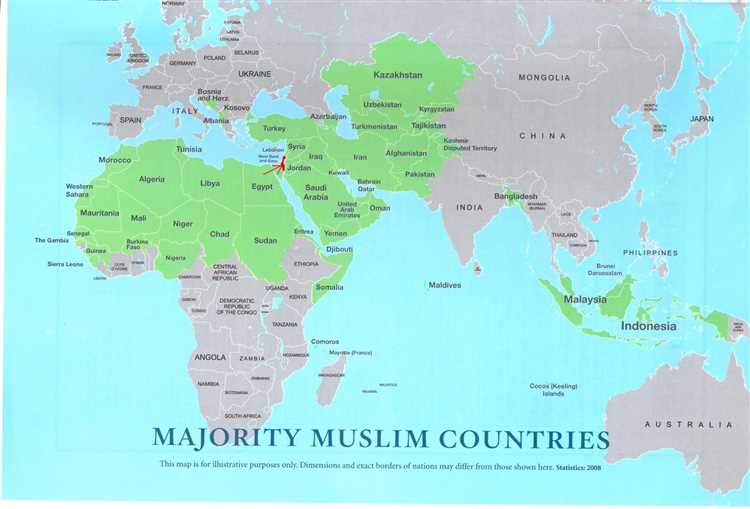
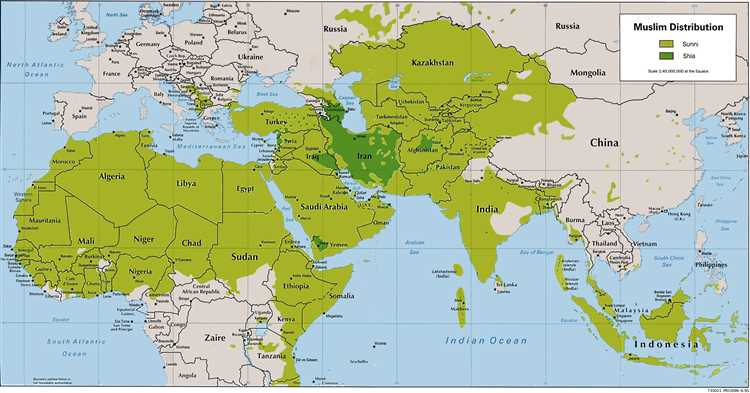
The Islamic world is a vast and diverse collection of cultures, traditions, and peoples, stretching from North Africa to Southeast Asia. Spanning centuries of history and encompassing a wide range of artistic, intellectual, and scientific achievements, embracing the Islamic world allows us to explore a rich tapestry of human experience and expression.
One of the key features of the Islamic world is its religious and cultural heritage. Islam is a monotheistic religion that originated in the Arabian Peninsula in the 7th century. Its teachings and values have shaped the lives and beliefs of millions of people around the world. From the architecture of mosques to the calligraphy of the Quran, Islamic art and culture reflect the importance of faith and spirituality in Islamic societies.
The Islamic world is also known for its intellectual and scientific contributions. During the Islamic Golden Age, which spanned from the 8th to the 14th centuries, Muslim scholars made significant progress in various fields such as mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy. These advancements had a profound impact on the development of knowledge in the Western world and continue to be studied and celebrated today.
Furthermore, exploring the Islamic world allows us to appreciate the diversity of its peoples and cultures. From the nomads of the Sahara Desert to the urbanites of Istanbul, from the rice farmers of Indonesia to the poets of Persia, the Islamic world encompasses a wide range of lifestyles, traditions, and languages. By immersing ourselves in the stories, traditions, and cuisine of different Islamic communities, we gain a deeper understanding of the beauty and complexity of the human experience.
In conclusion, discovering the richness and diversity of the Islamic world is an opportunity to explore the multifaceted nature of human civilization. Through an exploration of its religious and cultural heritage, intellectual and scientific achievements, and the diversity of its peoples and cultures, we can deepen our understanding of the intricate tapestry of our world and foster greater appreciation and respect for the contributions and experiences of the Islamic world.
Understanding the Islamic World: A Journey of Discovery
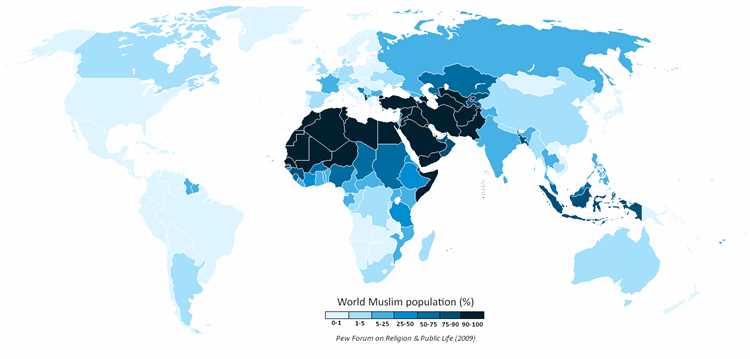
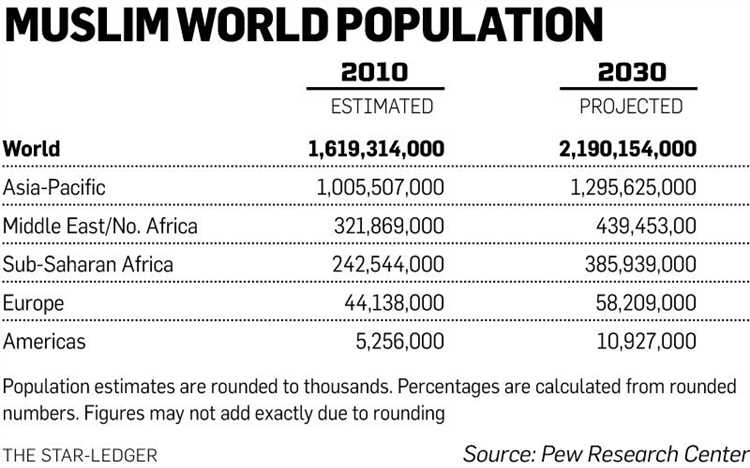
The Islamic world is a vast and diverse religious and cultural domain that spans across multiple continents and countries. With over 1.8 billion followers, Islam is the second-largest religion in the world. Exploring the richness and diversity of the Islamic world is a fascinating journey that allows us to understand its history, beliefs, and practices.
One of the fundamental aspects of the Islamic world is its religious texts. The Quran, the holy book of Islam, is considered the word of God as revealed to the Prophet Muhammad. It serves as a guide for Muslims, providing them with spiritual guidance, moral principles, and a code of conduct. Understanding the teachings of the Quran is crucial in comprehending the Islamic faith and its significance in the lives of its followers.
Another important aspect of the Islamic world is its rich history and cultural heritage. From the golden age of Islamic civilization that gave birth to great scholars, scientists, and artists to the magnificent architecture of mosques and palaces, the Islamic world has a deep and influential history. Exploring the contributions of Islamic scholars in fields such as mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy is essential to appreciate the intellectual achievements of this civilization.
The Islamic world is also characterized by its diverse and vibrant cultures and traditions. Islam is practiced by people from diverse backgrounds, ethnicities, and languages. Each country and region within the Islamic world has its own unique set of customs, traditions, and celebrations. From the colorful festivals like Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha to local cuisines and traditional clothing, there is a wealth of cultural diversity within the Islamic world waiting to be discovered.
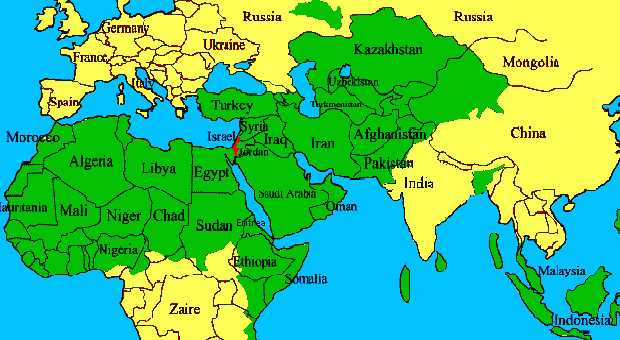
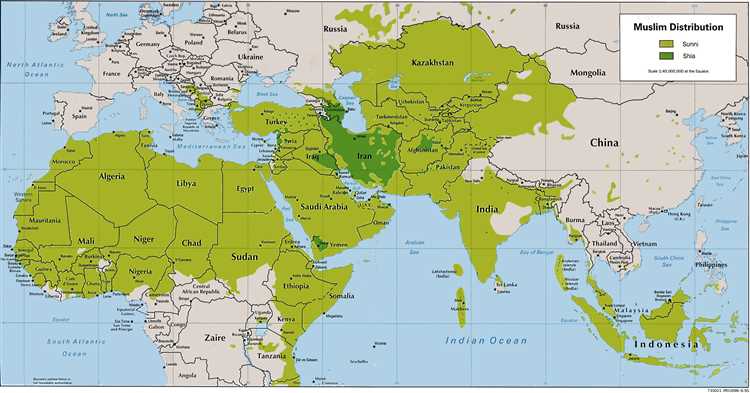
A journey of discovery in the Islamic world would be incomplete without exploring the different sects and interpretations within Islam. From Sunni to Shia and other sects, Muslims have diverse beliefs and practices. Understanding the differences and nuances between these sects and how they influence the daily lives of Muslims is crucial to gaining a comprehensive understanding of the Islamic world.
