Psychological trauma is a complex and highly individualized experience that can have a profound impact on a person’s mental and emotional well-being. It refers to the emotional and psychological distress that occurs as a result of experiencing or witnessing a deeply distressing or disturbing event.
Causes of psychological trauma can vary widely, and can include experiences such as physical or sexual abuse, accidents, natural disasters, combat, or the sudden loss of a loved one. Trauma can also result from ongoing experiences of neglect, bullying, or psychological abuse. Each person’s experience of trauma is unique, and what may be traumatic for one person may not be traumatic for another.
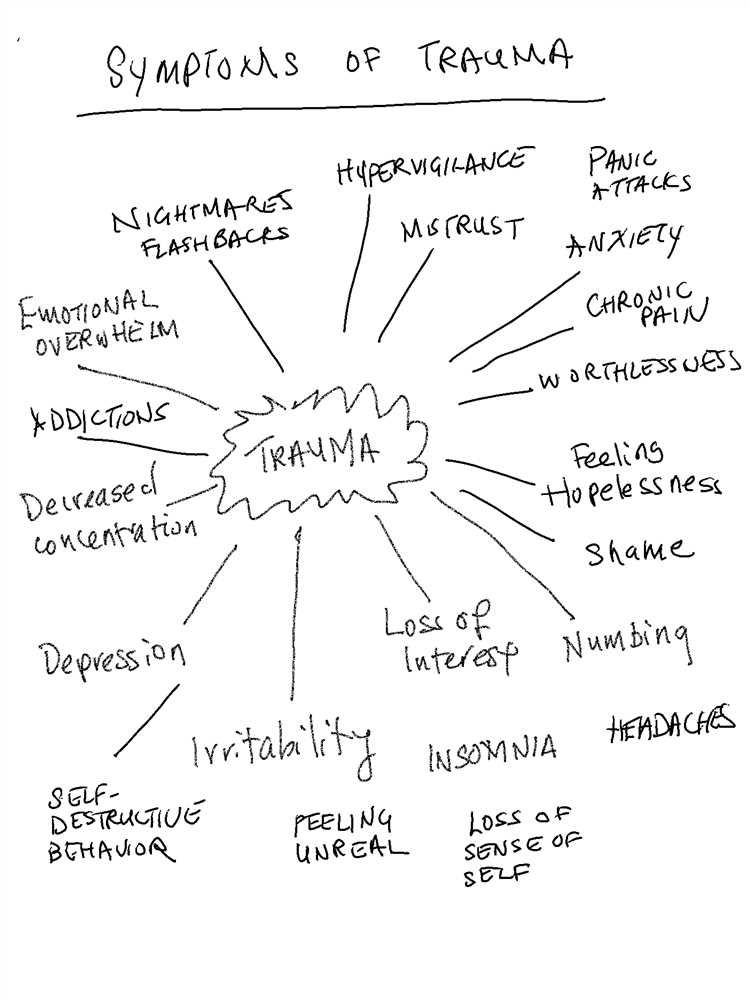
Common symptoms of psychological trauma
include intrusive thoughts or flashbacks, nightmares, difficulty sleeping, irritability, anger, difficulty concentrating, feeling emotionally numb, and avoiding situations or places that remind them of the traumatic event. These symptoms can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life, relationships, and overall well-being.
Treating psychological trauma often involves a combination of therapy and other support services. Therapy can help individuals process and make sense of their traumatic experiences, develop coping mechanisms, and work towards healing and recovery. In some cases, medication may also be prescribed to help manage symptoms such as anxiety or depression.
What is Psychological Trauma?
Pychological trauma refers to the lasting impact of an event or series of events that overwhelms an individual’s ability to cope, often resulting in significant distress and impairment in functioning. These events are often emotionally or physically threatening and can involve actual or perceived harm to oneself or others. Traumatic experiences can be caused by a single incident, such as a violent assault or a natural disaster, or can be the result of ongoing situations, such as childhood abuse or war experiences.
