Islamic mortgages, also known as Halal mortgages, are a type of home financing that adhere to the principles of Islamic law, or Shariah. These mortgages are specifically designed for Muslim homebuyers who want to avoid the payment of interest, which is considered riba, or usury, under Islamic law.
The main difference between Islamic mortgages and conventional mortgages is the way in which the financing is structured. In a conventional mortgage, the lender provides the borrower with the necessary funds to purchase a property, and the borrower pays the lender back in installments with interest. Islamic mortgages, on the other hand, use a concept called Murabaha or Ijara, which are forms of purchase and lease agreements respectively.
In a Murabaha mortgage, the bank acts as a middleman between the buyer and the seller. The bank purchases the property at market value and then sells it to the buyer at a higher price. This higher price includes the bank’s profit, which is agreed upon at the time of the transaction. Instead of paying interest, the buyer repays the bank in installments over an agreed-upon period of time.
Ijara mortgages, on the other hand, involve the bank purchasing the property and then leasing it to the buyer. The buyer pays the bank rent, which is set at a mutually agreed-upon rate, and has the option to purchase the property at the end of the lease term. This lease-purchase arrangement allows the buyer to gradually acquire ownership of the property without paying interest.
Islamic mortgages provide a financial solution for Muslim homebuyers who want to adhere to the principles of Islamic law while still being able to purchase a home. By avoiding the payment of interest, these mortgages allow buyers to own a property without compromising their religious beliefs. Understanding how Islamic mortgages work is essential for anyone considering this type of financing option.
What is an Islamic Mortgage?
An Islamic mortgage, also known as a sharia-compliant mortgage or halal mortgage, is a type of mortgage that adheres to the principles of Islamic law, known as Shariah. Shariah prohibits the payment or receipt of interest, also known as riba. Therefore, Islamic mortgages are structured in a way that avoids the use of interest.
In an Islamic mortgage, the lender and the borrower enter into a partnership arrangement, where the lender provides the necessary funds to purchase the property, and the borrower agrees to pay back the lender over a specified period. Instead of charging interest, the lender is entitled to a share of the rental income generated by the property, or a share of the profits if the property is sold.
This partnership arrangement is usually facilitated through one of the following Islamic financing structures:
- Murabaha: In this structure, the lender purchases the property and then sells it to the borrower at a higher price. The borrower repays the lender in installments over a specified period.
- Ijara: This structure involves the lender purchasing the property and then renting it out to the borrower. The borrower pays rent to the lender, and at the end of the agreed-upon period, the ownership of the property is transferred to the borrower.
- Musharaka: In this structure, the lender and the borrower enter into a joint ownership agreement. The borrower gradually buys out the lender’s share in the property, and once the ownership is fully transferred, the partnership is dissolved.
Islamic mortgages provide an alternative for Muslims who wish to finance their homes without engaging in interest-based transactions. These mortgages are structured to be compliant with Islamic principles and offer a way for Muslims to fulfill their housing needs while adhering to their religious beliefs.
Key Principles of Islamic Mortgages
An Islamic mortgage, also known as a halal mortgage or sharia-compliant mortgage, operates on the principles of Islamic finance. These principles aim to provide financial services that align with the teachings of Islam.
- Prohibition of Interest (Riba): Islamic mortgages avoid charging or paying interest, as it is considered exploitative and unfair. Instead of charging interest, the lender and borrower enter into a partnership where they share the ownership and risk of the property.
- Asset-Based Financing (Murabaha): Islamic mortgages utilize the concept of murabaha, which involves the purchase and sale of goods at a marked-up price. In the context of a mortgage, the lender purchases the property from the seller and sells it to the borrower at an agreed-upon price, which includes an agreed-upon profit margin.
- Sharing of Profits and Losses (Musharakah): The borrower and lender share both the profits and losses associated with the property. In the case of a mortgage, the borrower makes regular payments, part of which goes towards repaying the lender’s ownership share, and the remaining portion is used to increase the borrower’s ownership share over time.
- Prohibition of Uncertainty (Gharar): Islamic mortgages avoid uncertainty and speculative practices. Lenders must disclose all necessary details about the property and the terms of the agreement upfront to ensure transparency and avoid any elements of ambiguity or excessive risk.
- Asset Ownership (Musharakah Mutanaqisah): Islamic mortgages are structured in a way that allows the borrower to gradually purchase the lender’s ownership share over time. This process is typically achieved through regular payments, which increase the borrower’s ownership stake until full ownership is attained.
By adhering to these key principles, Islamic mortgages provide an alternative financing option for individuals who wish to avoid traditional interest-based mortgages while still being able to purchase a property.
Sharia Compliance and Islamic Mortgages
Sharia compliance is an essential aspect of Islamic mortgages. Islamic banking operates under the principles of Sharia law, which prohibits the payment or receipt of interest (riba) and the involvement in businesses that are considered haram (forbidden) by Islamic principles, such as gambling, alcohol, or pork.
In order to ensure sharia compliance, Islamic mortgages are structured differently from conventional mortgages. Instead of charging interest, Islamic mortgages use a system called Murabaha, Musharaka, or Ijara.
- Murabaha: This is a cost-plus financing model. The bank purchases the property and sells it to the customer at a higher price, allowing the customer to pay it back in installments over an agreed period.
- Musharaka: This is a partnership-based financing model. The bank and the customer enter into a partnership where both parties contribute funds to purchase the property. The customer pays rent to the bank while gradually increasing their ownership share.
- Ijara: This is a leasing-based financing model. The bank purchases the property and leases it to the customer for an agreed period. The customer pays rent, which is considered as a return on the bank’s investment.
It is important to note that the profit and risk are shared between the bank and the customer in these models, reflecting the principles of Islamic finance.
