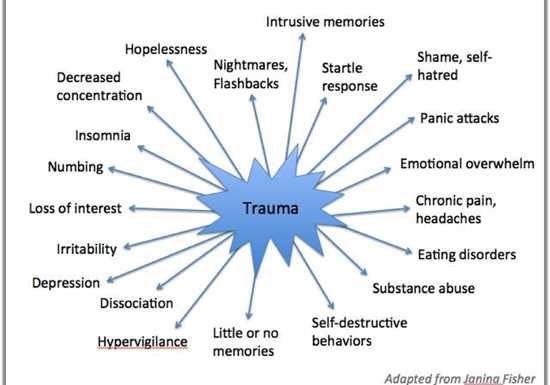
Experiencing trauma can have a profound impact on an individual’s mental health. Trauma refers to any event or series of events that is deeply distressing and overwhelming, leaving a lasting impression on a person’s mind. This can include incidents such as physical or sexual abuse, natural disasters, accidents, and witnessing violence or death.
The link between trauma and mental health is complex and multifaceted. While each person’s response to trauma is unique, many individuals who have experienced trauma may develop mental health issues as a result. Common mental health conditions associated with trauma include post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, anxiety, and substance abuse disorders.
In individuals with PTSD, the impact of trauma can be particularly severe. This condition is characterized by intrusive memories, flashbacks, nightmares, and a constant state of hypervigilance. Those with PTSD may also experience avoidance behaviors, such as avoiding places or situations that remind them of the trauma, as well as changes in mood and cognition.
It is important to recognize and understand the link between trauma and mental health in order to provide appropriate support and care for individuals who have experienced trauma. By raising awareness about the impact of trauma on mental health, we can promote understanding, empathy, and access to effective treatment options for those who need it most.
“It is important to recognize and understand the link between trauma and mental health in order to provide appropriate support and care for individuals who have experienced trauma.”
The Overwhelming Effects of Trauma on Mental Well-being
Trauma can have a profound impact on an individual’s mental well-being. Whether it is experienced directly or witnessed, trauma can lead to a range of emotional and psychological difficulties. Understanding the effects of trauma on mental health is crucial in order to provide appropriate support and treatment for those who have experienced it.
1. Emotional Impact:
Trauma can result in overwhelming emotions such as fear, anger, sadness, and guilt. These emotions may be triggered by reminders of the traumatic event and can be difficult to manage. Individuals may also experience a sense of numbness or detachment from their emotions, making it challenging to connect with others or engage in daily activities.
2. Cognitive Effects:
Trauma can disrupt an individual’s cognitive functioning, leading to difficulties with memory, concentration, and problem-solving. They may also experience intrusive thoughts or flashbacks of the traumatic event, which can be distressing and interfere with their ability to focus or stay present.
3. Behavioral Changes:
Trauma can result in changes in behavior, such as avoidance of situations or places that remind them of the trauma. Individuals may also engage in self-destructive behaviors, such as substance abuse or self-harm, as a way to cope with the overwhelming emotions they are experiencing. Sleep disturbances and altered eating patterns are also common.
4. Interpersonal Difficulties:
Trauma can impact the way individuals relate to others. They may have difficulty trusting others or forming close relationships. They may also struggle with feelings of shame or guilt, believing that they are responsible for what has happened to them. These difficulties can lead to social isolation and further exacerbate their mental health challenges.
5. Physical Health Consequences:
The effects of trauma are not limited to mental health alone. It can also have physical health consequences, such as chronic pain, headaches, and gastrointestinal problems. Research has shown that trauma can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of developing chronic illnesses.
In conclusion, trauma can have overwhelming effects on an individual’s mental well-being. It can impact their emotions, cognition, behavior, relationships, and physical health. Recognizing these effects and providing appropriate support and treatment is essential in helping individuals recover and improve their overall well-being.
Exploring the Development of Psychological Disorders Post-Trauma
Experiencing a traumatic event can have a lasting impact on an individual’s mental health. Many individuals who have experienced trauma go on to develop psychological disorders as a result of their experiences. Understanding the development and progression of these disorders is crucial in providing appropriate support and treatment.
1. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- PTSD is one of the most well-known psychological disorders that can develop after trauma.
- Characteristic symptoms include intrusive memories, nightmares, and flashbacks of the traumatic event.
- Individuals with PTSD may also experience hyperarousal, avoidance behavior, and negative changes in thoughts and mood.
- Treatment for PTSD often involves a combination of therapy and medication.
2. Depression
- Depression commonly co-occurs with traumatic experiences.
- Individuals may experience persistent feelings of sadness, loss of interest, and changes in appetite or sleep patterns.
- Depression can make it difficult for individuals to function in their daily lives.
- Treatment for depression may include therapy, medication, or a combination of both.
3. Anxiety Disorders
- Anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder, may develop after trauma.
- Individuals may experience excessive worry, fear, and avoidance of triggering situations or objects.
- Anxiety disorders can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life.
- Treatment options for anxiety disorders include therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
4. Substance Abuse Disorders
- Substance abuse disorders may develop as individuals attempt to cope with the psychological distress caused by trauma.
- Individuals may turn to drugs or alcohol as a means of escaping or numbing their emotions.
- Substance abuse further exacerbates mental health issues and can lead to a cycle of addiction.
- Treatment for substance abuse disorders often involves a combination of therapy, medication, and support groups.
5. Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
- BPD is characterized by unstable moods, relationships, and self-image.
- Experiencing trauma can contribute to the development of BPD.
- Individuals with BPD may engage in impulsive behavior and have difficulty regulating their emotions.
- Treatment for BPD typically involves a combination of therapy, medication, and skills training.
Conclusion
Understanding the development of psychological disorders post-trauma is essential in providing effective support and treatment for individuals who have experienced trauma. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of these disorders can help healthcare professionals and loved ones provide the necessary assistance and intervention.
The Relationship between Trauma and Substance Abuse
There is a strong connection between trauma and substance abuse. Many individuals who have experienced trauma turn to substances as a way to cope with the overwhelming emotions and memories associated with the traumatic event.
1. Self-Medication:
One reason for the link between trauma and substance abuse is self-medication. Trauma survivors often struggle with symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), such as anxiety, depression, and nightmares. They may use drugs or alcohol as a way to numb these distressing feelings and escape from the painful memories.
2. Avoidance:
Substance abuse can also be a form of avoidance for trauma survivors. By using drugs or alcohol, individuals can temporarily forget about the trauma and avoid confronting the emotional pain associated with it. This avoidance may provide temporary relief, but it can ultimately lead to a cycle of dependency and increased psychological distress.
3. High-Risk Behaviors:
Individuals who have experienced trauma may engage in high-risk behaviors as a result of substance abuse. They may take risks while under the influence of substances, which can further exacerbate the effects of trauma and increase their chances of re-traumatization.
4. Ongoing Trauma:
In some cases, substance abuse can contribute to ongoing trauma. Individuals who are under the influence of drugs or alcohol may engage in risky situations or become victims of violence, putting them at a higher risk for experiencing additional trauma.
5. Comorbidity:
The co-occurrence of trauma and substance abuse is not a coincidence. Research has shown that there is a high rate of comorbidity between PTSD and substance use disorders. This means that individuals who have experienced trauma are more likely to develop substance abuse problems, and vice versa.
Conclusion:
Understanding the relationship between trauma and substance abuse is crucial in order to provide effective treatment for individuals who are struggling with both. It is important to address the underlying trauma and provide alternative coping strategies to break the cycle of self-medication and address the root causes of substance abuse.
Understanding the Role of Trauma in Anxiety and Depression
Anxiety and depression are two of the most common mental health disorders, affecting millions of people worldwide. While there are various factors that can contribute to the development of these conditions, trauma has been identified as a significant underlying cause.
Trauma refers to any event or experience that is deeply distressing or disturbing and exceeds a person’s ability to cope. It can result from a range of sources, such as physical or sexual abuse, natural disasters, accidents, or witnessing violence. Traumatic experiences can be singular events or ongoing, such as prolonged abuse or neglect.
