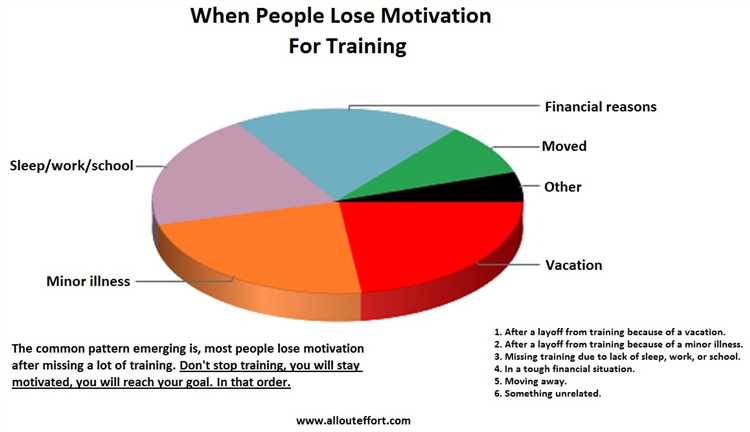
Have you ever started a new project, full of excitement and motivation, only to find that your motivation quickly fizzles out? You’re not alone. Many of us experience bursts of motivation that quickly fade away, leaving us feeling stuck and unmotivated. But why does this happen?
The answer lies in what psychologists call the motivation graph. This graph illustrates the natural pattern of motivation over time. At the beginning of a project, our motivation is typically high. We’re enthusiastic about the possibilities and eager to get started. This initial spike in motivation is often referred to as the “honeymoon phase.”
However, as time goes on, our motivation tends to decrease. We may encounter obstacles or setbacks that dampen our enthusiasm. The initial excitement wears off, and we find it harder to stay motivated. This decrease in motivation is often referred to as the “plateau phase.”
Understanding the motivation graph can help us better navigate the ups and downs of motivation. Instead of feeling discouraged when our motivation wanes, we can recognize it as a normal part of the process. By adopting strategies to maintain and reignite our motivation, we can keep moving forward towards our goals, even when the initial excitement wears off.
Understanding the Motivation Graph
The motivation graph is a visual representation of how motivation changes over time. It shows that motivation is not a constant state, but rather something that fluctuates based on various factors and circumstances. By understanding the motivation graph, we can better understand how to manage and maintain our motivation levels.
1. The Ups and Downs:
The motivation graph typically starts with a high point, representing the initial excitement and enthusiasm that comes with starting something new. However, as time goes on and challenges arise, motivation can start to decrease. This is known as the “dip” or the low point on the motivation graph. It’s important to recognize that experiencing dips in motivation is normal and to be expected.
2. External Factors:
There are many external factors that can influence motivation levels. These can include things like stress, lack of support or resources, and unexpected setbacks. Understanding the impact of these factors on motivation can help us better navigate through them and minimize their negative effects.
3. Internal Factors:
Internal factors, such as self-belief, mindset, and personal goals, also play a significant role in determining motivation levels. Having a clear sense of purpose and a positive mindset can help maintain motivation, even during challenging times. Learning to identify and cultivate these internal factors is key to sustaining motivation in the long term.
4. The Importance of Momentum:
Momentum is a crucial component of the motivation graph. Once motivation starts to decline, it can be challenging to regain momentum. However, by taking small steps and celebrating small wins, we can build momentum and increase motivation. Breaking tasks down into manageable chunks and setting achievable goals can help maintain momentum and prevent motivation from dropping too low.
5. The Role of Environment:
The environment in which we find ourselves can have a significant impact on motivation. Surrounding ourselves with positive and supportive people, creating an organized and clutter-free workspace, and having a routine can help create an environment that fosters motivation. Making intentional changes to our environment can help us stay motivated and focused on our goals.
6. Strategies for Boosting Motivation:
Understanding the motivation graph can also provide insights into strategies for boosting motivation. These strategies can include setting specific and achievable goals, practicing self-care and relaxation techniques, seeking support and accountability from others, and finding ways to make the task at hand more enjoyable or meaningful. Experimenting with different strategies can help identify what works best for individuals.
Conclusion:
The motivation graph is a powerful tool for understanding the dynamics of motivation. By recognizing that motivation is not a static state and is influenced by various factors, we can develop strategies to maintain and boost motivation levels. Understanding the ups and downs, the role of internal and external factors, the importance of momentum, and the impact of the environment can help us navigate through challenges and stay motivated towards achieving our goals.
