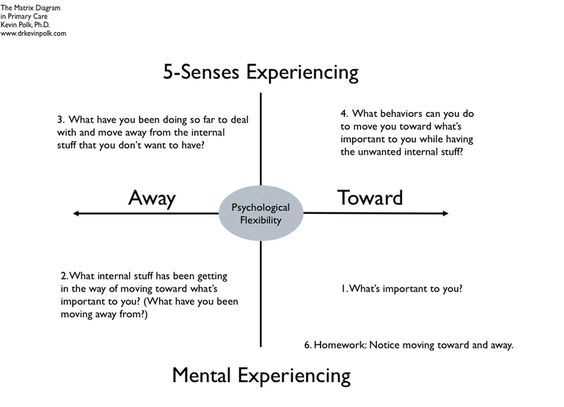
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on helping individuals develop psychological flexibility and live a more meaningful life. It is rooted in the belief that suffering is a natural part of the human experience and that trying to avoid or control unwanted thoughts, emotions, and sensations often leads to more pain and suffering.
Unlike traditional forms of therapy that aim to eliminate or reduce symptoms, ACT teaches individuals how to accept and be present with their thoughts and feelings, while also taking committed action toward their values and goals. The goal of ACT is not to get rid of difficult thoughts and emotions, but rather to learn how to respond to them in a way that is more in line with one’s values and leads to greater psychological well-being.
One of the key principles of ACT is mindfulness, which involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment. By practicing mindfulness, individuals can develop a greater awareness of their thoughts and feelings, and learn how to relate to them in a more flexible and compassionate way.
Another important component of ACT is acceptance, which involves embracing and making room for difficult thoughts and emotions, rather than trying to avoid or control them. When individuals are able to accept their experiences, they are less likely to get caught up in a struggle against their own thoughts and feelings, and can instead focus on taking action toward their values.
Commitment is the final piece of the puzzle in ACT. Commitment involves identifying one’s values and taking committed action toward them, even when faced with difficult thoughts or emotions. By living in alignment with one’s values, individuals can find greater meaning and fulfillment in their lives, even in the presence of pain and discomfort.
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): A Comprehensive Guide
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is a psychological approach that emphasizes the acceptance of one’s thoughts and feelings while committing to actions that align with one’s values. Developed in the 1980s by psychologist Steven C. Hayes, ACT is a form of cognitive behavioral therapy that has gained popularity in recent years.
Core Concepts of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
ACT is based on the following core concepts:
- Acceptance: Instead of trying to suppress or control unpleasant thoughts and feelings, ACT encourages individuals to acknowledge and accept them as a natural part of being human. This allows individuals to let go of the struggle and create space for positive change.
- Cognitive Defusion: ACT helps individuals recognize that they are not their thoughts. Through cognitive defusion techniques, such as observing thoughts as passing mental events, individuals can distance themselves from unhelpful thoughts and gain perspective.
- Values: ACT emphasizes the identification of personal values and taking committed action based on those values. By clarifying what is important to them, individuals can make choices that align with their values and lead to a more fulfilling life.
- Committed Action: ACT encourages individuals to take effective action towards their goals and values, even in the presence of challenging thoughts and emotions. This involves setting actionable steps and persisting through difficulties.
Components of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
ACT incorporates several components to help individuals develop psychological flexibility:
- Mindfulness: Mindfulness is a key component of ACT, as it helps individuals become aware of their thoughts, emotions, and bodily sensations without judgment. By practicing mindfulness, individuals can increase their ability to observe and accept their internal experiences.
- Experiential Exercises: ACT includes various experiential exercises, such as metaphors, visualization, and role plays, to help individuals explore their thoughts and emotions in a safe and supportive environment. These exercises aim to increase psychological flexibility and promote self-awareness.
- Values Assessment: ACT involves a values assessment process, where individuals identify their most important values in different areas of life, such as relationships, career, health, and personal growth. This assessment serves as a foundation for setting goals and making choices aligned with one’s values.
- Behavioral Activation: ACT emphasizes taking action and engaging in meaningful activities that align with one’s values. This involves setting specific goals and breaking them down into actionable steps to promote behavior change and increased life satisfaction.
