Internet gaming disorder has become a major concern in today’s digital age. With the increasing popularity of online gaming, more and more individuals are developing a problematic pattern of gaming that affects their daily life. It is important to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this disorder in order to provide proper support and intervention.
The causes of internet gaming disorder can vary from person to person. For some individuals, it may be a way to escape from reality and seek comfort in a virtual world. Others may have a predisposition to addictive behaviors, making them more susceptible to developing a gaming disorder. Additionally, the ease of access to online games and the social aspect of gaming can also contribute to the development of this disorder.
Symptoms of internet gaming disorder can manifest both physically and mentally. Individuals may experience withdrawal symptoms when they are not able to play games, such as irritability, restlessness, and difficulty concentrating. They may also neglect other important aspects of their life, such as work, school, or relationships, in order to spend more time gaming. This can lead to social isolation and a decline in overall well-being.
Treatment for internet gaming disorder typically involves a combination of therapy and lifestyle changes. Cognitive-behavioral therapy can help individuals identify the underlying causes of their gaming addiction and develop healthier coping mechanisms. Additionally, setting limits on gaming time, finding alternative activities, and improving social support can all be beneficial in the recovery process.
In conclusion, internet gaming disorder is a growing concern in today’s society. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this disorder, we can work towards providing proper support and intervention for individuals struggling with this addiction.
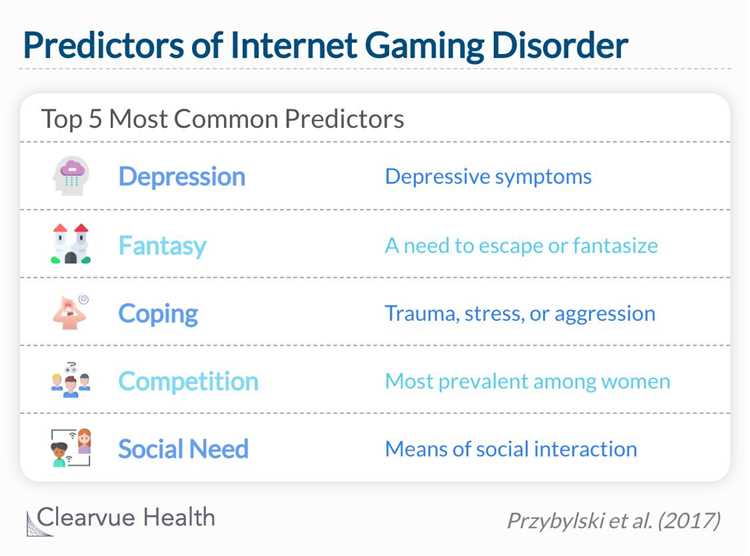
Causes of Internet Gaming Disorder
Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) is a relatively new condition that has gained attention in recent years. It is characterized by excessive and problematic gaming behavior, leading to negative consequences in various areas of life. While the exact causes of IGD are not fully understood, several factors have been identified as potential contributors to the development of this disorder.
- Biological factors: Some studies suggest that certain individuals may have a predisposition to develop IGD due to biological factors. Genetic factors, such as specific gene variants or neurotransmitter imbalances, may increase the risk of developing problematic gaming behaviors.
- Psychological factors: Psychological factors, such as personality traits and mental health conditions, can play a role in the development of IGD. Individuals with high levels of impulsivity, sensation-seeking, or difficulties with emotion regulation may be more susceptible to developing problematic gaming habits.
- Social factors: Social factors, including peer influence and social isolation, can contribute to the development of IGD. People who have a strong desire to fit in or who lack social support may turn to internet gaming as a way to escape or cope with their feelings of loneliness or social difficulties.
- Environmental factors: Environmental factors, such as access to high-speed internet and availability of online games, can also impact the development of IGD. The easy accessibility and constant availability of online games can make it harder for individuals to control their gaming habits and lead to excessive and problematic gaming behavior.
It is important to note that IGD is a complex condition, and multiple factors likely interact to contribute to its development. Further research is needed to better understand the causes of IGD and to develop effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Symptoms of Internet Gaming Disorder
Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) is a condition characterized by excessive and uncontrollable gaming habits that interfere with a person’s daily life and well-being. Individuals with IGD exhibit several symptoms that can help identify the disorder. The following are some common symptoms:
- Preoccupation with gaming: Individuals with IGD often think about gaming all the time. They may constantly plan their gaming sessions, think about strategies, or fantasize about their next achievements.
