When it comes to incorporating the words and ideas of others into our own writing, there are two main techniques that we can use: paraphrasing and verbatim quoting. Both methods have their merits and can be effective in different situations. In this article, we will explore the similarities and differences between paraphrasing and verbatim quoting, and the factors that may influence which method is most appropriate to use.
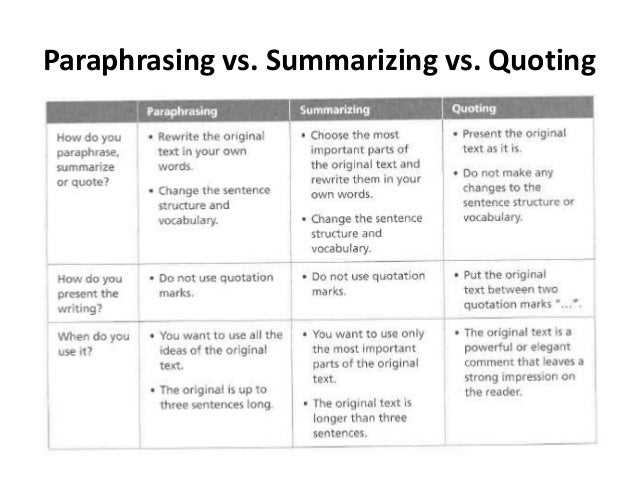
Paraphrasing involves restating the original source material in our own words, while still expressing the same meaning. This technique allows us to convey the information and ideas of the original source while putting it into our own voice and style. Paraphrasing is often used to clarify complex concepts or ideas, simplify language, or provide a concise summary of a longer passage.
On the other hand, verbatim quoting involves directly copying the original source material word for word, enclosing it in quotation marks. This technique is useful when we want to highlight the exact wording of the original source, preserve the author’s unique style, or provide evidence to support our arguments. Verbatim quotes are especially effective when the language used by the original author is particularly powerful or memorable.
While paraphrasing and verbatim quoting have their distinct characteristics, there are also some similarities between the two methods. Both techniques require a deep understanding of the original source material, as well as the ability to analyze and synthesize information effectively. In addition, both paraphrasing and verbatim quoting require proper citation to give credit to the original author and avoid plagiarism.
It is important to note that both paraphrasing and verbatim quoting have their place in academic and professional writing. The choice of which method to use depends on the purpose of our writing, the intended audience, and the nature of the source material.
By understanding the similarities and differences between paraphrasing and verbatim quoting, we can make informed choices when incorporating external information into our own work, ensuring that we are effectively communicating our ideas while respecting the ideas and words of others.
Understanding Paraphrasing and Verbatim Quoting: Key Definitions
When it comes to incorporating information from other sources into your writing, it’s important to understand the concepts of paraphrasing and verbatim quoting. These techniques allow you to effectively present the ideas of others while maintaining proper attribution and avoiding plagiarism. Let’s explore the key definitions of paraphrasing and verbatim quoting:
Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing involves restating someone else’s ideas or information in your own words. It is a valuable skill in academic writing as it demonstrates your understanding of the original source while allowing you to present the information in a way that suits your own writing style. The goal of paraphrasing is to convey the same meaning as the original source, but with different wording and sentence structure.
When paraphrasing, it is essential to avoid copying the original source word-for-word and to use your own language and sentence structure. Additionally, proper citation must still be provided to give credit to the original author.
Verbatim Quoting
Verbatim quoting involves directly using the exact words and phrases from a source, enclosed within quotation marks. This technique is useful when you want to capture the precise wording of the original author or when the specific language of the source is particularly important to your argument or analysis. Verbatim quoting allows you to present evidence or support for your ideas by directly quoting from credible sources.
When using verbatim quotes, it is important to accurately reproduce the original source text, including punctuation and capitalization. Any modifications, such as omitting or inserting words, should be indicated using square brackets or ellipses, respectively. Proper citation is necessary to attribute the quoted material to its original author.
