Stress is an undeniable part of life. Whether it’s the pressure of meeting deadlines at work, juggling multiple responsibilities, or dealing with unexpected challenges, stress can have a profound impact on our well-being. To effectively manage stress, it is important to understand its underlying causes and explore coping mechanisms that can help us navigate through difficult times.
The stress and coping theory provides valuable insights into how stress affects individuals and offers practical strategies to deal with it. According to this theory, stress is not solely determined by external events, but also by an individual’s perception and appraisal of those events. In other words, it is not the situation itself that causes stress, but how we interpret and respond to it.
Understanding the stress and coping theory can help us develop healthier ways to cope with stress. It emphasizes the importance of self-awareness and recognizing the signs of stress in our lives. By identifying our triggers and understanding how they affect us, we can take proactive steps to alleviate or manage stress before it becomes overwhelming.
“The greatest weapon against stress is our ability to choose one thought over another.” – William James
Furthermore, the stress and coping theory highlights the significance of coping mechanisms in maintaining psychological well-being. Coping mechanisms are strategies or behaviors we adopt to deal with the demands and challenges of life. While some coping mechanisms may provide temporary relief, others can be detrimental in the long run. It is essential to identify healthy coping mechanisms that promote resilience and adaptive responses to stress.
In conclusion, understanding the stress and coping theory is essential in managing stress effectively. By recognizing the role of perception, self-awareness, and coping mechanisms, we can develop strategies to navigate through stressful situations. Remember, stress is a normal part of life, but how we choose to respond to it can make all the difference in maintaining our well-being.
The Stress and Coping Theory
Stress is a common part of everyday life, and everyone experiences it to some degree. However, not all stress is bad. In fact, some stress can be beneficial in motivating individuals to achieve their goals and perform at their best. The stress and coping theory aims to understand how individuals perceive and respond to stressors, and how they can effectively manage stress.
Understanding Stress
Stress is typically defined as a psychological and physiological response to challenging or threatening situations. It can be caused by a variety of factors such as work-related pressures, relationship difficulties, financial problems, or traumatic events. When individuals perceive a situation as stressful, their body activates the stress response, releasing stress hormones that prepare the body for a fight-or-flight response. This can lead to physical symptoms like increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and heightened alertness.
The Stress and Coping Theory
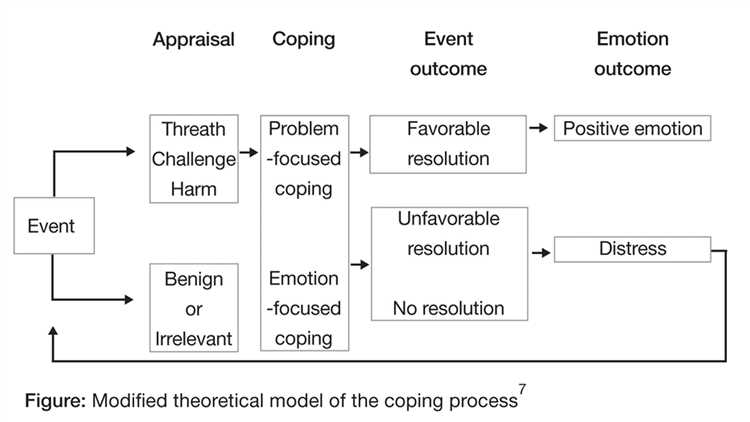
The stress and coping theory, developed by psychologist Richard Lazarus and Susan Folkman, proposes that individuals actively engage in a cognitive and behavioral effort to manage the stress they experience. According to this theory, stress is not solely determined by external events, but by how individuals appraise and cope with those events.
Primary Appraisal:
Primary appraisal involves evaluating the significance of a stressor. Individuals assess whether the stressor is a threat, harm, or challenge. If the stressor is perceived as a threat or harm, it is more likely to result in stress. On the other hand, if the stressor is seen as a challenge, it may lead to a positive response.
Secondary Appraisal:
Secondary appraisal involves assessing one’s ability to cope with the stressor. Individuals evaluate their available resources, skills, and support networks to determine if they can effectively handle the stressor. This appraisal can influence the individual’s level of perceived stress.
Coping Strategies:
Once the stressor is appraised, individuals employ coping strategies to manage the stress. Coping strategies can be categorized into two main types: problem-focused coping and emotion-focused coping. Problem-focused coping aims to address the root cause of the stressor, while emotion-focused coping focuses on regulating one’s emotional response to the stressor.