Applications of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
ACT has been found to be effective in treating a wide range of psychological and emotional difficulties, including:
- Anxiety disorders
- Depression
- Substance abuse
- Chronic pain
- Eating disorders
- Stress management
- Workplace issues
Conclusion
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is a comprehensive approach that combines mindfulness, acceptance, cognitive defusion, values clarification, and committed action to promote psychological flexibility and well-being. By accepting and embracing their thoughts and feelings, individuals can make choices and take actions that lead to a more fulfilling and meaningful life.
Understanding Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on helping individuals develop psychological flexibility and live a meaningful life. It is based on the idea that suffering is a normal part of the human experience and that attempts to avoid or control painful thoughts and emotions can actually create more suffering.
In ACT, individuals are encouraged to accept their thoughts and feelings rather than trying to get rid of them. This involves developing an attitude of open curiosity and non-judgment toward internal experiences. By practicing acceptance, individuals can learn to coexist with difficult thoughts and emotions without being controlled by them.
ACT also emphasizes the importance of committing to actions that are in line with one’s values and larger goals. This commitment to action is based on the understanding that meaningful life experiences and fulfillment are achieved through taking steps toward personal values, even in the presence of discomfort or difficulty.
The therapy process typically involves several core processes and techniques, including:
- Defusion: Helping individuals become “unstuck” from their thoughts by recognizing them as mental events rather than objective truths.
- Acceptance: Encouraging individuals to experience their thoughts, feelings, and sensations fully and without trying to change or avoid them.
- Contact with the present moment: Focusing attention on the present moment and engaging fully in what is happening here and now.
- The observing self: Cultivating a sense of self-awareness and detachment from one’s thoughts and emotions.
ACT is also known for using various metaphorical and experiential exercises to help individuals understand and practice these processes. These exercises may involve mindfulness practices, role-playing, guided imagery, and other experiential techniques.
By learning and practicing the core processes and techniques of ACT, individuals can develop greater psychological flexibility, improve their ability to handle difficult thoughts and emotions, and live a more fulfilling and meaningful life.
Key Principles of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is a form of cognitive-behavioral therapy focused on mindfulness, acceptance, and commitment to living a meaningful life. Here are the key principles of ACT:
- Acceptance: ACT emphasizes the importance of accepting all thoughts and feelings, including those that are difficult or uncomfortable. The goal is not to change or eliminate these thoughts and feelings, but to accept them as they are.
- Defusion: Defusion refers to the process of distancing oneself from problematic thoughts and beliefs. Instead of automatically believing or reacting to these thoughts, individuals are encouraged to observe them with mindfulness and create some space between themselves and their thoughts.
- Mindfulness: Mindfulness involves being fully present and aware of the current moment, without judgment or attachment. By practicing mindfulness, individuals can observe their thoughts and feelings without getting caught up in them or trying to change them.
- Self-as-context: ACT recognizes that individuals have a larger sense of self that is separate from their thoughts and feelings. This “observer self” or “self-as-context” remains constant even as thoughts and emotions come and go.
- Values: ACT encourages individuals to clarify their values and what is truly important to them. By aligning their actions with their values, individuals can live a more meaningful and fulfilling life.
- Committed Action: The final principle of ACT is committed action, which involves taking steps towards living a valued and meaningful life. This may involve setting goals, making plans, and taking consistent action even in the face of difficulties or setbacks.
In summary, Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is based on several key principles including acceptance, defusion, mindfulness, self-as-context, values, and committed action. By practicing these principles, individuals can develop psychological flexibility and live a more meaningful life.
The Role of Acceptance in Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
Acceptance plays a crucial role in Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) as one of its key components. ACT is a form of psychotherapy that aims to help individuals develop psychological flexibility and engage in valued actions. It emphasizes the importance of accepting negative thoughts, feelings, and experiences rather than trying to eliminate or change them.
Understanding Acceptance
In the context of ACT, acceptance refers to the willingness to experience and fully engage with the present moment, even if it is uncomfortable or distressing. It involves acknowledging and allowing all thoughts and feelings to arise naturally without judgment or attempts to control them.