To ensure compliance, Islamic mortgages require additional checks and documentation to validate the property’s compliance with Sharia law. These checks include verifying the property’s source and legitimacy, as well as ensuring that it is not involved in any prohibited activities.
In addition to avoiding interest and haram activities, Islamic mortgages also uphold ethical and social responsibility principles. For example, some Islamic mortgages offer a charitable giving component, where a percentage of the profit goes toward charitable causes, or the bank invests in renewable energy and other sustainable projects.
Overall, Sharia compliance is a crucial element of Islamic mortgages, ensuring that they adhere to the principles of Islamic finance and meet the ethical and social responsibilities associated with them.
Types of Islamic Mortgages
Islamic mortgages, also known as home financing or home purchase plans, follow the principles of Islamic finance. There are several types of Islamic mortgages available to cater to different needs and circumstances. Here are some common types:
- Murabaha: A murabaha mortgage involves the bank purchasing the property on behalf of the customer and then selling it to them at a higher price, which is paid in installments. The bank’s profit is determined upfront and agreed upon by both parties.
- Musharaka: With a musharaka mortgage, the bank and the customer enter into a joint partnership to purchase the property. The customer makes regular payments to the bank, which includes a share of the property’s rental income. Over time, the customer’s ownership share increases, and the bank’s share decreases.
- Ijara: An ijara mortgage is a leasing arrangement where the bank purchases the property and leases it to the customer for a specified period. The customer pays rent, which includes both a rental component and a portion that goes towards the purchase of the property. At the end of the lease term, ownership is transferred to the customer.
- Mudaraba: In a mudaraba mortgage, the bank acts as the financier and the customer acts as the entrepreneur. The bank provides the funds to purchase the property, and the customer manages the property. Profits are shared between the bank and the customer based on pre-agreed ratios, while losses are borne by the bank.
- Diminishing Musharaka: A diminishing musharaka mortgage is similar to musharaka, but with a predefined schedule for the customer to gradually buy out the bank’s share of the property over time. The customer makes regular payments to the bank, which includes rent and a portion that goes towards buying out the bank’s share. Eventually, the customer becomes the sole owner of the property.
Each type of Islamic mortgage has its own advantages and considerations. It’s important for individuals to carefully evaluate their needs and preferences and consult with Islamic finance experts to choose the most suitable option for their situation.
It’s worth noting that the availability of these types of mortgages may vary depending on the country and financial institutions. It’s important to consult with local experts and verify the specific options available in a given jurisdiction.
Understanding Murabaha Islamic Mortgages
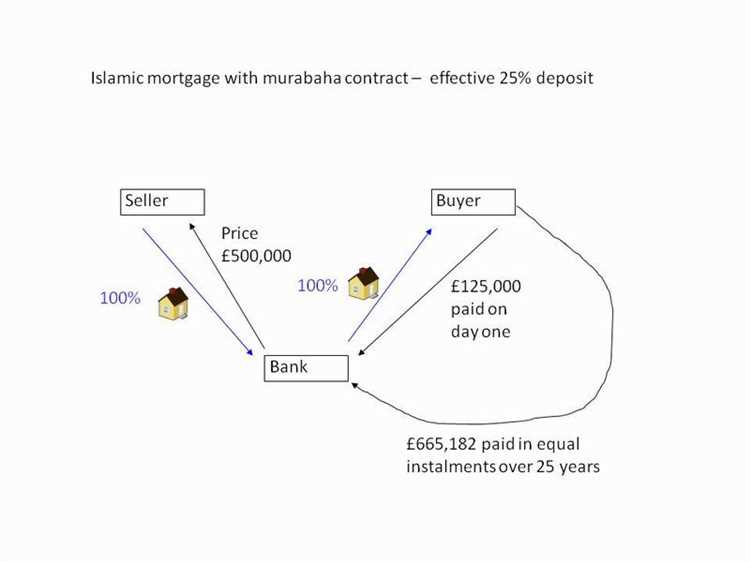
Murabaha is a commonly used Islamic financing structure for mortgages. In a Murabaha mortgage, the bank or financial institution purchases the property on behalf of the customer and then sells it to the customer at an agreed-upon price, which includes an agreed-upon profit margin for the bank.
The key features of a Murabaha Islamic mortgage include:
- No interest: Murabaha mortgages are designed to be in line with Islamic principles, which prohibit charging or paying interest. Instead, the profit is derived from the agreed-upon profit margin included in the purchase price.
- Property ownership: The bank or financial institution, in this case, holds the legal ownership of the property until the mortgage is fully paid off. However, the customer has the right to occupy and use the property throughout the mortgage period.
- Repayment terms: Murabaha mortgages usually have fixed repayment terms, typically ranging from 5 to 30 years, depending on the agreement between the bank and the customer. The customer makes regular payments to the bank, which include the agreed-upon profit margin.
It’s important to note that Murabaha mortgages are considered a form of debt financing in Islamic finance. Therefore, the customer is obligated to pay back the full amount of the mortgage, including the purchase price and the agreed-upon profit margin.
In case the customer fails to make the mortgage payments, the bank may take legal actions to recover the outstanding amount, which may include selling the property. However, the bank is expected to give the customer a reasonable grace period and explore alternative arrangements before resorting to such measures.
Overall, Murabaha Islamic mortgages provide a Sharia-compliant alternative for individuals who wish to purchase a property without engaging in conventional interest-based mortgages.
Understanding Ijarah Islamic Mortgages
An Ijarah Islamic mortgage, also known as an Ijarah finance arrangement, is a type of home financing option available for Muslims who wish to purchase a property in a Sharia-compliant manner. It is based on the principles of Ijarah, which is a type of lease contract.
