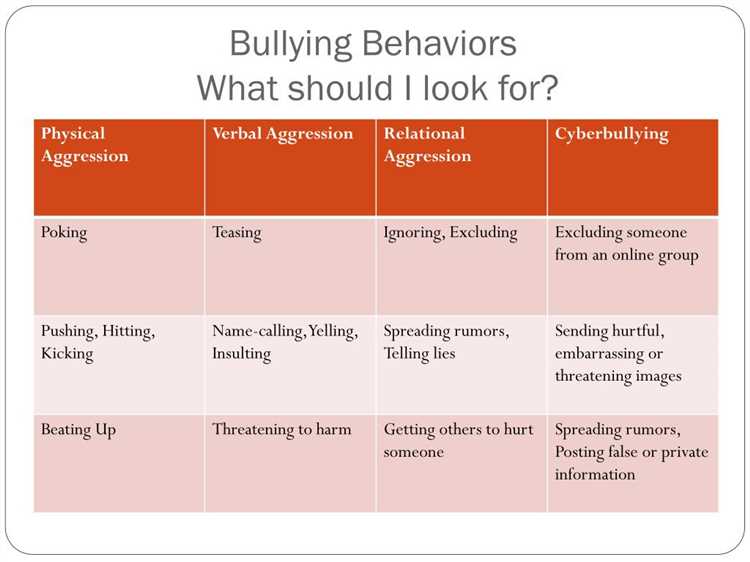
Childhood bullying is a prevalent issue that affects millions of children worldwide. It is a form of aggressive behavior that can have long-lasting effects on both the bully and the victim. While many factors contribute to the occurrence of bullying, one important aspect that researchers have been exploring is the impact of personality traits.
Personality traits play a crucial role in shaping an individual’s behavior, including their likelihood to engage in bullying. Some personality traits, such as aggressiveness, impulsivity, and low empathy, have been found to be associated with an increased risk of becoming a bully. These traits can manifest early in childhood and persist into adolescence and adulthood.
On the other hand, certain personality traits, such as high levels of empathy, self-confidence, and assertiveness, have been found to reduce the likelihood of engaging in bullying behavior. Children with these traits are more likely to intervene and stand up for others who are being bullied, creating a safer and more inclusive environment.
Understanding the impact of personality traits on childhood bullying is crucial for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. By identifying children with high-risk personality traits early on, educators, parents, and mental health professionals can implement targeted interventions to address the underlying issues and promote positive social interactions. Additionally, fostering positive personality traits in all children can help create a culture of empathy, respect, and acceptance, which can ultimately contribute to a reduction in bullying behaviors.
Understanding the Relationship: Personality Traits and Childhood Bullying
Bullying is a pervasive issue in today’s society, especially among children. It can have long-lasting effects on both the bully and the victim, impacting their mental and emotional well-being. One important factor that contributes to the occurrence of bullying is the personality traits of the individuals involved.
1. Aggression: Aggression is a key personality trait that is often associated with bullying behavior. Children who are high in aggression tend to be more prone to engage in acts of bullying. They may exhibit hostile behavior, have difficulty controlling their anger, and have a higher tendency towards physical aggression.
2. Empathy: On the other hand, empathy plays a crucial role in preventing bullying. Children with low levels of empathy may struggle to understand the feelings of others, making it easier for them to engage in bullying behavior. Empathy is an important factor in developing positive relationships and fostering compassionate behavior.
3. Self-esteem: Low self-esteem has been identified as a common characteristic of both bullies and victims. Bullies may resort to aggressive behavior as a means to boost their own self-esteem, while victims may also have low self-esteem, making them more susceptible to bullying. Addressing self-esteem issues in both bullies and victims is essential in preventing and mitigating bullying.
4. Social skills: The ability to navigate social interactions and form positive relationships is vital in preventing bullying. Children with poor social skills may struggle to communicate effectively, establish friendships, and resolve conflicts peacefully. This can contribute to a higher likelihood of bullying or being bullied.
5. Impulsivity: Impulsive children may be more likely to engage in aggressive behavior without considering the consequences. Their impulsive nature can lead to impulsive acts of bullying, causing harm to others. Teaching impulse control strategies and promoting self-regulation can help mitigate impulsive behavior and reduce the occurrence of bullying.
| Personality Traits | Bullies | Victims |
|---|---|---|
| Aggression | High | Low |
| Empathy | Low | High |
| Self-esteem | Low | Low |
| Social skills | Poor | Poor |
| Impulsivity | High | High |
Understanding the relationship between personality traits and childhood bullying is crucial in developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. By addressing and targeting specific personality traits associated with bullying, we can create a safer and more inclusive environment for all children.