Acceptance is different from resignation or passivity. It does not mean giving up or tolerating suffering indefinitely. Instead, it means acknowledging the reality of the situation and making a conscious choice to stop struggling against it. By accepting the present moment, individuals can focus their energy on taking meaningful action and living in alignment with their values, rather than getting caught up in futile attempts to avoid or suppress painful experiences.
The Benefits of Acceptance
Practicing acceptance in ACT offers several benefits:
- Reduced psychological distress: Accepting negative thoughts and emotions can help individuals reduce their psychological distress and prevent the amplification of negative emotions through avoidance or rumination.
- Increased emotional resilience: By accepting all emotions, even the unpleasant ones, individuals can develop greater emotional resilience and flexibility. They become less likely to be overwhelmed by difficult emotions and better equipped to respond effectively to challenging situations.
- Improved self-awareness: Acceptance allows individuals to observe their thoughts and emotions without judgment, leading to greater self-awareness and insight into their patterns of thinking and behavior.
- Enhanced ability to focus on what matters: Acceptance helps individuals redirect their attention away from unhelpful thoughts and emotions and focus on taking valued action. It enables them to live in accordance with their values and pursue meaningful goals.
Cultivating Acceptance in ACT
ACT provides various techniques and exercises to help individuals cultivate acceptance:
- Mindfulness practices: Mindfulness exercises, such as meditation and body scans, are central to ACT. They help individuals develop present-moment awareness and non-judgmental acceptance of their thoughts, emotions, and bodily sensations.
- Defusion techniques: Defusion techniques aim to help individuals become less fused with their thoughts and learn to observe them more objectively. These techniques involve creating distance from thoughts and recognizing them as simply mental events rather than absolute truths.
- Values clarification: ACT emphasizes the importance of clarifying one’s values and using them as a guide for decision-making and action. By identifying and aligning actions with their values, individuals can develop a sense of purpose and fulfillment.
- Committed action: Acceptance is not the endpoint in ACT but a means to take committed action. Individuals are encouraged to set meaningful goals based on their values and commit to taking small steps towards them, even in the presence of discomfort or difficult emotions.
In summary
Acceptance is a fundamental aspect of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT). By practicing acceptance, individuals can learn to acknowledge and allow their thoughts and feelings without judgment or resistance. This acceptance enables them to focus on living a meaningful and valued life, rather than being stuck in unhelpful patterns of avoidance or control.
The Role of Commitment in Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
In Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), commitment plays a crucial role in helping individuals live a more meaningful and satisfying life. It is a key component of the therapy and is often referred to as the “C” in ACT.
Commitment in ACT refers to the willingness of individuals to take action and make choices that align with their values and goals, despite the presence of difficult thoughts, emotions, or sensations. It involves actively engaging in behaviors that are consistent with one’s values and moving towards a meaningful life, regardless of internal struggles.
When individuals are committed to their values, they are able to make choices that lead to a more fulfilled life, rather than being controlled by their thoughts, emotions, or past experiences. It allows individuals to focus on what truly matters to them and take steps towards creating a life that is in line with their values.
Commitment in ACT is not about forcing oneself to do something or pushing through discomfort. It is about making choices based on one’s values and taking action in a way that is compassionate and self-caring. It involves acknowledging and accepting the difficulties that may arise along the way, while still moving forward towards a meaningful life.
In ACT, commitment is often cultivated through the use of values clarification exercises, where individuals explore what is truly important to them and what they want their life to stand for. This helps individuals establish a clearer understanding of their values and serves as a guide for making committed choices.
Overall, commitment is a fundamental aspect of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy. It empowers individuals to live a life that is aligned with their values and goals, even in the face of challenges and discomfort. By making committed choices, individuals can create a more meaningful and fulfilling life.
Techniques Used in Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) utilizes a variety of techniques to help individuals develop psychological flexibility and overcome difficulties. These techniques are designed to help clients accept their thoughts and emotions, commit to their values, and take action towards creating a meaningful life.