Psychological trauma can have a profound impact on a person’s mental, emotional, and physical well-being. It can disrupt the individual’s sense of safety, trust, and control, leaving them feeling vulnerable and helpless. Trauma can also lead to a variety of symptoms and reactions, which can vary from person to person.
Common symptoms of psychological trauma include:
- Re-experiencing: Intrusive memories, flashbacks, or nightmares related to the traumatic event.
- Avoidance: Avoiding reminders of the traumatic event, including people, places, or activities.
- Hyperarousal: Feeling constantly on edge, easily startled, and having difficulty sleeping or concentrating.
- Negative changes in thoughts and mood: Feeling numb, detached, or experiencing a persistent negative outlook on life.
- Changes in behavior: Engaging in self-destructive behaviors, isolating oneself from others, or having difficulty maintaining relationships.
It is important to note that not everyone who experiences a traumatic event will develop psychological trauma, as individuals have different levels of resilience and coping mechanisms. However, for those who do develop trauma, seeking professional help is crucial for healing and recovery.
Treatment for psychological trauma often involves a combination of therapy approaches and techniques, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), and medication when necessary. These interventions aim to help individuals process and manage their trauma-related symptoms, develop healthier coping strategies, and regain a sense of control and empowerment in their lives.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of psychological trauma, it is important to reach out to a mental health professional for support and guidance. With proper help and support, healing and recovery from psychological trauma is possible.
Causes of Psychological Trauma
- Experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event: Psychological trauma can be caused by directly experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event such as physical or sexual assault, natural disasters, accidents, or acts of violence.
- Childhood trauma: Adverse childhood experiences, such as abuse, neglect, or the loss of a loved one, can lead to psychological trauma later in life.
- War and conflict: People who have served in the military or have been exposed to war or conflict may develop psychological trauma due to the stress and violence they experienced.
- Severe accidents or injuries: Survivors of severe accidents or injuries, such as car crashes or serious falls, can develop psychological trauma as a result of the physical and emotional impact of the event.
- Medical trauma: Trauma can also be caused by experiencing or witnessing traumatic medical events, such as a life-threatening illness, surgery, or medical procedures.
- Chronic abuse or harassment: Continuous exposure to abuse, harassment, or bullying can lead to psychological trauma over time.
- Loss and grief: The death of a loved one, a significant loss, or ongoing grief can cause psychological trauma.
- Interpersonal violence: Being a victim of interpersonal violence, such as domestic violence or sexual assault, can result in psychological trauma.
It’s important to note that not everyone who experiences a traumatic event will develop psychological trauma, as the impact of trauma can vary from person to person. Additionally, individuals may have a higher risk of developing psychological trauma if they have a history of trauma, a lack of social support, prior mental health issues, or other risk factors.
Understanding the causes of psychological trauma can help in the prevention, early intervention, and treatment of trauma-related conditions. It is crucial to seek professional help if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of psychological trauma to address the underlying causes and find effective treatment approaches.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Psychological Trauma
Psychological trauma can manifest in various ways, and it is essential to recognize the symptoms to provide proper support and treatment. The following are common symptoms that may indicate the presence of psychological trauma:
- Flashbacks: Individuals who have experienced trauma may have vivid and distressing memories of the traumatic event. They may feel as if they are reliving the event and have difficulty distinguishing between the past and the present.
- Avoidance: People with psychological trauma may actively avoid situations, places, or people that remind them of the traumatic event. They may isolate themselves and withdraw from activities they once enjoyed.
- Hyperarousal: Those affected by trauma may constantly feel on edge, irritable, or have difficulty concentrating. They may have an exaggerated startle response or experience difficulties with sleep, such as insomnia or nightmares.
- Emotional numbness: Psychological trauma can lead to a sense of detachment and emotional numbness. Individuals may find it challenging to experience emotions or have a reduced range of emotional expression.