Under an Ijarah Islamic mortgage, the bank purchases the property and leases it to the customer for a specific period of time. The customer pays rent to the bank for the use of the property. The rent payments are usually structured in a way that allows the customer to gradually acquire ownership of the property over time.
The structure of an Ijarah Islamic mortgage is as follows:
- The customer selects a property they wish to purchase.
- The bank purchases the property from the seller and becomes the owner.
- The bank leases the property to the customer for a specified period of time. The lease contract includes the rental payments and other terms and conditions.
- The customer pays rent to the bank on a monthly basis.
- A portion of the rental payment is usually allocated towards the purchase of the property. This is known as the “rent-to-purchase” ratio.
- Once the specified period of time has elapsed, the customer has the option to purchase the property from the bank at a pre-determined price.
It’s important to note that under an Ijarah Islamic mortgage, the bank remains the legal owner of the property throughout the lease period. However, the customer has the right to use and possess the property as if they were the owner.
One of the key benefits of an Ijarah Islamic mortgage is that it is an interest-free financing option, as interest is prohibited in Islamic finance. Instead of charging interest, the bank earns a profit through the rental payments. Additionally, the structure of the rent-to-purchase ratio allows customers to gradually acquire ownership of the property without having to take on a conventional mortgage.
Overall, Ijarah Islamic mortgages provide Muslims with a Sharia-compliant option for purchasing a property without having to engage in interest-based transactions. They offer a way to achieve homeownership while adhering to Islamic principles.
Understanding Musharakah Islamic Mortgages
The Musharakah Islamic mortgage is a type of financing arrangement based on the principles of partnership and profit sharing. In Musharakah, two parties come together to pool their resources and share profits and risks associated with the investment.
How Musharakah works:
- The first step in a Musharakah Islamic mortgage is for the bank and the customer to pool their resources to purchase a property.
- Both parties contribute a certain amount of funds towards the purchase, either in equal or proportional shares.
- The ownership of the property is shared based on the contribution of each party.
- The bank and the customer then enter into a partnership agreement, which outlines the terms and conditions of the investment.
- Any profits generated from the investment are shared based on the pre-agreed ratio. This ratio is typically determined based on the initial contribution of each party.
- In case of any losses, they are shared in proportion to each party’s investment.
Benefits of Musharakah Islamic Mortgages:
- Musharakah promotes the concept of shared ownership and responsibility, ensuring a fair and equitable distribution of profits and losses between the bank and the customer.
- It provides an alternative financing option for individuals who want to avoid conventional interest-based mortgages due to religious beliefs or personal preferences.
- The Musharakah Islamic mortgage allows individuals with limited funds to partner with the bank, enabling them to purchase a property that they may not have been able to afford on their own.
Considerations for Musharakah Islamic Mortgages:
- As Musharakah is based on the concept of profit sharing, it is essential for both parties to have a clear understanding of the investment and the potential risks involved.
- The partnership agreement should clearly define the responsibilities and rights of each party, including the distribution of profits and the sharing of any potential losses.
- It is advisable to consult with an Islamic scholar or an expert in Islamic finance to ensure compliance with Shariah principles and guidelines.
In conclusion, Musharakah Islamic mortgages provide an alternative financing option that aligns with Islamic principles by promoting shared ownership and profit sharing. This type of mortgage can be beneficial for individuals who want to avoid conventional interest-based mortgages and are looking for a more equitable and ethical financing option.
Understanding Diminishing Musharakah Islamic Mortgages
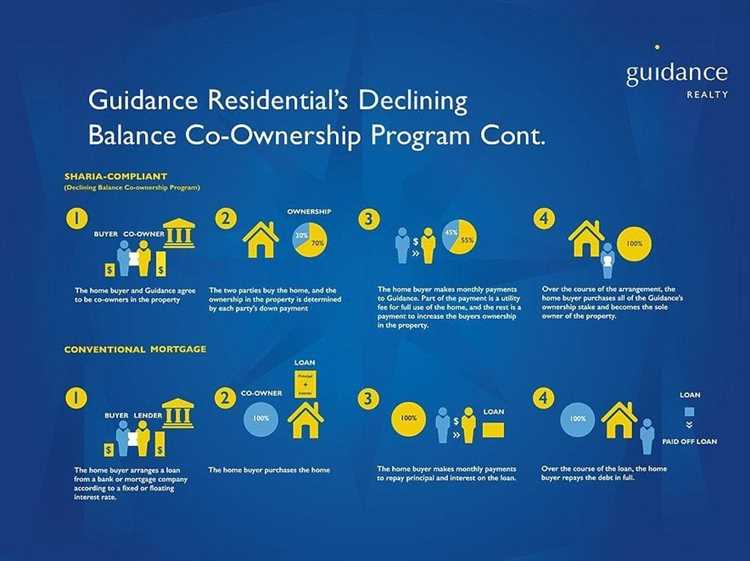
A Diminishing Musharakah Islamic mortgage is a type of home financing that adheres to Islamic principles. It is a partnership-based arrangement between the bank or financial institution and the buyer, where the property is jointly owned by both parties. This type of mortgage is also known as a “co-ownership” or “partnership” mortgage.
In a Diminishing Musharakah Islamic mortgage, the bank or financial institution provides a portion of the property’s purchase price and the buyer contributes the remaining portion. The buyer and the bank become co-owners of the property, with the buyer holding a majority share. The buyer then makes regular payments to the bank to gradually purchase the bank’s share of the property.
The key feature of a Diminishing Musharakah Islamic mortgage is that the bank also shares in the risk of the investment. This means that if the property’s value decreases, both the buyer and the bank bear the loss. On the other hand, if the value of the property increases, both parties share in the profit proportionate to their ownership shares.