Research has shown a strong correlation between trauma and the development of anxiety and depression. People who have experienced trauma are more likely to develop symptoms of these disorders compared to those who have not. This connection can be explained by several mechanisms:
- Hyperarousal: Trauma can lead to chronic hypervigilance and an overactive stress response system. This heightened state of arousal can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders, where individuals constantly anticipate danger or threat.
- Intrusive thoughts and flashbacks: Trauma can cause distressing and intrusive memories of the traumatic event, leading to flashbacks and nightmares. These symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) are closely associated with the development of depression.
- Broken sense of self: Traumatic experiences can shatter a person’s sense of safety, trust, and identity. This disruption to one’s core beliefs and self-concept can contribute to feelings of hopelessness, worthlessness, and despair, which are common features of depression.
- Maladaptive coping strategies: Many individuals rely on unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as substance abuse or self-harm, to numb emotional pain or regain a sense of control. These maladaptive strategies can worsen symptoms of anxiety and depression.
It is important to note that not everyone who experiences trauma will develop anxiety or depression. Resilience, social support, and individual differences in coping mechanisms play a significant role in determining how trauma affects mental health. Additionally, the severity, duration, and frequency of traumatic experiences also influence the likelihood of developing these conditions.
Addressing trauma is crucial for the effective treatment of anxiety and depression. Traditional therapy approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help individuals process and heal from traumatic experiences. By challenging distorted beliefs and learning adaptive coping strategies, individuals can reduce anxiety, alleviate depressive symptoms, and regain a sense of control over their lives.
In conclusion, trauma plays a significant role in the development of anxiety and depression. Understanding this connection is vital for effective mental health treatment and support. By addressing trauma, individuals can work towards healing and recovery from these debilitating conditions.
PTSD: Unraveling the Lifelong Consequences of Trauma
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. Whether it is a natural disaster, combat, physical assault, or a severe accident, the impact of trauma can have long-lasting effects on a person’s mental well-being, even years after the event has occurred.
PTSD is characterized by a variety of symptoms that can significantly impair a person’s daily functioning. These symptoms may include intrusive memories of the traumatic event, nightmares, flashbacks, intense anxiety or distress, difficulty concentrating, emotional numbness, and avoidance of triggers that remind them of the trauma.
One of the defining features of PTSD is its ability to persist long after the traumatic event has ended. Many individuals who experience trauma may initially have symptoms of acute stress disorder, which may resolve within a few weeks. However, for some individuals, these symptoms may persist and develop into PTSD.
The lifelong consequences of PTSD can be far-reaching and impact various areas of a person’s life. Individuals with PTSD often experience significant difficulties in their relationships, work, and overall quality of life. The symptoms of PTSD can also lead to other mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety disorders, and substance abuse.
It is essential to recognize the long-term consequences of trauma and provide adequate support and treatment for individuals with PTSD. Effective treatments, such as trauma-focused therapy and medication, can help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Unraveling the effects of trauma
The effects of trauma on the brain are complex and can cause lasting changes in the way it functions. When a person experiences trauma, the amygdala, which is responsible for processing emotions, goes into overdrive. This hyperactivity can lead to an exaggerated fear response, making individuals more likely to perceive non-threatening situations as dangerous.
The hippocampus, another part of the brain involved in memory formation, may also be affected by trauma. In individuals with PTSD, the hippocampus may shrink in size, affecting their ability to process and recall memories correctly. This may explain why individuals with PTSD often experience difficulties with memory and have intrusive memories of the traumatic event.
Furthermore, trauma can disrupt the body’s stress response system, known as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. This disruption can lead to an imbalance in stress hormones, such as cortisol, which may contribute to the development of PTSD and its associated symptoms.
The importance of early intervention
Early intervention following a traumatic event is crucial in preventing the long-term consequences of trauma. Providing support and resources to individuals who have experienced trauma can help reduce the risk of developing PTSD.