- Physical symptoms: Trauma can also manifest as physical symptoms such as headaches, stomachaches, or unexplained pain without any underlying medical cause.
- Changes in mood and behavior: Individuals with psychological trauma may experience sudden changes in their mood. They may become easily irritable, have outbursts of anger, or exhibit reckless behavior. They may also lose interest in activities they once found enjoyable.
- Distorted beliefs and thoughts: Trauma can lead to the development of negative beliefs about oneself, others, and the world. These distorted thoughts may include feelings of guilt, shame, or a sense of doom.
It is important to note that not everyone who experiences trauma will exhibit all of these symptoms. Additionally, the severity and duration of symptoms may vary. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of psychological trauma, it is crucial to seek professional help from a mental health professional who can provide appropriate assessment and treatment.
Types of Psychological Trauma
- Acute Trauma: This type of trauma occurs as a result of a single traumatic event, such as a car accident, natural disaster, or violent attack. Acute trauma can cause significant distress and may lead to symptoms such as flashbacks, nightmares, and an ongoing sense of unease.
- Chronic Trauma: Chronic trauma refers to repeated exposure to traumatic events or ongoing traumatic experiences. This can occur in situations such as ongoing abuse, military combat, or living in a warzone. Chronic trauma can lead to long-lasting negative effects on a person’s mental and emotional well-being.
- Complex Trauma: Complex trauma involves exposure to multiple traumatic events over an extended period, often starting in childhood. Examples of complex trauma include experiencing multiple types of abuse, neglect, or growing up in a chaotic and unstable environment. Complex trauma can have profound and lasting effects on a person’s psychological functioning.
- Secondary Trauma: Secondary trauma, also known as vicarious trauma, occurs when individuals are indirectly exposed to traumatic events through hearing or witnessing accounts of trauma experienced by others. This can happen to professionals working in fields such as healthcare, law enforcement, or disaster response.
Note: It’s important to recognize that trauma is a complex and individual experience, and these categories are not exhaustive. Some people may experience trauma that falls into multiple categories or doesn’t neatly fit into any specific classification. Additionally, trauma can manifest differently in each person, with unique symptoms and reactions.
The Impact of Psychological Trauma on Mental Health
Psychological trauma can have a significant impact on a person’s mental health. Whether it is caused by a single traumatic event or a series of repeated traumas, the consequences can be long-lasting and pervasive.
Emotional Scars: One of the most noticeable impacts of trauma is the emotional scars it leaves behind. Individuals who have experienced trauma may struggle with intense emotions such as fear, anger, sadness, and guilt. These emotions can be overwhelming and may cause mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Behavioral Changes: Trauma can also lead to significant behavioral changes. It may cause individuals to isolate themselves from others, avoid certain situations or triggers, or engage in self-destructive behaviors such as substance abuse. These behavioral changes are often a way for individuals to cope with the distressing emotions associated with trauma.
Cognitive Effects: Trauma can also affect a person’s cognitive functioning. It may impair their ability to concentrate, make decisions, and process information. They may also experience intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, and nightmares related to the traumatic event.
Interpersonal Difficulties: Trauma can cause difficulties in interpersonal relationships. Individuals who have experienced trauma may struggle with trust issues, have difficulty forming and maintaining healthy relationships, and may isolate themselves from others as they fear being hurt again.
Physical Symptoms: The impact of psychological trauma is not limited to mental health. It can also manifest in physical symptoms such as headaches, stomachaches, fatigue, and sleep disturbances. These physical symptoms are often a result of the toll that trauma takes on the body.
Chronic Health Conditions: Long-term exposure to trauma can increase the risk of developing chronic health conditions. Studies have shown a link between trauma and conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. The stress and physiological changes associated with trauma can contribute to the development of these conditions.