Here are some key techniques used in ACT:
- Mindfulness: Mindfulness is a fundamental component of ACT. It involves paying attention to the present moment with openness, curiosity, and without judgment. Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation and mindful breathing, help individuals observe their thoughts and emotions without getting caught up in them.
- Defusion: Defusion techniques aim to help individuals create distance from their thoughts and see them as separate from who they are. By recognizing that thoughts are simply mental events and not necessarily facts, individuals can reduce their impact and influence on their behavior.
- Acceptance: Acceptance involves allowing unpleasant thoughts, emotions, and sensations to come and go without struggling or trying to avoid them. This technique helps individuals build a willingness to experience difficult emotions and develop psychological flexibility.
- Values clarification: Values clarification is an important part of ACT, as it helps individuals identify what truly matters to them in life. By clarifying and committing to their values, individuals can make choices and take actions that align with their long-term goals and aspirations.
- Committed action: Committed action refers to taking concrete steps towards living a meaningful life based on one’s values. This can involve setting specific goals, making behavior changes, and persisting in the face of obstacles. ACT encourages individuals to engage in actions that are consistent with their values, even when discomfort or fear arises.
- Self-as-context: Self-as-context is a technique used to help individuals differentiate themselves from their thoughts and emotions. By recognizing that they are the observer or container of their experiences, individuals can cultivate a sense of self that is more stable and unchanging, even in the presence of difficult thoughts and emotions.
These techniques are integrated into ACT therapy sessions through a collaborative and experiential approach. The therapist helps the individual explore their thoughts, emotions, and values while providing support and guidance in applying these techniques to their daily lives.
By practicing and incorporating these techniques, individuals can develop greater psychological flexibility and lead a more fulfilling and meaningful life.
Applications of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) has been found to be effective in treating a wide range of psychological issues and improving overall mental well-being. Some of the key applications of ACT include:
- Anxiety disorders: ACT has been shown to be effective in helping individuals manage and reduce symptoms of anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and panic disorder. By focusing on acceptance of anxious thoughts and feelings, and committing to valued actions, ACT helps individuals develop psychological flexibility and reduce the impact of anxiety on their lives.
- Depression: ACT has also been found to be helpful in treating depression. By teaching individuals to accept their negative thoughts and feelings without judgment, and to commit to actions that align with their values, ACT helps individuals build greater psychological resilience and improve their overall mood and well-being.
- Chronic pain: ACT has been shown to be effective in managing chronic pain conditions. By teaching individuals to accept their pain without struggling against it, and to take steps towards engaging in meaningful activities despite the pain, ACT helps individuals reduce their suffering and improve their quality of life.
- Substance abuse: ACT has been used successfully in the treatment of substance abuse disorders. By helping individuals develop acceptance and mindfulness skills, and by encouraging them to commit to a life that is in line with their values and goals, ACT supports individuals in reducing their dependence on substances and building a life that is fulfilling and meaningful.
- Workplace stress: ACT interventions have shown promise in reducing workplace stress and improving job satisfaction. By helping individuals accept the stressors they encounter at work and commit to actions that align with their values, ACT promotes psychological flexibility and resilience in the face of workplace challenges.
- Relationship problems: ACT can also be applied to improving relationships. By teaching individuals to accept their own and their partner’s imperfections, and to commit to actions that foster intimacy and connection, ACT helps couples develop healthier patterns of communication and resolve conflicts in a more effective and compassionate manner.
These are just a few examples of the many applications of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy. ACT’s focus on acceptance, mindfulness, and values-based action makes it a versatile approach that can be tailored to address a wide range of psychological and emotional challenges.
Benefits of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) offers a range of benefits for individuals struggling with various mental health concerns. Here are some of the key benefits of ACT:
- Increased Psychological Flexibility: ACT helps individuals develop psychological flexibility, which allows them to adapt to difficult situations and handle emotional challenges effectively.
- Enhanced Emotional Well-being: Through ACT, individuals learn to accept and make space for uncomfortable emotions, allowing them to experience greater emotional well-being and resilience.
- Reduced Psychological Distress: ACT techniques, such as mindfulness and acceptance, help individuals reduce psychological distress, such as anxiety and depression.
