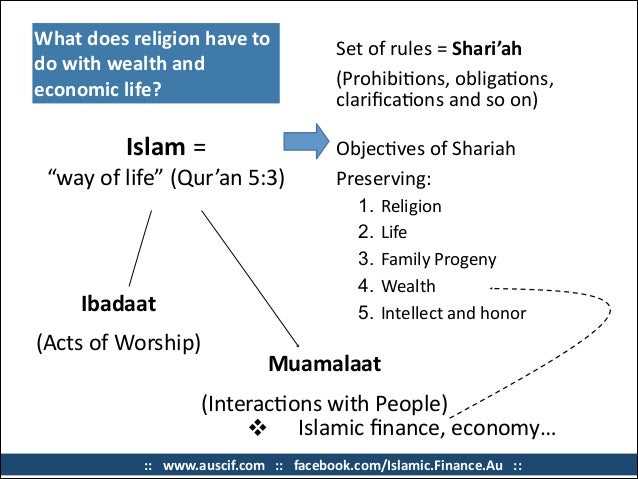
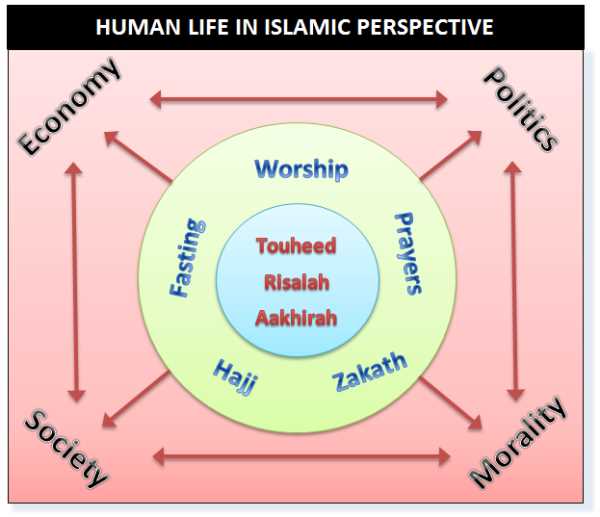
Islamic finance is a financial system that operates according to Islamic principles and laws, which are based on the teachings of the Quran and the Shariah. It is a system that is rooted in ethics, fairness, and social justice, and it aims to provide financial services that are in line with Islamic beliefs and values.
One of the key concepts in Islamic finance is the prohibition of Riba, or interest. In Islamic finance, money is not considered a commodity that can generate profit on its own, but rather a medium of exchange. Therefore, the charging or payment of interest is seen as exploitative and unjust, as it creates a power imbalance between the lender and the borrower. Instead of interest, Islamic finance uses a concept called profit-sharing, where both the lender and the borrower share in the risk and the returns of a project or an investment.
Another important concept in Islamic finance is the prohibition of Gharar, or uncertainty. Islamic finance promotes transparency and clarity in financial transactions, and prohibits any form of speculation or gambling. Contracts in Islamic finance must be based on real assets or services, and should not involve any element of uncertainty or excessive risk.
Islamic finance also places a strong emphasis on ethical investments and socially responsible finance. Investments in industries such as gambling, alcohol, pork, and weapons are strictly prohibited, as they are deemed harmful to society. Instead, Islamic finance encourages investments in sectors that promote social welfare, such as healthcare, education, and renewable energy.
In conclusion, Islamic finance is a unique financial system that operates according to Islamic principles and values. It is based on the concepts of fairness, transparency, and social responsibility, and aims to provide ethical and socially beneficial financial services. By understanding the basics of Islamic finance, individuals and institutions can contribute to building a more inclusive and sustainable financial system.
The Concept of Islamic Finance
Islamic finance is a system of financial principles rooted in Islamic law (Shariah) that governs the economic and financial activities of Muslims. It is based on the principles of justice, fairness, and ethical conduct, and seeks to create an equitable and socially responsible financial system.
One of the key principles of Islamic finance is the prohibition of interest, or usury (riba), which is seen as exploitative and harmful. Instead, Islamic finance promotes profit-sharing and risk-sharing arrangements, where the lender and borrower share the risks and rewards of the investment.
Islamic finance also prohibits investments in businesses that are considered to be haram (forbidden) according to Islamic principles. This includes industries such as alcohol, gambling, pork, and usury. Islamic finance focuses on ethical investments that are socially responsible and have a positive impact on society.
In addition to these principles, Islamic finance also emphasizes the concept of fairness and justice in financial transactions. Contracts and agreements in Islamic finance must be transparent and mutually beneficial, with both parties fully informed and consenting. It also encourages responsible lending and borrowing practices, and discourages excessive speculation and excessive risk-taking.
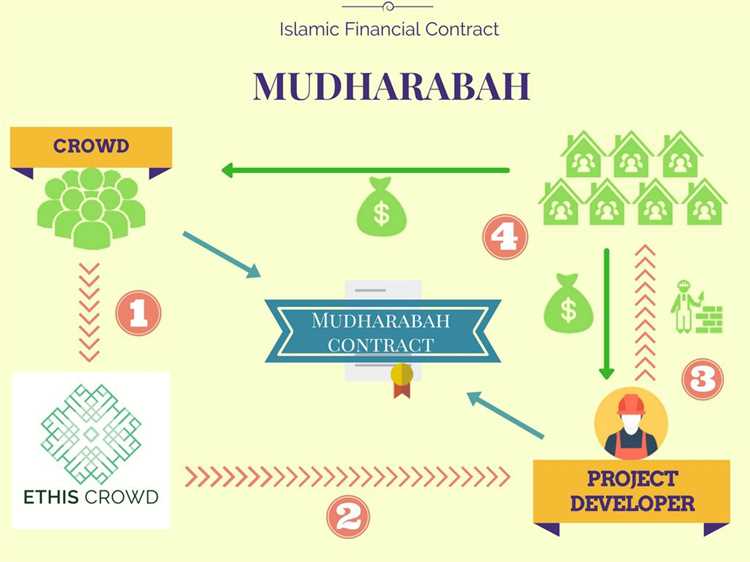
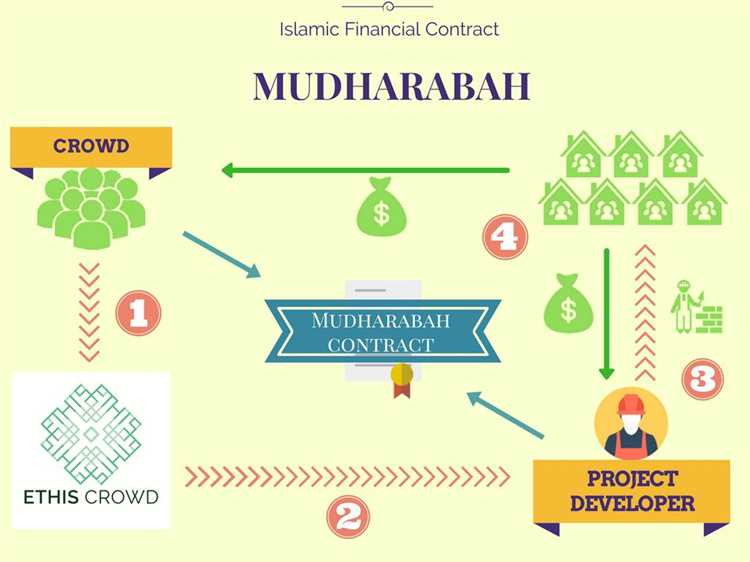
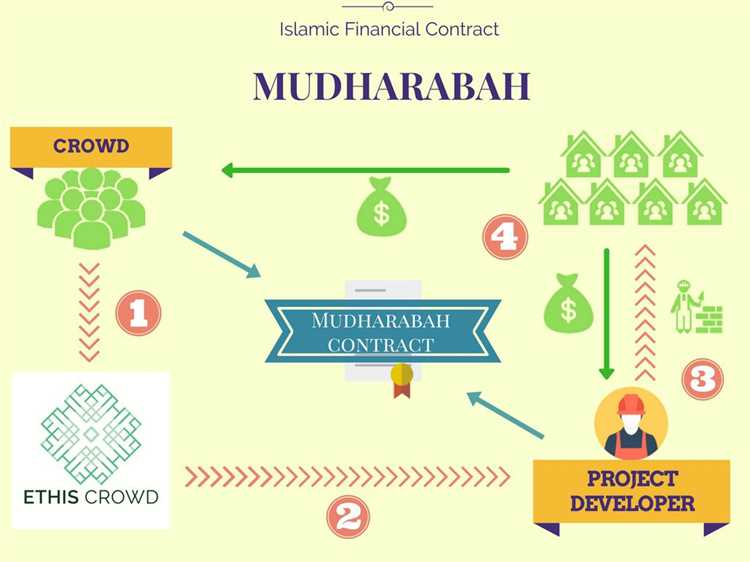
In order to meet the requirements of Shariah, Islamic finance uses a variety of financial instruments and structures that comply with the principles of Islamic law. These include profit-sharing agreements (mudarabah), joint ventures (musharakah), leasing contracts (ijara), and Islamic bonds (sukuk). These financial instruments are designed to provide financing and investment opportunities in a way that aligns with Islamic principles.