Key Differences
The key difference between paraphrasing and verbatim quoting lies in the level of similarity to the original source. Paraphrasing involves rephrasing the ideas in your own words, while verbatim quoting uses the exact words from the original source. Paraphrasing allows you to present the same information with different wording and sentence structure, while verbatim quoting retains the original language and phrasing.
While paraphrasing allows for more flexibility and integration of the source material into your own writing, verbatim quoting is more suited for capturing the original author’s specific words and phrases. Both techniques require proper citation to give credit to the original author and avoid plagiarism.
Paraphrasing: A Closer Look at Rewording and Restating
Paraphrasing is the act of rewording or restating someone else’s ideas or words in your own language, while maintaining the original meaning. It involves taking the information from the source and presenting it in a different form without changing the message. Paraphrasing is an essential skill used in academic writing, research, and other professional contexts.
When paraphrasing, it is important to understand the original text and its key points. This process requires careful reading and comprehension, as well as the ability to convey the main ideas in a clear and concise way. Paraphrasing allows you to express the same information using different words and sentence structures, while avoiding plagiarism.
One common technique in paraphrasing is to use synonyms or different expressions to replace specific words or phrases from the original text. This helps to maintain the meaning while providing a fresh perspective. Additionally, paraphrasing may involve restructuring sentences or changing the order of ideas to create a more coherent flow of information.
- Benefits of Paraphrasing:
- Enhances understanding: Paraphrasing requires a deep understanding of the source material, enabling you to grasp the concepts and ideas in a meaningful way.
- Improves writing skills: Paraphrasing allows you to develop your writing skills by practicing how to express ideas in your own words while maintaining clarity and coherence.
- Strengthens critical thinking: Through paraphrasing, you engage with the source material more actively, evaluating the information and presenting it from a different perspective.
- Avoids plagiarism: Paraphrasing ensures that you are not copying someone else’s work verbatim and helps you credit the original author by providing proper citations.
Paraphrasing is an effective tool for summarizing, simplifying complex ideas, or explaining information in a way that is easier for the audience to understand. By expressing the content in your own words, you can also add your own insights or interpretations, making the information more personalized and engaging for your readers.
In conclusion, paraphrasing is a valuable skill that allows you to restate someone else’s ideas in your own words, while maintaining the original meaning. It is a useful technique for academic writing, research, and professional communication, offering benefits such as improved understanding, writing skills, critical thinking, and avoiding plagiarism.
Verbatim Quoting: Examining Directly Quoting Text
Verbatim quoting is the act of directly copying and preserving the exact wording of a source in quotation marks. It is an important tool in academic writing and research that allows writers to maintain the integrity and precision of the original author’s words.
When using verbatim quoting, it is crucial to follow the guidelines for accurate and ethical use of quotations. This includes clearly indicating that the text is taken directly from the source and providing appropriate citation to give credit to the original author.
Verbatim quoting can be used to:
- Highlight important or memorable phrases or statements
- Provide evidence or support for arguments
- Engage with and analyze the language used by the author
However, it is essential to use verbatim quotes judiciously and selectively. Over-reliance on direct quotes can make the writing seem unoriginal and lack original analysis. Writers should strive to balance verbatim quotes with their own interpretations and insights.
When using verbatim quotes, it is important to consider the following:
- Quotations should be accurate and faithfully reproduce the original wording and punctuation.
- Long quotes should be indented or set apart from the rest of the text to distinguish them visually.
- Quotations should be integrated smoothly into the writer’s own sentence structure and flow.
- When necessary, it is acceptable to modify a quote slightly for clarity or grammatical correctness, but such changes should be clearly indicated using brackets or ellipses.
In conclusion, verbatim quoting is a valuable tool in academic writing that allows writers to directly convey the words and intentions of the original author. However, it should be used judiciously and ethically, and always accompanied by proper citation to give credit and respect to the source.
Similarities: Overlapping Elements in Paraphrasing and Verbatim Quoting
While paraphrasing and verbatim quoting are distinct approaches to incorporating information from sources into one’s own work, there are certain elements that overlap between the two methods:
- Source Attribution: Both paraphrasing and verbatim quoting require proper attribution of the original source. This is necessary to give credit to the original author and avoid plagiarism.