The Rise and Fall of Motivation
Understanding the different stages of motivation can help us better utilize and sustain it in our lives. Motivation is not a constant state but rather a fluctuating graph that goes through various phases. By understanding this graph, we can navigate it more effectively and optimize our efforts towards achieving our goals.
1. Initial Excitement:
In the beginning, when we set a new goal or embark on a new project, we often experience a surge of motivation. This initial excitement is fueled by the anticipation of the outcome and the potential rewards that lie ahead. It is essential to take advantage of this phase by channeling the energy towards planning and taking the first steps towards our goals.
2. Plateau:
After the initial surge, motivation tends to plateau. This phase is characterized by a steadier level of motivation, where the initial excitement diminishes, and the reality of the effort required sets in. It is during this phase that we need to focus on building discipline and resilience to push through the challenges.
3. The Dip:
At some point, our motivation may experience a dip. This could be due to setbacks, failures, or simply a loss of interest. It is crucial to recognize this dip and actively seek ways to re-engage our motivation. This could involve re-evaluating our goals, finding new sources of inspiration, or revisiting the initial reasons why we set out on this path.
4. Upswing:
With the right strategies and mindset, motivation can be revived, leading to an upswing. This phase is characterized by renewed energy and a rekindled passion for our goals. It is important to capitalize on this upswing by setting smaller, achievable milestones and celebrating progress along the way.
5. Continual Maintenance:
Motivation requires continual maintenance to sustain it over the long term. This involves creating a supportive environment, setting realistic expectations, and implementing habits and routines that align with our goals. Regularly reassessing our progress and adjusting our strategies can help us stay motivated and on track.
In conclusion, motivation is not a linear journey but rather a dynamic graph that goes through various stages. By understanding and navigating these stages, we can harness and sustain motivation to achieve our goals effectively.
Factors Affecting Motivation Levels
There are several factors that can affect motivation levels. These factors can vary from person to person and situation to situation. Understanding and managing these factors can help individuals and organizations maintain high levels of motivation. Here are some of the key factors:
- Goals: Setting clear and achievable goals is essential for motivation. When individuals have specific goals to work towards, they are more likely to stay motivated and focused.
- Rewards and Recognition: The promise of rewards or recognition for achieving goals can be a powerful motivator. People are more likely to be motivated when they know that their efforts will be acknowledged and rewarded.
- Support and Resources: Access to support and resources can greatly impact motivation levels. When individuals have the necessary tools and assistance to complete their tasks, they are more likely to stay motivated and perform well.
- Work Environment: The work environment plays a significant role in motivation. A positive and supportive work environment can help individuals feel motivated and engaged, while a negative or stressful environment can lead to demotivation.
- Autonomy: Having a sense of autonomy and control over one’s work can increase motivation. When individuals have the freedom to make decisions and work in their own way, they are more likely to feel motivated and engaged.
- Challenge: A certain level of challenge in tasks can be motivating. When individuals are faced with challenging tasks that require them to stretch their abilities, they are more likely to feel motivated and fulfilled.
- Interest and Passion: Interest and passion for the work at hand can be a powerful motivator. When individuals are engaged in tasks that align with their interests and passions, they are more likely to stay motivated and perform at their best.
These are just a few of the factors that can affect motivation levels. It’s important to note that motivation is a complex phenomenon and can be influenced by a combination of factors. By understanding and addressing these factors, individuals and organizations can help maintain and increase motivation levels over time.
The Importance of Setting Realistic Goals
Setting goals can be a powerful motivator, but it’s important to set goals that are realistic and achievable. When you set realistic goals, you give yourself something concrete to work towards and increase your chances of success.
Here are a few reasons why setting realistic goals is important:
- Focus and Clarity: When you have realistic goals, you know what you’re working towards and can develop a clear roadmap to achieve them. This focus helps you stay on track and avoid wasting time and energy on tasks that don’t contribute to your goals.
- Motivation and Confidence: Setting realistic goals provides you with a sense of purpose and motivation. When you achieve these goals, it boosts your confidence and motivates you to set and achieve even bigger goals in the future.
- Progress Tracking: Realistic goals provide you with measurable milestones to track your progress. This allows you to assess how far you’ve come and make any necessary adjustments to your strategies or timeline.
- Avoid Burnout: Setting realistic goals helps prevent burnout. When you set goals that are too ambitious or unattainable, you may end up feeling overwhelmed and demotivated. By setting realistic goals, you can maintain a healthy work-life balance and avoid excessive stress.
Remember that setting realistic goals doesn’t mean you can’t aim high. It simply means setting goals that are challenging yet attainable with effort and dedication. A good approach is to break larger goals into smaller, more manageable tasks or milestones.