The Role of Aggression: How Personality Traits Influence Bullying Behavior
Personality traits play a significant role in shaping an individual’s behavior, including their propensity for engaging in bullying behavior. One key personality trait that has been found to have a strong influence on bullying behavior is aggression. Aggression refers to behavior that is intended to cause harm or injury to another person.
Individuals with high levels of aggression are more likely to engage in bullying behavior. They may have a tendency to use physical or verbal aggression to exert power and dominance over others. This aggressive behavior can manifest itself in various forms of bullying, such as physical bullying, verbal bullying, or relational bullying.
In addition to aggression, other personality traits can also influence bullying behavior. For example, individuals who have low levels of empathy may be more likely to engage in bullying behavior. Empathy refers to the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. Lack of empathy can make it difficult for individuals to consider the negative impact their actions may have on others, making them more likely to engage in bullying.
Similarly, individuals with low self-esteem may also be more prone to engaging in bullying behavior. Low self-esteem can lead to feelings of insecurity and a desire to bring others down in order to feel better about oneself. This can manifest in bullying behavior as a means of gaining power and control over others.
To further understand the role of aggression and other personality traits in bullying behavior, researchers have conducted numerous studies. These studies have consistently found a positive correlation between aggression and bullying behavior, supporting the idea that aggression is a significant predictor of bullying.
| Personality Trait | Influence on Bullying Behavior |
|---|---|
| Aggression | Strong positive influence |
| Empathy | Negative influence (low empathy) |
| Self-esteem | Negative influence (low self-esteem) |
It is important to note that while these personality traits can predispose individuals to engage in bullying behavior, they are not the sole determinants. Other factors, such as social environment and learned behavior, also play a significant role in shaping bullying behavior.
Understanding the role of aggression and other personality traits in bullying behavior can help inform prevention and intervention efforts. By addressing and targeting these underlying personality traits, it may be possible to reduce the occurrence of bullying and promote healthier social interactions among children. Schools and parents can play a crucial role in fostering empathy, self-esteem, and peaceful conflict resolution skills, which can help prevent the development of bullying behavior.
In conclusion, aggression and other personality traits have a significant influence on bullying behavior. Recognizing and addressing these traits can contribute to more effective strategies to prevent and intervene in bullying situations, ultimately promoting a safer and more inclusive environment for children.
Empathy and its Impact on Bullying: The Importance of Emotional Intelligence
Bullying is a complex issue that affects many children and has long-lasting psychological effects. While various factors contribute to the occurrence of bullying, one crucial aspect that often goes unnoticed is empathy and emotional intelligence.
What is empathy?
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. It is an essential emotional skill that enables individuals to connect with others, perceive their emotions, and respond appropriately. Empathetic individuals can recognize when someone is in pain, both physically and emotionally, and offer support and understanding.
How does empathy impact bullying?
Empathy serves as a powerful tool in preventing and addressing bullying. When children possess high levels of empathy, they are more likely to recognize the emotions of their peers and understand the consequences of their actions. This understanding motivates them to approach others with kindness, respect, and compassion.
On the other hand, a lack of empathy can contribute to the occurrence and perpetuation of bullying. Bullies who exhibit low empathy levels struggle to comprehend the pain and suffering they inflict on others. They may be unable to understand or care about the feelings of their victims, leading them to engage in harmful behavior without remorse.
The role of emotional intelligence in empathy and bullying
Emotional intelligence is closely linked to empathy and plays a vital role in addressing bullying. Emotionally intelligent individuals possess the ability to recognize and understand both their own emotions and the emotions of others. They can regulate their emotions, navigate social situations effectively, and display empathy towards others.
To combat bullying, it is essential to develop children’s emotional intelligence. By teaching them how to identify and manage their emotions, as well as recognize the feelings of their peers, we can foster a more empathetic and understanding environment.
Practical strategies to promote empathy and emotional intelligence
- Teach children about emotions: Introduce children to a wide range of emotions and help them understand these emotions in themselves and others.
- Encourage perspective-taking: Encourage children to imagine how others might feel in certain situations. This exercise helps them to understand different perspectives and develop empathy.
- Model empathetic behavior: Children learn by observing, so it is important for adults to model empathy in their own interactions. Show children what it means to be kind, compassionate, and understanding.