- Accuracy: Whether paraphrasing or using a verbatim quote, it is important to accurately convey the information from the source. The meaning and intent of the original text should be preserved.
- Contextualization: Both paraphrasing and verbatim quoting necessitate providing context for the information being presented. This helps the audience understand the relevance and significance of the quoted or paraphrased material.
Additionally, both paraphrasing and verbatim quoting should be used ethically and responsibly. Care should be taken to ensure that the original author’s ideas are accurately represented, and any changes made during paraphrasing or selection of verbatim quotes should not distort the original meaning.
Differences: Contrasting Approaches and Techniques
Paraphrasing and verbatim quoting are two distinct approaches to incorporating information from external sources into a written work. While both methods serve to support arguments and provide evidence, they differ in their approach and techniques.
1. Language Usage
One significant difference between paraphrasing and verbatim quoting lies in their use of language. Paraphrasing involves expressing someone else’s ideas or information in your own words, while verbatim quoting involves directly copying the original text word for word. Paraphrasing allows for greater flexibility in how the information is presented, whereas verbatim quoting maintains the original language and wording.
2. Expression and Interpretation
Paraphrasing and verbatim quoting also differ in how they allow for expression and interpretation. Paraphrasing provides an opportunity to interpret the original text and express ideas in the author’s own voice. It allows for better integration of the information into the overall flow and tone of the piece. Verbatim quoting, on the other hand, provides a direct representation of the original author’s words, which allows for less interpretation and expression in the author’s voice.
3. Length and Precision
The length and precision of the information can also vary between paraphrasing and verbatim quoting. Paraphrasing often involves condensing and summarizing the original text to convey the main ideas concisely. It allows for flexibility in deciding which details to include or omit. Verbatim quoting, however, maintains the original length and precision of the source text, making it useful when it is crucial to capture the exact wording or when specific details need to be preserved.
4. Citations and References
Finally, the requirements for citations and references differ between paraphrasing and verbatim quoting. Paraphrasing requires attributing the ideas and information to the original source but does not necessarily require quotation marks. Verbatim quoting, on the other hand, requires the use of quotation marks to indicate a direct quotation, in addition to the citation and reference.
| Aspect | Paraphrasing | Verbatim Quoting |
|---|---|---|
| Language Usage | Expressed in own words | Exact copy of original text |
| Expression and Interpretation | Allows for interpretation and personal expression | Represents original author’s words without interpretation |
| Length and Precision | Summarized and condensed while conveying main ideas | Maintains original length and precision |
| Citations and References | Requires attribution without necessarily using quotation marks | Requires attribution and the use of quotation marks for direct quotations |
In summary, paraphrasing involves expressing ideas in one’s own words, allowing for interpretation and flexibility in language usage. Verbatim quoting, on the other hand, directly copies the original text, maintaining its language and wording. The techniques used for paraphrasing and verbatim quoting differ in terms of expression, length, and citations, offering writers various options for incorporating external information into their works.
Use Cases: When to Choose Paraphrasing or Verbatim Quoting
When it comes to deciding whether to use paraphrasing or verbatim quoting in your writing, there are certain use cases where one option may be more suitable than the other. Consider the following scenarios:
-
Preserving the original wording: If the exact wording of the source material is important or contributes to the emphasis or impact of your point, verbatim quoting is the preferred method. This is particularly useful when analyzing specific language or discussing the author’s writing style or tone.
-
Focusing on the meaning and ideas: When the emphasis is on conveying the main ideas or concepts from the source material rather than the specific wording, paraphrasing is a suitable choice. Paraphrasing allows you to express the ideas in your own words, demonstrating your understanding of the topic.
-
Reducing the length: Paraphrasing can be useful when you need to condense and simplify information from the source material, especially if space is limited or you want to present the information in a more concise manner.
-
Blending multiple sources: If you want to combine information from multiple sources, paraphrasing allows you to integrate different perspectives and ideas into a cohesive argument or discussion. Verbatim quoting can be used selectively to highlight specific points or support certain statements.
