Depression is a common mental health disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life and overall well-being. While several factors contribute to the development of depression, including genetic and environmental factors, recent research has shown a potential link between vitamin D deficiency and depression.
Vitamin D is a crucial nutrient that plays a vital role in various bodily functions, such as bone health, immune system regulation, and mood regulation. It is primarily synthesized in the skin when exposed to sunlight, but it can also be obtained through diet and supplements.
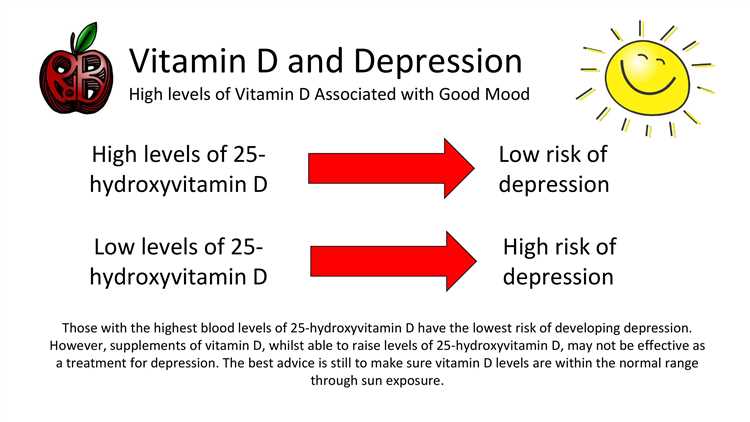
Studies have found that individuals with depression tend to have lower levels of vitamin D compared to those without depression. This relationship suggests that proper levels of vitamin D may play a role in the prevention and treatment of depression. Researchers believe that vitamin D influences the production and release of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, which are known to regulate mood.
While the exact mechanisms through which vitamin D affects depression are still not fully understood, increasing evidence suggests that optimizing vitamin D levels may be an important strategy in managing depression. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate levels of vitamin D supplementation based on individual needs.
The Importance of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. It is commonly known as the “sunshine vitamin” because our bodies can produce it when exposed to sunlight. However, it can also be obtained through certain foods and supplements.
One of the main functions of vitamin D is to help regulate the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, which are essential for strong bones and teeth. Without adequate levels of vitamin D, our bodies cannot properly absorb these minerals, leading to a higher risk of bone disorders such as osteoporosis and rickets.
Vitamin D also plays a vital role in supporting our immune system. It helps to regulate immune responses, reducing the risk of infections and autoimmune diseases. Studies have shown that individuals with low levels of vitamin D are more susceptible to illnesses such as the common cold, influenza, and even certain cancers.
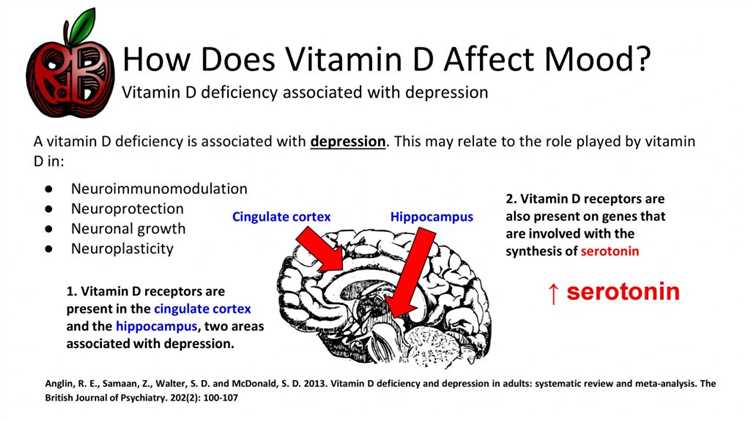
Furthermore, vitamin D has been linked to mental health and depression. Research suggests that vitamin D deficiency may increase the risk of developing depression and other mood disorders. It is believed that vitamin D helps regulate neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin, which plays a key role in mood regulation.