Islamic finance has experienced significant growth in recent years, with Islamic banks and financial institutions operating in various countries around the world. It offers an alternative financial system that is based on ethical principles and addresses concerns about the fairness and stability of conventional finance. By promoting transparency, fairness, and responsibility, Islamic finance aims to create a more inclusive and sustainable financial system.
Principles of Islamic Finance
Islamic finance is guided by several key principles that differentiate it from conventional finance. These principles are rooted in Islamic law, or Shariah, and are designed to promote ethical and fair financial practices. Here are some of the main principles of Islamic finance:
- Prohibition of interest (Riba): Islamic finance prohibits the payment or receipt of interest, as it is seen as exploitative and unfair. Instead, profit and loss sharing arrangements are used in Islamic finance transactions.
- Prohibition of uncertainty (Gharar): Islamic finance discourages transactions that involve excessive uncertainty or ambiguity. Contracts must have clear terms and conditions to avoid any ambiguity or deception.
- Prohibition of gambling (Maysir): Islamic finance prohibits any form of gambling or speculative activities. Transactions should be based on productive economic activities and not rely on chance or speculation.
- Prohibition of financing forbidden activities: Islamic finance avoids providing funds for activities that are prohibited in Islam, such as gambling, alcohol, pork, or any other unethical or illegal activities.
Islamic finance also emphasizes the concept of fairness and social responsibility. It encourages economic development and aims to promote the well-being and prosperity of society as a whole. Additionally, Islamic finance promotes risk-sharing and encourages the sharing of profits and losses between the parties involved in a financial transaction.
Overall, these principles guide the operations of Islamic financial institutions and ensure that the financial system operates in a transparent and ethical manner. It provides an alternative approach to finance that aligns with Islamic values and promotes economic stability and social welfare.
The Prohibition of Interest (Riba)
In Islamic finance, the concept of interest is strictly prohibited. This concept, known as Riba, refers to the charging or receiving of any excess or additional amount on a loan or debt. Riba is considered exploitative and unjust, as it allows lenders to benefit unfairly at the expense of borrowers.
Islam promotes the idea of economic justice and fairness, and therefore, the prohibition of interest is a fundamental principle in Islamic finance. Instead, Islamic finance adopts profit-sharing and risk-sharing arrangements that are in line with the principles of Shariah (Islamic law).
There are two main types of Riba:
- Riba al-Fadl: This refers to the prohibition of excess in exchange. This type of Riba pertains to the exchange of commodities of the same type but in unequal quantities. For example, if someone sells 1kg of wheat for 2kg of wheat, the second quantity would be considered Riba al-Fadl.
- Riba al-Nasi’ah: This refers to the prohibition of excess in lending. This type of Riba is related to lending money or any other fungible item with the condition that the borrower would have to pay back more than the amount borrowed. Any additional amount charged as interest or as a condition of time is considered Riba al-Nasi’ah and is strictly prohibited.
To avoid Riba, Islamic finance has developed various alternative mechanisms such as profit-sharing contracts like Mudarabah (partnership), Musharakah (joint venture), and Ijarah (leasing). These contracts focus on sharing profits and losses between parties involved in a transaction.
Overall, the prohibition of interest (Riba) is a central tenet in Islamic finance, emphasizing the fair and equitable treatment of individuals and discouraging exploitative practices in financial transactions.
Key Islamic Financial Instruments
Islamic finance offers a range of financial instruments that comply with the principles of Shariah law. These instruments provide alternative ways for individuals and businesses to access funding, invest their money, and manage risk, all while adhering to Islamic principles. Some of the key Islamic financial instruments include:
- Murabaha: a cost-plus financing arrangement where a seller sells an asset to a buyer at an agreed-upon cost plus an agreed-upon profit margin. The buyer pays the cost plus profit over an agreed-upon period.
- Mudarabah: a profit-sharing partnership between two parties, where one party provides the capital (the investor) and the other party provides the expertise and management (the entrepreneur). Profits are shared based on agreed-upon ratios, while losses are borne by the investor.
- Wakala: a contract in which one party (the principal) appoints another party (the agent) to carry out a specific task or service on their behalf. The agent is compensated with a pre-agreed fee, while the principal retains ownership of the assets.
- Ijarah: a leasing contract where one party (the lessor) allows another party (the lessee) to use an asset for a specified period in exchange for regular payments. At the end of the lease term, the lessee may have the option to purchase the asset.
- Sukuk: Islamic bonds that represent ownership in a tangible asset or a pool of assets. The returns to investors are generated through the income generated by the underlying assets, making them a form of asset-backed securities.
These instruments are just a few examples of the wide range of financial products available in Islamic finance. Each instrument has its own unique structure and features that comply with Shariah principles, providing individuals and businesses with diverse options to meet their financial needs while adhering to their religious beliefs.
Islamic Banking and Financial Institutions
Islamic banking refers to the system of banking that operates in accordance with Islamic principles and laws, also known as Shariah. Islamic financial institutions include banks, investment firms, insurance companies, and other financial entities that provide services in line with Shariah guidelines.
Islamic banking has gained popularity in recent years due to its ethical and equitable nature. It follows a unique set of principles that prohibit certain activities considered unethical in Islam, such as charging interest (riba), engaging in speculative transactions (gharar), and investing in businesses that are considered haram (forbidden) such as alcohol, gambling, or pork-related businesses.
In Islamic banking, instead of receiving interest on loans, both parties enter into a partnership agreement where the bank shares the profit or loss with the customer. Islamic financial institutions also focus on ensuring that the financing provided is asset-backed and based on real economic activities, rather than speculative or interest-based transactions.
Islamic banking and financial institutions offer a range of products and services tailored to the needs of their customers while operating within the framework of Shariah. These include:
- Mudarabah: This refers to a partnership arrangement where one party provides the funds (capital provider) and the other party manages the funds (entrepreneur). The profit generated is shared according to an agreed ratio, while any loss is borne solely by the capital provider.
- Murabaha: This is a cost-plus financing arrangement where the bank purchases an asset on behalf of the customer and sells it to the customer at a higher price, allowing the customer to pay in installments.
- Ijarah: This involves leasing an asset to a customer for a specified period in exchange for rental payments. At the end of the lease, the customer may have the option to purchase the asset.
- Sukuk: Also known as Islamic bonds, sukuk represents ownership in an underlying asset or investment project. Unlike conventional bonds that pay interest, sukuk holders receive a share in the profits generated by the asset or project.
Islamic banking and financial institutions have rapidly expanded in recent years, not only in Muslim-majority countries but also in non-Muslim majority countries. This growth can be attributed to the increasing demand for ethical financial services globally and the recognition of Islamic finance as a viable alternative to conventional banking.