Managing Stress
Understanding and managing stress is essential for overall well-being. Some effective strategies for stress management include:
- Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to reduce physiological stress responses.
- Engaging in regular physical exercise, which promotes the release of endorphins and improves mood.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, sufficient sleep, and avoiding excessive alcohol or drug use.
- Seeking social support from friends, family, or support groups, as they can provide emotional and practical assistance during stressful times.
- Developing problem-solving skills to address stressors and finding effective solutions.
- Engaging in leisure activities that provide enjoyment and relaxation.
In conclusion, the stress and coping theory highlights the role of cognition and behavior in managing stress. By understanding how individuals perceive and appraise stressors, and employing effective coping strategies, individuals can better manage and reduce stress in their lives.
The Impact of Stress on Health
Stress is a normal reaction that the body experiences in response to various challenges or demands. While short-term stress can actually be beneficial and help us perform better, long-term or chronic stress can have a negative impact on our physical and mental health.
Physical Health
- Cardiovascular System: Prolonged stress can contribute to the development of cardiovascular problems, such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
- Immune System: Chronic stress weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and diseases.
- Digestive System: Stress can disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive system, leading to problems like irritable bowel syndrome, ulcers, and acid reflux.
- Sleep: Stress can interfere with sleep patterns, making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep, leading to sleep deprivation and related health issues.
Mental Health
- Anxiety and Depression: Chronic stress can contribute to the development or worsening of anxiety and depression disorders.
- Cognitive Functioning: Prolonged stress can impair memory, concentration, and decision-making abilities.
- Mood: Stress can lead to irritability, anger, and mood swings.
- Substance Abuse: Some individuals may turn to substance abuse as a means to cope with stress, leading to further mental health problems.
Behavioral Impact
In addition to the physical and mental health consequences, stress can also impact a person’s behavior:
- Increased Risky Behaviors: Some individuals may engage in risky behaviors like unhealthy eating, substance abuse, or excessive alcohol consumption as a way to cope with stress.
- Social Withdrawal: Stress can lead to social isolation and withdrawal from social activities, which can further exacerbate feelings of loneliness and depression.
- Work Performance: Chronic stress can negatively affect work performance, leading to decreased productivity and increased absenteeism.
- Relationships: Stress can strain relationships and lead to conflicts with friends, family, and colleagues.
Managing Stress for Better Health
To minimize the negative impact of stress on health, it is important to develop healthy coping mechanisms:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and avoiding excessive alcohol or drug use can help manage stress.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help reduce stress levels.
- Social Support: Building strong support networks and seeking help from friends, family, or professionals can provide emotional support during stressful times.
- Time Management: Organizing tasks and setting realistic goals can help reduce stress associated with work or daily responsibilities.
By understanding the impact of stress on health and implementing effective stress management strategies, individuals can improve their overall well-being and reduce the negative consequences of chronic stress.
Signs and Symptoms of Stress
Stress is a natural response to life’s challenges and demands. It can manifest in various ways and affect individuals differently. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of stress is crucial for understanding and managing its impact on overall well-being.
Physical Symptoms
- Headaches: Frequent headaches or migraines can be a sign of chronic stress.
- Insomnia: Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep can indicate high levels of stress.
- Increased heart rate: Stress hormones can cause an accelerated heart rate.
- Muscle tension: Stress can lead to muscle tightness or pain, particularly in the neck, shoulders, and back.
- Changes in appetite: Stress can affect appetite, leading to overeating or loss of appetite.
Emotional Symptoms
- Irritability: Feeling easily angered or frustrated, even by small things, is a common emotional symptom of stress.
- Anxiety: Excessive worry, racing thoughts, and a sense of unease can indicate high levels of stress.
- Sadness: Chronic stress can contribute to feelings of sadness or depression.
- Difficulty concentrating: Stress can impair focus and attention, making it hard to concentrate on tasks.
- Emotional instability: Fluctuating moods, ranging from irritability to tearfulness, are common when experiencing stress.
Cognitive Symptoms
- Memory problems: Stress can make it challenging to remember details or concentrate on information.
- Racing thoughts: A mind full of racing thoughts or an inability to quiet the mind can indicate stress.
- Difficulty making decisions: Stress can make decision-making more challenging, leading to indecisiveness.
Behavioral Symptoms
- Increased substance use: Stress may lead to a higher reliance on drugs or alcohol to cope.
- Social withdrawal: Feeling overwhelmed by stress can cause individuals to isolate themselves socially.