- Practice active listening: Teach children the importance of active listening, where they give their full attention to others and validate their feelings.
- Provide opportunities for empathy-building activities: Engage children in activities that promote empathy, such as volunteering or participating in community service projects.
Conclusion
Empathy and emotional intelligence are crucial factors in combatting bullying and creating a kinder, more respectful society. By fostering empathy in children, we can empower them to understand, connect with, and support others, creating a positive and inclusive environment for all.
The Power of Social Influence: How Personality Traits Affect Peer Group Dynamics
Peer groups play a crucial role in shaping an individual’s behavior, attitudes, and beliefs, especially during childhood and adolescence. These groups have the power to influence various aspects of a child’s life, including their involvement in bullying. Research has shown that certain personality traits can significantly impact peer group dynamics and contribute to the occurrence of bullying behaviors.
1. Dominance: Individuals who possess dominant personality traits tend to seek power and control within their peer groups. They may engage in bullying behaviors to establish their dominance and maintain their social status. These individuals often become the leaders or influencers within their peer groups, shaping the group’s dynamic and setting the tone for acceptable behavior.
2. Aggression: Aggressive individuals often exhibit hostility, impulsivity, and a lack of empathy towards others. These personality traits can contribute to the development of bullying behaviors within peer groups. Aggressive individuals may intentionally harm or intimidate others to assert their dominance or to fulfill their own desires, disregarding the feelings and well-being of their peers.
3. Conformity: Some individuals have a strong desire to conform to social norms and fit in with their peer group. These individuals may engage in bullying behaviors to gain the acceptance and approval of their peers. By conforming to the group’s behavior, these individuals may overlook the negative consequences of their actions and continue to engage in bullying behaviors, even if they personally disagree with them.
4. Empathy: Empathy plays a crucial role in preventing and addressing bullying behaviors within peer groups. Individuals who possess high levels of empathy are more likely to consider the feelings and perspectives of their peers. They are less likely to engage in or support bullying behaviors and may actively intervene to prevent bullying incidents. Peer groups that consist of empathetic individuals create a positive and inclusive environment where bullying is less likely to occur.
5. Self-esteem: Individuals with low self-esteem may be more vulnerable to engaging in bullying behaviors or becoming victims of bullying. Low self-esteem can lead individuals to seek validation and acceptance from their peers, sometimes resorting to aggressive or manipulative behaviors. Peer groups that promote positive self-esteem and provide support to their members can mitigate the occurrence of bullying behaviors.
Conclusion: Personality traits have a significant impact on peer group dynamics, including the occurrence of bullying behaviors. Understanding how personality traits influence these dynamics can help identify individuals at risk of engaging in bullying and inform the development of prevention and intervention strategies. By promoting empathy, self-esteem, and positive social norms within peer groups, we can create a supportive and inclusive environment that discourages bullying behaviors.
The Vulnerability Factor: Personality Traits that Make Children more Prone to Bullying
Bullying is a widespread issue that affects many children and can have long-lasting negative effects on their mental and emotional well-being. While there are multiple factors that contribute to bullying, one important aspect that needs to be addressed is the role of personality traits in making some children more vulnerable to being bullied.
Research conducted in this field has identified several personality traits that increase a child’s likelihood of becoming a target for bullying:
- Low self-esteem: Children with low self-esteem often have a negative self-image and a lack of confidence, making them an easy target for bullies. They are more likely to believe the negative remarks made by bullies and internalize them, leading to further emotional distress.
- Passivity and submissiveness: Children who are passive and submissive in nature are less likely to stand up for themselves and defend against bullies. They may have difficulty asserting themselves and may not have developed the necessary social skills to navigate bullying situations effectively.
- Sensitivity: Highly sensitive children tend to be more affected by negative experiences, including bullying. They may take the bully’s words and actions more personally, which can lead to increased emotional distress and a greater impact on their overall well-being.
- Lack of social skills: Children who struggle with social skills may have difficulty making friends, establishing positive relationships, and asserting themselves effectively. Their difficulty in navigating social situations can make them targets for bullying, as bullies often pick on children who are socially isolated.
- Anxiety: Children with high levels of anxiety may display signs of worry, fear, and vulnerability, making them more attractive targets for bullies. Their anxious disposition may also affect their ability to respond effectively to bullying situations, further exacerbating their vulnerability.