In conclusion, Islamic banking and financial institutions operate in accordance with Shariah principles, offering a range of products and services that align with Islamic values. By adhering to ethical guidelines, Islamic banking aims to promote fairness, transparency, and shared risk between the institution and its customers.
The Role of Sharia Advisors
Sharia advisors play a crucial role in the functioning of Islamic financial institutions. They ensure that all financial activities and products comply with Islamic principles and are in accordance with Sharia law.
Sharia advisors are typically scholars with expertise in both Islamic jurisprudence (fiqh) and finance. They are responsible for providing guidance and making sure that financial transactions and contracts are structured in a way that avoids prohibited elements such as interest (riba), speculation (gharar), and uncertainty (maysir).
One of the key responsibilities of Sharia advisors is to evaluate and approve financial products and services offered by Islamic financial institutions. They thoroughly analyze the structure, terms, and conditions of these products to ensure they are compliant with Sharia principles. This includes examining the source and use of funds, reviewing the mechanisms used for profit calculation, and assessing the level of risk associated with the product.
Sharia advisors also play a role in the ongoing monitoring and supervision of Islamic financial institutions. They review the institution’s policies, procedures, and practices to ensure they are in line with Sharia requirements. They may participate in regular audits and inspections to ensure compliance and address any issues that may arise.
In addition to their oversight role, Sharia advisors are also involved in providing consultation and advice to Islamic financial institutions. They assist in the development of new products and services, ensuring that they comply with Sharia principles and meet the needs of the market. They also provide guidance on complex financial transactions, helping institutions navigate the intricacies of Islamic finance.
Overall, Sharia advisors play a critical role in upholding the integrity and authenticity of Islamic finance. Their expertise and guidance help ensure that Islamic financial institutions operate in a manner that aligns with Sharia principles, providing Muslims with ethical and compliant financial solutions.
Supervision and Regulation of Islamic Finance
Like conventional finance, Islamic finance also requires supervision and regulation to ensure compliance with sharia principles and to maintain the stability and integrity of the financial system. The supervision and regulation of Islamic finance are carried out by various regulatory bodies and institutions at both national and international levels.
At the national level, each country with Islamic financial institutions typically has its own regulatory framework for overseeing Islamic finance activities. These frameworks are usually based on the principles and guidelines provided by sharia boards and international standards such as the Accounting and Auditing Organization for Islamic Financial Institutions (AAOIFI) and the Islamic Financial Services Board (IFSB).
Regulatory bodies responsible for overseeing Islamic finance may have specific departments or divisions dedicated to the supervision of Islamic financial institutions. These departments or divisions are tasked with ensuring compliance with sharia principles, monitoring the financial health and stability of Islamic banks and other financial institutions, and enforcing regulations and guidelines.
In addition to national regulatory bodies, there are also international organizations that play a role in the supervision and regulation of Islamic finance. The International Islamic Financial Market (IIFM) and the International Islamic Liquidity Management Corporation (IILM) are examples of such organizations. They develop and promote standardized sharia-compliant financial products and market infrastructure to facilitate the growth and development of Islamic finance globally.
Supervision and regulation of Islamic finance also involve the establishment and operation of sharia boards. Sharia boards are independent bodies of Islamic scholars and experts who provide religious guidance and supervision to Islamic financial institutions. They ensure that the operations and products of Islamic banks and institutions comply with sharia principles. Sharia boards review and approve the contracts, transactions, and investment activities of Islamic financial institutions to certify their compliance with sharia rules.
In conclusion, the supervision and regulation of Islamic finance are essential for maintaining the integrity, stability, and compliance of the Islamic financial system. National regulatory bodies, international organizations, and sharia boards all play a crucial role in ensuring that Islamic financial institutions operate in accordance with sharia principles and adhere to regulatory standards.
Islamic Capital Markets
Islamic capital markets play a crucial role in Islamic finance by facilitating the trading of Sharia-compliant financial instruments and providing a platform for investors to raise capital and invest their funds in a halal manner.
These markets operate in accordance with the principles of Islamic law, or Sharia, which prohibits the charging or receiving of interest (known as riba) and prohibits investing in businesses that engage in prohibited activities such as gambling, alcohol, or pork products.
The key components of Islamic capital markets include:
- Sukuk: Also known as Islamic bonds, sukuk are financial instruments that comply with Sharia principles. Unlike conventional bonds that pay interest, sukuk represent ownership in a tangible asset or a specific project. Investors receive a share of the profits generated by the asset or project rather than interest.
- Equity Markets: Islamic equity markets allow investors to buy and sell shares of companies that comply with Sharia principles. These companies must generate profits from halal activities and avoid any engagement in prohibited industries. Sharia advisors ensure compliance with Islamic principles by conducting regular audits and screening processes.
- Funds and Investment Vehicles: Islamic capital markets also provide various funds and investment vehicles that allow investors to pool their resources and invest in diversified portfolios of Sharia-compliant assets. These funds may focus on specific industries, geographical areas, or investment strategies.
- Derivatives: Islamic capital markets offer Sharia-compliant derivatives that allow investors to hedge their positions and manage risks. These derivatives are structured to comply with Islamic principles and do not involve prohibited elements such as uncertainty (gharar) or gambling (maysir).
- Indices: Islamic capital markets have developed various indices that track the performance of Sharia-compliant companies. These indices provide benchmarks for Islamic investors and help them make informed investment decisions based on the performance of halal companies.
- Regulatory Framework: Islamic capital markets operate under a regulatory framework that ensures compliance with Islamic principles. Regulatory bodies and Sharia boards oversee the operations of these markets, ensuring that financial instruments and transactions adhere to Sharia guidelines.
Overall, Islamic capital markets provide a platform for investors to participate in financial activities that align with their religious beliefs. These markets have witnessed significant growth over the years, with countries such as Malaysia, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE emerging as major players in the Islamic finance industry.
Takaful: Islamic Insurance
Takaful is a form of Islamic insurance that is based on the principles of mutual cooperation and shared responsibility. It is an alternative to conventional insurance, which is not compliant with Islamic principles due to the involvement of interest, uncertainty, and gambling.
How Does Takaful Work?
In a takaful arrangement, participants join together to form a cooperative pool or fund. Each participant contributes a certain amount of money, known as a contribution or premium, into the pool. This pool is managed by a takaful operator, who acts as the custodian of the funds.
The Principles of Takaful:
- Mutual Cooperation: Participants agree to share risks and help each other in times of need.
- Shared Responsibility: Participants contribute to the pool, and each individual’s loss is covered by the contributions of the entire group.
- No Interest: Takaful does not involve any interest-based transactions or investments.
- No Uncertainty (Gharar): Takaful contracts are based on transparency and avoiding any ambiguity or uncertainty.
- No Gambling (Maysir): Takaful does not involve speculative or gambling-related activities.
The Takaful Operator’s Role:
The takaful operator is responsible for managing the takaful pool and ensuring compliance with Islamic principles. The operator collects contributions from participants, invests the funds in Shariah-compliant investments, and pays claims and benefits to participants when needed.
The Takaful Model:
Takaful can generally be categorized into two main models:
- Mudarabah Model: Under this model, the takaful operator acts as an agent or entrepreneur, and participants provide the capital. Any surplus generated from the takaful pool is shared between the participants and the operator based on a pre-determined profit-sharing ratio.
- Wakalah Model: In this model, the takaful operator acts as an agent or trustee, and participants bear all the investment risks. The operator charges a fee for managing the takaful pool and may share any surplus with the participants in the form of a bonus.
Benefits of Takaful:
- Compliance with Islamic Principles: Takaful provides a Shariah-compliant alternative to conventional insurance.
- Shared Risk and Responsibility: Participants contribute towards a common pool, ensuring that the burden of loss is shared.
- Profit-Sharing: In some models, participants may receive a share in the surplus generated by the takaful pool.
- Focus on Social Welfare: Takaful promotes the concept of mutual aid and solidarity among participants.