- Procrastination: Chronic stress can lead to avoidance behavior and difficulty initiating tasks.
- Changes in sleep patterns: Both insomnia and excessive sleeping can be signs of stress.
- Restlessness: Feeling constantly on edge or unable to relax is a common behavioral symptom of stress.
It’s important to remember that everyone experiences stress differently, and the signs and symptoms can vary from person to person. If you notice any of these signs in yourself or someone you know, it may be beneficial to seek support and develop healthy coping strategies to manage stress effectively.
Understanding the Stress and Coping Theory
The Stress and Coping Theory is a psychological framework that helps us understand how people perceive and respond to stressors in their lives. It was developed by psychologist Richard Lazarus in the 1960s and has since been widely used in the field of stress research and management.
The theory suggests that stress occurs when individuals perceive a demand or event, known as a stressor, as exceeding their ability to cope. This perception is subjective and can vary from person to person, as different individuals may have different levels of resilience and coping strategies.
According to Lazarus, stress involves two primary processes: appraisal and coping. Appraisal refers to the individual’s assessment of the significance of the stressor and its potential impact on their well-being. It involves evaluating whether the stressor is a threat or a challenge and determining the available resources to cope with it.
Coping, on the other hand, refers to the strategies and actions individuals employ to manage the stressor and alleviate its effects. Coping mechanisms can be classified into two broad categories: problem-focused coping and emotion-focused coping. Problem-focused coping involves actively addressing the stressor and attempting to change the situation or reduce its negative impact. Emotion-focused coping, on the other hand, focuses on managing the emotional distress associated with the stressor, rather than directly addressing the stressor itself.
The effectiveness of coping strategies can vary depending on the nature of the stressor and individual factors such as personality, social support, and previous experience. Some individuals may rely more on problem-focused coping, while others may find emotion-focused coping more adaptive in certain situations.
It is important to note that the Stress and Coping Theory does not view stress as purely negative. Lazarus emphasized that stress can also have positive aspects, such as providing motivation and stimulating personal growth. The theory recognizes that individuals may vary in their ability to perceive stressors as challenges rather than threats, and this can influence their overall well-being.
In conclusion, the Stress and Coping Theory provides a framework for understanding how individuals perceive and respond to stressors in their lives. By examining the appraisal and coping processes, researchers and practitioners can design interventions and strategies to help individuals effectively manage and adapt to stress.
Strategies for Managing Stress
Stress can have a significant impact on our mental and physical well-being. Here are some strategies to help manage stress:
- Identify the source of stress: Take some time to reflect and identify the specific situations or factors that are causing stress in your life. This awareness can help you develop targeted strategies for managing those sources of stress.
- Practice stress-reducing techniques: Engage in activities that help you relax and relieve stress. These may include deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies that bring you joy.
- Establish a healthy lifestyle: Regular physical exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep can help reduce stress levels. Taking care of your body sets a strong foundation for managing stress effectively.
- Set realistic goals and priorities: Evaluate your responsibilities and set achievable goals. Avoid taking on too much at once and learn to prioritize tasks. This can help prevent feeling overwhelmed.
- Practice time management: Develop effective time management skills to balance your responsibilities and allocate time for relaxation and self-care. Planning and organizing your tasks can help reduce stress caused by deadlines and time pressure.
- Seek support from others: Reach out to trusted friends, family, or professionals for support. Talking through your stressors and feelings can provide relief and different perspectives.
- Engage in physical activities: Participating in regular physical activities, such as walking, jogging, or dancing, can help release endorphins and reduce stress levels. Find activities that you enjoy and make them a part of your routine.
- Practice self-care: Set aside time each day for activities that you enjoy and that help you relax. This may include reading, listening to music, taking a bath, or any other activity that helps you recharge.
Remember, everyone experiences stress differently, so it’s important to find strategies that work for you. Experiment with different techniques and approaches until you find a combination that helps you effectively manage stress and maintain your well-being.
Building Resilience for Stressful Situations
Resilience refers to the ability to bounce back and recover from difficult or stressful situations. It is a crucial skill to have in today’s fast-paced and ever-changing world. By building resilience, individuals can better cope with stress, manage challenges, and maintain their mental and emotional well-being.
Here are some strategies to help build resilience:
- Develop a support network: Surround yourself with friends, family, or a community who can provide emotional support and understanding during difficult times. Having a support system can make you feel less alone and provide different perspectives and insights.
