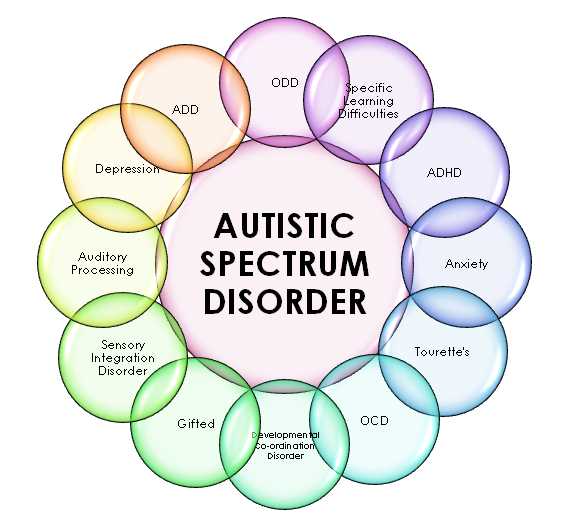
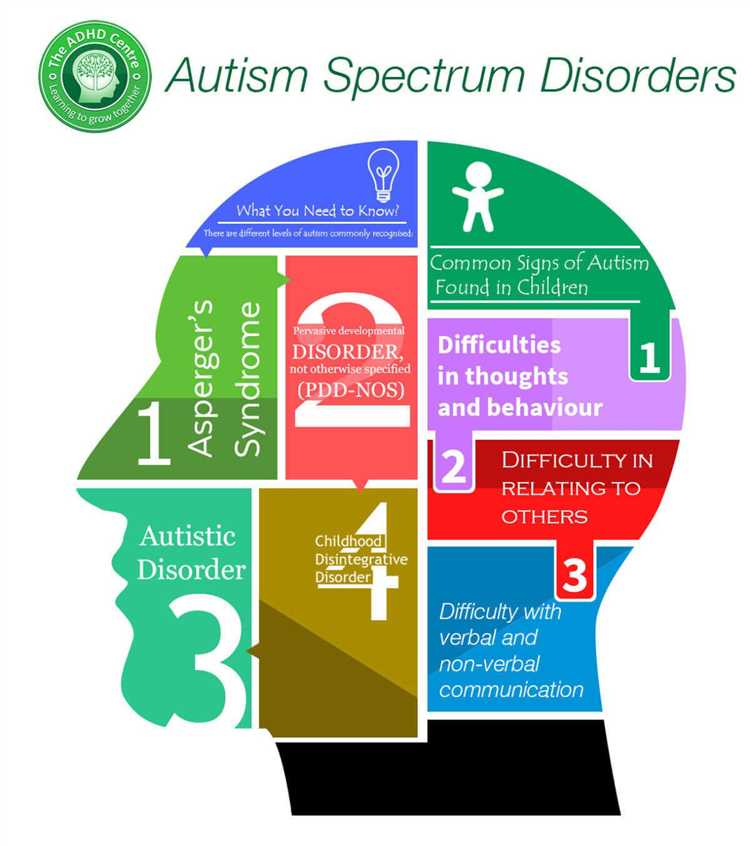
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects individuals’ social interaction, communication skills, and behavior. It is typically diagnosed in early childhood, usually by the age of 2 or 3. ASD is a lifelong condition that affects people across all racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic groups.
One of the main symptoms of ASD is a difficulty in social interaction. Children with ASD may struggle with making eye contact, interpreting facial expressions, and understanding social cues. They may also have difficulty developing and maintaining relationships with others. Additionally, individuals with ASD may exhibit repetitive behaviors, restricted interests, and a heightened sensitivity to sensory stimuli.
The exact cause of ASD is not yet fully understood, but it is thought to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Research has shown that individuals with ASD often have certain genetic mutations or abnormalities that affect the development and function of their brain. However, it is believed that other factors, such as prenatal and perinatal complications, maternal infections during pregnancy, and exposure to certain environmental toxins, may also play a role in the development of ASD.
There is currently no cure for ASD, but there are treatments and interventions that can help individuals with ASD improve their symptoms and quality of life. Early intervention is key, as it can help children with ASD develop necessary skills and overcome challenges. Some common treatments for ASD include behavioral therapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy, and medication to manage certain symptoms, such as anxiety or hyperactivity.