Here are the main steps involved in a Diminishing Musharakah Islamic mortgage:
- The buyer approaches a bank or financial institution for home financing.
- The buyer and the bank enter into a partnership agreement, outlining the terms and conditions of the joint ownership.
- The bank provides a portion of the property’s purchase price.
- The buyer contributes the remaining portion of the purchase price.
- The property is registered in the name of both the buyer and the bank as co-owners.
- The buyer makes regular payments to the bank, which include the repayment of the bank’s share of the property.
- Over time, the buyer’s ownership share increases, while the bank’s ownership share decreases.
- Once the buyer has fully paid off the bank’s share, the property becomes solely owned by the buyer.
It’s important to note that in a Diminishing Musharakah Islamic mortgage, the regular payments made by the buyer are not considered as interest. Instead, they are seen as part of the purchase price of the bank’s share of the property. This makes it compliant with Islamic principles, which prohibit the charging or receiving of interest.
Overall, a Diminishing Musharakah Islamic mortgage provides an alternative financing option for individuals who wish to adhere to Islamic principles. It allows individuals to become homeowners while sharing the risks and rewards of the investment with the bank or financial institution.
Understanding Wakala Islamic Mortgages
A Wakala Islamic Mortgage is a type of home financing product offered by Islamic financial institutions. It is based on the principle of Wakala, which is an agent-principal relationship.
In a Wakala Islamic Mortgage, the bank acts as an agent (Wakil) on behalf of the customer (Mudarib) for the purpose of acquiring a property. The bank charges a fee for its services, which is agreed upon in advance.
The main features of a Wakala Islamic Mortgage are as follows:
- Property Selection: The customer selects a property and requests the bank to act as an agent for its acquisition.
- Agency Agreement: The bank and the customer enter into an agency agreement (Wakala contract) stating the terms and conditions of the agent-principal relationship.
- Fee Structure: The bank charges a Wakala fee for its services, which can be either a fixed amount or a percentage of the property price.
- Financing: The bank provides the necessary funds to purchase the property. The customer pays back the bank in installments over an agreed-upon period of time.
- Ownership: The property is registered in the name of the customer from the start of the Wakala contract. The bank does not have an ownership interest in the property.
It’s important to note that a Wakala Islamic Mortgage is different from a conventional mortgage. In a conventional mortgage, the bank lends money to the customer, charges interest, and has an ownership interest in the property. In contrast, a Wakala Islamic Mortgage is based on the principles of Islamic finance, which prohibits the charging or receiving of interest and emphasizes equitable relationships between parties.
In conclusion, a Wakala Islamic Mortgage is a Sharia-compliant home financing product that allows customers to purchase a property with the help of a bank acting as an agent. It is an alternative to conventional mortgages and provides a way for individuals to fulfill their housing needs while adhering to Islamic principles.
Advantages of Islamic Mortgages
Islamic mortgages, also known as halal mortgages, offer several advantages over conventional mortgages. These advantages make them a preferred choice for many Muslim individuals who want to buy a home while adhering to their religious beliefs.
- Compliance with Islamic Law: Islamic mortgages are structured in a way that they comply with the principles of Shariah, the Islamic law. This means that the transaction is free from any interest (riba) or exploitative elements, which is prohibited in Islam.
- Shared Risk and Profits: In Islamic mortgages, the bank and the homeowner enter into a partnership, where the bank purchases the home and the homeowner pays rent to the bank while gradually buying a portion of the property. This shared arrangement ensures that both parties share the risk and profits of the property.
- No Penalties for Early Repayment: Unlike conventional mortgages, Islamic mortgages do not charge penalties for early repayment. This gives homeowners the flexibility to pay off their mortgage faster without incurring additional costs.
- Transparent and Ethical: Islamic mortgages follow the principles of transparency and ethics. All terms and conditions of the mortgage are clearly disclosed, and the contracts are based on mutual consent and understanding between the parties involved.
- No Uncertainty: Islamic mortgages avoid uncertainty (gharar) by offering fixed terms and conditions. This provides borrowers with a sense of security, as they know exactly how much they need to pay and for how long.
- Social Responsibility: Islamic mortgages prioritize social responsibility by avoiding investments in industries that are considered unethical or harmful, such as alcohol, gambling, and tobacco. This allows borrowers to align their financial decisions with their religious and ethical beliefs.
These advantages make Islamic mortgages a viable option for individuals who seek to purchase a home in a way that complies with their Islamic faith and values.
Disadvantages of Islamic Mortgages
While Islamic mortgages can provide an alternative solution for Muslims who wish to adhere to Sharia law while purchasing a property, there are also several disadvantages to consider.
- Limited Availability: Islamic mortgages are not as widely available as conventional mortgages, making it more difficult for Muslims to find suitable financing options.
- Higher Costs: Islamic mortgages often come with higher costs and fees compared to conventional mortgages. This can include higher administration fees, valuation fees, or property survey fees.
- Complex Structure: Islamic mortgages tend to have a more complex structure compared to conventional mortgages. The involvement of a third-party Islamic bank or financial institution, as well as the use of contracts such as Murabaha or Ijara, can make the process more intricate and time-consuming.
- Limited Product Options: Islamic mortgages may have limited product options compared to conventional mortgages. This can limit the choices available to borrowers in terms of interest rates, repayment terms, and loan features.
- Restrictions on Property Usage: Some Islamic mortgages may come with restrictions on property usage. For example, certain contracts may prohibit the renting out of the property or using it for commercial purposes.
- Availability of Islamic Scholars: In some cases, borrowers may be required to consult with Islamic scholars to ensure compliance with Sharia law. This can add an additional layer of complexity and delay to the mortgage application process.