In conclusion, takaful is an Islamic insurance concept based on the principles of mutual cooperation and shared responsibility. It provides a Shariah-compliant alternative to conventional insurance, ensuring compliance with Islamic principles. By pooling resources and sharing risks, takaful promotes a sense of social welfare and financial security among participants.
The Importance of Ethical and Social Responsibility
One of the fundamental principles of Islamic finance is the emphasis on ethical and social responsibility. This principle is rooted in the belief that money should be used in a way that benefits individuals and society as a whole, and that financial transactions should not harm others or the environment.
By adhering to ethical and social responsibility principles, Islamic finance aims to promote fairness, justice, and equality in financial transactions. It prohibits practices such as charging interest (riba), speculation (gharar), and gambling (maysir), which are considered unethical and exploitative.
Instead, Islamic finance encourages investment in real assets and productive economic activities that generate value and benefit society. This can include financing projects in sectors such as renewable energy, healthcare, education, and affordable housing, among others.
Furthermore, Islamic finance promotes risk-sharing and the principle of shared prosperity. In Islamic banking, profits and losses are shared between the bank and its customers, creating a more equitable and fair system. This encourages responsible lending practices and discourages reckless behavior that can lead to financial crises.
In addition to promoting ethical behavior in financial transactions, Islamic finance also incorporates social responsibility principles. Islamic financial institutions are expected to consider the impact of their investments on society and the environment. This includes avoiding investments in sectors that are harmful or unethical, such as alcohol, tobacco, gambling, and weapons.
Islamic financial institutions also have a responsibility to contribute to the development and well-being of society. They are encouraged to allocate a portion of their profits to charitable causes, known as zakat or sadaqah. This helps to address social inequality, poverty, and other societal issues.
Overall, the importance of ethical and social responsibility in Islamic finance is a key factor that sets it apart from conventional finance. By promoting fairness, justice, and responsible behavior, Islamic finance aims to create a more sustainable and equitable financial system that benefits individuals, society, and the environment.
Islamic Finance and Economic Development
Islamic finance plays a significant role in promoting economic development in Muslim-majority countries and beyond. It offers an alternative financial system that is based on Islamic principles and values, which can lead to more inclusive and sustainable economic growth.
Here are some ways Islamic finance contributes to economic development:
- Equity-based financing: Islamic finance emphasizes equity participation rather than debt financing. This encourages entrepreneurs to share risks and rewards, promoting entrepreneurship and innovation. Equity-based financing also helps to address income inequality by providing opportunities for less privileged individuals to participate in economic activities.
- Ethical and socially responsible investing: Islamic finance promotes ethical and socially responsible investing by adhering to strict Shariah guidelines. This encourages investments in socially beneficial sectors such as healthcare, education, and renewable energy. By allocating resources towards these sectors, Islamic finance contributes to the overall development of society.
- Microfinance and poverty alleviation: Islamic microfinance institutions provide financial services to low-income individuals and micro-entrepreneurs who are excluded from the conventional banking system. Islamic microfinance follows the principles of fairness and compassion, helping to alleviate poverty and promote financial inclusion.
- Infrastructure financing: Islamic finance can facilitate infrastructure development by providing long-term financing solutions. Islamic project finance structures, such as the Istisna’a and Ijara, enable the financing of large-scale infrastructure projects. This helps to address the infrastructure gap in many developing countries, promoting economic growth and job creation.
Furthermore, Islamic finance promotes financial stability by discouraging excessive risk-taking and speculation. The prohibition of usury (interest) and Islamic principles of risk sharing help to ensure a more stable and resilient financial system.
In conclusion, Islamic finance contributes to economic development by promoting equity-based financing, ethical investing, microfinance for poverty alleviation, and infrastructure financing. By adhering to Islamic principles, this alternative financial system fosters economic growth that is sustainable, inclusive, and socially responsible.
The Global Growth of Islamic Finance
Islamic finance has experienced significant growth in recent years, both in Muslim-majority countries and in Muslim-minority countries around the world. This growth can be attributed to several factors, including increasing awareness of and demand for Islamic financial products, the expansion of Islamic banking and finance institutions, and the development of supportive regulatory frameworks.
One key driver of the global growth of Islamic finance is the increasing demand for Sharia-compliant financial products and services. Sharia, or Islamic law, prohibits the payment or receipt of interest (riba) and prohibits investments in businesses that are considered haram (forbidden) such as those involved in alcohol, gambling, or pork. Islamic finance offers alternative modes of financing that are compliant with Sharia principles, such as profit-sharing arrangements (Mudarabah), cost-plus financing (Murabaha), and leasing (Ijarah).
This demand for Sharia-compliant financial products has been fueled by the growing Muslim population and increasing religiosity among Muslims. According to estimates, the global Muslim population is projected to reach 2.2 billion by 2030, representing a significant consumer base for Islamic finance.
In addition to the increase in demand, the growth of Islamic finance has also been supported by the expansion of Islamic banking and finance institutions. These institutions, including Islamic banks, insurance companies (Takaful), and asset management firms, have been established to cater to the specific needs of Muslim consumers. They operate according to Sharia principles and offer a range of products and services that align with Islamic ethical and financial guidelines.
Furthermore, many countries have developed supportive regulatory frameworks to facilitate the growth of Islamic finance. These frameworks include the establishment of Islamic finance regulatory bodies, the introduction of tax incentives for Islamic financial institutions, and the issuance of Sharia-compliant financial instruments and sukuk (Islamic bonds).
The global growth of Islamic finance is not limited to Muslim-majority countries. Muslim-minority countries, such as the United Kingdom, the United States, and Singapore, have also witnessed an increase in the adoption and promotion of Islamic finance. This is driven by the recognition of the potential economic benefits of Islamic finance, as well as the desire to attract investment from Muslim countries.
In conclusion, the global growth of Islamic finance can be attributed to increasing demand for Sharia-compliant financial products, the expansion of Islamic banking and finance institutions, and the development of supportive regulatory frameworks. As Islamic finance continues to gain momentum, it is expected to play an increasingly important role in the global financial system.
Islamic Finance and Financial Inclusion
Financial inclusion refers to the provision of affordable financial products and services to individuals and communities who have traditionally been excluded from the mainstream financial system. Islamic finance, with its unique principles and mechanisms, plays a significant role in promoting financial inclusion in Muslim-majority countries and beyond.
One of the key principles of Islamic finance is the prohibition of interest (riba). Instead, Islamic finance promotes profit-sharing (mudarabah) and asset-based financing (murabahah). These principles make Islamic finance more accessible and inclusive, as they avoid the accumulation of debt and promote the sharing of risks and profits.
Islamic microfinance, a subset of Islamic finance, specifically focuses on providing financial services to low-income individuals and communities. This includes offering small loans, insurance products, and savings accounts that adhere to Islamic principles. Islamic microfinance institutions have emerged to cater to the financial needs of those who may not have access to traditional banking services.
Another way Islamic finance promotes financial inclusion is through the concept of zakat. Zakat is an obligatory charity that Muslims are required to pay, usually a percentage of their wealth or income, to support the less fortunate in society. Islamic financial institutions often collect zakat and distribute it to those in need. This helps alleviate poverty and contributes to the overall economic development of communities.
In addition, Islamic finance emphasizes ethical and responsible financing practices. This includes avoiding investments in activities deemed haram (forbidden) in Islam, such as gambling, alcohol, and tobacco. By promoting ethical financing, Islamic finance encourages economic activities that are socially responsible and sustainable, further contributing to financial inclusion.
Islamic finance has gained recognition for its potential to address the financial needs of underserved populations, both in Muslim-majority countries and globally. Governments, international organizations, and development agencies are increasingly exploring and supporting Islamic finance as a means to promote financial inclusion and poverty reduction.
In conclusion, Islamic finance has the potential to support financial inclusion by providing accessible and ethical financial products and services. Through its principles, mechanisms, and focus on responsible financing, Islamic finance helps bridge the gap between excluded individuals and the mainstream financial system, promoting economic empowerment and poverty reduction.