The Islamic world is a complex and multifaceted entity that offers endless opportunities for exploration and understanding. By delving into its religious texts, history, cultures, and sects, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the richness and diversity of the Islamic world and the significant contributions it has made to human civilization.
Exploring the Cultural Significance
The Islamic world is rich in cultural significance, and exploring its various aspects allows us to appreciate its diversity. From art and architecture to literature and music, Islamic culture has made a significant impact on the world.
One of the most iconic features of Islamic culture is its distinctive architecture. With its intricate geometric patterns, calligraphy, and domes, Islamic architecture is instantly recognizable. The mosques, madrassas, and palaces showcase the craftsmanship and skill of Islamic artisans throughout history.
Islamic art is known for its intricate designs and attention to detail. Arabic calligraphy, in particular, is considered a form of art in itself. The use of geometric patterns and motifs in Islamic art reflects the emphasis on unity and harmony found in Islamic teachings.
Literature also plays a significant role in Islamic culture. The Quran, considered the holy book of Islam, is not only a religious text but also serves as a source of inspiration for poets and writers. Islamic literature encompasses a wide range of topics, including philosophy, history, and poetry, and has greatly influenced world literature.
Music is another important aspect of Islamic culture. Traditional Islamic music incorporates various instruments, such as the oud, rebab, and ney. It often features melodic and rhythmic patterns influenced by Arabic, Turkish, and Persian traditions. Islamic music has a soothing and contemplative quality that is enjoyed by people of different faiths and backgrounds.
Islamic festivals and traditions also provide a glimpse into the cultural richness of the Islamic world. Ramadan, for example, is a month of fasting and spiritual reflection for Muslims worldwide. The celebration of Eid al-Fitr at the end of Ramadan is marked by feasting, gift-giving, and prayer, bringing communities together.
| Key Points |
|---|
|
Unveiling the Historical Legacy
The Islamic world has a rich and diverse history that spans over a millennium. From the rise of the Islamic civilization in the 7th century to the present day, the impact of the Islamic world can be seen in various fields such as art, science, literature, and architecture.
One of the significant aspects of the historical legacy of the Islamic world is the preservation of knowledge. During the Islamic Golden Age, which lasted from the 8th to the 14th century, Islamic scholars translated and preserved ancient Greek, Roman, and Persian texts. This led to the dissemination of knowledge across different regions, contributing to the advancement of various fields.
Islamic art is another testament to the historical legacy of the Islamic world. Islamic art is known for its intricate designs, geometric patterns, and calligraphy. It reflects the unity and diversity within the Islamic world, incorporating influences from different cultures and regions. From the stunning mosques of Istanbul to the Alhambra in Spain, Islamic art showcases the rich artistic traditions of the Islamic world.
The Islamic world also has a rich literary tradition. From the poetry of Rumi and Hafez to the philosophical works of Avicenna and Averroes, Islamic literature has made significant contributions to the world of literature and intellectual thought. These works have been translated into numerous languages and continue to inspire readers around the globe.
Another aspect of the historical legacy of the Islamic world is its architectural marvels. From the Great Mosque of Cordoba to the Taj Mahal, Islamic architecture is known for its grandeur and attention to detail. The use of symmetrical designs, domes, and arches is iconic to Islamic architecture and has influenced architectural styles around the world.
This glimpse into the historical legacy of the Islamic world only scratches the surface of its richness and diversity. Exploring further reveals a vast and diverse range of contributions in various fields. From Spain to Southeast Asia, the influence of the Islamic world can be seen in different regions, showcasing the interconnectedness of civilizations and the enduring legacy of Islamic culture.
Appreciating the Architectural Marvels
One of the most striking aspects of the Islamic world is its rich architectural heritage. From grand mosques to breathtaking palaces, Islamic architecture is known for its intricate designs, meticulous details, and impeccable craftsmanship. Here are some architectural marvels that highlight the diversity and beauty of the Islamic world:
-
Hagia Sophia, Istanbul, Turkey: Originally built as a Byzantine church, Hagia Sophia later converted into a mosque and is a testament to the blended styles of Islamic and Byzantine architecture. Its massive dome and intricate mosaics are awe-inspiring.
-
Alhambra, Granada, Spain: This fortress and palace complex showcases the exquisite craftsmanship of Islamic architecture during the Nasrid dynasty. The elaborate stucco work, colorful tiles, and serene gardens make it a UNESCO World Heritage site.
-
Taj Mahal, Agra, India: Known as the jewel of Muslim art in India, the Taj Mahal is a mausoleum made entirely of white marble. Its symmetrical layout, elegant arches, and intricate stone inlay work reflect the perfect harmony of Islamic and Indian architectural styles.
-
Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque, Abu Dhabi, UAE: Considered one of the largest mosques in the world, the Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque features a blend of Persian, Mughal, and Moorish architectural elements. Its white marble façade, intricate floral designs, and exquisite chandeliers create a serene atmosphere.
These architectural marvels, among many others, highlight the influence of Islamic culture and the immense creativity of Islamic architects throughout history. They serve as a reminder of the rich and diverse heritage of the Islamic world, and the importance of appreciating and preserving these architectural treasures.
Tracing the Roots of Islamic Art
Islamic art is a rich and diverse artistic tradition that has its roots in the religion of Islam. It encompasses a wide range of artistic expressions, including calligraphy, geometric patterns, floral motifs, and intricate designs.
The roots of Islamic art can be traced back to the 7th century, when Islam emerged in the Arabian Peninsula. At this time, the Islamic faith spread rapidly, and with it came a unique and distinctive artistic style.
One of the key features of Islamic art is its prohibition of depicting sentient beings, such as humans and animals, in a realistic manner. This prohibition stems from the Islamic belief in the unity and oneness of God, and the idea that only God has the power to create living beings. As a result, Islamic art developed its own unique visual language, relying heavily on calligraphy and geometric patterns to convey its spiritual and aesthetic messages.
Calligraphy, or the art of beautiful writing, is a central component of Islamic art. The Arabic script, which is used to write the Quran, became the primary medium for Islamic calligraphy. Calligraphers would meticulously write verses from the Quran or other religious texts, often employing intricate and decorative styles to enhance the visual appeal of the words.
Geometric patterns are another important element of Islamic art. These patterns are often based on square or hexagonal grids and can be found in numerous architectural and decorative elements, such as tiles, carpets, and ceramics. The repetition and symmetry found in these patterns are thought to reflect the harmony and order of the universe, as well as the divine perfection of God.
In addition to calligraphy and geometric patterns, Islamic art also incorporates floral motifs and intricate designs. Flowers, such as roses and lilies, are often depicted in stylized forms, while intricate designs, such as arabesques and interlacing patterns, are used to embellish various surfaces.
The rich and diverse tradition of Islamic art is a testament to the beauty and creativity of Muslim cultures throughout history. With its emphasis on spirituality, intricate craftsmanship, and aesthetic beauty, Islamic art continues to inspire and captivate audiences around the world.
Connecting through Islamic Music
Music is a universal language that has the power to bring people together and transcend cultural boundaries. In the Islamic world, music has played a crucial role in connecting people and expressing their faith. Islamic music, also known as nasheed or Islamic chants, has a rich history and is deeply rooted in Islamic culture.
Islamic music encompasses a wide range of genres and styles, reflecting the diversity of the Islamic world. It can be vocal or instrumental, and often incorporates traditional instruments such as the oud, qanun, and daf. Nasheed, in particular, is a type of Islamic music that focuses on praising Allah and conveying religious messages.
One of the unique characteristics of Islamic music is its emphasis on spirituality and devotion. It is believed that listening to and participating in Islamic music can inspire a sense of peace and harmony, and strengthen one’s connection with the divine. Many Islamic musicians use their music as a means of spreading messages of love, compassion, and unity.
Islamic music is not limited to religious functions and rituals; it can also be enjoyed as a form of entertainment. Many Islamic music festivals and concerts take place around the world, attracting audiences from diverse backgrounds. These events provide an opportunity for people to come together, celebrate their shared cultural heritage, and appreciate the beauty of Islamic music.
Additionally, Islamic music has transcended geographical boundaries with the advent of technology. Online platforms and streaming services have made it easier for people from different parts of the world to access and enjoy Islamic music. This has further facilitated the global connection and appreciation of Islamic culture.
In conclusion, Islamic music serves as a powerful tool for connecting people and promoting harmony. Through its rich history, diverse genres, and emphasis on spirituality, Islamic music has the ability to inspire and unite people from various cultures and backgrounds.