It is important for individuals considering an Islamic mortgage to carefully weigh these disadvantages against their personal financial situation and religious beliefs before making a decision.
Islamic Mortgages vs Conventional Mortgages
Islamic mortgages and conventional mortgages differ in several key aspects:
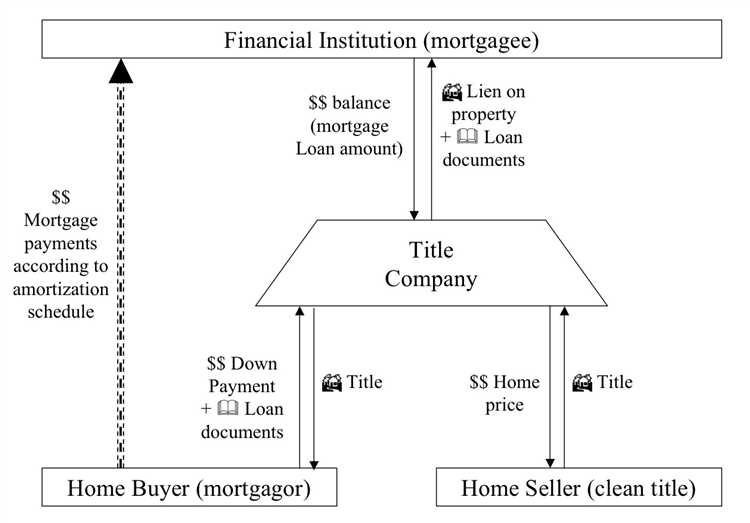
- Interest: One of the fundamental differences between Islamic mortgages and conventional mortgages is the presence of interest. Conventional mortgages charge interest, which is considered riba (usury) and is prohibited in Islamic finance. Islamic mortgages, on the other hand, do not charge interest but may involve other mechanisms such as profit-sharing or rental agreements.
- Ownership: In conventional mortgages, the lender transfers ownership of the property to the borrower, who then pays back the loan with interest over a specified period. In Islamic mortgages, the lender retains ownership of the property until the borrower pays off the loan. The borrower effectively purchases the property from the lender in installments, with each payment increasing their ownership stake.
- Risk-sharing: Islamic mortgages are structured to include risk-sharing between the lender and the borrower. If the property value decreases, both parties bear the loss proportionally. In conventional mortgages, the borrower bears the full risk of property value fluctuations.
- Prohibited activities: Islamic mortgages avoid financing properties that are involved in activities prohibited by Islamic principles, such as the sale of alcohol, pork, or gambling. Conventional mortgages do not have such restrictions.
It’s important to note that the differences between Islamic mortgages and conventional mortgages are based on Islamic principles and may vary depending on the specific financial institutions and products available.
Steps to Obtain an Islamic Mortgage
Obtaining an Islamic mortgage involves several steps that borrowers need to follow. Here is an overview of the process:
- Research and Compare: Start by researching different Islamic mortgage options available in the market. Compare interest rates, terms and conditions, and payment plans offered by various lenders.
- Calculate Affordability: Determine your affordability by evaluating your income, expenses, and financial goals. This step will help you understand how much you can afford and how much you need to borrow.
- Select a Lender: Once you have conducted thorough research, select a lender that offers an Islamic mortgage product that aligns with your requirements.
- Submit Application: Fill out the application form provided by the lender. Ensure that you provide accurate and complete information to avoid any delays in the process.
- Provide Documents: Gather all the required documents such as proof of income, employment details, identification proof, bank statements, etc. Submit these documents along with your application form.
- Assessment and Approval: The lender will assess your application and review your documents. They will evaluate your creditworthiness, financial stability, and the viability of the property you intend to purchase. If everything meets their criteria, they will approve your application.
- Agree on Terms: Once your application is approved, review the terms and conditions of the mortgage agreement. Make sure you understand all the terms, including the repayment plan, penalties, and clauses related to early payment or refinancing.
- Sign the Contract: If you are satisfied with the terms and conditions, sign the mortgage contract along with any other necessary legal documents provided by the lender.
- Arrange for Funds: After signing the contract, you will need to arrange for the funds for the down payment and any other associated costs such as legal fees, appraisal fees, etc.
- Completion and Disbursement: Once all the funds are in place, the lender will disburse the mortgage amount to the seller or the developer, depending on the type of property you are purchasing.
It is important to remember that the exact process and requirements may vary depending on the lender and the specific Islamic mortgage product. It is advisable to consult with a financial advisor or the representative of the chosen lender to fully understand the process and any additional steps that may be involved.
Islamic Mortgage Providers
Islamic mortgage providers, also known as Islamic banks or Islamic finance institutions, offer alternative financing options for individuals and businesses that comply with Islamic principles. These providers offer a range of options that are compliant with Shariah law, providing customers with an ethical and religiously acceptable way to purchase or finance a property.
Here are some of the well-known Islamic mortgage providers:
- Al Rayan Bank: Al Rayan Bank is one of the largest Islamic banks in the UK. They offer a variety of Islamic mortgages, including fixed-rate, variable-rate, and offset options.
- Gatehouse Bank: Gatehouse Bank is a Shariah-compliant bank based in the UK. They offer residential and commercial property finance solutions, including Islamic mortgages.
- Bank Islam Malaysia Berhad: Bank Islam is one of the largest Islamic banks in Malaysia. They provide various Islamic mortgage products, such as home financing-i and property financing-i.
- Dubai Islamic Bank: Dubai Islamic Bank is a leading Islamic bank in the UAE. They offer Islamic mortgage solutions for UAE nationals and expatriates, including options for properties under construction.
These are just a few examples of prominent Islamic mortgage providers. It’s important to research and compare different options to find the provider that best suits your needs and preferences.