Challenges and Opportunities in Islamic Finance
Challenges
- Regulatory Challenges: Islamic finance faces regulatory challenges due to its unique nature and principles. Ensuring compliance with Shariah laws while aligning with international financial regulations can be complex and requires constant monitoring and adaptation.
- Lack of Awareness: One of the challenges faced by Islamic finance is the lack of awareness among potential customers. Many people are unaware of the principles and benefits of Islamic finance, which can hinder its growth and adoption.
- Standardization: The lack of standardized practices and products in Islamic finance creates challenges in terms of consistency and comparability. Standardization efforts are ongoing, but there is still a need for further harmonization of regulations and practices.
- Talent and Expertise: Islamic finance requires specialized knowledge and expertise in both Islamic jurisprudence and financial principles. The shortage of skilled professionals in this field can pose challenges in developing and managing Islamic financial products and services.
- Market Fragmentation: Islamic finance operates in a fragmented market, with different regulatory frameworks and market practices across various countries. This fragmentation can hinder the growth and efficiency of the industry and pose challenges for cross-border transactions.
Opportunities
- Market Potential: Islamic finance offers significant potential in Muslim-majority countries and beyond. With a population of over 1.8 billion Muslims worldwide, there is a large untapped market for Islamic financial products and services.
- Ethical Investments: Islamic finance promotes ethical and socially responsible investing by avoiding sectors such as alcohol, gambling, and interest-based activities. This provides an opportunity for investors looking for ethical investment options.
- Inclusive Finance: Islamic finance emphasizes financial inclusion and aims to provide access to financial services for all segments of society. This aligns with the goals of promoting financial inclusion and reducing poverty, making it an attractive option for governments and policymakers.
- Infrastructure Development: Islamic finance can play a vital role in financing infrastructure projects, including renewable energy, transportation, and housing. The large-scale financing needs for infrastructure development present significant opportunities for Islamic finance institutions.
- Innovation and Fintech: The emergence of fintech in the Islamic finance industry presents opportunities for innovation and the development of new digital solutions. Fintech can help address some of the challenges faced by Islamic finance, such as standardization and access to Islamic financial products.
In conclusion, while Islamic finance faces challenges in terms of regulatory compliance, lack of awareness, and standardization, it also presents significant opportunities in terms of market potential, ethical investments, inclusive finance, infrastructure development, and fintech innovation.
Islamic Financial Education and Awareness
Islamic finance is a rapidly growing industry that is gaining recognition worldwide. To ensure the success and growth of this sector, education and awareness play a vital role.
1. Education:
Proper education is crucial for individuals, professionals, and organizations involved in Islamic finance. It helps them understand the principles and concepts of Islamic finance and equips them with the necessary skills to work in this field. Islamic finance education can be imparted through various channels, including:
- Universities and educational institutions offering specialized courses and degrees in Islamic finance.
- Certification programs that provide in-depth knowledge of Islamic finance principles and practices.
- Seminars, workshops, and conferences conducted by industry experts and scholars.
2. Public Awareness:
Creating awareness among the general public about Islamic finance is essential to its growth and acceptance. This can be done through:
- Public campaigns, advertisements, and media promotions explaining the benefits and principles of Islamic finance.
- Engaging with religious institutions and scholars to highlight the Islamic perspective on finance and economics.
- Publishing articles, books, and online resources to provide easy access to information about Islamic finance.
3. Collaboration:
Collaboration between Islamic financial institutions, regulators, and educational institutions is crucial for the development of Islamic finance education. This collaboration can include:
- Sharing resources and expertise between institutions to enhance the quality of education and research in Islamic finance.
- Developing standardized curriculum and certification programs that meet international standards.
- Organizing joint conferences, seminars, and workshops to facilitate knowledge exchange and networking opportunities.
4. Research and Innovation:
Continuous research and innovation are key to the growth and development of Islamic finance. Research institutes and universities should focus on conducting research that addresses the challenges and opportunities in Islamic finance. This will contribute to the innovation of new products and services.
| Benefits of Islamic Financial Education and Awareness: |
|---|
| The benefits of Islamic financial education and awareness are manifold: |
| 1. Enhanced Financial Literacy: Islamic financial education improves individuals’ understanding of financial concepts and helps them make informed financial decisions. |
| 2. Increased Trust and Confidence: Public awareness of Islamic finance builds trust and confidence among potential customers and investors. |
| 3. Professional Development: Education in Islamic finance provides professionals with the necessary skills and knowledge for successful careers in the industry. |
| 4. Economic Growth: A well-educated workforce in Islamic finance contributes to the growth and development of the economy. |
In conclusion, Islamic financial education and awareness are crucial for the growth and success of the industry. It is important to invest in education, create public awareness, encourage collaboration, and promote research to ensure the continued development of Islamic finance.
Islamic Finance and Sustainable Development Goals
Islamic finance can play a crucial role in achieving sustainable development goals (SDGs) by promoting ethical business practices, ensuring financial inclusion, and supporting environmentally friendly investments. The principles of Islamic finance align with many of the goals set forth by the United Nations in the SDGs.
1. Poverty alleviation: Islamic finance promotes financial inclusion by providing access to financial services for people who are traditionally excluded from the conventional banking system. This can help alleviate poverty by enabling individuals and businesses to access capital and engage in economic activities.
2. Economic growth: Islamic finance encourages equitable distribution of wealth and promotes economic growth through ethical and responsible investment practices. By adhering to principles of fairness and justice, Islamic financial institutions contribute to a more stable and sustainable economic system.
3. Gender equality: Islamic finance promotes gender equality by encouraging equal access to financial services and supporting initiatives that empower women economically. Islamic financial institutions often offer products and services tailored to women’s needs, such as microfinance programs that help women start and grow their businesses.
4. Climate action: Islamic finance encourages environmentally friendly investments and discourages activities that harm the environment. Sharia-compliant financial products and services prioritize sustainability and socially responsible investments, which can contribute to climate action and address environmental challenges.
5. Responsible consumption and production: Islamic finance promotes responsible consumption and production by encouraging ethical business practices that prioritize social and environmental considerations. Islamic financial institutions often provide funding for projects and businesses that adhere to sustainable practices.
6. Quality education: Islamic finance can support quality education by providing funding for educational institutions and initiatives. Many Islamic financial institutions offer education financing options that comply with Sharia principles, allowing individuals to pursue higher education without compromising their religious beliefs.
7. Peace, justice, and strong institutions: Islamic finance promotes principles of justice and fairness, which are fundamental to achieving peace and establishing strong institutions. By emphasizing ethical behavior and transparent financial practices, Islamic financial institutions contribute to the development of a just and stable society.
In conclusion, Islamic finance can play a significant role in achieving the sustainable development goals by promoting inclusive and sustainable economic growth, addressing social and environmental challenges, and fostering ethical business practices. By aligning with the principles of Islamic finance, individuals and institutions can contribute to a more sustainable and equitable future.
The Role of Islamic Finance in Poverty Alleviation
The principles of Islamic finance have the potential to play a significant role in poverty alleviation. Unlike conventional finance, which focuses solely on profit-making, Islamic finance considers the social and ethical aspects of financial transactions.
Zakat: One of the key pillars of Islamic finance is zakat. This is a mandatory charitable contribution that Muslims are obliged to give, typically a percentage of their wealth. Zakat is intended to help those in need and alleviate poverty. The funds collected through zakat are distributed to the poor, needy, orphans, and other particularly vulnerable groups in the society.
Interest-Free Financing: Islamic finance operates on the principle of interest-free financing, as charging interest (or riba) is prohibited in Islam. This approach allows individuals who may not have access to conventional financial services or credit to obtain financing without incurring interest charges. By providing interest-free financing, Islamic financial institutions enable low-income individuals to invest, start businesses, and improve their livelihoods.