Delving into Islamic Calligraphy
Islamic calligraphy, also known as “Islamic ornamental writing,” is a unique art form that holds deep cultural and religious significance in the Islamic world. It involves the artistic writing of Arabic letters, words, and verses from the Quran to create visually stunning and spiritually meaningful artwork.
The Origins and Evolution
Islamic calligraphy has its roots in the early days of Islam, where Arabic script became the language of the religion and its holy book, the Quran. It started as a way to transcribe and preserve the religious texts accurately. Over time, the writing style evolved into an expressive art form, with calligraphers adding decorative elements and creating intricate compositions.
The Importance of Arabic Script
In Islamic calligraphy, Arabic script is not merely a means of communication but a form of worship and an artistic expression of the divine. The beauty of calligraphy lies in the way letters and words are shaped, elongated, and intertwined to create an aesthetic harmony. It is believed that the visual elegance of the writing reflects the beauty of the Quran and the words of Allah.
Styles and Techniques
Islamic calligraphy encompasses various styles, each with its own unique characteristics. Some of the most prominent styles include:
- Kufic: This style is known for its bold, geometric shapes and straight, angular lines.
- Naskh: Naskh is characterized by its fluid, cursive style and rounded forms.
- Thuluth: Thuluth is known for its tall, elongated letters and elegant curves.
- Diwani: Diwani features strong, sweeping curves and is often used for decorative purposes.
Calligraphers use various tools, such as a bamboo or reed pen, along with ink made from natural materials to create their artwork. They employ techniques like scaling, spacing, and proportionate lettering to achieve balance and harmony in their compositions.
The Symbolism
Islamic calligraphy carries significant symbolism and serves as a visual representation of Islamic teachings and values. It is often used to decorate mosques, Quranic texts, and religious manuscripts. The emphasis on abstract art in Islamic calligraphy reflects the Islamic belief in the transcendence of Allah beyond human comprehension and the focus on the spiritual rather than materialistic aspects of life.
The Influence
The influence of Islamic calligraphy extends far beyond religious contexts. It has permeated various forms of Islamic art, including architecture, ceramics, textiles, and book illustration. The intricate patterns and flowing lines seen in calligraphy have become defining features of Islamic art and have influenced artists around the world.
In conclusion, Islamic calligraphy represents a unique blend of religious devotion, artistic expression, and cultural heritage. Its rich history, diverse styles, and deep symbolism make it an essential and captivating part of the Islamic world’s artistic tradition.
Fathoming the Islamic Philosophical Tradition
The Islamic philosophical tradition is a rich and diverse body of thought that has evolved over a span of more than a thousand years. It encompasses a wide range of philosophical perspectives and approaches, drawing on a variety of sources including Greek philosophy, Islamic theology, and mysticism.
One of the key figures in the development of Islamic philosophy was Ibn Sina, also known as Avicenna, who lived in the 10th and 11th centuries. Ibn Sina was a polymath who made significant contributions to a wide range of fields including logic, metaphysics, and medicine. His most famous work, “The Book of Healing,” is a comprehensive encyclopaedia of knowledge that covers topics ranging from philosophy and theology to physics and psychology.
Another important figure in the Islamic philosophical tradition was Al-Farabi, who lived in the 9th and 10th centuries. Al-Farabi sought to reconcile Greek philosophy with Islamic theology, in particular by exploring the relationship between reason and revelation. He argued that philosophy could serve as a guide to understanding the religious teachings of Islam, and that reason and revelation were not incompatible but rather complementary.
One of the distinctive features of Islamic philosophy is its emphasis on the concept of unity. Islamic philosophers often sought to integrate different strands of thought, drawing on the teachings of Plato, Aristotle, and other Greek philosophers, as well as Islamic theology and mysticism. This integrative approach led to the development of a unique philosophical tradition that blended elements of Greek philosophy with Islamic ideas.
The Islamic philosophical tradition also placed a strong emphasis on ethics and morality. Islamic philosophers sought to explore questions of virtue, human nature, and the nature of the good life. They developed sophisticated ethical theories that drew on both reason and revelation, seeking to provide guidance on how to live a moral and virtuous life in accordance with Islamic teachings.
In conclusion, the Islamic philosophical tradition is a rich and diverse body of thought that has evolved over many centuries. It has drawn on a wide range of sources and approaches, and has sought to integrate different strands of thought in a way that is both intellectually rigorous and spiritually meaningful.
Deciphering Islamic Jurisprudence
Islamic jurisprudence, also known as fiqh, plays a crucial role in the lives of Muslims around the world. It refers to the principles and rules derived from Islamic sources such as the Quran and the Sunnah (teachings and practices of the Prophet Muhammad).
The Sources of Islamic Jurisprudence
- The Quran: The Quran, the holy book of Islam, is considered the primary source of Islamic law. It contains guidance on various aspects of life, including legal matters.
- The Sunnah: The Sunnah consists of the actions, sayings, and approvals of the Prophet Muhammad. It provides practical examples and explanations for the application of Quranic teachings.
- Ijma: Ijma refers to the consensus of scholars on a particular legal issue. It is derived from the understanding and interpretation of the Quran and the Sunnah by the Muslim community throughout history.
- Qiyas: Qiyas involves reasoning by analogy, where a ruling is derived by comparing a new situation to an existing one that has already been addressed in Islamic sources.
The Schools of Islamic Jurisprudence
Over the centuries, different schools of Islamic jurisprudence have developed, each with its own methodology and interpretations. The major schools include:
- Hanafi: This school is followed by a large number of Muslims, especially in South Asia, and focuses on rationalism and the use of reason in interpreting Islamic law.
- Maliki: The Maliki school is predominant in North and West Africa. It places importance on the customs and practices of the people in a particular region.
- Shafi’i: The Shafi’i school is followed by Muslims in Southeast Asia. It emphasizes the importance of tradition and the principles derived from the Quran and the Sunnah.
- Hanbali: The Hanbali school is strict in its adherence to the literal meaning of the Quran and the Hadith (narrations about the Prophet’s actions and sayings).
The Role of Islamic Jurisprudence in Society
Islamic jurisprudence provides guidance on various aspects of life, including personal behavior, family matters, commerce, and criminal law. It helps to ensure justice, ethics, and harmony within the Muslim community. Islamic jurists, known as scholars or muftis, analyze the sources of Islamic law and apply them to contemporary situations.
Challenges and Adaptations
The interpretation and application of Islamic law can vary among different regions and cultures, leading to different practices and customs. In today’s rapidly changing world, there is a need to adapt Islamic jurisprudence to address new challenges and contemporary issues while remaining true to the core principles of Islam.
| Major Schools of Islamic Jurisprudence | Region | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Hanafi | South Asia, Central Asia, Turkey | Rationalist approach, emphasis on reason |
| Maliki | North and West Africa | Focus on local customs and practices |
| Shafi’i | Southeast Asia, Egypt | Tradition and principles derived from Quran and Sunnah |
| Hanbali | Saudi Arabia, Qatar | Literal interpretation of Quran and Hadith |
Overall, Islamic jurisprudence is a dynamic field that continues to evolve and adapt to the changing needs and circumstances of Muslims worldwide. Its principles and rules provide a framework for Muslims to navigate their lives in accordance with their faith.
Exploring Islamic Economic Systems
The Islamic economic system is based on the principles of Sharia, or Islamic law. It aims to create a just and equitable society by promoting the principles of fairness, equality, and social justice. Here are some key aspects of the Islamic economic system:
- Zakat: Zakat is a form of mandatory charity in Islam. It is a means of redistributing wealth and helping the less fortunate in society. Muslims are required to give a portion of their wealth to those in need, typically 2.5% of their total savings and assets.
- Riba: Riba refers to the prohibition on usury or interest. Islamic economic systems discourage the charging and paying of interest, as it is seen as exploitative and unfair. Instead, profit-sharing arrangements and ethical investment practices are encouraged.
- Halal: Halal refers to what is permissible or lawful in Islam. Islamic economic systems promote halal business practices, which include ethical sourcing, fair trade, and avoiding industries that are considered haram (forbidden), such as alcohol, gambling, and pork.
- Ijara: Ijara is a form of leasing or renting in Islamic finance. It allows individuals and businesses to access assets without engaging in interest-based transactions. Under an ijara contract, the lessor retains ownership of the asset while the lessee pays a predetermined rental fee.
Islamic economic systems also promote ethical business conduct, transparency, and accountability. They emphasize the importance of avoiding fraud, deceit, and unfair competition. In addition, the concept of musharakah (partnership) is encouraged, where profits and losses are shared among business partners.
Overall, the Islamic economic system aims to create a society that is based on ethical principles and social justice. It seeks to strike a balance between economic growth and the well-being of individuals and society as a whole, while also taking into consideration the spiritual and moral aspects of life.