- Improved Relationships: By focusing on developing values-based actions and effective communication, ACT can help individuals improve their relationships and enhance their social connections.
- Increased Self-awareness: ACT promotes self-awareness by helping individuals observe their thoughts, emotions, and sensations non-judgmentally, leading to a deeper understanding of themselves.
- Effective for Various Mental Health Concerns: ACT has been found to be beneficial for a wide range of mental health concerns, including anxiety disorders, depression, substance abuse, eating disorders, and chronic pain.
- Long-lasting Results: ACT focuses on helping individuals develop skills and strategies that can be utilized throughout their lives, ensuring long-lasting effects even after therapy has ended.
Overall, Acceptance and Commitment Therapy offers individuals a unique approach to managing their mental health concerns by promoting acceptance, mindfulness, and values-based actions. With its focus on psychological flexibility and personal growth, ACT can help individuals lead more fulfilling and meaningful lives.
Finding an Acceptance and Commitment Therapy Practitioner
If you are interested in trying Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) and want to work with a practitioner, you have several options for finding a qualified therapist.
1. Ask for recommendations: Start by asking your healthcare provider, such as your primary care physician, psychiatrist, or psychologist, if they know any ACT practitioners they can recommend. They may have connections or be able to provide you with a list of therapists in your area who specialize in this approach.
2. Search online directories: There are many online directories that list mental health professionals, including ACT practitioners. Websites like Psychology Today, GoodTherapy, and the Association for Contextual Behavioral Science (ACBS) have directories that allow you to search for practitioners based on location and specialty.
3. Contact local mental health organizations: Reach out to local mental health organizations, such as the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI), to inquire about ACT practitioners in your community. These organizations often maintain lists of therapists who specialize in various therapeutic approaches.
4. Seek referrals from support groups: If you are part of a support group for a specific mental health condition or issue, ask fellow members if they have worked with or know any ACT practitioners. They may be able to provide personal recommendations based on their own experiences.
5. Check with your insurance provider: If you have health insurance, contact your insurance provider to see if they cover ACT therapy and whether they have a list of in-network practitioners. This can help you narrow down your options and ensure that you can receive affordable treatment.
6. Consider online therapy platforms: Online therapy platforms, such as BetterHelp and Talkspace, offer access to a wide range of therapists who provide ACT treatment. These platforms often provide user reviews and ratings to help you choose the right practitioner for your needs.
7. Attend workshops or training events: Keep an eye out for workshops, seminars, or training events in your area that focus on ACT. Attending these events can give you the opportunity to learn more about the therapy approach and potentially connect with practitioners who can provide treatment.
8. Consult with local universities or research institutes: Universities or research institutes in your area may have psychology or mental health departments that offer ACT therapy or can recommend practitioners. Reach out to them for guidance and information on accessing this type of treatment.
Remember, finding the right therapist is crucial for the success of your therapy journey. Take the time to research and consider your options, and don’t hesitate to contact multiple practitioners to ask questions and find the best fit for your needs.
Questions and answers
What is Acceptance and Commitment Therapy?
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is a form of psychotherapy that helps individuals develop psychological flexibility and build a rich and meaningful life.
How does ACT work?
ACT introduces mindfulness skills and values-driven actions to help individuals overcome harmful thoughts and emotions, and to create behavior patterns that align with their personal values.
What are the main principles of ACT?
The main principles of ACT include acceptance, cognitive defusion, being present, self-as-context, values, committed action, and contact with the present moment.
Is ACT effective for treating mental health conditions?
Yes, ACT has been found to be effective in treating a wide range of mental health conditions including anxiety disorders, depression, substance abuse, and chronic pain.
How is ACT different from other forms of therapy?
ACT differs from traditional therapies in that it focuses on acceptance of thoughts and feelings rather than trying to change or control them. It also emphasizes taking committed action towards living a meaningful life.
Can ACT be used in conjunction with other therapies or treatments?
Yes, ACT can be used as a standalone therapy or in combination with other therapies or treatments depending on individual needs and preferences.