Microfinance: Islamic finance also promotes the concept of microfinance, which involves providing small loans to low-income individuals to start or expand small businesses. Microfinance has proven to be an effective tool in poverty alleviation worldwide, as it empowers individuals to become self-sufficient and create employment opportunities for themselves and others. Islamic microfinance institutions adhere to the principles of Islamic finance, providing interest-free loans and promoting social justice.
Equity-Based Financing: Islamic finance emphasizes equity-based financing, such as profit-sharing partnerships (mudarabah) and joint ventures (musharakah). These financing models encourage risk-sharing and ensure that the burdens and benefits of business ventures are shared fairly among all parties involved. By promoting equity-based financing, Islamic finance helps to address the wealth inequality that often perpetuates poverty.
Ethical Investments: Islamic finance encourages ethical investments, avoiding industries that are considered socially or morally harmful, such as alcohol, gambling, or weapons. Instead, Islamic finance promotes investments in sectors that contribute to the well-being of society, such as healthcare, education, renewable energy, and affordable housing. By directing investments towards socially responsible sectors, Islamic finance contributes to poverty alleviation and sustainable development.
In conclusion, Islamic finance has a significant role to play in poverty alleviation. Through zakat, interest-free financing, microfinance, equity-based financing, and ethical investments, Islamic finance promotes social justice, economic empowerment, and sustainable development, ultimately helping to uplift individuals and communities out of poverty.
Islamic Finance and Environmental Sustainability
Islamic finance not only focuses on financial transactions that adhere to Islamic principles, but also promotes values of environmental sustainability. The principles of Islamic finance align with the concept of sustainable development, which seeks to meet the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Responsibility for the Environment
In Islamic finance, there is an emphasis on responsible and ethical behavior, including the responsible use and preservation of resources. This concept extends to the environment, with Islamic finance institutions encouraging investments in projects that have positive environmental impacts.
Prohibition of Harmful Activities
Islamic finance prohibits investments in activities that are considered harmful or detrimental to the environment. This includes activities such as gambling, alcohol, tobacco, and industries involved in pollution or destruction of natural resources.
Financing Sustainable Projects
Islamic finance institutions strive to promote sustainability by financing projects that have a positive impact on the environment. These projects can include renewable energy initiatives, green buildings, and environmentally friendly technologies.
Socially Responsible Investments
Islamic finance also promotes socially responsible investments, where investors consider not only financial returns but also the social and environmental impact of their investments. This encourages individuals and institutions to make more sustainable choices when investing their funds.
Partnerships for Sustainable Development
Islamic finance institutions often collaborate with other organizations and stakeholders to promote sustainable development. This can include partnering with government agencies, non-governmental organizations, and other financial institutions to support projects and initiatives that align with environmental sustainability goals.
Educating the Community
Islamic finance institutions also play a role in educating the community about the importance of environmental sustainability. They raise awareness about the impact of individual choices on the environment and promote responsible behavior.
In conclusion, Islamic finance not only provides a financial framework that adheres to Islamic principles but also promotes environmental sustainability. By embracing principles of responsible behavior, financing sustainable projects, and educating the community, Islamic finance contributes to a more sustainable future for all.
The Future of Islamic Finance
The future of Islamic finance looks promising, with continued growth and increasing recognition on a global scale. As the demand for Islamic financial products and services continues to rise, several trends and developments are expected to shape the future of the industry.
1. Increasing Global Reach:
The Islamic finance industry is no longer limited to Muslim-majority countries. It has gained traction in non-Muslim majority countries as well, with many international financial institutions and multinational corporations offering Sharia-compliant products and services. As the awareness and acceptance of Islamic finance continue to grow globally, the industry is expected to expand further.
2. Technological Advancements:
With the rapid advancement of technology, Islamic finance is embracing digital innovation. Fintech companies in the Islamic finance space have emerged, offering online platforms and mobile applications for convenient and accessible banking services. These technological advancements are expected to enhance the efficiency and accessibility of Islamic finance, attracting a wider customer base.
3. Product Innovation:
The future of Islamic finance lies in product innovation. In response to evolving market needs, financial institutions are developing new Sharia-compliant products that cater to a broader range of customers. This includes products such as green financing, microfinance, and takaful (Islamic insurance), which address social and environmental concerns, and support financial inclusion.
4. Standardization and Regulation:
Efforts are being made to establish common standards and regulations for Islamic finance to ensure consistency and integrity across markets. Organizations such as the Accounting and Auditing Organization for Islamic Financial Institutions (AAOIFI) and the Islamic Financial Services Board (IFSB) are working towards harmonizing regulations and enhancing transparency in the industry. Standardization and regulation will bring about increased confidence among investors and promote further growth.
5. Collaboration and Partnerships:
Collaboration between Islamic finance institutions, conventional financial institutions, and governments is crucial for the development and growth of the industry. Partnerships enable knowledge sharing, joint ventures, and access to larger markets. As Islamic finance continues to gain prominence, collaboration among various stakeholders will become increasingly important for its sustainability and expansion.
In conclusion, the future of Islamic finance looks bright, driven by increasing global reach, technological advancements, product innovation, standardization and regulation, and collaboration. These factors will contribute to the industry’s growth and enable it to meet the evolving financial needs of individuals and businesses worldwide.
Investing in Islamic Finance
Islamic finance offers a unique investment opportunity for individuals and institutions looking to adhere to the principles of Islamic law, known as Sharia. Sharia prohibits the earning of interest and the involvement in certain industries such as alcohol, gambling, and pork-related products. Therefore, Islamic finance provides a way for Muslims to invest their money in a manner that aligns with their religious beliefs.
Investing in Islamic finance can be done through various financial products that are designed to comply with Sharia principles. Some popular investment vehicles include:
- Sukuk (Islamic Bonds): Sukuk are financial instruments that represent ownership in an underlying asset. Instead of receiving interest, investors receive a share of the profits generated by the asset. This aligns with the Islamic principle of profit and loss sharing.
- Islamic Mutual Funds: These funds invest in companies that comply with Sharia principles and avoid those engaged in prohibited activities. Islamic mutual funds provide diversification and professional management for investors looking to adhere to Islamic law while growing their wealth.
- Islamic Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): REITs are investment vehicles that allow investors to pool their money to invest in real estate. Islamic REITs only invest in properties and businesses that comply with Sharia principles, such as avoiding investments in conventional banks or real estate that generates interest income.
- Islamic Equity Funds: These funds invest in stocks of companies that meet Sharia compliance criteria. They avoid stocks of companies involved in prohibited activities and adhere to specific financial ratios, ensuring they comply with Islamic principles.
Investing in Islamic finance provides the opportunity to grow wealth while remaining true to Islamic values. By investing in Sharia-compliant financial products, individuals can benefit from the potential returns of investment markets while avoiding the ethical concerns associated with conventional finance.
Islamic Finance and Fintech
The rapid advancements in technology have not only revolutionized the way we live and do business but have also had a significant impact on the world of finance. Islamic finance, which is based on the principles of Islamic law (Shariah), is no exception to this trend. Fintech (financial technology) has emerged as a game-changer in the field of Islamic finance, offering innovative solutions to cater to the unique needs of Islamic financial institutions and consumers.
Fintech has paved the way for the development of various digital platforms, applications, and services that offer Shariah-compliant financial products. These tools enable individuals and businesses to access Islamic financial services conveniently and efficiently.
One of the key areas where fintech has made a significant impact on Islamic finance is in the provision of Islamic banking services. Mobile banking apps and online banking platforms have made it easier for individuals to open Shariah-compliant bank accounts, apply for Islamic loans, and access various banking services through their smartphones or computers. This has enhanced financial inclusion and accessibility for Muslims around the world.
Fintech has also played a vital role in the growth of Islamic crowdfunding platforms. These platforms enable individuals and businesses to raise funds in a Shariah-compliant manner for various purposes, such as financing small businesses, real estate projects, or charitable initiatives. The use of blockchain technology has further enhanced the transparency and efficiency of these platforms, ensuring that funds are used in accordance with Shariah principles.