It is essential to recognize and address these personality traits in children who are more prone to bullying. By providing them with the necessary tools and support, such as building self-esteem, teaching assertiveness skills, and fostering social connections, we can help reduce their vulnerability to bullying and mitigate its negative effects.
| Personality Trait | Impact on Vulnerability to Bullying |
|---|---|
| Low self-esteem | Increases likelihood of believing negative remarks from bullies and internalizing them |
| Passivity and submissiveness | Makes it harder for children to assert themselves and defend against bullies |
| Sensitivity | Amplifies the emotional impact of bullying and negative experiences |
| Lack of social skills | Makes children more socially isolated and targets for bullying |
| Anxiety | Affects children’s ability to respond effectively to bullying situations |
The Role of Self-esteem: How Personality Traits Impact Bullying Victimization
Self-esteem is a crucial aspect of one’s personality that plays a significant role in determining vulnerability to bullying victimization in childhood. This section examines the relationship between self-esteem and bullying victimization, highlighting the impact of various personality traits on the likelihood of being targeted by bullies.
Low Self-esteem: Individuals with low self-esteem are more likely to become victims of bullying. They often lack confidence and have a negative self-perception, making them an easy target for bullies searching for vulnerabilities. Low self-esteem can lead to feelings of insecurity, fear, and a sense of powerlessness, making individuals more susceptible to sustained victimization.
High Self-esteem: On the other hand, individuals with high self-esteem tend to be less victimized by bullies. These individuals possess a strong sense of self-worth, are confident in their abilities, and have a positive self-image. Their high self-esteem acts as a protective factor, making it difficult for bullies to target them successfully.
Personality Traits: Several personality traits can impact the relationship between self-esteem and bullying victimization.
- Extraversion: Extraverted individuals tend to have higher self-esteem, as they are more outgoing and assertive. Their social skills and ability to interact with others can act as protective factors, reducing the likelihood of being victimized.
- Agreeableness: Individuals who are high in agreeableness are more likely to be victims of bullying due to their non-confrontational nature. They may have difficulty asserting themselves or setting boundaries, making them an attractive target for bullies.
- Conscientiousness: Conscientious individuals strive for perfection and place importance on following rules. While their high self-esteem may protect them to some extent, their adherence to rules and strong sense of responsibility can make them prime targets for bullies who enjoy breaking rules or disrupting order.
- Emotional Stability: Individuals with high emotional stability tend to have higher self-esteem and are less likely to be victimized. Their ability to handle stress, control their emotions, and cope with adversity makes it challenging for bullies to manipulate or exploit them.
- Openness to Experience: Open individuals who possess high self-esteem may be less likely to become victims of bullying. Their creativity, adaptability, and willingness to explore new ideas and perspectives can protect them from becoming targets.
Understanding the role of self-esteem and personality traits in bullying victimization is essential for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. By addressing low self-esteem and helping individuals build resilience, confidence, and assertiveness, it may be possible to reduce the prevalence and impact of childhood bullying.
The Connection between Personality Traits and Bullying in Adolescence
Bullying is a serious issue that affects many adolescents, causing emotional, psychological, and physical harm. Understanding the connection between personality traits and bullying behavior can help identify those at risk and develop interventions to prevent bullying.
1. Aggressiveness: Adolescents who exhibit high levels of aggressiveness are more likely to engage in bullying behavior. These individuals often have a strong need for power and control, and they may use bullying as a means to assert dominance over their peers.
2. Low Empathy: Lack of empathy is a common trait among adolescents who bully others. These individuals often struggle to understand and share the feelings of their victims, making it easier for them to justify their aggressive behavior.
3. Low Self-esteem: Adolescents with low self-esteem may resort to bullying as a way to feel better about themselves. By putting others down, they temporarily boost their own self-esteem and gain a sense of superiority.
4. Impulsivity: Impulsive individuals may engage in bullying behavior without fully considering the consequences of their actions. They act on their immediate desires and may not think about how their behavior affects others.
5. Lack of Social Skills: Adolescents who lack social skills may struggle to form positive relationships with their peers, leading them to resort to bullying as a way to gain attention and maintain a sense of social status.