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Zakat | Mandatory charity to help the needy |
| Riba | Prohibition on usury and interest |
| Halal | Permissible and lawful business practices |
| Ijara | Leasing and rental contracts |
| Ethical Conduct | Promotion of transparency, accountability, and fairness |
| Musharakah | Partnership based on profit-sharing and risk-sharing |
Gaining Insight into Islamic Medicine
Islamic medicine, also known as Arabic medicine, refers to the medical practices and knowledge developed in the Islamic Golden Age (8th-14th century). During this period, Muslim scholars made significant advancements in various fields of science, including medicine.
Islamic medicine was heavily influenced by the teachings of the Quran and the Hadith (sayings and actions of Prophet Muhammad). It combined the existing knowledge from different civilizations, such as the Greek, Persian, Indian, and Chinese, and expanded upon it through further research and innovation.
One of the key concepts in Islamic medicine was the idea of holistic health, which emphasized the importance of maintaining a balance between the mind, body, and spirit. Islamic physicians believed that diseases were caused by imbalances in these elements and focused on treating the root causes rather than just the symptoms.
Islamic medicine introduced many innovative medical practices and treatments. Islamic physicians made significant contributions to the fields of anatomy, pharmacology, surgery, and ophthalmology. They developed sophisticated tools and techniques, such as surgical instruments and anesthesia, and conducted groundbreaking research on the human body.
Islamic medicine also emphasized preventive medicine and the importance of a healthy lifestyle. Scholars wrote extensively on topics such as nutrition, hygiene, and physical exercise, providing guidelines for maintaining good health and preventing diseases.
The Islamic medical tradition also had a strong influence on Western medicine. Many works of Islamic medicine were translated into Latin and became essential texts for European scholars during the Renaissance. Islamic medical knowledge and practices formed the foundation for the development of modern medicine.
- In summary, Islamic medicine represents a rich and diverse tradition that made significant contributions to the field of medicine. It combined ancient knowledge with new innovations and focused on holistic health and preventive medicine. The legacy of Islamic medicine continues to inspire and influence modern medical practices and research.
Discovering the Contributions of Islamic Scientists
The Islamic world has a rich history of scientific achievements that span various disciplines such as mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and optics. Islamic scientists made significant contributions to the development of these fields, laying the foundation for many scientific advancements we enjoy today.
1. Mathematics:
-
Al-Khwarizmi: Known as the “father of algebra,” Al-Khwarizmi developed the fundamental concepts of algebra and pioneered the use of decimal numbers and decimal fractions.
-
Al-Kindi: Often referred to as the “philosopher of the Arabs,” Al-Kindi made important contributions to cryptography and introduced Indian numerals to the Islamic world, which later influenced the development of Western numerals.
2. Astronomy:
-
Al-Battani: Al-Battani is renowned for his accurate observations of celestial phenomena and for his refinement of astronomical calculations. His work greatly influenced the European Renaissance astronomers.
-
Al-Farabi: Al-Farabi contributed to astronomy by explaining the principles of celestial motion and developing an improved model of the planetary system.
3. Medicine:
-
Ibn Sina (Avicenna): Ibn Sina’s influential book, “The Canon of Medicine,” became a central medical text in Europe for centuries. He made significant advancements in medicine, including his groundbreaking work on contagious diseases.
-
Al-Razi (Rhazes): Al-Razi’s contributions to medicine include his discoveries in pharmacology, the classification of diseases, and the development of clinical observation techniques.
4. Optics:
-
Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen): Alhazen is often considered the “father of modern optics.” His work on the properties of light, optics, and visual perception laid the foundation for the scientific understanding of vision.
-
Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen): Alhazen’s theories and experiments on optics were influential in the development of the scientific method and had a significant impact on Western scientists like Isaac Newton.
These are just a few examples of the remarkable scientific contributions made by Islamic scientists. Their work not only advanced scientific knowledge but also fostered a spirit of intellectual curiosity that continues to inspire generations of scientists around the world.
Understanding Islamic Education and Scholarship
The Islamic world has a long and rich tradition of education and scholarship. Islamic education encompasses a wide range of subjects, including religious studies, mathematics, science, philosophy, and literature. This integrated approach to education has been an important part of Islamic culture since the early days of Islam.
Islamic Education System:
- The foundation of Islamic education is the Quran, which is considered the holy book of Islam. Students begin their education by memorizing and reciting the Quran. This helps them develop a strong understanding of Islamic principles and teachings.
- In addition to the Quran, Islamic education also includes the study of Hadith, which are the sayings and actions of the Prophet Muhammad. Hadith provide guidance on various aspects of life and are an important source of Islamic law and ethics.
- Islamic education is often provided in madrasas, which are religious schools. These schools can be found throughout the Islamic world and offer a structured curriculum that covers a wide range of subjects.
- Students in madrasas often study Arabic, as it is the language of the Quran and serves as the medium for Islamic scholarship. They also study subjects such as theology, jurisprudence, and Arabic literature.
Scholarship and Intellectual Traditions:
- The Islamic world has a rich tradition of scholarship, with many major contributions to fields such as mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy. Islamic scholars made significant advancements in these fields during the Islamic Golden Age, from the 8th to the 14th centuries.
- One of the most famous Islamic scholars is Ibn Sina (Avicenna), who made important contributions to medicine and philosophy. His influential work, “The Canon of Medicine,” remained a standard medical textbook in Europe for several centuries.
- The Islamic world also preserved and translated many ancient Greek and Roman texts, which were later rediscovered and had a profound impact on the European Renaissance. Islamic scholars played a crucial role in preserving knowledge during this period.
- Islamic scholarship is characterized by a strong emphasis on reason, logic, and intellectual inquiry. Scholars often engaged in vigorous debates and discussions to advance knowledge and deepen their understanding of various subjects.
Conclusion:
Understanding Islamic education and scholarship is crucial for appreciating the richness and diversity of the Islamic world. The integrated approach to education, the emphasis on the Quran and Hadith, and the tradition of intellectual inquiry have contributed to the development of a unique Islamic intellectual tradition that continues to thrive to this day.
Uncovering the Role of Women in Islam
Islam has a rich history and diverse culture, one aspect of which is the role of women in society. While stereotypes and misconceptions may paint a limited picture, the reality is that women in Islam have played various roles throughout history, having both contributed to and been influenced by the religion’s development.
One important point to note is that Islam grants women many fundamental rights and protections. Women have the right to an education, the right to own property, the right to work, and the right to choose their own spouse. These rights were revolutionary at the time of Islam’s inception and continue to shape the lives of Muslim women today.
Islamic history is replete with stories of strong and influential women. One example is Khadija bint Khuwaylid, the first wife of Prophet Muhammad. Khadija was a successful businesswoman, known for her intelligence and financial acumen. Another notable figure is Aisha bint Abu Bakr, one of Muhammad’s wives and a scholar of Islam. Aisha’s contributions to Islamic jurisprudence and Hadith studies continue to be respected and studied to this day.
Contrary to popular belief, Islam does not oppress women. However, cultural practices and interpretations of religious texts in different regions have led to varying degrees of gender inequality. It is important to differentiate between cultural practices and Islamic teachings when discussing the role of women in Islam.
It is also worth noting that Muslim women are not a monolithic group. They come from different backgrounds, cultures, and countries, each with its own unique practices and interpretations of Islam. This diversity is reflective of the broader Muslim community, which spans multiple continents and comprises over a billion people.
Efforts are underway within Muslim communities to challenge patriarchal norms and promote gender equality. Many Muslim women are leading the charge in advocating for women’s rights and reinterpreting religious texts to ensure they are in line with principles of equality and justice.
In conclusion, the role of women in Islam is complex and multifaceted. While some may view Islam as oppressive to women, it is important to recognize the diverse and dynamic nature of the religion and its followers. Muslim women have played and continue to play important roles in society, and their contributions should be acknowledged and celebrated.
Examining Islamic Governance and Politics
Islamic governance and politics encompass a wide range of principles and practices that shape the political systems in Muslim-majority countries. While there is a great diversity of political structures and approaches within the Islamic world, there are also some common elements that reflect Islamic values and norms.
Sharia Law: One of the fundamental aspects of Islamic governance is the adherence to Sharia law, which is derived from the teachings of the Quran and the Hadith (sayings and actions of the Prophet Muhammad). Sharia law covers various aspects of life, including family, business, criminal justice, and governance. It serves as a guide for Muslims in their personal and public lives, including political decision-making.
Caliphate: Historically, the caliphate was the political and religious leadership of the Muslim community. The caliph, also known as the successor of the Prophet Muhammad, was responsible for governing and implementing Islamic law. While the traditional caliphate system no longer exists in its original form, the concept of leadership and governance in Islam continues to be influenced by the Caliphate ideal.
Political Structures: Islamic countries have diverse political structures, ranging from constitutional monarchies to republics and theocracies. In some countries, Islamic law is integrated into the legal system, while in others it coexists with secular laws. Political parties, both religious and secular, play a significant role in the political landscape, with parties often competing for power and influence.
Islamic Law and Human Rights: The implementation of Sharia law in some Islamic countries has raised debates and controversies regarding human rights. Critics argue that some interpretations of Sharia can be discriminatory towards women, religious minorities, and individuals with differing beliefs. However, proponents of Islamic governance argue that Sharia law provides a comprehensive and just framework that guarantees social and economic justice for all.