Moreover, fintech has facilitated the development of Islamic robo-advisory platforms. These platforms use algorithms and artificial intelligence to provide automated investment advice based on Shariah principles. Investors can input their preferences and risk appetite, and the robo-advisory platform will generate a personalized investment portfolio consisting of Shariah-compliant assets.
Another area where fintech has made significant strides in Islamic finance is in the provision of Islamic insurance (Takaful). Innovative digital platforms have made it easier for individuals to purchase and manage Takaful policies, file claims, and access various insurance services. These platforms have also improved the transparency of Takaful operations by providing real-time updates and detailed information about the underlying Shariah-compliant investments.
Overall, the integration of fintech in Islamic finance has brought numerous benefits, including increased accessibility, efficiency, transparency, and convenience. It has opened up new avenues for Islamic financial institutions to expand their reach and cater to the growing demand for Shariah-compliant financial products and services.
Islamic Finance and Islamic Social Finance
In addition to providing financial services that comply with Islamic principles, Islamic finance also promotes the concept of Islamic social finance. Islamic social finance refers to financial instruments and institutions that are designed to address social and economic issues while adhering to Islamic principles.
Zakat: One of the key pillars of Islamic social finance is Zakat, which is an obligatory form of charitable giving in Islam. Muslims who meet specific wealth criteria are required to give a portion of their wealth to support the less fortunate members of society. Zakat is often collected by Islamic financial institutions and distributed to those in need.
Sadaqah: Sadaqah is a voluntary form of charitable giving in Islam. Muslims are encouraged to give Sadaqah throughout the year to help the poor, support community development projects, and provide relief during times of crisis. Islamic financial institutions often provide platforms for individuals to make Sadaqah donations and support various charitable causes.
Waqf: Waqf is a form of Islamic endowment where assets, such as land or buildings, are dedicated to support charitable causes or provide ongoing benefits for society. The income generated from these assets is used for various purposes, such as funding education, healthcare, and social welfare projects. Islamic financial institutions play a role in managing and investing Waqf assets to ensure their long-term sustainability.
Microfinance: Islamic microfinance focuses on providing financial services to individuals and small businesses who are unable to access conventional banking services. These services include microcredit, microsaving, and microinsurance, all of which operate in accordance with Islamic principles. Islamic microfinance institutions aim to alleviate poverty and promote economic development within Muslim communities.
Socially Responsible Investments (SRI): Islamic finance promotes investing in socially responsible projects and companies. Investments in sectors such as alcohol, gambling, and tobacco are prohibited, while investments in environmentally friendly initiatives, renewable energy, and ethical industries are encouraged. Islamic financial institutions provide Sharia-compliant investment options that align with the values and principles of socially responsible investing.
Overall, Islamic social finance encompasses a range of financial mechanisms that contribute to social and economic development while upholding Islamic principles of fairness, justice, and compassion.
Islamic Finance and Corporate Governance
Islamic finance not only focuses on providing financial services that align with Shariah principles, but it also emphasizes the importance of ethical business practices and corporate governance. Islamic financial institutions adhere to certain principles and guidelines that promote transparency, fairness, and accountability in their operations.
One of the key principles of Islamic finance is the concept of “shared risk and reward.” This principle dictates that both the financier (provider of capital) and the entrepreneur (user of capital) share both the profits and losses generated by a business venture. This encourages a balanced and equitable distribution of wealth and ensures that the interests of all parties involved are considered.
In Islamic finance, corporate governance plays a critical role in ensuring compliance with Shariah principles and promoting ethical conduct. Corporate governance frameworks in Islamic financial institutions typically include:
- Shariah supervisory boards: These boards comprise of Islamic scholars who are responsible for ensuring that all financial transactions and products offered by the institution comply with Shariah principles.
- Transparency and disclosure: Islamic financial institutions are required to provide clear and comprehensive information about their operations, financial statements, and governance structure to their stakeholders.
- Accountability and oversight: Islamic financial institutions are accountable to their shareholders and stakeholders and are subject to regulatory oversight to ensure adherence to Shariah principles and ethical standards.
- Audit and risk management: Islamic financial institutions employ rigorous auditing and risk management practices to identify and mitigate any potential risks and ensure the soundness of their operations.
Furthermore, ethical considerations are an integral part of Islamic finance and corporate governance. Islamic financial institutions are encouraged to avoid unethical practices, such as dealing with interest (riba), excessive speculation (gharar), and investments in industries that are prohibited in Islam (e.g., alcohol, gambling).
In conclusion, Islamic finance goes beyond Shariah-compliant financial products and services. It emphasizes the importance of ethical business practices and corporate governance to ensure transparency, fairness, and accountability. With its focus on shared risk and reward, Islamic finance promotes a more inclusive and equitable financial system.
Islamic Finance and Risk Management
Risk management plays a crucial role in Islamic finance as it is based on the principles of fairness, ethical conduct, and sharing of risks and rewards. Islamic financial institutions employ various risk management techniques to ensure compliance with Islamic law (Shariah) and to protect their clients’ interests.
1. Shariah Compliance
Islamic finance requires strict adherence to Shariah principles, which prohibit interest (riba), excessive uncertainty (gharar), and investments in prohibited activities (haram). To ensure Shariah compliance, Islamic financial institutions employ Shariah boards or committees consisting of Islamic scholars who review and approve the financial products and activities of the institution.
2. Profit-and-Loss Sharing
One of the fundamental principles of Islamic finance is the sharing of risks and rewards between the provider of funds (investor) and the user of funds (entrepreneur). In profit-and-loss sharing arrangements, such as musharakah (partnership) and mudarabah (investment management), both parties share in the profits and losses generated by the investment. This incentivizes better risk management as both parties have a stake in the success of the investment.
3. Asset-Backed Financing
In Islamic finance, transactions must be backed by tangible assets and real economic activities. This reduces the risk of speculative transactions and encourages investment in productive and tangible assets. Asset-backed financing provides a form of security for the investor, as their funds are tied to a specific asset. If the borrower defaults, the investor can take possession of the asset to recover their investment.
4. Risk-Sharing Techniques
Islamic financial institutions use a range of risk-sharing techniques to manage risks, including takaful (Islamic insurance). Takaful involves pooling funds from participants to provide coverage against specified risks. The risk and cost of claims are shared among the participants, and any surplus is distributed back to them according to the principle of fairness.
5. Strong Governance and Risk Management Frameworks
To ensure effective risk management, Islamic financial institutions must establish robust governance and risk management frameworks. This includes implementing systems and processes for risk identification, assessment, and mitigation. Regular monitoring and reporting of risks are also crucial to ensure timely actions can be taken to address any potential issues.
6. Ethical Investment Criteria
Islamic finance promotes ethical and socially responsible investments. Investments in industries such as alcohol, tobacco, gambling, and weapons are prohibited. Instead, Islamic financial institutions focus on sectors that contribute to the welfare of society, such as healthcare, education, renewable energy, and infrastructure development. This ensures that investments align with ethical values and contribute positively to the economy and society.
Conclusion
Risk management is an integral part of Islamic finance, focusing on compliance with Shariah principles, profit-and-loss sharing, asset-backed financing, risk-sharing techniques, strong governance frameworks, and ethical investment criteria. By incorporating these principles, Islamic finance aims to create a fair and ethical financial system that supports economic growth while minimizing risks for all stakeholders.
The Role of Islamic Finance in Wealth Management
Islamic finance plays a significant role in wealth management, offering unique principles and practices that align with the values and beliefs of Muslims. It provides a framework for individuals and institutions to manage their wealth in a way that is both financially beneficial and in accordance with Islamic principles.
One of the key principles of Islamic finance is the prohibition of interest, known as riba. In traditional finance, interest is a fundamental mechanism for generating returns on investments. However, in Islamic finance, interest is considered exploitative and is therefore prohibited. Instead, Islamic finance employs profit-sharing agreements, where financial institutions and clients share the profits and losses of investments.