- Practice self-care: Taking care of yourself physically, mentally, and emotionally is essential for building resilience. Engage in activities that bring you joy and relaxation, such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies. Prioritize self-care to replenish your energy and enhance your overall well-being.
- Manage stress effectively: Learn and practice stress management techniques, such as deep breathing, mindfulness, or engaging in activities that help you relax. By managing stress effectively, you can prevent it from overwhelming you and improve your ability to handle challenging situations.
- Develop problem-solving skills: Enhance your problem-solving abilities by identifying and breaking down complex problems into smaller, manageable tasks. This approach can help reduce feelings of being overwhelmed and increase your confidence in dealing with difficult situations.
- Cultivate optimism: Adopting a positive outlook and seeking opportunities for growth and learning can help build resilience. Focus on the possibilities and potential solutions rather than dwelling on negative aspects of a situation. This mindset shift can empower you to handle stressors more effectively.
- Build flexibility: Recognize that change is a part of life and develop flexibility in your thinking and approach. Being adaptable and open to new perspectives and ideas can help you navigate uncertain or challenging situations with greater ease.
In conclusion, building resilience is essential for effectively coping with stress and managing challenging situations. By developing a support network, practicing self-care, managing stress effectively, enhancing problem-solving skills, cultivating optimism, and building flexibility, individuals can strengthen their resilience and maintain their well-being in the face of adversity.
Seeking Professional Help for Stress Management
Managing stress can be challenging, especially when it becomes overwhelming and starts affecting various aspects of your life. In such situations, seeking professional help can be extremely beneficial in understanding and effectively managing stress.
A professional stress management therapist or counselor can provide you with the necessary tools and strategies to cope with stress. They have the expertise and experience to assess your specific situation, identify the underlying causes of your stress, and develop a personalized plan to address it.
During therapy sessions, you may engage in various techniques, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, relaxation exercises, and mindfulness practices. These approaches can help you identify negative thought patterns, learn new coping skills, and cultivate a sense of calm and balance.
One of the key advantages of seeking professional help for stress management is the objective perspective they offer. They can provide a safe and non-judgmental space for you to express your thoughts and emotions freely. By talking through your stressors with a trained professional, you can gain valuable insights and develop healthier ways of dealing with them.
Furthermore, professional help can assist you in developing a comprehensive stress management plan that not only addresses the immediate symptoms of stress but also focuses on long-term prevention. They can help you establish healthy habits, such as maintaining a balanced lifestyle, engaging in regular physical activity, and practicing effective stress-reducing techniques.
It’s important to remember that seeking professional help for stress management is not a sign of weakness, but rather a proactive step towards taking control of your well-being. As stress can have severe physical and mental health implications, reaching out to a trained professional can significantly improve your overall quality of life.
| Benefits of Seeking Professional Help for Stress Management: |
|
If you feel overwhelmed by stress and its impact on your life, consider seeking professional help. Remember, taking care of your mental and emotional well-being is crucial for leading a fulfilling and balanced life.
Questions and answers
What is the stress and coping theory?
The stress and coping theory is a psychological model that explains how individuals appraise and respond to stressful situations. It suggests that individuals go through a two-step process when faced with stress: they first appraise the stressor and then use coping mechanisms to deal with it.
How does the stress and coping theory help in understanding stress?
The stress and coping theory provides insight into the cognitive and emotional processes that occur when individuals experience stress. It helps us understand why some people are more resilient in the face of stress, while others may become overwhelmed and develop stress-related illnesses. By understanding these processes, we can develop effective strategies to manage stress.
What are the different types of coping mechanisms?
There are several types of coping mechanisms individuals may use to deal with stress. Some common ones include problem-focused coping (taking action to solve the problem), emotion-focused coping (regulating emotions related to the stressor), and meaning-focused coping (finding meaning or a sense of purpose in the stressful situation).
How can I manage my stress using the stress and coping theory?
To manage stress using the stress and coping theory, it is important to first appraise the stressor, understanding its significance and impact. Then, identify coping mechanisms that are effective for you, such as seeking social support, practicing relaxation techniques, or engaging in physical exercise. It’s also important to make self-care a priority, getting enough sleep, eating well, and engaging in activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
Why do some people handle stress better than others?
Some people handle stress better than others due to a combination of factors. These may include genetic predispositions, learned coping skills, social support networks, and individual resilience. Additionally, someone’s perception and interpretation of the stressor can influence how they cope with it. It’s important to remember that everyone’s response to stress is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another.