Political Challenges and Dynamics: Like any political system, Islamic governance faces various challenges and dynamics. These include maintaining a balance between religious principles and modern governance, addressing socioeconomic disparities, managing diverse ethnic and religious communities, and navigating geopolitical influences. Political leaders and scholars constantly grapple with these challenges as they seek to create stable and inclusive societies in accordance with Islamic principles.
In conclusion, Islamic governance and politics are complex and multifaceted. They are shaped by religious principles, historical traditions, and contemporary realities. Understanding the diverse approaches to governance in the Islamic world is essential to appreciate the richness and diversity of this region.
Discovering the Spirituality of Islam
Islam, which means “submission to God,” is not just a religion, but a complete way of life. It promotes a strong sense of spirituality and teaches its followers to seek a deep connection with the divine.
At the core of Islamic spirituality is the belief in the oneness of God (Allah) and the recognition of His infinite power and wisdom. Muslims are taught to have a personal and intimate relationship with Allah, and to turn to Him in times of need and guidance.
The spiritual practices in Islam are often referred to as the Five Pillars of Islam. These pillars include:
- Shahada: The declaration of faith, which involves expressing a belief in the oneness of God and the prophethood of Muhammad.
- Salah: The ritual prayer performed five times a day, which serves as a way to connect with Allah and seek His guidance and forgiveness.
- Zakat: The giving of alms or charity to the less fortunate in society, which serves as a means of purifying one’s wealth and demonstrating compassion.
- Sawm: The fasting during the holy month of Ramadan, which helps Muslims develop self-discipline, empathy, and a deeper appreciation for the blessings of life.
- Hajj: The pilgrimage to the holy city of Mecca, which is a once-in-a-lifetime obligation for every able-bodied and financially capable Muslim. It is a powerful spiritual experience that symbolizes unity, humility, and the endurance of hardships.
In addition to these pillars, Muslims are encouraged to engage in various acts of worship and spiritual practices, such as reading and reflecting on the Quran, supplicating to Allah through prayers, seeking knowledge, maintaining good character, and performing acts of kindness and service to humanity.
Islamic spirituality also emphasizes the concept of Tawhid, which means the unity and uniqueness of Allah. Muslims believe that everything in the universe is created and governed by Allah’s divine will, and they strive to align their thoughts, actions, and intentions with His guidance.
Furthermore, Islamic spirituality encourages individuals to strive for ihsan, which means excellence or perfection in worship. It involves performing acts of worship with sincerity, humility, and with the intention of seeking Allah’s pleasure rather than seeking validation from others.
In summary, the spirituality of Islam is rooted in the belief in the oneness of God and encompasses various practices, rituals, and attitudes that aim to establish a deep connection with Allah and lead a virtuous life. It provides a framework for individuals to cultivate a sense of inner peace, purpose, and fulfillment in their journey towards the divine.
Appreciating Islamic Festivals and Traditions
The Islamic calendar is filled with festivals and traditions that hold great significance for Muslims around the world. These celebrations not only mark important religious events but also provide an opportunity for communities to come together, share their joy, and strengthen their bonds.
Eid al-Fitr:
Eid al-Fitr, also known as the Festival of Breaking the Fast, marks the end of Ramadan. It is a time of great joy and gratitude, as Muslims celebrate the successful completion of their month-long fasting and spiritual reflection. Families gather to pray together, exchange gifts, and enjoy special feasts. The day begins with congregational prayers at mosques, followed by visits to family and friends. Children often receive new clothes and toys, and homes are decorated with festive lights and ornaments.
Eid al-Adha:
Eid al-Adha, also known as the Festival of Sacrifice, commemorates the obedience of Prophet Ibrahim (Abraham) and his willingness to sacrifice his son as an act of faith. Muslims around the world observe this festival by sacrificing an animal, usually a sheep or goat, and distributing the meat to the less fortunate. The day begins with congregational prayers, followed by a feast with family and friends. It is a time for reflection on sacrifice, gratitude, and generosity.
Mawlid al-Nabi:
Mawlid al-Nabi, also known as the Birth of the Prophet Muhammad, is a celebration of the birth anniversary of the Prophet. Muslims gather to recite religious hymns, listen to sermons, and participate in processions. It is a time to reflect on the life and teachings of the Prophet and to renew one’s commitment to following his example of compassion, justice, and peace.
Ramadan:
Ramadan is the holiest month in the Islamic calendar. It is a month of fasting, prayer, and self-reflection. Muslims abstain from food, drink, and other physical needs from dawn until sunset. The fast is broken each evening with a meal called iftar, where families come together to share food and prayers. Ramadan is also a time for increased acts of charity and generosity, as Muslims strive to purify their hearts and cultivate empathy for those less fortunate.
Hajj:
Hajj is an annual pilgrimage to the holy city of Mecca in Saudi Arabia. It is considered one of the Five Pillars of Islam and is obligatory for all able-bodied Muslims who can afford it. During Hajj, millions of Muslims from around the world gather to perform a series of rituals, including circling the Kaaba, standing on the plains of Arafat, and throwing pebbles at the pillars of Mina. The pilgrimage is a powerful experience of unity, humility, and submission to God.
The richness and diversity of Islamic festivals and traditions showcase the beauty of the Islamic faith and its values of love, peace, and unity. By appreciating and understanding these celebrations, we can foster greater intercultural understanding and build bridges of friendship and respect.
Exploring the Diversity of Islamic Clothing
Islamic clothing encompasses a wide range of styles and traditions, reflecting the diversity of cultures and regions within the Islamic world. From modest traditional garments to contemporary designs, Islamic clothing is rich in history and showcases the values and beliefs of its wearers.
Hijab:
The hijab, a headscarf worn by many Muslim women, is one of the most recognizable elements of Islamic clothing. It serves as a symbol of religious devotion and modesty. While the styles and fabrics used may vary, the hijab is commonly worn to cover the hair and neck, leaving the face visible.
Abaya:
The abaya is a loose-fitting robe-like garment that is worn by many Muslim women in the Middle East and other parts of the Islamic world. It is typically black and covers the entire body, including the head and sometimes the face. The abaya is often worn over other clothing and is commonly associated with modesty and discretion.
Dishdasha:
The dishdasha, also known as a thobe or kandura, is a traditional garment worn by men in many Arab countries, such as Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and the United Arab Emirates. It is a long, ankle-length robe made of lightweight fabric, often in white or other light colors. The dishdasha is typically worn with a head covering, such as a keffiyeh or a ghutra.
Shalwar Kameez:
The shalwar kameez is a traditional outfit worn by both men and women in many parts of the Islamic world, particularly in South Asia. It consists of loose-fitting trousers, known as shalwar, and a long tunic-like shirt, known as kameez. The fabrics, colors, and patterns used in shalwar kameez vary across regions and cultures, making it a versatile and diverse form of Islamic clothing.
Turban:
The turban is a traditional head covering worn by many Muslim men, particularly in parts of North Africa and the Indian subcontinent. It is typically made of a long cloth that is wrapped around the head in various styles and can be worn in different colors and patterns. The turban is not only a form of religious expression but also serves practical purposes, such as protection from the sun or cold.
Conclusion:
The diversity of Islamic clothing reflects the rich heritage and cultural traditions of the Islamic world. From the hijab and abaya to the dishdasha and shalwar kameez, these garments not only serve as a means of modesty and religious expression but also showcase the creativity and individuality of those who wear them. By exploring and appreciating the diversity of Islamic clothing, we can gain a deeper understanding of the traditions and values of the Islamic world.
Unraveling the Mysteries of Islamic Sufism
Sufism is a mystical branch of Islam that delves into the inner dimensions of the religion. Rooted in the belief of pursuing a closer relationship with God through self-reflection and spiritual practices, Sufism has captivated the hearts and minds of Muslims across the world. This article aims to unveil some of the mysteries surrounding this profound spiritual tradition.
Origins and Development
Sufism emerged in the early days of Islam, drawing inspiration from the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad. Its development can be traced back to the ascetic practices of certain individuals who sought to detach themselves from worldly affairs and focus solely on their connection with the Divine.
Principles and Beliefs
The central concept of Sufism is the idea that human beings have a spiritual essence or soul that serves as a conduit for connecting with God. This belief forms the foundation for various practices and rituals, such as meditation, chanting, and whirling dances, all aimed at purifying the soul and attaining a state of spiritual enlightenment.
Seeking the Divine
Sufis believe in the notion of “fana,” which means annihilation of the self, and “baqa,” which refers to subsistence in God. They strive to detach themselves from their ego and worldly desires, aiming to reach a state of complete surrender to the will of God. This process of self-transcendence allows them to experience a profound connection with the Divine.
Teachings of the Masters
Sufism is often transmitted through the teachings and guidance of spiritual masters, known as “qa’ims” or “sheikhs.” These individuals have undergone rigorous spiritual training and are believed to possess deep insight and wisdom. They guide their disciples on the path to spiritual awakening, helping them navigate the complexities of inner exploration and self-discovery.