In addition to its physical and mental health benefits, vitamin D also plays a role in maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system. Studies have shown that individuals with low levels of vitamin D have an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. Vitamin D helps to regulate blood pressure, reduce inflammation, and improve overall cardiovascular function.
It is important to note that while sunlight is an excellent source of vitamin D, excessive exposure without protection can lead to skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer. Therefore, it is essential to strike a balance between getting enough sunlight for vitamin D synthesis and protecting our skin from harmful UV rays.
Overall, vitamin D is a vital nutrient that plays a crucial role in various aspects of our health. Ensuring adequate vitamin D levels through sunlight, diet, or supplementation can help support our bones, boost our immune system, improve our mental health, and promote overall well-being.
Understanding Depression
Depression is a mental health disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities. It affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves, and can lead to various emotional and physical problems.
Depression can occur due to a combination of genetic, biological, environmental, and psychological factors. It affects people of all ages, races, and socioeconomic backgrounds.
Some common symptoms of depression include:
- Feelings of sadness or emptiness
- Lack of energy
- Loss of interest in activities
- Changes in appetite or weight
- Sleep disturbances
- Irritability or restlessness
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Feelings of guilt or worthlessness
- Physical symptoms such as headaches or stomachaches
Depression is a serious condition and can significantly impact a person’s daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. It is important to seek help from a healthcare professional if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of depression.
Treatment for depression often includes a combination of therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. In some cases, increasing vitamin D levels through supplementation may also be beneficial.
Research has shown that there may be a link between vitamin D deficiency and depression. Vitamin D plays a crucial role in brain function and is involved in the regulation of mood. Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with an increased risk of depression.
It is important to note that while vitamin D supplementation may be helpful for some individuals with depression, it is not a substitute for proper medical treatment. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements or treatments for depression.
The Role of Vitamin D in Mental Health
Vitamin D is a crucial nutrient that plays a significant role in maintaining good overall health. It is well-known for its role in promoting strong bones and a healthy immune system. However, recent research has also highlighted the importance of vitamin D in maintaining good mental health.
Studies have found a strong association between vitamin D deficiency and mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. Research suggests that vitamin D plays a vital role in the regulation of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that is responsible for mood regulation. Low levels of vitamin D can lead to decreased serotonin levels, which can contribute to the development of mental health issues.
In addition to its direct role in mood regulation, vitamin D also plays a crucial role in brain development and function. It has been found to have neuroprotective effects, helping to protect against cognitive decline and the development of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Furthermore, vitamin D deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of seasonal affective disorder (SAD), a type of depression that occurs during the winter months when sunlight exposure is limited. Sunlight is the primary source of vitamin D, and reduced sunlight exposure during the winter can lead to vitamin D deficiency and subsequently increase the risk of SAD.
Increasing evidence suggests that supplementation with vitamin D can improve symptoms of depression and other mental health disorders. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen, as proper dosing is crucial to achieve optimal results.
In conclusion, vitamin D plays a crucial role in mental health. Its deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. Supplementing with vitamin D may be beneficial for individuals with mental health issues, but professional guidance is necessary to ensure proper dosage and effectiveness.
Research Findings on Vitamin D and Depression
Several studies have explored the relationship between vitamin D levels and depression. Here are some key research findings:
1. Correlation between vitamin D deficiency and depression:
Multiple studies have found an association between low vitamin D levels and an increased risk of developing depression. Researchers have observed that individuals with depression often have lower levels of vitamin D compared to those without depression.
2. Potential role of vitamin D in regulating mood:
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in the regulation of mood. Studies suggest that vitamin D receptors are present in various brain regions associated with mood, including the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Vitamin D may help regulate the release of neurotransmitters and modulate inflammation, both of which have been implicated in depression.
3. Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and vitamin D:
Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that occurs in specific seasons, usually in winter when sunlight exposure is reduced. Research shows that SAD may be linked to vitamin D deficiency due to reduced sun exposure. Supplementing with vitamin D has been found to improve symptoms of SAD in some individuals.