Islamic mortgage providers operate in compliance with Islamic finance principles, which prohibit the charging or earning of interest (riba) on financial transactions. Instead, they utilize alternative financing arrangements such as cost-plus financing (Murabaha), lease-to-own (Ijara), and partnership (Musharakah).
Before choosing an Islamic mortgage provider, it is recommended to consult with religious scholars or experts in Islamic finance to ensure that the product and terms are in accordance with Shariah law.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
It is worth noting that the availability and terms of Islamic mortgage products may vary depending on the specific provider and the country or region in which they operate. It is important to thoroughly review the terms and conditions of any Islamic mortgage product before entering into an agreement.
Overall, Islamic mortgage providers offer a unique and ethical financing alternative for individuals and businesses that adhere to Islamic principles. By avoiding interest-based transactions, these providers cater to the needs and preferences of those seeking Shariah-compliant financing options.
Factors to Consider when Choosing an Islamic Mortgage
When choosing an Islamic mortgage, there are several factors that you should consider in order to make an informed decision. These factors can help you determine the suitability of the mortgage for your financial needs and preferences.
- Sharia Compliance: Ensure that the mortgage is compliant with Sharia law. This means that the mortgage should be structured in a way that avoids charging or paying interest, as interest is prohibited in Islamic finance.
- Profit Calculation: Understand how the profit calculations are done by the lender. Different lenders may have different methods of calculating profit, so it’s important to know how it will affect your monthly payments and the overall cost of the mortgage.
- Repayment Options: Consider the repayment options available to you. Islamic mortgages may offer various repayment structures, such as fixed-rate, variable-rate, or even flexible repayment options. Choose an option that suits your financial situation and preferences.
- Early Repayment: Find out if there are any penalties or fees associated with early repayment. Some Islamic mortgages may charge a penalty if you choose to repay the mortgage before the agreed-upon term. Consider this factor if you plan to make early repayments.
- Transparency: Look for a lender that is transparent in its dealings. This means that the lender should disclose all the necessary information about the mortgage, including all the terms and conditions, fees, and charges. Ensure that you fully understand the terms before signing any agreements.
- Support: Consider the level of support provided by the lender. It’s important to choose a lender that offers good customer service and is responsive to your inquiries and concerns throughout the mortgage process.
- Comparison: Take the time to compare different Islamic mortgage options available in the market. Look at the rates, fees, terms, and customer reviews of different lenders. This will help you find the best Islamic mortgage that meets your needs and offers favorable terms.
Taking these factors into consideration will help you make an informed decision when choosing an Islamic mortgage. It’s important to understand the terms and conditions, as well as the overall cost of the mortgage, to ensure that it aligns with your financial goals and beliefs.
Common Misconceptions about Islamic Mortgages
Islamic mortgages, also known as halal mortgages, are a form of financing that adhere to Islamic principles. However, there are several misconceptions surrounding these mortgages. It is important to separate fact from fiction to have a better understanding of how Islamic mortgages work.
1. Islamic mortgages are only for Muslims.
This is a common misconception that Islamic mortgages are only available for Muslims. In reality, Islamic mortgages are available to anyone, regardless of their religious beliefs. It is a financial product that follows Islamic principles and can be accessed by anyone who meets the eligibility criteria.
2. Islamic mortgages are more expensive than conventional mortgages.
Some people believe that Islamic mortgages come with higher costs compared to conventional mortgages. However, this is not necessarily true. While there may be some differences in the fee structure and terms, the overall cost of an Islamic mortgage can be competitive with conventional mortgages. It is important to compare different offers from various lenders to make an informed decision.
3. Islamic mortgages involve hidden fees and charges.
Another misconception is that Islamic mortgages come with hidden fees and charges that are not disclosed upfront. In reality, Islamic mortgages operate on the principles of transparency and fairness. Lenders are required to disclose all fees and charges involved in the mortgage, ensuring transparency and accountability.
4. Islamic mortgages do not allow early repayment.
Contrary to popular belief, Islamic mortgages do allow early repayments or settlements. However, the terms and conditions for early repayments may vary between lenders. It is important to check the terms of the mortgage agreement to understand the options available for early repayment.
5. Islamic mortgages are only available for residential properties.
Some people believe that Islamic mortgages can only be used to finance residential properties. However, Islamic mortgages can also be used to finance commercial properties, as long as they comply with Islamic principles. There are Sharia-compliant financing options available for various types of properties, including residential, commercial, and buy-to-let properties.
6. Islamic mortgages involve a higher risk of foreclosure.
Islamic mortgages are structured in a way to avoid interest-based transactions, which reduces the risk of foreclosure. In case of financial hardship, Islamic lenders typically offer flexible solutions such as payment rescheduling or restructuring to help borrowers avoid foreclosure. It is important to communicate with the lender in case of any financial difficulties to find a suitable solution.
7. Islamic mortgages are not widely available.
Islamic mortgages have gained popularity in recent years, and many financial institutions now offer these products. While availability may vary in different regions, Islamic mortgages are becoming more widely available as the demand for Sharia-compliant financing increases. It is advisable to research and compare different lenders to find the best Islamic mortgage option suitable for your needs.
By understanding these common misconceptions about Islamic mortgages, individuals can make informed decisions when considering this type of financing. It is always recommended to seek professional advice and thoroughly research different options before committing to a mortgage.
Islamic Mortgages and Investment Properties
Islamic mortgages are also available for individuals looking to finance investment properties. These mortgages adhere to the principles of Islamic finance and are structured to be Sharia-compliant.
Investment properties can include residential or commercial properties, and Islamic mortgages for investment properties provide a Halal alternative to traditional mortgages. Here are some key considerations when it comes to Islamic mortgages and investment properties:
- Ownership: Islamic financing follows the principle of shared ownership. Instead of lending money, the Islamic financial institution may purchase the investment property in partnership with the borrower. The ownership is divided between the borrower and the financial institution based on their respective contributions.