- Conclusion: Psychological trauma has far-reaching effects on a person’s mental health. It can lead to emotional scars, behavioral changes, cognitive impairments, difficulties in interpersonal relationships, physical symptoms, and an increased risk of chronic health conditions. Recognizing the impact of trauma on mental health is essential for providing appropriate support and treatment to those who have experienced it.
Treatment Options for Psychological Trauma
Psychological trauma can have a profound impact on individuals, affecting their mental health and overall well-being. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available to help individuals recover from trauma.
1. Therapy: Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is an effective treatment option for psychological trauma. It involves working with a trained therapist who can help individuals process their traumatic experiences, develop coping mechanisms, and regain control over their lives. Different types of therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), and trauma-focused therapy, may be used depending on the individual’s needs and preferences.
2. Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage the symptoms of psychological trauma. Antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and sleep aids can be prescribed to address specific symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. However, medication alone is often not enough and is typically used in conjunction with therapy.
3. Support groups: Joining a support group can provide individuals with psychological trauma the opportunity to connect with others who have experienced similar experiences. Support groups provide a safe and non-judgmental environment where individuals can share their stories, receive validation, and learn from others’ coping strategies. Being part of a support group can foster a sense of belonging, reduce feelings of isolation, and provide a valuable support network.
4. Self-care: Engaging in self-care activities is an essential aspect of healing from psychological trauma. This can include practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques, engaging in regular physical exercise, getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, and engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation. Taking care of oneself physically, emotionally, and mentally can contribute to overall well-being and aid in the recovery process.
5. Education and psychoeducation: Understanding trauma and its effects can be empowering for individuals. Psychoeducation involves learning about the impact of trauma, the common symptoms experienced, and coping strategies. Education and psychoeducation can help individuals gain insight into their experiences, normalize their reactions, and provide them with tools to manage their symptoms effectively.
6. Alternative approaches: Some individuals may find benefit from complementary and alternative approaches such as yoga, acupuncture, meditation, or art therapy. These approaches can help individuals reduce stress, promote relaxation, and foster self-expression, allowing individuals to process their traumatic experiences in a different way.
In conclusion, treatment options for psychological trauma encompass a range of approaches. It is important for individuals to explore different options and find what works best for them in their healing journey. Remember that every individual’s experience with trauma is unique, and there is no one-size-fits-all approach to treatment.
Supporting Individuals with Psychological Trauma
Providing support to individuals who have experienced psychological trauma is essential for their healing and recovery. Here are some ways to support individuals with trauma:
- Listening and Validation:
- It is important to provide a safe and nonjudgmental space for individuals to share their experiences. Active listening and validating their feelings can help them feel heard and understood.
- Empathy and Compassion:
- Show empathy and compassion towards individuals with trauma. Acknowledge their pain and struggles, and let them know that you are there for support.
- Education and Awareness:
- Help individuals understand their trauma by providing educational resources and information about the causes, symptoms, and effects of trauma. This can empower them to gain a better understanding of their experiences.
- Encouraging Professional Help:
- Suggest and encourage individuals to seek professional help from therapists or counselors who specialize in trauma. Professional help can provide the necessary support and guidance for their recovery.
- Creating a Safety Plan:
- Work together with the individual to create a safety plan that outlines strategies for managing triggers and coping with distressing situations. This can help them feel more in control and prepared.
- Building a Support Network:
- Assist the individual in connecting with support groups or other survivors of trauma. Having a support network can provide comfort, understanding, and a sense of belonging.
- Encouraging Self-Care:
- Emphasize the importance of self-care activities such as exercise, healthy eating, practicing relaxation techniques, and engaging in enjoyable hobbies. Encourage individuals to prioritize their well-being.
- Reducing Stigma:
- Challenge and educate others about the misconceptions surrounding trauma. Promote compassion, understanding, and acceptance towards individuals with trauma.
- Patience and Understanding:
- Recognize that healing from trauma is a process that takes time and varies for each individual. Show patience and understanding as they navigate their recovery journey.