-
Avoiding plagiarism: Both paraphrasing and verbatim quoting are effective ways to avoid plagiarism. Paraphrasing involves rephrasing the original content in your own words, while verbatim quoting involves using the exact words of the source and properly citing the author. Both methods require appropriate citation to give credit to the original author.
Ultimately, the decision to use paraphrasing or verbatim quoting depends on the specific requirements of your writing task and the message you want to convey. It is important to consider the purpose, tone, and target audience of your work to determine which method best suits your needs.
Effectiveness and Accuracy: Evaluating the Results
When it comes to paraphrasing and verbatim quoting, evaluating the effectiveness and accuracy of the results is crucial. Both methods have their own advantages and limitations, and understanding how they impact the overall quality of the text is important.
Effectiveness:
Paraphrasing can be highly effective in conveying the author’s ideas in a more concise and clear manner. By using one’s own words and sentence structure, the paraphrased text can be better tailored to the target audience or the desired tone of the writing. It allows for better integration of the ideas into the flow of the overall text.
On the other hand, verbatim quoting can be effective when it is necessary to maintain the exact wording and style of the original source. This is particularly important in cases where the author’s words carry a significant impact or when it is important to provide evidence or support for an argument.
Accuracy:
Paraphrasing requires a deep understanding of the original source material in order to accurately convey the intended meaning. It involves interpreting and rephrasing the information in a way that captures the essence of the original text. When done properly, paraphrasing can maintain the accuracy of the information while presenting it in a new form.
Verbatim quoting, on the other hand, ensures the highest level of accuracy as it preserves every word and phrase from the original source. It allows readers to directly access the author’s exact words, ensuring that there is no room for interpretation or misrepresentation.
Evaluating the Results:
When evaluating the results, it is important to consider the purpose and objectives of the writing. If the goal is to summarize or explain complex ideas, paraphrasing may be more effective. However, if the intention is to present evidence or support arguments, verbatim quoting may be necessary to maintain accuracy and credibility.
Additionally, evaluating readability and coherence is essential. Paraphrased text should flow smoothly and seamlessly within the overall writing, without disrupting the reader’s comprehension. Verbatim quoting, while accurate, may result in a text that feels disjointed and less fluent.
Furthermore, the appropriate use of citations and references must be considered. Paraphrasing requires proper attribution and citation to acknowledge the original source, while verbatim quoting relies on quotation marks and accurate referencing to avoid plagiarism and maintain academic integrity.
In conclusion, both paraphrasing and verbatim quoting have their own strengths in terms of effectiveness and accuracy. The choice between the two methods depends on the specific requirements of the writing and the overall goals of the author. By carefully evaluating the results, writers can ensure that their text is both effective in conveying ideas and accurate in representing the original source material.
Question and answer:
What is the difference between paraphrasing and verbatim quoting?
Paraphrasing and verbatim quoting are two different methods of incorporating another person’s ideas or words into your own writing. Paraphrasing involves rephrasing the original source material in your own words, while verbatim quoting means directly copying the source word-for-word.
Which method is more preferable: paraphrasing or verbatim quoting?
The choice between paraphrasing and verbatim quoting depends on the context and purpose of your writing. Paraphrasing is often preferred when you want to summarize or restate an idea in a more concise or accessible manner. Verbatim quoting is useful when you want to provide direct evidence or support for your arguments, or when you want to preserve the original language or style of the source.
Are there any situations where verbatim quoting is necessary?
Verbatim quoting is necessary when you need to provide accurate evidence or quotations from a source. This is particularly important in academic writing, legal documents, or when reporting statements made by someone in an interview or speech. In these cases, it is crucial to use quotation marks and provide proper attribution to the original source.
Can paraphrasing be considered plagiarism?
Paraphrasing can be considered plagiarism if it is not done properly. Plagiarism occurs when you present someone else’s ideas or words as your own without proper attribution. To avoid plagiarism when paraphrasing, it is important to rephrase the original material in your own words and to provide proper citations or references to the original source.