, dignity, and equality. Acceptance means embracing differences and realizing that every individual, regardless of their abilities or disabilities, has the right to live a fulfilling life. By accepting individuals with ASD for who they are, we can foster a sense of belonging and reduce the stigma and discrimination they often face.
Furthermore, awareness and acceptance can lead to increased support and resources for individuals with ASD. When society understands the challenges and needs of individuals with ASD, it becomes easier to advocate for appropriate services, educational opportunities, and employment options. This, in turn, can improve the overall well-being and independence of individuals with ASD.
- Building awareness of ASD can be done through education and information dissemination. Schools, workplaces, and community organizations can provide training sessions or workshops about ASD, its characteristics, and how to support individuals with ASD effectively.
- Organizing events and campaigns dedicated to raising awareness and promoting acceptance of ASD can also have a significant impact. These events can bring together individuals with ASD, their families, and the broader community to foster understanding and create a more inclusive society.
- In addition, promoting acceptance involves challenging stereotypes and misconceptions about ASD. This can be achieved through media campaigns, storytelling, and sharing personal experiences of individuals with ASD to break down barriers and foster empathy.
In conclusion, awareness and acceptance of Autism Spectrum Disorder are essential for creating a more inclusive and supportive society. By raising awareness and promoting acceptance, we can help individuals with ASD lead fulfilling lives and contribute their unique talents to the world.
Questions and answers
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental disorder that affects social interaction, communication skills, and behavior. It is characterized by difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and repetitive patterns of behavior.
What are the symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder?
The symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder include difficulty in social interaction, such as maintaining eye contact or participating in conversations, repetitive behaviors or interests, difficulty in understanding and expressing emotions, and sensory sensitivities.
When is Autism Spectrum Disorder usually diagnosed?
Autism Spectrum Disorder is usually diagnosed in early childhood, typically between the ages of 2 and 3. However, some individuals may not receive a diagnosis until later in life.
Can Autism Spectrum Disorder be cured?
There is currently no cure for Autism Spectrum Disorder. However, early intervention and appropriate therapies can help individuals with ASD improve their social skills, communication abilities, and overall quality of life.
Is there a genetic component to Autism Spectrum Disorder?
Yes, there is a genetic component to Autism Spectrum Disorder. Research suggests that certain genes may increase the risk of developing ASD, but it is not entirely clear how genetics contribute to the disorder.
What are some common misconceptions about Autism Spectrum Disorder?
Some common misconceptions about Autism Spectrum Disorder include the belief that all individuals with ASD are intellectually disabled, that they lack empathy, or that they are incapable of forming meaningful relationships. These misconceptions are not true as every individual with ASD is unique and has their own strengths and challenges.
How can society better support individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder?
Society can better support individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder by promoting understanding, acceptance, and inclusion. This can be done through education and awareness campaigns, providing appropriate resources and support services, and creating inclusive environments where individuals with ASD can thrive.