- Profit and Loss Sharing: In Islamic mortgages for investment properties, the profit and loss are shared between the borrower and the financial institution based on their ownership percentages. If the property generates rental income, the profits are distributed according to the agreed-upon ratios.
- No Interest: Islamic mortgages for investment properties do not involve charging or earning interest. Instead, the financial institution may charge a rental fee for their share of the property ownership. This fee is agreed upon at the beginning and remains fixed throughout the financing period.
- Additional Costs: When financing an investment property through an Islamic mortgage, both the borrower and the financial institution may also agree on sharing other costs such as property maintenance, insurance, and taxes. These costs are distributed based on their ownership portions.
It is important for individuals considering Islamic mortgages for investment properties to work with Islamic financial institutions or lenders who specialize in Sharia-compliant financing. These institutions will have the expertise to structure the mortgage in accordance with Islamic principles and provide the necessary guidance throughout the financing process.
By choosing an Islamic mortgage for investment properties, individuals can adhere to Islamic principles while still accessing the benefits of real estate investment. It is essential to carefully review the terms and conditions of the mortgage agreement and seek clarification on any aspects that are not clear.
Islamic Mortgages for Non-Muslims
Islamic mortgages are not restricted to Muslims only, and non-Muslims can also benefit from them. These mortgages are based on ethical and transparent principles, making them an attractive option for individuals of all backgrounds and beliefs.
Here are some key points to consider if you are a non-Muslim looking into Islamic mortgages:
- Interest-Free: Islamic mortgages operate on the basis of profit-sharing instead of charging interest. This feature can be particularly appealing to non-Muslims who have ethical concerns about conventional interest-based mortgages.
- Shared Ownership: Islamic mortgages often involve a partnership between the homeowner and the lender. This partnership allows the homeowner to gradually acquire full ownership of the property over time through periodic payments.
- Ethical Criteria: Islamic mortgages adhere to ethical principles, which means that they are committed to avoiding investments in sectors such as alcohol, gambling, and other activities that are deemed unethical or harmful to society.
- Transparent Contracts: Islamic mortgages emphasize transparency in their contracts. All terms and conditions are clearly specified, ensuring that both parties have a clear understanding of their rights and obligations.
It is important for non-Muslims to thoroughly research and understand the specific terms and conditions of Islamic mortgages before entering into any agreement. Consulting with financial experts or mortgage advisors who have experience with Islamic finance can also be beneficial.
Overall, Islamic mortgages offer an alternative that aligns with ethical values and provides a unique approach to financing homeownership. Non-Muslims who value transparency, fairness, and ethical principles may find Islamic mortgages to be a suitable option for their needs.
Islamic Mortgages and Refinancing
Islamic mortgages, also known as Sharia-compliant mortgages or home financing, are designed to adhere to Islamic principles and avoid interest-based transactions. In Islamic finance, interest (usury) is seen as exploitative and forbidden.
When it comes to refinancing with an Islamic mortgage, the process is slightly different compared to traditional mortgages.
What is refinancing?
Refinancing is the process of replacing an existing mortgage with a new one. It is often done to take advantage of better interest rates or to access equity in the property.
Islamic refinancing options
There are different types of refinancing options available in Islamic financing:
- Murabaha: Murabaha is a cost-plus-profit arrangement. In refinancing, it involves selling the property to the financing institution at an agreed-upon price, which is then repurchased by the homeowner on a deferred payment basis.
- Ijara: In Ijara, the financial institution purchases the property from the homeowner and leases it back to them. This lease agreement includes a clause giving the homeowner an option to buy the property at an agreed-upon price.
- Musharakah Mutanaqisah: This is a co-ownership agreement where the financial institution and the homeowner contribute towards the purchase of the property. The homeowner pays rent and buys the financial institution’s share over time until they become the sole owner.
Benefits of refinancing with an Islamic mortgage
- Adherence to Islamic principles: Islamic mortgages provide an alternative for Muslims who want to avoid interest-based transactions in line with their beliefs.
- Favorable terms: Refinancing with an Islamic mortgage can provide access to better terms and rates compared to traditional mortgages.
- Flexible options: There are various refinancing options available in Islamic financing, allowing homeowners to choose the one that suits their needs and goals.
- Equity access: Refinancing can provide homeowners with the opportunity to access the equity in their property for other purposes, such as home renovations or investments.
Conclusion
Islamic mortgages and refinancing offer a viable alternative for Muslim homeowners who want to adhere to Islamic principles while benefiting from homeownership and refinancing opportunities. By understanding the different types of Islamic refinancing options available, homeowners can make informed decisions that align with their beliefs and financial goals.
Islamic Mortgages and Home Insurance
When obtaining an Islamic mortgage, it is important to consider the issue of home insurance. Home insurance provides protection for your property and belongings in case of any unforeseen events or damage. However, traditional home insurance may not be compatible with the principles of Islamic finance.
In conventional mortgages, home insurance is typically included in the mortgage agreement. However, Islamic mortgages operate based on the principles of Islamic finance, which prohibit the charging or payment of interest. Traditional home insurance policies often include interest-based elements, such as charging interest on monthly premiums or investing premiums in interest-based financial instruments. These elements are not permissible in Islamic finance.
As a result, specialized Islamic home insurance products have been developed to cater to the needs of individuals seeking Sharia-compliant options. These insurance products are designed to comply with the principles of Islamic finance, ensuring that they do not involve any elements of interest or prohibited activities.