In conclusion, Autism Spectrum Disorder is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder that affects individuals’ social interaction, communication skills, and behavior. While the exact cause is still unknown, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Although there is no cure for ASD, early intervention and various therapies can help individuals with ASD improve their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects the way individuals perceive and interact with the world. It is characterized by difficulties in social interaction and communication, as well as restricted and repetitive behavior patterns.
Symptoms:
- Social difficulties: Individuals with ASD may have difficulties with social interaction, including difficulties with nonverbal communication, lack of empathy, and difficulty making and maintaining friendships.
- Communication challenges: Many individuals with ASD struggle with verbal and nonverbal communication. They may have delayed speech or be nonverbal, and may have difficulty understanding and using gestures, facial expressions, and tone of voice.
- Repetitive behavior: Individuals with ASD often engage in repetitive behaviors or have narrow interests. They may have specific routines or rituals that they need to follow, and may become upset or anxious if these routines are disrupted.
- Sensory sensitivities: Many individuals with ASD are sensitive to sensory stimuli, such as noise, lights, smells, or textures. They may be over- or under-responsive to certain sensory inputs, leading to discomfort or distress.
Causes:
The exact cause of ASD is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some research suggests that certain genes may increase the risk of developing ASD, but environmental factors may also play a role, such as prenatal exposure to certain substances or complications during pregnancy or delivery.
Treatments:
While there is no cure for ASD, early intervention and appropriate support can greatly improve the quality of life for individuals with ASD. Treatment options may include behavioral therapy, speech and language therapy, occupational therapy, and medication for managing associated symptoms, such as anxiety or attention difficulties.
| Symptoms | Causes | Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| Social difficulties | Genetic and environmental factors | Behavioral therapy, social skills training |
| Communication challenges | Prenatal exposure, complications during pregnancy or delivery | Speech and language therapy, augmentative and alternative communication |
| Repetitive behavior | Applied behavior analysis, cognitive-behavioral therapy | |
| Sensory sensitivities | Sensory integration therapy, environmental adaptations |
In conclusion, Autism Spectrum Disorder is a complex disorder that affects individuals in various ways. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help individuals with ASD receive the support they need to navigate the world and live fulfilling lives.
Symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects social interaction, communication, and behavior. The symptoms of ASD can vary widely from person to person, but there are some common signs and behaviors to look out for.
- Social Challenges: Individuals with ASD often have difficulty with social interactions. They may struggle with making eye contact, understanding social cues, and forming and maintaining relationships. They may also have difficulty understanding and empathizing with the emotions and perspectives of others.
- Communication Difficulties: Many individuals with ASD have difficulty with verbal and nonverbal communication. They may have delayed speech development or difficulty initiating and maintaining conversations. They may also have a tendency to take language literally, leading to misunderstandings.
- Repetitive Behaviors: Individuals with ASD often engage in repetitive behaviors or restrictive, fixated interests. These behaviors can include repetitive motions (such as hand flapping or rocking), adherence to strict routines or rituals, or intense interests in specific topics.
- Sensory Sensitivities: Many individuals with ASD are highly sensitive to sensory stimuli, such as loud noises, bright lights, or certain textures. They may react strongly to these stimuli or seek out certain sensory experiences.
- Difficulty with Changes: Individuals with ASD often struggle with changes to routine or unexpected events. They may become upset or anxious in response to changes and may have difficulty adapting to new situations or environments.
It’s important to remember that the symptoms of ASD can vary greatly from person to person. Some individuals may exhibit all of these symptoms, while others may only exhibit a few. Additionally, the severity of the symptoms can also vary, with some individuals experiencing mild difficulties while others have more significant challenges.
If you suspect that you or someone you know may have ASD, it’s important to seek a professional evaluation for an accurate diagnosis. Early intervention and appropriate support can make a big difference in managing the symptoms and improving quality of life for individuals with ASD.
Possible Causes of Autism Spectrum Disorder
The exact cause of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is still unknown, but researchers have identified several factors that may play a role in its development. These factors include:
- Genetics: Studies have shown that there is a genetic component to ASD. Certain genes are believed to increase the risk of developing the disorder. However, no single gene has been found to be responsible for all cases of ASD.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors during pregnancy or early childhood may increase the risk of developing ASD. These factors include prenatal exposure to certain drugs or chemicals, maternal infections during pregnancy, and complications during birth.