Trauma-informed care, which acknowledges the impact of trauma on an individual’s mental health and well-being, is essential in providing effective treatment and support. Understanding the link between trauma and mental health is the first step in unraveling the lifelong consequences of trauma and promoting resilience in individuals who have experienced trauma.
In conclusion
PTSD represents the lifelong consequences of trauma and highlights the need for effective treatment and support. Recognizing the impact of trauma on mental health is crucial in identifying individuals who may be at risk of developing PTSD and providing them with the necessary resources and interventions. By unraveling the lifelong consequences of trauma, we can work towards promoting resilience and improving the overall well-being of those who have experienced trauma.
The Impact of Trauma on Cognitive Functioning
Experiencing trauma can have a significant impact on an individual’s cognitive functioning. Cognitive functioning refers to the mental processes and abilities that help us think, remember, reason, and solve problems. When someone experiences trauma, their cognitive functioning can be disrupted in various ways.
- Memory: Trauma can affect an individual’s memory in multiple ways. Some individuals may experience difficulty recalling specific details of the traumatic event, while others may have fragmented or flashbulb memories. Additionally, trauma can interfere with the individual’s ability to encode and retrieve new information.
- Attention and concentration: Trauma can lead to difficulties in focusing and maintaining attention. Individuals may struggle to concentrate on tasks or become easily distracted. They may also experience hypervigilance, a state of heightened awareness and constantly scanning the environment for potential threats.
- Executive functioning: Trauma can impair an individual’s executive functioning, which includes skills such as planning, organizing, problem-solving, and decision-making. These difficulties can make it challenging for individuals to set goals, prioritize tasks, and make sound judgments.
- Processing speed: Trauma can slow down cognitive processing speed, leading to delays in responding to information or completing tasks. Individuals may find it harder to think quickly and may experience a sense of mental sluggishness.
- Emotional regulation: Trauma can disrupt an individual’s ability to regulate emotions effectively. They may experience heightened emotional reactivity, difficulty controlling anger or sadness, and may be more prone to mood swings.
It’s important to note that the impact of trauma on cognitive functioning can vary from person to person. Some individuals may exhibit mild cognitive impairments, while others may experience more severe difficulties. The specific type and severity of trauma, as well as individual factors such as resilience and support systems, can influence the extent of cognitive impairments.
Understanding the impact of trauma on cognitive functioning is crucial for mental health professionals as it can inform assessment, diagnosis, and treatment approaches. By addressing the cognitive challenges associated with trauma, healthcare providers can help individuals regain their cognitive abilities and improve their overall mental well-being.
Healing from Trauma: The Importance of Seeking Help
Trauma can have a profound impact on an individual’s mental health. Whether it’s experiencing a life-threatening event, surviving physical or emotional abuse, or enduring the loss of a loved one, trauma can leave deep emotional scars that can affect a person’s daily life.
While some individuals are able to cope with trauma on their own, seeking help is crucial for many others. It’s important to recognize that healing from trauma is a journey, and professional support can make a significant difference in the recovery process.
Why seek help?
- Validation and understanding: Speaking with a mental health professional can provide validation for the experiences and emotions associated with trauma. They can provide a safe space for individuals to share their stories, and a therapist can help them make sense of their feelings and reactions.
- Coping strategies: Trauma can bring about a range of emotions and often leads to difficulties in managing daily life. A therapist can teach coping strategies and provide tools to help individuals navigate their emotions in a healthier way.
- Addressing underlying issues: Trauma can be intertwined with other mental health conditions such as anxiety or depression. Seeking help can help identify and address these underlying issues, improving overall mental well-being.
Types of professionals who can help:
There are various mental health professionals trained to specifically work with individuals who have experienced trauma:
- Therapists: Licensed therapists, such as psychologists, social workers, or counselors, can provide talk therapy to address trauma and its impact on mental health.
- Psychiatrists: Psychiatrists are medical doctors who can provide both therapy and medication management for trauma-related mental health conditions.
- Support groups: Support groups consisting of individuals who have experienced similar traumas can also be valuable in the healing process. Sharing experiences and finding common ground can be incredibly empowering.