Unity and Love
Sufism emphasizes the importance of love and unity, believing that all creation is interconnected and that God resides within every being. Sufis strive to cultivate a sense of universal love and compassion, transcending the boundaries of race, religion, and nationality. This philosophy of inclusivity and acceptance sets Sufism apart as a unifying force within the Islamic world.
The Influence of Sufism
Throughout history, Sufism has profoundly influenced various aspects of Islamic culture, including literature, music, and art. The poetry of Rumi, for example, is renowned for its profound insights into spirituality and love. Sufi music, with its mesmerizing chants and melodies, has captivated audiences across the world, invoking a sense of peace and tranquility.
| Key Concepts | Key Figures |
|
|
Unraveling the mysteries of Islamic Sufism requires delving into its rich history, core beliefs, and practices. This spiritual tradition has captivated millions of Muslims around the world, offering a pathway to inner peace, enlightenment, and a deep connection with the Divine.
Understanding the Rituals of Islamic Worship
Islamic worship, also known as Salah or Salat, is the most important practice in the religion of Islam. It is a physical, mental, and spiritual act of submission to Allah, the Arabic word for God. The rituals of Islamic worship are designed to bring Muslims closer to Allah and establish a personal connection with Him.
1. Purification:
-
Muslims begin their worship by performing a ritualistic cleansing known as ablution or wudu. This involves washing specific parts of the body, such as the hands, face, and feet, with clean water. It symbolizes the purification of the body and soul before standing before Allah in prayer.
2. Adhan:
-
Before each prayer time, the call to prayer, known as the adhan, is recited. The adhan is traditionally performed by a muezzin from a mosque’s minaret, but it can also be done individually. It serves as a reminder for Muslims to stop their activities and prepare for worship.
3. Prayer Postures:
-
Muslims perform their prayers in a specific manner, involving various postures. These postures include standing, bowing, prostrating, and sitting. Each posture has its own significance and is accompanied by specific prayers and recitations from the Quran.
4. Congregational Prayers:
-
While Muslims can perform their prayers individually, congregational prayers, known as Salah al-Jama’ah, are highly encouraged. These prayers are performed in congregation with other Muslims, led by an imam. They foster a sense of unity and community among believers.
5. Friday Prayer:
-
Friday prayer, also known as Jummah prayer, is an important weekly congregational prayer for Muslims. It is held on Fridays at the mosque and is considered obligatory for adult Muslim men. The Friday prayer includes a sermon delivered by the imam, followed by the congregational prayer.
6. Sujood:
-
Sujood refers to the prostration that Muslims perform during their prayers. It involves placing the forehead, nose, hands, knees, and toes on the ground in submission to Allah. It is a humbling act that symbolizes complete surrender and recognition of Allah’s greatness.
7. Tasbih:
-
Muslims often use a string of beads, known as a tasbih or misbaha, to keep track of their repetitive recitation of praises to Allah. This practice, called dhikr, involves the repetition of specific phrases, such as “Subhan Allah” (glory be to Allah) or “Allahu Akbar” (Allah is the greatest).
8. Time and Direction:
-
Muslims are required to perform their prayers at specific times throughout the day, known as the five daily prayers or Salat al-Fajr, Dhuhr, Asr, Maghrib, and Isha. The timing of these prayers is determined by the position of the sun. Muslims also face the Kaaba in Mecca, Saudi Arabia, during their prayers, which serves as a focal point of unity and direction.
9. Personal Connection:
-
Islamic worship is not just a series of rituals; it is an opportunity for Muslims to establish a personal connection with Allah. It is a time to seek forgiveness, ask for guidance, express gratitude, and offer supplications for oneself and others. Prayer is considered a means of spiritual purification and a way to attain closeness to Allah.
In conclusion, the rituals of Islamic worship encompass various aspects, including purification, prayer postures, congregational prayers, and personal connection with Allah. These rituals serve as a way for Muslims to express their devotion, seek spiritual growth, and strengthen their relationship with Allah.
Tracing the Spread of Islam
Islam, founded by Prophet Muhammad in the 7th century, rapidly spread across the Arabian Peninsula and eventually reached every corner of the world. The spread of Islam was driven by various factors, including military conquests, trade networks, and the appeal of its message.
Military Conquests
- One of the key factors in the rapid spread of Islam was the military conquests led by Muslim armies.
- Islamic warriors, driven by religious zeal, expanded the Islamic empire through numerous successful military campaigns.
- The early expansion of Islam included the conquest of Persia, Egypt, and North Africa, and later expanded into Europe, India, and Southeast Asia.
Trade Networks
- Islam spread along major trade routes, such as the Silk Road and the Indian Ocean trade routes, which facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and religious beliefs.
- Muslim merchants played a crucial role in the spread of Islam as they traveled to different regions and shared their faith with the local populations.
- The establishment of Muslim trading colonies in various parts of the world also contributed to the spread of Islam.
Message of Islam
- The simplicity and inclusiveness of the Islamic message attracted people from diverse backgrounds.
- Islam preached monotheism, social justice, and equality among all believers, irrespective of their social status or ethnicity.
- The appeal of Islam’s promise of salvation and a direct connection with God resonated with many people.
Conversion and Cultural Assimilation
- As Islam spread to new regions, local populations sometimes embraced the faith willingly, attracted by its teachings.
- In other cases, conversion to Islam was encouraged or enforced through political and social pressures imposed by Muslim rulers.
- Over time, Islamic culture and practices assimilated with local customs, resulting in the emergence of diverse cultural expressions within the Islamic world.
Conclusion
The spread of Islam was a complex process influenced by military conquests, trade networks, the appeal of its message, and the assimilation of local cultures. Today, Islam is one of the world’s major religions, with a rich and diverse cultural heritage encompassing various regions and traditions.
Glimpsing the History of Islamic Empires
The history of Islamic empires is a rich and complex tapestry that spans over a millennium. From the rise of the Rashidun Caliphate in the 7th century to the height of the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century, these empires have left a lasting impact on the world.
One of the earliest and most influential Islamic empires was the Umayyad Caliphate, which emerged after the death of the Prophet Muhammad. The Umayyads expanded their empire through military conquests, stretching from Spain in the west to parts of India in the east. They built grand palaces, mosques, and cities, such as Damascus, which became cultural and intellectual centers of the Islamic world.
In the 9th century, the Abbasid Caliphate overthrew the Umayyads and established their capital in Baghdad. The Abbasids were known for their patronage of art, science, and literature, which flourished during their rule. They also developed a sophisticated bureaucracy and legal system, and their caliphate became a beacon of knowledge and enlightenment.
Another significant Islamic empire was the Mughal Empire, which ruled over much of the Indian subcontinent from the 16th to the 19th century. The Mughals were known for their architectural marvels, such as the Taj Mahal, and their vibrant culture and arts. They also fostered religious tolerance and cultural exchange, leaving a lasting legacy in the region.
One cannot discuss the history of Islamic empires without mentioning the Ottoman Empire. Established in the 13th century, the Ottomans went on to conquer Constantinople and expand their empire across Europe, Asia, and Africa. Under their rule, the empire became a center of Islamic civilization, known for its military prowess, impressive architecture, and diverse society.
The history of Islamic empires is a testament to the richness and diversity of the Islamic world. From the Arab lands of the Umayyads to the Indian subcontinent of the Mughals and the cross-continental empire of the Ottomans, these empires have shaped the course of history and left a lasting impact on the world we live in today.
Recognizing the Contributions of Islamic Scholars
Islamic scholars have made significant contributions to various fields of knowledge throughout history. Their discoveries, inventions, and theories have had a profound impact on the development of science, medicine, mathematics, philosophy, and many other disciplines. It is important to recognize and appreciate the intellectual heritage of Islamic scholars and their contributions to the world.
One of the most significant contributions of Islamic scholars is in the field of astronomy. During the Islamic Golden Age, scholars like Al-Farabi, Al-Battani, and Al-Biruni made remarkable advancements in this field. They developed precise astronomical instruments, accurately measured celestial bodies, and developed theories about their motions. Their work influenced the European Renaissance and laid the foundation for modern astronomy.
Islamic scholars also played a crucial role in the development of medicine. The famous scholar Ibn Sina, also known as Avicenna, wrote the Canon of Medicine, which became a standard textbook in many medical schools throughout Europe for centuries. His works on anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology were groundbreaking and significantly advanced medical knowledge. Other Islamic scholars, such as Ibn Rushd and Ibn Zuhr, also made important contributions to medical science.
Mathematics is another field in which Islamic scholars excelled. The numerals we use today, known as Arabic numerals, were actually developed by Islamic mathematicians. They also introduced the concept of zero and made significant advancements in algebra, trigonometry, and geometry. Scholars like Al-Khwarizmi, Al-Biruni, and Omar Khayyam contributed greatly to the field of mathematics and their works had a lasting impact on European mathematicians during the Middle Ages.