By setting realistic goals, you can harness the power of motivation and increase your chances of long-term success. So take the time to evaluate your goals and make sure they are realistic and aligned with your abilities and resources.
How to Stay Motivated Even When the Graph is Low
Staying motivated can be challenging, especially when you’re experiencing a low point on the motivation graph. However, there are strategies you can implement to help you maintain motivation and push through those difficult times. Here are some tips:
- Set specific goals: Having clear and specific goals can give you something to work towards, even when your motivation is low. Break down larger goals into smaller, attainable ones, and celebrate each achievement along the way.
- Find your why: Understanding the reasons behind your goals and the impact they will have on your life can help reignite your motivation. Reflect on why you started in the first place and reconnect with your purpose.
- Practice self-care: Take care of yourself both physically and mentally. Make sure you’re getting enough sleep, eating well, and finding time for activities you enjoy. Taking care of yourself will help replenish your energy and increase your motivation.
- Surround yourself with positive influences: Spend time with people who inspire and motivate you. Seek out mentors or join communities of like-minded individuals who can support and encourage you during difficult times.
- Break tasks into smaller steps: When faced with a daunting task, divide it into smaller, more manageable steps. This can help make it feel less overwhelming and keep you motivated as you make progress.
- Track your progress: Keep a record of your accomplishments, no matter how small. Seeing your progress on paper can boost your motivation and serve as a reminder of how far you’ve come.
- Stay focused: Minimize distractions and create a dedicated workspace where you can concentrate on your goals. Prioritize your tasks and eliminate unnecessary activities that may be draining your motivation.
- Visualize success: Imagine yourself achieving your goals and experiencing the benefits. Visualizing success can help fuel your motivation and create a positive mindset.
Remember, motivation is not constant, and it’s natural to have ups and downs. By implementing these strategies, you can stay motivated and navigate through low points on the motivation graph with resilience and determination.
Exploring Different Motivational Techniques
- Setting Goals: Establishing clear, specific, and achievable goals helps individuals remain focused and motivated. Breaking down big goals into smaller milestones can provide a sense of progress and accomplishment.
- Providing Feedback: Regularly giving constructive feedback and recognition for efforts and achievements can boost morale and motivation. Positive reinforcement can also encourage continuous improvement.
- Reward Systems: Implementing reward systems, such as incentives or bonuses, can motivate individuals to work harder and achieve better results. Rewards can help create a sense of excitement and provide tangible recognition for successful outcomes.
- Creating a Supportive Environment: Cultivating a positive and supportive work or learning environment fosters motivation. Encouraging teamwork, collaboration, and open communication allows individuals to feel valued and supported, motivating them to perform at their best.
- Autonomy and Ownership: Providing individuals with a sense of autonomy and ownership over their tasks and projects can increase motivation. Allowing individuals to have control over their work processes and decisions can enhance their engagement and commitment.
- Continuous Learning and Development: Offering opportunities for personal and professional development can fuel motivation. Providing training, workshops, or mentorship programs can inspire individuals to acquire new skills and enhance their knowledge, promoting growth and motivation.
- Challenging Work: Assigning meaningful and challenging tasks can stimulate motivation. Engaging individuals in work that aligns with their interests and capabilities can foster a sense of purpose and drive to excel.
- Celebrating Achievements: Recognizing and celebrating individual and team achievements helps boost motivation. Acknowledging milestones and successes can create a positive and encouraging atmosphere, inspiring individuals to continue their efforts.
Incorporating a combination of these motivational techniques can help individuals maintain their motivation over time. It is important to understand that motivation is not a constant state and can fluctuate, so it is necessary to consistently assess and adjust these techniques to meet changing needs and circumstances. By utilizing effective motivational strategies, individuals can stay engaged, focused, and driven to achieve their goals.
The Role of Self-Discipline in Sustaining Motivation
While motivation can be a powerful force to initiate action, it often fades away over time. This is where self-discipline becomes crucial in sustaining motivation and achieving long-term goals.
What is self-discipline?
Self-discipline is the ability to control one’s actions, emotions, and desires in order to achieve a desired goal. It involves making conscious choices and resisting temptations that may hinder progress towards the goal.
How does self-discipline sustain motivation?
1. Consistency: Self-discipline allows individuals to maintain consistent effort and focus on their goals, even when the initial motivation wanes. It helps in establishing a routine and sticking to it, even when faced with distractions or setbacks.