- Withdrawal symptoms: When unable to play games, individuals with IGD may experience withdrawal symptoms such as irritability, restlessness, or anxiety. They may feel a strong urge to return to gaming to relieve these symptoms.
- Tolerance: Over time, individuals with IGD may develop an increasing need to spend more time gaming or engage in more intense gaming activities to achieve the same level of satisfaction.
- Loss of interest in other activities: People with IGD often lose interest in previously enjoyable activities or hobbies. They may neglect social interactions, school, work, or other responsibilities due to their preoccupation with gaming.
- Neglecting personal hygiene: Individuals with IGD may neglect their personal hygiene and fail to take care of their physical appearance due to spending excessive amounts of time gaming.
- Difficulty controlling gaming habits: Despite attempts to cut back or control their gaming habits, individuals with IGD struggle to do so. They may feel unsuccessful or powerless in their attempts to reduce their gaming time.
- Continued gaming despite negative consequences: Despite experiencing negative consequences such as strained relationships, poor academic or work performance, or health issues, individuals with IGD continue to prioritize gaming over other aspects of their lives.
- Deceptive behavior: Some individuals with IGD may exhibit deceptive behavior to hide the extent of their gaming habits. They may lie about the amount of time spent gaming or attempt to hide the negative consequences of their gaming activities.
It is important to note that the presence of these symptoms alone does not necessarily indicate Internet Gaming Disorder. A professional evaluation by a qualified healthcare provider is required for an accurate diagnosis.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of Internet Gaming Disorder, seeking professional help is recommended. Treatment options such as therapy, counseling, and support groups can be beneficial in managing and overcoming this disorder.
Effects of Internet Gaming Disorder
1. Physical health consequences:
- Increased risk of obesity due to sedentary lifestyle associated with excessive gaming
- Poor posture and musculoskeletal disorders resulting from long hours spent sitting in front of a computer
- Decreased physical fitness and stamina due to lack of exercise
- Sleep disturbances, including insomnia and irregular sleep patterns
- Eye strain and vision problems due to excessive screen time
2. Psychological and emotional consequences:
- Decreased academic/work performance and productivity
- Impaired social relationships and isolation from friends and family
- Difficulty concentrating and paying attention to non-gaming tasks
- Increased irritability, anger, and aggression when gaming is interrupted or restricted
- Feelings of guilt, shame, or self-loathing due to lack of control over gaming habits
3. Behavioral consequences:
- Neglect of personal hygiene and self-care
- Skipping meals or unhealthy eating habits
- Disrupted daily routine and schedule
- Withdrawal from offline activities and hobbies
- Loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities
4. Financial consequences:
- Excessive spending on in-game purchases or subscriptions
- Loss of income or employment due to neglecting work responsibilities
- Debt or financial difficulties resulting from excessive spending on gaming-related expenses
5. Academic consequences:
- Decreased school performance and grades
- Poor time management and difficulty balancing gaming with academic responsibilities
- Lack of motivation and interest in educational pursuits
- Increased risk of dropping out of school or failing to complete assignments
6. Social consequences:
- Isolation from real-life social interactions and friendships
- Reduced participation in social activities and events
- Difficulty forming or maintaining meaningful relationships
- Increased risk of online harassment or bullying
- Negative impact on family relationships and dynamics
7. Cognitive consequences:
- Impaired decision-making and problem-solving skills
- Reduced attention span and ability to focus on tasks
- Decreased memory and learning capabilities
- Difficulty adapting to new situations or changes
- Impaired impulse control and inability to resist gaming urges
It is important to note that the effects of internet gaming disorder can vary from individual to individual, and the severity of these effects may depend on various factors such as frequency and duration of gaming, underlying mental health conditions, and overall lifestyle choices. Seeking professional help and support is crucial for individuals struggling with internet gaming disorder to mitigate these negative consequences and regain control over their lives.
Diagnosis of Internet Gaming Disorder
Diagnosing Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) involves evaluating the individual’s behavior and determining if it meets the diagnostic criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA).
Diagnostic criteria for Internet Gaming Disorder:
- Preoccupation with gaming – the individual thinks about gaming activities excessively, even when not playing.