- Brain Development: Abnormalities in brain structure or function have been observed in individuals with ASD. It is believed that these abnormalities may disrupt the development of neural circuits that are involved in communication and social interaction.
- Immune System Dysfunction: Some studies have suggested a link between immune system dysfunction and ASD. It is believed that an abnormal immune response may contribute to the development of the disorder.
It is important to note that these factors do not directly cause ASD, but rather increase the risk of developing the disorder. Additionally, it is likely that ASD is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, rather than a single cause.
Researchers are still conducting studies to better understand the causes of ASD. By gaining a better understanding of these causes, it may be possible to develop more effective treatments and interventions for individuals with ASD.
Treatments for Autism Spectrum Disorder
There is no known cure for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), but there are various treatment options available that can help individuals with ASD manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. These treatments can also assist in developing their communication, social, and coping skills.
1. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA):
ABA is a widely-used behavioral therapy that focuses on breaking down skills into smaller components and then teaching them through repetition and positive reinforcement. ABA therapy can help individuals with ASD improve their language and communication, social interaction, and daily living skills.
2. Occupational Therapy (OT):
OT helps individuals with ASD develop skills required for day-to-day activities, such as dressing, eating, and personal hygiene. This therapy also targets sensory integration to help individuals with sensory sensitivities manage their responses to different sensory stimuli.
3. Speech Therapy:
Speech therapy assists individuals with ASD in developing communication skills, including expressive language (verbal or non-verbal), receptive language, and social communication. This therapy focuses on improving language comprehension, articulation, and pragmatics.
4. Medication:
Although there is no medication that can cure autism, certain medications can help manage specific symptoms associated with ASD. Medications such as antipsychotics may be prescribed to address irritability, aggression, and self-injurious behaviors. Other medications may be used to manage ADHD symptoms or anxiety.
5. Social Skills Training:
Individuals with ASD often struggle with social interaction and communication. Social skills training aims to teach social cues, empathy, appropriate behavior, and social problem-solving techniques. This training can be delivered in a group or individual setting.
6. Alternative and Complementary Therapies:
Some individuals with ASD may benefit from alternative or complementary therapies, such as dietary interventions, nutritional supplements, acupuncture, or yoga. However, it is important to note that the effectiveness of these therapies may vary, and individuals should consult with healthcare professionals before trying them.
7. Parent-Mediated Interventions:
Parents play a crucial role in the development and well-being of their child with ASD. Parent-mediated interventions involve providing parents with strategies and techniques to support their child’s learning and development at home. These interventions can help enhance communication, social skills, and behavioral management.
8. Educational Support:
Children and adults with ASD often require specialized educational support. This can include individualized education plans (IEPs), special education classrooms, or educational programs tailored to the needs of individuals with ASD. These educational supports aim to provide a structured learning environment and personalized instruction.
It is important to remember that each individual with ASD is unique and may benefit from different combinations of treatments. Therefore, it is crucial to work closely with healthcare professionals and therapists to develop a personalized treatment plan based on the individual’s specific needs and goals.
Behavioral Therapies for Autism Spectrum Disorder
Behavioral therapies are a common and effective treatment approach for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). These therapies focus on changing or improving specific behaviors, such as communication skills, social interactions, and repetitive behaviors. There are several types of behavioral therapies that can be used to help individuals with ASD, including:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): ABA is the most widely used and well-established behavioral therapy for ASD. It involves breaking down complex behaviors into smaller, manageable components and teaching those components systematically. ABA is highly individualized and focuses on promoting positive behaviors while decreasing negative behaviors.
- Discrete Trial Training (DTT): DTT is a specific type of ABA that involves breaking skills or tasks into discrete, teachable steps. Each step is taught and reinforced individually, allowing the individual with ASD to master one step before moving on to the next. DTT is often used to teach functional skills, such as self-care or academic tasks.