- Self-Education:
- Continuously educate yourself about trauma and its impact. This can help you provide informed support and avoid unintentionally triggering or retraumatizing individuals.
Remember, supporting individuals with trauma requires patience, empathy, and understanding. By providing a safe and supportive environment, you can contribute to their healing and recovery.
Coping Strategies for Dealing with Psychological Trauma
Experiencing psychological trauma can be incredibly difficult, but there are coping strategies that can help individuals deal with the aftermath. These strategies can empower individuals to regain a sense of control and work towards healing and recovery.
1. Seek Support
One of the most important coping strategies for dealing with psychological trauma is seeking support. Reach out to trusted friends, family members, or professionals who can provide a listening ear and offer guidance.
2. Practice Self-Care
Self-care is crucial during the healing process. Engage in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as exercising, practicing mindfulness or meditation, taking baths, or engaging in hobbies. Taking care of your physical and emotional well-being is essential in coping with trauma.
3. Educate Yourself
Understanding the nature of psychological trauma can be helpful in the recovery process. Take the time to educate yourself about trauma, its causes, symptoms, and effects. This knowledge can provide a sense of validation and help in finding appropriate treatment and support.
4. Express Emotions
Allowing yourself to feel and express your emotions is an important part of healing. This can be done through journaling, artwork, music, or talking with a therapist. Acknowledging and processing emotions can help in the recovery process.
5. Establish Healthy Boundaries
Setting boundaries is essential in protecting yourself during the healing process. Recognize what you are comfortable with and communicate your needs and limits to others. Surrounding yourself with supportive and understanding individuals can also contribute to your healing.
6. Practice Relaxation Techniques
Engaging in relaxation techniques can help reduce anxiety and stress associated with trauma. This can include deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery. Experiment with different techniques to find what works best for you.
7. Create a Safety Plan
For individuals who have experienced trauma, creating a safety plan can be beneficial. This can involve identifying triggers, developing strategies for managing distressing situations, and establishing emergency contacts. Having a plan in place can help individuals feel more secure and in control.
8. Consider Therapy
Therapy can be an effective tool in dealing with psychological trauma. A trained therapist can provide a safe and supportive environment for individuals to process their experiences and develop healthy coping mechanisms. There are various forms of therapy available, so it’s important to find a therapist who specializes in trauma treatment.
9. Practice Patience and Self-Compassion
Dealing with psychological trauma takes time, so it’s important to be patient with yourself. Healing is not a linear process, and setbacks may occur. Practice self-compassion and remind yourself that you are doing the best you can.
Coping with psychological trauma is a personal journey, and each individual may find different strategies helpful. It’s important to remember that healing is possible and that with support and self-care, individuals can move towards recovery.
Questions and answers
What is psychological trauma?
Psychological trauma refers to the emotional and psychological response to an event or experience that is deeply distressing or disturbing. It can result from a single event or a series of events that overwhelm an individual’s ability to cope.
What are some common causes of psychological trauma?
Psychological trauma can be caused by various events, such as physical or sexual abuse, natural disasters, car accidents, war or combat experiences, the death of a loved one, or witnessing a violent incident. It can also result from ongoing stress, such as living in a violent or dysfunctional environment.
What are the symptoms of psychological trauma?
The symptoms of psychological trauma vary from person to person, but common symptoms include flashbacks or nightmares of the traumatic event, avoidance of reminders of the trauma, feelings of detachment or numbness, anxiety, depression, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and changes in sleep or appetite.
How is psychological trauma treated?
Psychological trauma can be treated using various therapeutic approaches, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), and exposure therapy. Medications may also be prescribed to alleviate symptoms of depression or anxiety. It is important to seek help from a trained mental health professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Is it possible to recover from psychological trauma?
Yes, it is possible to recover from psychological trauma with the right support and treatment. Recovery can vary in duration and intensity for each individual, but with proper therapy, coping strategies, and a strong support system, individuals can regain a sense of control and well-being.