Islamic home insurance products operate on the basis of the concept of tabarru, where policyholders contribute a portion of their premium into a common fund. This fund is then used to provide coverage and support in case of any covered events or damages. The contributions made by policyholders are considered charitable donations and not the payment of interest.
It is important for individuals seeking Islamic mortgages to ensure that their home insurance is compatible with the principles of Islamic finance. This can be done by reviewing the terms and conditions of the insurance policy and consulting with Islamic finance experts or scholars. They can provide guidance on the compliance of the insurance product and ensure that it meets the ethical and Islamic requirements.
In conclusion, when obtaining an Islamic mortgage, it is necessary to consider home insurance that aligns with the principles of Islamic finance. Specialized Islamic home insurance products are available to cater to the needs of individuals seeking Sharia-compliant options. These insurance products operate based on the concept of tabarru, ensuring that they do not involve any interest-based elements. It is essential to review the terms and conditions of the insurance policy and consult with experts to ensure its compliance with Islamic principles.
Islamic Mortgages and Taxes
Islamic mortgages, also known as halal mortgages, are structured in a way that complies with Islamic laws and principles. As a result, the way taxes are handled in Islamic mortgages may differ from conventional mortgages. Here are some important points to consider regarding Islamic mortgages and taxes:
- No interest payments: Islamic mortgages do not involve the payment or accrual of interest. Instead, they are based on a profit-sharing model or a rent-to-own model. This means that no interest-related tax deductions or benefits apply to Islamic mortgages.
- Treatment of rental income: In a rent-to-own Islamic mortgage, the monthly payments made by the homeowner include both a portion of rent and a portion of the purchase price. The portion of rent is subject to income tax, while the portion of the purchase price is not taxable.
- Capital gains tax: When an Islamic mortgage is used to purchase a property, any potential capital gains from the sale of that property may be subject to capital gains tax. This tax is applied on the difference between the selling price and the original purchase price of the property.
- Zakat obligation: Zakat is an obligatory charitable contribution for Muslims, based on their wealth and assets. In some cases, Islamic mortgages may affect the calculation of Zakat, especially if the homeowner is using the property for investment purposes.
It is important to consult with a tax advisor or Islamic finance expert to understand the specific tax implications of Islamic mortgages in your country or jurisdiction. Laws and regulations may vary, and it is crucial to comply with them to ensure a proper understanding of your tax obligations.
Important Considerations for Islamic Mortgages
When considering an Islamic mortgage, there are several important factors to keep in mind:
- Sharia Compliance: Ensure that the mortgage product is Sharia-compliant and adheres to Islamic principles. It should be approved by a Sharia board or experts knowledgeable in Islamic finance.
- Property Suitability: Determine if the property you want to purchase is suitable for an Islamic mortgage. Some lenders may have restrictions on certain types of properties or locations.
- Terms and Conditions: Carefully review the terms and conditions of the mortgage, including the repayment structure, profit rates, and any additional fees or charges. Ensure that you fully understand the obligations and responsibilities associated with the mortgage.
- Shared Ownership: If you are entering into a shared ownership arrangement, such as a diminishing Musharakah or a partnership agreement, understand the implications and risks involved. It is important to have a clear understanding of how the ownership and profit sharing will work.
- Early Repayment: Check if there are any penalties or charges for early repayment. Some Islamic mortgages may have restrictions or charges if you plan to settle the mortgage earlier than the agreed-upon term.
- Mortgage Provider: Research and choose a reputable and reliable mortgage provider that specializes in Islamic finance. Check their track record, customer reviews, and the level of expertise they have in the field.
- Independent Advice: It is always advisable to seek independent financial advice before entering into any mortgage agreement. An independent advisor can help you understand the implications, risks, and suitability of the mortgage product.
By carefully considering these important factors, you can make an informed decision regarding an Islamic mortgage that aligns with your financial goals and religious beliefs.
FAQ
What is an Islamic mortgage?
An Islamic mortgage, also known as a halal mortgage, is a financial product that is compliant with Islamic law. It is designed for Muslim individuals who want to purchase a property without resorting to conventional mortgage options that involve interest.
How does an Islamic mortgage differ from a conventional mortgage?
An Islamic mortgage is based on the principles of Islamic finance, which prohibit the payment or receipt of interest (riba). Instead of charging interest on a loan, Islamic mortgages use alternative structures such as renting, leasing, or partnership arrangements to enable individuals to buy a property.
What are the main features of an Islamic mortgage?
An Islamic mortgage typically involves an Islamic bank or financial institution purchasing the property on behalf of the customer and then selling it to the customer at an agreed price. The customer makes regular payments to the bank, which consist of both the repayment of the principal amount and a profit margin. Once the customer’s payments are complete, the ownership of the property is transferred to them.
Are there any specific requirements for applying for an Islamic mortgage?
Islamic mortgages are available to both Muslims and non-Muslims. However, the eligibility criteria may vary depending on the financial institution. Some Islamic banks may require applicants to provide proof of income, employment status, and creditworthiness, just like conventional mortgage applications.
What types of Islamic mortgages are available?
There are several types of Islamic mortgages available, including the Murabaha, Musharakah, and Ijara contracts. The Murabaha contract involves the bank selling the property to the customer at a marked-up price, while the Musharakah contract involves the bank partnering with the customer and sharing the costs and risks of owning the property. The Ijara contract is a lease-to-own agreement where the bank purchases the property and leases it to the customer, with the option to buy at the end of the lease term.
Is it more expensive to get an Islamic mortgage compared to a conventional mortgage?
An Islamic mortgage may involve higher upfront costs compared to a conventional mortgage due to the alternative structures and processes used. However, the long-term costs and monthly payments may be similar to conventional mortgages. It is recommended to compare different Islamic mortgage offers and seek advice from experts to make an informed decision.