- Positive Behavioral Support (PBS): PBS focuses on identifying and modifying environmental factors that may contribute to challenging behaviors in individuals with ASD. It aims to create a supportive and predictable environment that promotes positive behaviors and reduces the occurrence of problem behaviors. PBS often involves creating behavior support plans and implementing strategies to teach alternative behaviors.
- Social Skills Training (SST): SST targets the development and improvement of social skills in individuals with ASD. It involves teaching skills such as initiating and maintaining conversations, taking turns, sharing, and interpreting nonverbal cues. SST can be delivered in group settings or on an individual basis, depending on the individual’s needs and preferences.
In addition to these behavioral therapies, other treatment approaches such as speech therapy, occupational therapy, and medication management may also be recommended for individuals with ASD. It is important to work closely with a multidisciplinary team of professionals to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses the specific needs and challenges of each individual with ASD.
It is worth noting that the effectiveness of behavioral therapies can vary greatly from person to person. Some individuals with ASD may make significant improvements with intensive behavioral interventions, while others may show more modest gains. Additionally, the earlier the interventions are started, the better the outcomes tend to be.
In conclusion
Behavioral therapies play a crucial role in the treatment of autism spectrum disorder. These therapies focus on teaching and reinforcing positive behaviors while reducing problem behaviors. By addressing specific areas of challenge, such as communication and social interactions, individuals with ASD can improve their overall quality of life and reach their full potential.
Medications for Autism Spectrum Disorder
While there is no cure for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), medications can be prescribed to help manage certain symptoms associated with the condition. However, it’s important to note that medication should always be used in conjunction with other forms of therapy and support.
Common medications for ASD:
- Antipsychotic medications: These medications are often prescribed to help manage behaviors such as aggression, self-injury, and irritability. They help regulate certain brain chemicals and can help improve social interactions and communication skills.
- Stimulant medications: Stimulants are commonly prescribed to manage symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) that often co-occur with ASD. These medications can help improve focus, attention, and impulse control.
- Antidepressant medications: Antidepressants may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of anxiety and depression that can occur in individuals with ASD. These medications can help improve mood and overall well-being.
- Anti-anxiety medications: Individuals with ASD may experience high levels of anxiety, and anti-anxiety medications can help reduce feelings of fear and panic. These medications can also help improve sleep patterns and reduce restlessness.
- Sleep medications: Sleep disturbances are common in individuals with ASD, and sleep medications may be prescribed to help regulate sleep patterns and improve overall quality of sleep.
It’s important to work closely with a healthcare professional when considering medication options for ASD. They will be able to assess symptoms, conduct a thorough evaluation, and recommend the most appropriate medication based on individual needs and circumstances. Regular monitoring and adjustments may be necessary to ensure effectiveness and minimize side effects.
Please note that autism is a complex spectrum disorder, and medication effects can vary from individual to individual. It’s important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before starting or changing any medication regimen.
In conclusion: While medications can be a helpful tool in managing symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder, they should always be used in conjunction with other therapies and interventions. It’s important to remember that each individual with ASD is unique, and a personalized treatment plan should be developed in consultation with healthcare professionals and caregivers.
Alternative Therapies for Autism Spectrum Disorder
While there is no cure for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), there are a variety of alternative therapies that can help individuals with ASD improve their symptoms and quality of life. These alternative therapies focus on addressing the core deficits of ASD, such as difficulties with social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors.
1. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
ABA is a widely recognized and evidence-based therapy for individuals with ASD. It involves breaking down behaviors into smaller components and teaching new skills through positive reinforcement and repetition. ABA therapy can help improve social skills, language development, and reduce challenging behaviors.
2. Occupational Therapy (OT)
Occupational therapy aims to improve an individual’s ability to perform everyday activities and enhance their participation in school, work, and social environments. OT for ASD may address sensory sensitivities, motor skills, self-care skills, and social skills through various activities and interventions.
3. Speech Therapy (ST)
Speech therapy focuses on improving communication skills, including speech, comprehension, and social interaction. Speech therapists may use a variety of techniques, such as picture cards, visual aids, and play-based activities to develop language skills and enhance communication abilities.
4. Sensory Integration Therapy
Sensory integration therapy aims to address sensory sensitivities and challenges that individuals with ASD may experience. It involves exposing individuals to various sensory stimuli in a controlled environment to help them regulate their responses and improve sensory processing abilities.