Islamic scholars were not only focused on scientific and medical fields but also made significant contributions to philosophy, literature, and arts. Philosophers like Al-Farabi, Ibn Sina, and Ibn Rushd made important philosophical works that influenced European thinkers during the Renaissance. Islamic literature, such as the works of Persian poets Rumi and Hafez, have been widely celebrated and continue to inspire people around the world.
Overall, the contributions of Islamic scholars have been immeasurable and have enriched the world with their knowledge and ideas. It is important to recognize and acknowledge their achievements, as they have shaped our understanding of the world and continue to inspire future generations.
Understanding the Concept of Jihad in Islam
Jihad, derived from the Arabic word “j-h-d,” means to strive or struggle. In the Islamic context, Jihad is often misunderstood and associated solely with fighting or violence. However, it encompasses a much broader meaning and is rooted in the teachings of Islam.
Jihad can be categorized into two main types:
- Jihad of the heart and soul: This form of Jihad refers to the inner struggle to purify oneself and adhere to the commandments of Allah. It involves striving to overcome personal flaws, such as greed, envy, and pride, and striving to increase one’s piety, humility, and devotion to Allah.
- Jihad of the hand and sword: This aspect of Jihad refers to physical struggle or defense against aggression, oppression, or injustice. It allows Muslims to protect themselves, their families, and their communities from harm and ensure the freedom to practice their religion. However, it is important to note that Jihad of the hand and sword should be carried out within the boundaries of Islamic law and under the guidance of legitimate authorities.
The concept of Jihad emphasizes the importance of self-defense and preserving justice, but it does not encourage random violence or the targeting of innocent individuals. Islam strictly prohibits the killing of non-combatants, women, children, and the elderly, as well as the destruction of places of worship, regardless of the circumstances.
Moreover, Jihad also extends beyond the realm of physical combat and self-defense. It includes efforts to improve oneself and society through acts of charity, education, and other forms of positive contribution. Muslims are encouraged to engage in acts of benevolence and work towards the betterment of their communities and the world at large.
It is crucial to highlight that Jihad is not equivalent to terrorism. Terrorism is a distortion of the Islamic teachings and violates the principles of Islam. Islam promotes peace, justice, and compassion, and it is the duty of Muslims to uphold these values in their lives.
The understanding of Jihad in Islam is multifaceted and deep-rooted in the principles of justice, self-defense, and striving for self-improvement. It is essential to explore its various dimensions to gain a comprehensive understanding of this concept within the larger context of the Islamic faith.
Appreciating the Beauty of Islamic Gardens
Islamic gardens are known for their breathtaking beauty and serene atmosphere. These gardens are not just spaces for plants and flowers, but they are designed as holistic environments that foster a sense of peace, tranquility, and harmony with nature. From the design to the elements used, each aspect of an Islamic garden has a deeper significance and purpose.
One key element of Islamic gardens is the use of water features. Water symbolizes purity and life, and it is a central element in Islamic garden design. Fountains, pools, and flowing streams create a soothing sound and provide a cooling effect, adding to the overall ambience of the garden. These water features are often surrounded by lush greenery, creating a refreshing and relaxing environment for visitors.
Another characteristic of Islamic gardens is the presence of shaded areas. These shaded areas, often created by trees or architectural structures, provide relief from the scorching sun and invite visitors to rest and contemplate. Many Islamic gardens include pergolas or trellises covered with climbing plants, offering a cool and shaded retreat. These shaded areas also serve as gathering spaces for social interactions and contemplation.
Islamic gardens are often adorned with colorful flowers and fragrant plants. These vibrant colors and scents enhance the sensory experience and create a visually stunning display. Various flowers, such as roses and jasmine, are commonly found in Islamic gardens, as they hold cultural and symbolic significance in Islamic art and literature.
In addition to the aesthetic beauty, Islamic gardens often incorporate symbolic and spiritual elements. These gardens are designed to reflect the Islamic concept of paradise, with elements representing the four rivers of paradise or the Islamic depiction of heaven. The use of geometric patterns and symmetrical designs in the layout of the garden is another characteristic feature inspired by Islamic art and architecture.
The design and layout of Islamic gardens vary across different regions and time periods, reflecting the diversity of Islamic culture and history. From the famous gardens of Alhambra in Spain to the Mughal gardens of India, each garden showcases a unique fusion of artistic styles and horticultural techniques.
In conclusion, Islamic gardens are a true testament to the beauty and creativity of Islamic culture. These gardens provide an opportunity to appreciate the harmony between nature, art, and spirituality. Visiting an Islamic garden is not just a visual experience but also a sensory journey that offers moments of tranquility and reflection.
Exploring Islamic Literature and Poetry
Introduction: Islamic literature and poetry hold a significant place in the cultural and intellectual heritage of the Islamic world. Through the centuries, Muslim writers and poets have left an indelible mark on the literary landscape, creating masterpieces that continue to inspire and captivate readers worldwide.
Themes and Styles: Islamic literature and poetry encompass a wide range of themes and styles, reflecting the diverse cultures and traditions within the Islamic world. From the mystical verses of Rumi to the historical epics of Ibn Khaldun, Islamic literature offers a rich tapestry of narratives that explore love, spirituality, social justice, and the complexities of human existence.
Key Figures: Numerous luminaries have emerged from the Islamic literary tradition. One of the most celebrated figures is Jalaluddin Rumi, a 13th-century Persian poet and scholar whose mystical poetry has become immensely popular worldwide. Other notable figures include Ibn Arabi, Hafiz, and Omar Khayyam, each contributing to the richness and diversity of Islamic literature.
Forms of Expression: Arabic is the language of the Quran, and as such, it plays a pivotal role in Islamic literature and poetry. However, other languages such as Persian, Turkish, and Urdu have also served as mediums of expression in the Islamic literary tradition. Islamic literature encompasses various forms, including ghazals, qasidas, rubaiyats, and masnavis, each with its own unique structure and rhythm.
Legacy and Influence: Islamic literature and poetry have had a profound impact not only within the Islamic world but also on global literary traditions. Translations of Islamic literary works have contributed to the enrichment and evolution of literature in other languages, allowing readers worldwide to experience the beauty and wisdom of Islamic literary traditions.
Cultural Significance: Islamic literature and poetry serve as windows into the history, culture, and values of the Islamic world. They shed light on the diversity and richness of Islamic civilization, providing insights into the intellectual, spiritual, and artistic achievements of Muslim societies throughout history.
| Notable Works | Author | Language |
|---|---|---|
| The Rubaiyat | Omar Khayyam | Persian |
| The Masnavi | Jalaluddin Rumi | Persian |
| The Muqaddimah | Ibn Khaldun | Arabic |
| The Divine Comedy | Abdullah Ibn Arabi | Arabic |
Conclusion: Exploring Islamic literature and poetry is a journey that unveils the beauty, depth, and diversity of the Islamic world. From the works of its celebrated poets and thinkers to the rich tapestry of themes and styles, Islamic literature continues to inspire and enrich the global literary landscape.
Gaining an Insight into Islamic Fashion
Islamic fashion is a diverse and vibrant industry that reflects the values and traditions of Muslim culture. It encompasses a wide range of styles and designs, allowing individuals to express their faith while remaining fashionable. Here are a few key aspects to consider when exploring Islamic fashion:
- Modesty: Modesty is an essential component of Islamic clothing. Muslim women often wear loose-fitting garments that cover their bodies, including the headscarf (hijab), which covers the hair and neck.
- Abayas and Jilbabs: An abaya is a loose, full-length coat worn by women in many Muslim countries. It is often made of flowing fabric and can come in various colors and styles. Jilbabs are similar garments that cover the body but are usually worn with a headscarf.
- Hijabs: Hijabs come in a variety of styles, including the popular rectangular scarf style or the more modern turban style. They can be made from a range of fabrics, from lightweight chiffon to heavier wool for colder weather.
- Accessories: Islamic fashion also includes a wide range of accessories that can be used to complement an outfit. These can include statement necklaces, colorful handbags, and stylish shoes, all while still adhering to modesty guidelines.
- Modest Swimwear: Islamic fashion also extends to swimwear, with specially designed options that cater to the requirements of modesty. Burkini, for example, is a full-coverage swimsuit that allows Muslim women to participate in water activities while maintaining their sense of modesty.
Overall, Islamic fashion embodies individuality and style while staying true to the principles of modesty and respect. It showcases the richness and diversity of Muslim culture, highlighting the unique attire and fashion choices of individuals around the world. Whether it’s traditional clothing or modern interpretations, Islamic fashion offers a wide array of options for everyone to enjoy.
Discovering the Intricacies of Islamic Banking
Islamic banking is a unique financial system that is based on the principles of Islamic law, also known as Shariah. Unlike conventional banking, which focuses on interest-based transactions, Islamic banking prohibits the payment or receipt of interest (riba) and promotes profit-sharing arrangements.