4. Vitamin D supplementation and depressive symptoms:
Several studies have investigated the effects of vitamin D supplementation on depressive symptoms. While results have been mixed, some clinical trials have shown that supplementing with vitamin D may help improve symptoms of depression, especially in individuals with low vitamin D levels.
5. Possible mechanisms underlying the vitamin D-depression link:
Researchers speculate that the relationship between vitamin D and depression may be due to various mechanisms. Vitamin D deficiency may lead to dysregulation of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, which plays a crucial role in mood regulation. Additionally, vitamin D deficiency may contribute to inflammation and oxidative stress, which are associated with the development and progression of depression.
6. The need for further research:
While the existing research indicates a potential link between vitamin D and depression, more studies are needed to establish a definitive cause-and-effect relationship. Randomized controlled trials with larger sample sizes and longer duration are necessary to determine the effectiveness of vitamin D supplementation as a treatment for depression.
How Vitamin D Deficiency Can Contribute to Depression
Vitamin D is a crucial nutrient that plays a significant role in our overall health and well-being. It is naturally produced in our bodies when our skin is exposed to sunlight. However, many people around the world suffer from vitamin D deficiency, especially in regions with limited sunlight exposure or during the winter months.
Research suggests that there is a strong link between vitamin D deficiency and depression. When our bodies do not receive enough vitamin D, it can lead to disturbances in brain chemistry, affecting our mood and emotions. Here are several ways in which vitamin D deficiency can contribute to depression:
- Decreased serotonin levels: Vitamin D helps regulate serotonin, a neurotransmitter responsible for feelings of happiness and well-being. When our bodies lack vitamin D, serotonin production may decrease, contributing to depression.
- Inflammatory response: Vitamin D deficiency can lead to an increased inflammatory response in the body. Chronic inflammation has been linked to depression and other mental health disorders.
- Impaired cognitive function: Vitamin D is essential for healthy brain function. Without adequate levels of vitamin D, cognitive function can be impaired, leading to symptoms of depression.
- Seasonal affective disorder (SAD): SAD is a type of depression that occurs during specific seasons, typically when sunlight exposure is limited. Vitamin D deficiency is commonly associated with SAD.
It is important to note that while vitamin D deficiency can contribute to depression, it is not the sole cause. Depression is a complex condition with various factors at play, including genetics, lifestyle, and life events. However, ensuring adequate vitamin D levels through sunlight exposure, diet, or supplementation can be beneficial for overall mental health and well-being.
It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance on managing vitamin D levels and addressing any symptoms of depression or related conditions.
The Benefits of Supplementing with Vitamin D
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining good health. While our bodies can produce vitamin D when exposed to sunlight, many people do not get enough sun exposure due to their lifestyle or geographical location. This is where vitamin D supplementation can be beneficial.
Supplementing with vitamin D can provide a range of health benefits, including:
- Improved bone health: Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption and helps maintain strong and healthy bones. It can reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures, especially in older adults.
- Enhanced immune function: Vitamin D plays a crucial role in supporting the immune system and promoting a healthy immune response. It can help reduce the risk of infections and autoimmune diseases.
- Reduced risk of depression: There is evidence to suggest a link between vitamin D deficiency and depression. Supplementing with vitamin D may help improve mood and reduce the symptoms of depression.
- Protection against chronic diseases: Vitamin D has been associated with a lower risk of various chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
- Support for brain health: Adequate vitamin D levels have been linked to better cognitive function and a reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease.
It’s important to note that while vitamin D supplementation can be beneficial, it should be done in consultation with a healthcare professional. They can help determine the appropriate dosage based on individual needs and monitor vitamin D levels through blood tests.
In conclusion, supplementing with vitamin D can provide various health benefits, including improved bone health, enhanced immune function, reduced risk of depression, protection against chronic diseases, and support for brain health. Incorporating vitamin D supplementation into your routine can help ensure optimal levels of this essential nutrient.