2. Delayed gratification: Self-discipline involves the ability to delay immediate gratification in favor of long-term rewards. It helps individuals stay committed to their goals, prioritize their actions, and make choices that align with their larger objectives.
3. Resilience: Self-discipline builds resilience and mental strength, enabling individuals to push through obstacles and setbacks. It helps develop a mindset of perseverance and determination, essential qualities for sustaining motivation in the face of challenges.
Tips for developing self-discipline:
- Set clear and specific goals: Clearly define what you want to achieve and break it down into smaller, manageable tasks.
- Create a routine: Establish a daily routine that incorporates actions and habits aligned with your goals.
- Develop a positive mindset: Cultivate a positive attitude towards challenges and setbacks, viewing them as opportunities for growth.
- Practice self-control: Train yourself to resist immediate gratification and make choices that align with your long-term goals.
- Seek support: Surround yourself with supportive individuals who can help keep you accountable and motivated.
The synergy between motivation and self-discipline:
Motivation and self-discipline are not mutually exclusive; in fact, they work hand in hand. While motivation provides the initial drive and enthusiasm, self-discipline sustains it and ensures consistent progress towards the goal. They form a symbiotic relationship, with motivation fueling the desire to pursue a goal and self-discipline providing the necessary structure and guidance to stay on track.
In conclusion, self-discipline plays a vital role in sustaining motivation and achieving long-term goals. By practicing self-discipline techniques and cultivating a positive mindset, individuals can overcome distractions, setbacks, and the inevitable decline of motivation, ultimately leading to successful outcomes.
Overcoming Obstacles and Rebuilding Motivation
In our journey towards achieving our goals, we often come across obstacles that can hinder our motivation. These obstacles can be external or internal factors that make it difficult to stay motivated. However, overcoming these obstacles is essential if we want to maintain our motivation and continue moving forward.
Here are some strategies to help you overcome obstacles and rebuild your motivation:
- Identify the obstacle: The first step in overcoming any obstacle is to identify what is causing the problem. Is it a lack of resources, a challenging task, or self-doubt? By understanding the root cause, you can develop a targeted plan to address it.
- Break it down: Sometimes obstacles can seem overwhelming, but breaking them down into smaller, manageable tasks can make them more achievable. Create a step-by-step plan that allows you to tackle each part of the obstacle separately.
- Seek support: Don’t be afraid to ask for help when you need it. Reach out to friends, family, or mentors who can provide guidance, advice, or simply a listening ear. Having a support system can make a significant difference in overcoming obstacles and rebuilding motivation.
- Stay positive: Maintaining a positive mindset can help you overcome even the toughest obstacles. Focus on the progress you have made, celebrate small wins, and remind yourself of your ultimate goal. Surround yourself with positive influences and inspirational messages to keep your motivation high.
- Learn from setbacks: Setbacks are an inevitable part of any journey. Instead of letting them demotivate you, view them as opportunities for growth and learning. Analyze what went wrong, identify any lessons or insights gained, and use that knowledge to make improvements and move forward.
- Visualize success: Visualization is a powerful tool for rebuilding motivation. Close your eyes and imagine yourself overcoming the obstacles and achieving your goals. Visualize the satisfaction and fulfillment you will feel. Use this visualization as a source of inspiration and a reminder of what you are working towards.
Remember, motivation may not last forever, but by consistently using these strategies to overcome obstacles, you can rebuild and maintain your motivation throughout your journey towards success.
Questions and answers
Why does motivation not last?
Motivation does not last because it is often a fleeting feeling that comes and goes. It is not sustainable in the long run. Our motivation levels can fluctuate based on various factors such as external circumstances, emotions, and personal mindset.
What is the motivation graph?
The motivation graph is a visual representation of how our motivation levels change over time. It typically starts off high when we are initially inspired or excited about a goal, but then it gradually decreases as time goes on. This graph helps us understand that motivation is not constant and can fluctuate throughout our journey.
How can we maintain motivation?
To maintain motivation, it is important to set realistic goals, break them down into smaller milestones, and celebrate each achievement along the way. It can also be helpful to have a support system or accountability partner who can keep us motivated and provide encouragement. Additionally, implementing positive habits, staying focused on the reasons why we want to achieve our goals, and practicing self-care can help sustain motivation.
What are some strategies for dealing with a dip in motivation?
When experiencing a dip in motivation, it can be helpful to reassess our goals and remind ourselves why we started in the first place. We can also try changing our environment or routine to inject some new energy and inspiration. Additionally, seeking support and motivation from others, revisiting past successes, and practicing self-reflection can all be effective strategies for overcoming a temporary lack of motivation.