5. Dietary Interventions
Some individuals with ASD may benefit from dietary interventions, such as eliminating certain foods or adding supplements. While the research in this area is limited, some parents and caregivers have reported improvements in behavior, gastrointestinal symptoms, and overall well-being with certain dietary modifications.
6. Music Therapy
Music therapy involves using music and musical activities to support individuals with ASD in improving their social, emotional, cognitive, and communication skills. Music can be a powerful tool for self-expression and can help individuals with ASD connect with others and regulate their emotions.
7. Animal-Assisted Therapy
Animal-assisted therapy involves interactions with trained animals, such as dogs or horses, to provide emotional support and improve social skills and emotional well-being. These therapy sessions can help individuals with ASD develop empathy, build relationships, and reduce anxiety and stress.
8. Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation practices can help individuals with ASD develop self-awareness, reduce anxiety, improve focus, and enhance overall well-being. These practices involve paying attention to the present moment without judgment and can be beneficial for individuals with ASD in managing their emotions and reducing stress.
9. Biofeedback
Biofeedback therapy involves monitoring and controlling specific physiological functions, such as heart rate or muscle tension, through visual or auditory feedback. This therapy can help individuals with ASD become more aware of their physiological processes and learn techniques to regulate their responses and manage stress.
10. Social Skills Training
Social skills training focuses on teaching individuals with ASD the skills necessary to navigate social interactions and build meaningful relationships. This therapy may involve role-playing, modeling appropriate behaviors, and providing guidance and feedback to improve social communication and interaction.
It is important to note that alternative therapies may not work for everyone with ASD, and it is essential to consult with professionals and experts to determine the most appropriate therapies for individual needs.
Social Support for Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often face unique challenges when it comes to social interaction and communication. However, social support can play a crucial role in their overall well-being and quality of life. Here are some ways in which social support can be beneficial for individuals with ASD:
- Family Support: Families play a significant role in the life of an individual with ASD. They can provide emotional support, understanding, and guidance, which can help in managing the challenges associated with ASD. Families can also actively participate in therapy sessions and educational programs to better understand and assist their loved ones with ASD.
- Peer Support: Peer support programs can provide individuals with ASD opportunities to interact with others who are facing similar challenges. This can help in building social skills, improving self-esteem, and fostering a sense of belonging. Peer support can be facilitated through group therapy sessions, social clubs, or online forums.
- Educational Support: Schools and educational institutions play a crucial role in providing social support for individuals with ASD. Teachers and staff members can create inclusive environments that promote understanding and acceptance. They can also implement individualized education plans (IEPs) that cater to the unique learning needs of individuals with ASD.
- Therapeutic Support: Therapists and professionals specializing in ASD can provide valuable social support through various therapeutic interventions. These interventions may include social skills training, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and speech therapy. Therapists can help individuals with ASD develop strategies to navigate social situations successfully.
- Community Support: Community support services, such as recreational programs or social clubs, can provide individuals with ASD opportunities to engage with their peers in a structured and supportive environment. Community support can help individuals with ASD build friendships, develop hobbies, and increase their overall social participation.
It is important to recognize that social support should be tailored to the individual needs and strengths of each person with ASD. What works for one person may not work for another. By providing appropriate social support, we can help individuals with ASD lead fulfilling and connected lives.
Questions and answers
What is autism spectrum disorder?
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a developmental disorder that affects communication and social interaction skills. It is a spectrum disorder, which means that the symptoms and severity of ASD can vary widely from person to person.
What are the symptoms of autism spectrum disorder?
The symptoms of autism spectrum disorder can vary, but some common signs include difficulties with social interactions, repetitive behaviors, limited interests, and difficulty with communication.
What causes autism spectrum disorder?
The exact cause of autism spectrum disorder is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. There is ongoing research to better understand the causes of ASD.
Can autism spectrum disorder be treated?
While there is no cure for autism spectrum disorder, early intervention and various therapies can help individuals with ASD improve their communication and social skills, manage their behaviors, and lead fulfilling lives.
What is the prevalence of autism spectrum disorder?
The prevalence of autism spectrum disorder has been increasing in recent years. Currently, it is estimated that about 1 in 54 children in the United States has been diagnosed with ASD.