Overcoming the barriers:
It’s common for individuals to face certain barriers when seeking help for trauma. Some of these barriers include:
- Stigma: The social stigma surrounding mental health can make individuals hesitant to seek help. It’s important to remember that seeking support is a sign of strength, not weakness.
- Financial limitations: Access to mental health services can be limited for those without insurance or the financial means to pay for therapy. However, many organizations offer affordable or sliding-scale options.
- Lack of awareness: Some individuals may not be aware of the available resources or may not recognize the impact of trauma on their mental health. Education and spreading awareness are key in addressing these barriers.
Conclusion:
Healing from trauma is a complex process that requires time, patience, and support. Seeking help from mental health professionals can provide valuable assistance in this journey. Remember, it’s never too late to seek help, and reaching out is the first step towards healing.
Building Resilience and Moving Forward after Trauma
Recovering from trauma and rebuilding your life can be a long and challenging journey. However, developing resilience is crucial in overcoming the impact of trauma on mental health. Resilience refers to the ability to bounce back from difficult experiences, adapt to adversity, and grow stronger as a result.
Here are some strategies that can help individuals build resilience and move forward after experiencing trauma:
- Seeking support: Reach out to friends, family, or support groups for emotional support. Connecting with others who have experienced similar traumas can provide validation and understanding. Consider seeking professional help from therapists or counselors specialized in trauma as well.
- Practicing self-care: Taking care of yourself physically, mentally, and emotionally is crucial. Engage in activities that you find pleasurable and relaxing. Practice self-compassion and prioritize your well-being.
- Developing coping mechanisms: Find healthy coping strategies to deal with stress and anxiety. This can include practicing relaxation techniques, mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies and creative outlets.
- Creating a support network: Surround yourself with people who uplift and support you. Build relationships with individuals who provide encouragement, understanding, and a safe environment to share your experiences.
- Setting realistic goals: Break larger goals into smaller, achievable steps. This can help you regain a sense of control and accomplishment, which can be empowering and boost your confidence.
- Establishing routines: Structure and predictability can be comforting after experiencing trauma. Create daily routines that provide stability and a sense of normalcy in your life.
- Practicing gratitude: Focusing on the positive aspects of your life can help shift your mindset and increase resilience. Keep a gratitude journal or take time each day to reflect on things you are grateful for.
- Educating yourself: Learn more about trauma and its effects on mental health. Understanding the impact of trauma can help you make informed decisions about your healing process and seek appropriate resources.
Remember, everyone’s healing journey is unique, and it’s important to be patient with yourself. Building resilience takes time, but with support, self-care, and a positive mindset, it is possible to move forward and lead a fulfilling life after trauma.
Questions and answers
How does trauma affect mental health?
Trauma can have a significant impact on mental health. It can lead to the development of mental health disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, anxiety, and substance abuse. Trauma can also affect a person’s ability to regulate emotions, form healthy relationships, and function well in daily life.
What are some common symptoms of trauma-related mental health disorders?
Common symptoms of trauma-related mental health disorders include recurring distressing memories or dreams of the traumatic event, flashbacks, avoidance of reminders of the trauma, irritability, difficulty concentrating, changes in sleep patterns, feelings of guilt or shame, and increased anxiety or fear.
Can trauma affect a person’s physical health?
Yes, trauma can have a significant impact on a person’s physical health. Chronic stress resulting from trauma can lead to a weakened immune system, increased risk of cardiovascular problems, and even physical pain. Trauma can also affect a person’s sleep patterns, appetite, and energy level.
Can trauma be treated?
Yes, trauma can be treated. There are various evidence-based therapies available, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), and trauma-focused therapy, which can help individuals process and cope with traumatic experiences. Medication can also be prescribed to manage symptoms of trauma-related disorders.
Is it possible to recover from trauma?
Yes, it is possible to recover from trauma. With appropriate treatment and support, individuals can learn to effectively manage their symptoms, reduce the impact of trauma on their lives, and improve their overall well-being. Recovery from trauma may be a gradual process, and it is essential for individuals to seek professional help and engage in self-care strategies.