Getting Enough Vitamin D: Natural Sources and Supplements
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. It has been linked to many aspects of our physical and mental health, including depression. To ensure that you are getting enough Vitamin D, it is important to include natural sources in your diet and consider supplements if necessary.
Natural Sources of Vitamin D:
- Sunlight: The best natural source of Vitamin D is sunlight. When your skin is exposed to sunlight, it produces Vitamin D naturally. However, it is important to be cautious about excessive sun exposure and always wear sunscreen to protect your skin from harmful UV rays.
- Fatty Fish: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of Vitamin D. They not only provide you with the necessary nutrients but also offer other health benefits such as omega-3 fatty acids.
- Egg yolks: Egg yolks are another good source of Vitamin D. Consuming eggs regularly can help increase your Vitamin D levels.
- Mushrooms: Certain types of mushrooms, such as shiitake and maitake, are known to contain Vitamin D. Including them in your diet can be a great way to boost your Vitamin D intake.
Vitamin D Supplements:
If you are unable to get enough Vitamin D from natural sources, you may consider taking supplements. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements. They can guide you about the appropriate dosage and help you understand if you actually need a supplement based on your individual needs and health condition.
Conclusion:
Getting enough Vitamin D is crucial for your overall health and well-being. While sunlight and natural food sources are the best ways to obtain Vitamin D, supplements can be considered if necessary. Remember to maintain a balanced diet, practice safe sun exposure, and consult with a healthcare professional to ensure you are meeting your Vitamin D needs.
Consult with a Healthcare Professional
If you are experiencing symptoms of depression or are concerned about your vitamin D levels, it is important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional. They will be able to assess your individual situation and provide personalized advice and recommendations.
A healthcare professional can help you determine if you are at a higher risk for vitamin D deficiency, such as if you have limited sun exposure, certain medical conditions, or take medications that may affect vitamin D absorption. They can also order blood tests to measure your vitamin D levels and diagnose any potential deficiencies.
If your healthcare professional determines that you have low vitamin D levels or are at risk for deficiency, they may recommend supplementation. They can provide guidance on the appropriate dosage and duration of supplementation based on your specific needs.
It is important to note that while vitamin D supplementation may be beneficial for some individuals, it is not a magic cure for depression. It should be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, which may also include therapy, lifestyle changes, and other interventions recommended by your healthcare professional.
Remember, self-diagnosis and self-treatment can be harmful, especially when it comes to mental health. By consulting with a healthcare professional, you can ensure that you are receiving appropriate care and support for your unique needs.
Questions and answers
Can low vitamin D levels lead to depression?
Yes, low vitamin D levels have been linked to an increased risk of depression. Several studies have found a significant association between low vitamin D levels and symptoms of depression. It is believed that vitamin D may play a role in the brain’s production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood.
How does vitamin D affect mental health?
Vitamin D is believed to play a role in the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood. Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with an increased risk of conditions such as depression and seasonal affective disorder. Vitamin D may also have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects, which can contribute to better mental health.
What are the symptoms of vitamin D deficiency?
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency can vary, but common signs may include fatigue, muscle weakness, bone pain, and a depressed mood. Some people may also experience frequent infections, hair loss, and difficulty healing wounds. It is important to note that these symptoms can be caused by other factors as well, so it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Can increasing vitamin D levels help improve symptoms of depression?
There is evidence to suggest that increasing vitamin D levels can improve symptoms of depression, especially in individuals with low levels of this vitamin. However, it is important to note that vitamin D supplementation alone may not be sufficient and should be combined with other treatments for depression, such as therapy or medication. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
What are some natural sources of vitamin D?
Natural sources of vitamin D include sunlight exposure, as the skin can produce vitamin D when exposed to UVB rays. Some dietary sources of vitamin D include fatty fish (such as salmon and mackerel), fortified dairy products, eggs, and mushrooms. However, it can be difficult to obtain sufficient vitamin D through diet alone, especially for individuals with limited sun exposure.