One of the key features of Islamic banking is the concept of risk-sharing. In Islamic finance, the bank and the customer share both profits and losses in a business venture. This encourages banks to be more involved in the operations and decision-making processes of the businesses they finance.
Another fundamental principle of Islamic banking is the prohibition of investments in industries that are considered unethical or harmful to society, such as gambling, alcohol, and tobacco. This ensures that Islamic financial institutions promote ethical and socially responsible investments.
Islamic banking also places a strong emphasis on the concept of fairness and justice in financial transactions. For example, Islamic banks cannot enter into contracts that involve excessive uncertainty (gharar) or speculation (maysir). This promotes stability and reduces the potential for financial crises.
In order to accommodate these principles, Islamic banks have developed a variety of financial products and services that comply with Shariah law. These include profit-sharing agreements (Mudarabah), investment partnerships (Musharakah), and leasing arrangements (Ijarah).
It is important to note that Islamic banking is not limited to Muslim-majority countries. In fact, it has gained popularity and recognition in many non-Muslim countries as well. This is because the principles of Islamic banking align with ethical and sustainable finance, which is increasingly being embraced by individuals and institutions around the world.
In conclusion, Islamic banking offers a unique and alternative approach to finance that is based on ethical principles and risk-sharing. Its emphasis on fairness, justice, and social responsibility sets it apart from conventional banking and contributes to the overall development of a more inclusive and sustainable global financial system.+
Examining Islamic Artifacts and Art Collections
Islamic artifacts and art collections are a rich source of information about the culture, history, and religious beliefs of the Islamic world. These artifacts and collections encompass a wide range of objects, including textiles, ceramics, woodwork, calligraphy, and metalwork.
One of the most prominent features of Islamic art is the extensive use of geometric patterns and intricate designs. Islamic artists often incorporate floral motifs, arabesques, and calligraphy into their work, creating visually stunning pieces. These patterns not only serve an aesthetic purpose but also have deeper symbolic meanings, representing the unity and order of the Islamic faith.
Islamic textiles, such as carpets and textiles, are highly valued for their exquisite craftsmanship. These textiles often feature intricate patterns, vibrant colors, and luxurious materials, making them highly sought after by collectors. Carpets, in particular, hold a special significance in Islamic art, as they are often used for prayer and are considered sacred objects.
Ceramics are another significant aspect of Islamic art. Islamic ceramics are known for their innovative designs and sophisticated glazing techniques. From the famous blue and white pottery of Persia to the intricate tile work of mosques, ceramics play an integral role in the artistic tradition of the Islamic world.
Woodwork also holds a prominent place in Islamic art. Intricately carved wooden screens, doors, and ceilings can be found in many Islamic architectural structures. These wooden pieces often feature geometric patterns and delicate details, showcasing the mastery of Islamic craftsmen.
Calligraphy, the art of beautiful writing, is highly revered in the Islamic world and is considered one of the highest forms of art. Islamic calligraphy is often found in religious texts, architectural elements, and decorative objects. The stylized Arabic script is a visual representation of the words of Allah, adding a spiritual dimension to the artistic expression.
Islamic metalwork encompasses a variety of objects, including ornate metal jewelry, weapons, and decorative metalwork. The intricate detailing and craftsmanship of Islamic metalwork exemplify the skill and talent of the craftsmen. Metalwork often features elements of calligraphy, geometric patterns, and floral motifs, creating visually stunning and culturally significant pieces.
| Name of Collection | Location |
|---|---|
| The Metropolitan Museum of Art | New York, USA |
| The Louvre Museum | Paris, France |
| The British Museum | London, United Kingdom |
| The Victoria and Albert Museum | London, United Kingdom |
These collections house a vast array of Islamic artifacts and provide an opportunity for visitors to explore and appreciate the diversity of Islamic art. Through examining these artifacts and art collections, one can gain a deeper understanding of the rich and vibrant cultural heritage of the Islamic world.
Gaining a Deeper Understanding of Islamic Philosophy
Islamic philosophy is a rich and diverse field of study that encompasses a wide range of topics, including theology, metaphysics, ethics, and logic. It is rooted in the teachings of the Qur’an and the Hadith, but also draws from the works of ancient Greek philosophers such as Plato and Aristotle.
One of the key principles of Islamic philosophy is the concept of tawhid, which is often defined as the belief in the oneness of God. This principle permeates all aspects of Islamic thought and is seen as the foundation for understanding the world and the human condition.
A central theme in Islamic philosophy is the exploration of the nature of existence and the relationship between God and the creation. It seeks to answer fundamental questions such as the purpose of life, the nature of reality, and the role of humans in the universe.
Islamic philosophers have made significant contributions to various disciplines, including mathematics, astronomy, and medicine. Scholars such as Al-Farabi, Avicenna, and Averroes sought to harmonize Greek philosophy with Islamic theology, and their works influenced European thought during the Middle Ages.
To gain a deeper understanding of Islamic philosophy, it is important to study the works of prominent philosophers and theologians. Some key texts to explore include Al-Farabi’s “The Book of Letters” and Avicenna’s “The Cannon of Medicine”. These texts provide valuable insights into the philosophical traditions of Islam.
Additionally, engaging in discussions and debates with scholars and experts in the field can help deepen your understanding of Islamic philosophy. There are also numerous online resources, academic journals, and books that provide comprehensive overviews of the subject.
Islamic philosophy offers a unique perspective on the world and human existence. By exploring its rich tradition, we can gain a deeper understanding of the intellectual and cultural contributions of the Islamic world.
Unveiling the History of Islamic Astronomy
The Islamic world has a rich and diverse history of scientific exploration and discovery, with astronomy playing a significant role. Islamic astronomers made important contributions to the field, building upon the knowledge of ancient civilizations and expanding the boundaries of scientific understanding.
Golden Age of Islamic Astronomy
During the Islamic Golden Age, from the 8th to the 14th centuries, Islamic astronomers made groundbreaking advancements in various areas of astronomy. They developed sophisticated instruments and techniques for observing celestial bodies.
Observatories and Instruments
- One of the most famous observatories during this period was the Maragheh Observatory in present-day Iran. It featured an impressive array of instruments, including an equatorial armillary sphere and an enormous mural sextant.
- The astrolabe, an essential instrument in Islamic astronomy, was widely used for measuring angles and determining the positions of stars and planets.
Advancements in Astronomical Theory
Islamic astronomers made significant advancements in astronomical theory, building upon the work of ancient Greek and Persian scholars. They developed new methods for calculating the positions of celestial objects and made important discoveries about planetary motion.
Al-Battani and His Observations
One of the most influential Islamic astronomers was Al-Battani, also known as Albategnius. He made precise observations of celestial bodies and refined existing theories about astronomical phenomena. His observations of the Moon and the planets played a crucial role in advancing our understanding of their motions.
Astronomical Works by Islamic Scholars
Islamic astronomers wrote numerous books and treatises on astronomy, which became influential works in the field. Some notable examples include Al-Biruni’s “The Mas’udi Canon” and Ibn al-Haytham’s “Book of Optics.” These works not only preserved the knowledge of the past but also pushed the boundaries of scientific understanding.
Legacy of Islamic Astronomy
The contributions of Islamic astronomers laid the foundation for modern astronomy. Their work was later built upon by European scholars during the Renaissance, leading to further advancements in the field. The discoveries and techniques of Islamic astronomers continue to be studied and admired today, highlighting the rich intellectual heritage of the Islamic world.
Question-answer:
What countries are part of the Islamic world?
The Islamic world includes countries such as Saudi Arabia, Iran, Turkey, Egypt, Indonesia, and many others. It spans across the Middle East, North Africa, parts of Europe, and Southeast Asia.
What are the main beliefs of Islam?
The main beliefs of Islam include the belief in one God (Allah) and the finality of the Prophet Muhammad’s message. The Five Pillars of Islam, which are the declaration of faith (Shahada), prayer (Salat), giving to the poor (Zakat), fasting during Ramadan (Sawm), and pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj), are also central to the faith.
What is the significance of Islamic art and architecture?
Islamic art and architecture have a rich cultural and religious significance. Islamic art is characterized by intricate geometric patterns, calligraphy, and arabesque designs. It is often used to decorate mosques and other religious buildings. Islamic architecture, such as the domes and minarets found in mosques, reflects the spiritual nature of the religion and creates a sense of awe and beauty.
What is the role of women in the Islamic world?
The role of women in the Islamic world varies depending on the country and cultural traditions. In many Muslim-majority countries, women have made significant advancements in education and the workforce. However, there are still challenges and inequalities that women face, such as limited access to certain rights and opportunities. It is important to note that Islam itself does not restrict women’s rights, but cultural and societal factors can influence gender roles and expectations.
What is the significance of the Quran for Muslims?
The Quran is the holy book of Islam and holds great significance for Muslims. It is believed to be the literal word of God as revealed to the Prophet Muhammad. The Quran serves as a guide for personal and communal life, providing moral, ethical, and legal principles. Muslims see the Quran as a source of wisdom, spiritual guidance, and a means of connecting with God.