6. Peer Influence: Peer influence plays a significant role in bullying behavior. Adolescents who have friends or peers who engage in bullying are more likely to participate in bullying themselves to fit in or gain acceptance within their social group.
| Personality Trait | Impact on Bullying Behavior |
|---|---|
| Aggressiveness | Increases likelihood of engaging in bullying behavior |
| Low Empathy | Difficulty understanding and sharing victims’ feelings |
| Low Self-esteem | Bullying as a means to feel superior and boost self-esteem |
| Impulsivity | Engaging in bullying behavior without considering consequences |
| Lack of Social Skills | Using bullying as a means to gain attention and social status |
| Peer Influence | Participation in bullying to fit in or gain acceptance |
It is important to note that while these personality traits may increase the likelihood of engaging in bullying behavior, they do not guarantee that an adolescent will become a bully. The complex interaction between individual traits, environmental factors, and social dynamics must be considered in the development of effective anti-bullying interventions.
Bullying prevention programs should focus on teaching empathy, conflict resolution skills, and positive relationship-building strategies. By addressing the underlying personality traits that contribute to bullying behavior, we can work towards creating a more inclusive and harmonious adolescence for all.
Addressing the Issue: Using Personality Trait-based Interventions to Prevent and Reduce Bullying
Bullying is a pervasive issue affecting children worldwide, with long-lasting negative consequences for both the victims and the bullies themselves. To effectively address this issue, it is crucial to understand the role of personality traits in shaping bullying behaviors. By targeting specific personality traits through interventions, we can develop strategies to prevent and reduce bullying.
1. Empathy-building programs:
Empathy is a key personality trait that promotes understanding, kindness, and compassion towards others. Incorporating empathy-building programs into schools and community organizations can help instill a sense of empathy in children, making them less likely to engage in bullying behaviors. These programs can include activities such as group discussions, role-plays, and community service projects that focus on developing empathy skills.
2. Anger management training:
Aggressive behavior and a lack of anger management skills are often associated with bullying. By providing anger management training, children can learn to control their impulses and emotions in more constructive ways. Teaching techniques such as deep breathing, recognizing triggers, and utilizing effective communication strategies can help children channel their anger in healthier ways, reducing the likelihood of engaging in bullying behaviors.
3. Social skills development:
Children who lack appropriate social skills may resort to bullying as a means of establishing power or gaining attention. By implementing social skills development programs, children can learn how to build positive relationships, communicate effectively, and resolve conflicts peacefully. These programs can include interactive activities, role-playing exercises, and group discussions to enhance social skills and build empathy.
4. Cognitive-behavioral therapy:
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has been proven effective in addressing various behavioral issues, including bullying. CBT interventions can help children identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to bullying behaviors. By developing positive self-esteem, improving problem-solving skills, and enhancing coping mechanisms, children can learn healthier ways to interact with their peers and manage conflicts.
5. Peer mediation programs:
Peer mediation programs involve training students to mediate conflicts among their peers. By empowering students to resolve conflicts peacefully and encouraging them to speak up against bullying, these programs create a positive and supportive peer culture. Peer mediation programs also promote empathy and teach students valuable communication and problem-solving skills that can deter bullying behaviors.
Conclusion:
Addressing the issue of childhood bullying requires a multi-faceted approach that takes into account the impact of personality traits on bullying behaviors. By implementing personality trait-based interventions such as empathy-building programs, anger management training, social skills development, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and peer mediation programs, we can create a supportive and nurturing environment that prevents and reduces bullying. It is essential to recognize that each child is unique and may require tailored interventions to address their specific needs.
Questions and answers
How do personality traits affect childhood bullying?
Personality traits play a significant role in childhood bullying. Certain traits such as aggressiveness, low empathy, and impulsivity are commonly associated with bullying behavior. These traits can increase the likelihood of a child engaging in bullying and make them less responsive to interventions.
What are some of the key personality traits that contribute to childhood bullying?
There are several key personality traits that contribute to childhood bullying. These include aggressiveness, low empathy, impulsivity, lack of self-control, and a tendency towards dominance. Children who possess these traits are more likely to engage in bullying behavior and have difficulty understanding the impact of their actions on others.
How can personality traits be used to identify potential bullies?
Personality traits can be used as indicators to identify potential bullies. By looking for traits such as aggressiveness, low empathy, impulsivity, and a lack of self-control in children, teachers and parents can take preventive measures to address these traits and intervene before bullying behavior manifests. Early identification and intervention can significantly reduce the likelihood of bullying.
Can personality traits be changed to prevent bullying?
While personality traits are relatively stable characteristics, they can be influenced and modified to prevent or reduce bullying behavior. By providing intervention strategies, teaching empathy and emotional regulation, and promoting positive behavioral patterns, children can learn to manage their traits and develop pro-social behaviors. With proper guidance and support, it is possible to help children with potentially harmful personality traits avoid engaging in bullying.