Another important aspect of Islamic finance is the emphasis on ethical and responsible investment practices. Islamic finance promotes investments in sectors that are deemed permissible, such as halal food, healthcare, education, and renewable energy, while avoiding sectors that are considered haram, such as alcohol, gambling, and weapons. This focus on ethical investing aligns with the values of many Muslims who seek to invest in a socially responsible manner.
In addition, Islamic finance provides various wealth management tools and products that cater to the specific needs of Muslim clients. For instance, Islamic banks offer Sharia-compliant savings accounts, investment funds, and insurance products. These financial instruments are designed to adhere to Islamic principles while providing the necessary services and options for individuals and institutions to effectively manage their wealth.
Furthermore, Islamic finance offers mechanisms for long-term wealth preservation and succession planning. For example, the concept of waqf, or endowment, allows individuals to permanently donate their assets to charitable causes, while still providing ongoing benefits to their families. This enables individuals to fulfill their social and religious obligations towards charity, while ensuring the long-term security of their wealth for future generations.
In conclusion, Islamic finance plays a crucial role in wealth management by providing a system that is in line with Islamic principles and offers unique solutions for individuals and institutions. It offers an alternative to conventional finance by prohibiting interest and promoting ethical investment practices. With its emphasis on responsible investing and tailored wealth management tools, Islamic finance provides Muslims with the means to effectively grow and preserve their wealth while adhering to their religious beliefs.
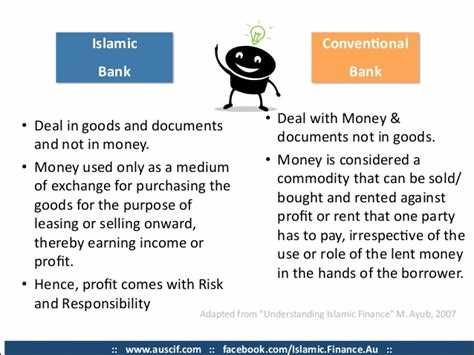
Comparing Islamic Finance with Conventional Finance
Islamic finance and conventional finance are two different financial systems that operate on contrasting principles and practices. While conventional finance is based on interest and can involve certain elements that are considered unethical in Islamic law, Islamic finance follows the principles of Shariah law and prohibits interest, speculation, and investments in industries considered haram (forbidden).
Interest (Riba)
- Conventional Finance: Conventional finance relies heavily on the concept of interest, or riba, to generate profits. Interest is charged on loans, mortgages, and other financial transactions, allowing lenders to earn a return on their investments.
- Islamic Finance: Islamic finance strictly prohibits riba. Instead of interest, Islamic finance promotes profit and risk-sharing agreements, where the lender and borrower share the risks and returns of the investment.
Unethical Investments
- Conventional Finance: Conventional finance may invest in industries or activities that are considered unethical, such as gambling, alcohol, tobacco, and weapons.
- Islamic Finance: Islamic finance strictly follows ethical guidelines outlined in Shariah law. Investments in industries or practices that are considered haram, such as gambling, alcohol, pork, and interest-based financial institutions, are strictly prohibited.
Speculation and Uncertainty (Gharar)
- Conventional Finance: Conventional financial transactions often involve speculation and uncertainty, such as short-selling, derivatives, and futures contracts.
- Islamic Finance: Islamic finance discourages speculation and uncertainty, or gharar, as it goes against the principles of Shariah law. Transactions must be based on tangible assets and must involve clear and transparent terms and conditions.
Asset-Backed Financing
- Conventional Finance: Conventional finance often relies on debt-based financing, where loans are provided based on creditworthiness and cash flows.
- Islamic Finance: Islamic finance promotes asset-backed financing, where transactions are based on tangible assets. Investments must be backed by physical assets or projects, ensuring that wealth is created through real economic activities.
Profit-Sharing and Loss-Bearing
- Conventional Finance: Conventional finance focuses on lending money and earning interest, with the lender bearing minimal risk.
- Islamic Finance: Islamic finance emphasizes profit-sharing and loss-bearing arrangements. Investments are structured in a way that both the lender and borrower share the risks and potential profits of the investment.
| Islamic Finance | Conventional Finance | |
|---|---|---|
| Interest (Riba) | Prohibited | Allowed and commonly practiced |
| Unethical Investments | Prohibited | Allowed |
| Speculation and Uncertainty (Gharar) | Discouraged and minimized | Commonly practiced |
| Asset-Backed Financing | Emphasized | Debt-based financing |
| Profit-Sharing and Loss-Bearing | Emphasized | Interest-focused |
The Impact of Islamic Finance on Financial Stability
Islamic finance has gained significant attention in recent years for its unique principles and practices. One of the key aspects of Islamic finance is its focus on financial stability. Unlike conventional finance, which has been criticized for contributing to financial crises, Islamic finance aims to promote stability and sustainability in the financial system.
Islamic finance operates on the principles of Shariah, or Islamic law, which prohibits usury (interest), speculation, and investment in certain activities deemed unethical, such as gambling and alcohol. These principles promote risk-sharing, transparency, and ethical conduct in financial transactions.
By adhering to these principles, Islamic finance can have a positive impact on financial stability in several ways:
- Risk-sharing: In Islamic finance, profit and loss are shared between the lender and borrower. This encourages a more equitable distribution of risk, as both parties have a stake in the success or failure of the investment. This reduces the likelihood of moral hazard and encourages responsible lending and borrowing.
- Asset-backed financing: Islamic finance promotes financing based on real assets instead of speculative activities. This reduces the likelihood of asset bubbles and excessive leveraging, which can contribute to financial instability. By focusing on tangible assets, Islamic finance encourages more prudent investment decisions.
- Prohibition of interest: The prohibition of interest in Islamic finance helps to prevent the accumulation of excessive debt, which can be a major source of financial instability. Instead of charging interest, Islamic financial institutions use profit-sharing arrangements or fee-based financing, which aligns the interests of the lender and borrower and reduces the risk of default.
- Transparency and ethical conduct: Islamic finance places a strong emphasis on transparency and ethical conduct in financial transactions. This helps to build trust between financial institutions and customers, reducing the risk of fraud and misconduct. By promoting ethical behavior, Islamic finance contributes to a more stable and sustainable financial system.
The impact of Islamic finance on financial stability has been recognized by regulators and policymakers around the world. Many countries, including those with significant Muslim populations, have taken steps to promote the development of Islamic finance as a means to enhance financial stability and inclusiveness.
However, it is important to note that Islamic finance is not without its challenges. The complex nature of Shariah compliance, limited standardization, and the need for specialized expertise are among the hurdles that need to be overcome for Islamic finance to reach its full potential. Nevertheless, the principles and practices of Islamic finance have the potential to make a significant positive impact on financial stability in the global economy.
FAQ
What is Islamic finance?
Islamic finance is a financial system that is based on the principles of Islamic law, also known as Shariah. It prohibits the earning of interest, as well as engaging in any business activities that are considered to be unethical or against moral values.
How does Islamic finance work?
Islamic finance works by adhering to the principles of Shariah law. It involves the use of financial instruments that are compliant with Islamic principles, such as profit-sharing agreements, leasing contracts, and joint ventures. The focus is on ensuring that all transactions are conducted in a fair and ethical manner.
What are some key principles of Islamic finance?
Some key principles of Islamic finance include the prohibition of interest (riba), the sharing of profit and loss (mudarabah), the prohibition of speculation (gharar), and the avoidance of unethical or harmful activities.
How does Islamic finance promote social justice?
Islamic finance promotes social justice by ensuring that wealth is distributed more equitably in society. It encourages the sharing of profits and losses, discourages excessive risk-taking, and focuses on financing projects that have a positive impact on the community, such as affordable housing and renewable energy projects.
Is Islamic finance restricted to Muslims only?
No, Islamic finance is not restricted to Muslims only. While it is rooted in Islamic principles, anyone can participate in Islamic finance as long as they are willing to comply with the ethical and legal requirements set out by Shariah law.