- Withdrawal symptoms – when attempting to reduce or stop gaming, the individual experiences restlessness, irritability, or other negative emotional and physical symptoms.
- Tolerance – needing to spend increasing amounts of time engaged in gaming activities to achieve the desired level of excitement or satisfaction.
- Unsuccessful attempts to control or reduce gaming – despite attempts to cut back, the individual is unable to control or stop gaming.
- Loss of interest in other activities – the individual loses interest in previously enjoyed activities in favor of gaming.
- Continued excessive use of gaming despite negative consequences – the individual persists in gaming despite experiencing negative consequences in personal, social, educational, or occupational areas of life.
- Deception or lying about gaming activities – the individual may lie to family members, friends, or therapists to conceal the extent of their gaming behavior.
- Escape or mood modification – gaming is used as a way to escape or relieve negative moods, such as feelings of helplessness, guilt, or anxiety.
- Interference with daily functioning – gaming activities disrupt or negatively impact the individual’s personal, social, educational, or occupational life.
To receive a diagnosis of Internet Gaming Disorder, an individual must exhibit at least five of the nine criteria within a 12-month period. It is important for clinicians to gather thorough information about the individual’s gaming habits, behaviors, and consequences to make an accurate diagnosis.
Evaluation and assessment:
Diagnosing Internet Gaming Disorder typically involves conducting a clinical interview with the individual to gather information about their gaming behavior, symptoms, and the impact of gaming on their life. Clinicians may also use validated assessment tools, such as questionnaires, to gather additional information.
The assessment process may also include gathering collateral information from family members or other significant individuals in the individual’s life. This can help provide a more comprehensive understanding of the individual’s gaming habits and their impact on relationships and daily functioning.
Co-occurring conditions:
It is important to note that Internet Gaming Disorder may co-occur with other mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), or substance use disorders. Clinicians must consider the presence of these co-occurring conditions and evaluate their impact on the individual’s gaming behavior and overall functioning.
Conclusion:
Diagnosing Internet Gaming Disorder involves evaluating the individual’s gaming behavior and determining if it meets the diagnostic criteria outlined in the DSM-5. The assessment process includes a clinical interview, assessment tools, and collateral information from significant others. It is essential to consider the presence of co-occurring conditions and their impact on the individual’s gaming behavior and overall well-being.
Prevention of Internet Gaming Disorder
Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) is a growing concern, with individuals increasingly spending excessive amounts of time playing online games, to the point where it negatively impacts their daily lives. To prevent the development or progression of IGD, several strategies can be implemented:
- Educate individuals about the risks: Raising awareness about the potential negative consequences of excessive internet gaming can help individuals make informed decisions and exercise self-control.
- Set limits: Establishing clear boundaries and time limits for gaming activities can help individuals maintain a healthy balance between gaming and other important activities such as work, school, and social interactions.
- Encourage alternative activities: Encouraging individuals to engage in a variety of activities beyond internet gaming, such as sports, hobbies, or creative pursuits, can help divert their attention from excessive gaming.
- Promote social interactions: Fostering social connections and encouraging individuals to engage in face-to-face interactions with friends and family can help reduce the excessive use of internet gaming as a means of socialization.
- Monitor and supervise: Parents and caregivers should monitor the gaming habits of children and adolescents, setting appropriate limits and providing guidance to ensure a healthy balance between gaming and other activities.
- Encourage healthy lifestyles: Promoting physical exercise, proper nutrition, and sufficient sleep can contribute to overall well-being and help individuals maintain a balanced and healthy lifestyle, reducing the likelihood of excessive internet gaming.
- Seek professional help: If someone is already experiencing symptoms of IGD or has a problematic relationship with online gaming, seeking professional help, such as therapy or counseling, can be beneficial in addressing the underlying issues and developing healthier habits.
By implementing these preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of developing Internet Gaming Disorder or minimize the negative impact of excessive gaming on their lives.
Treatment Options for Internet Gaming Disorder
Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) is a condition that can have significant negative impacts on an individual’s life, and treatment is often necessary to help individuals regain control over their gaming habits. There are several treatment options available for IGD, including:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a common form of psychotherapy that focuses on changing harmful thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. In the context of IGD, CBT can help individuals identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs about gaming and learn healthier coping strategies.
- Family Therapy: Family therapy involves working with the family unit as a whole to address the impact of IGD on relationships and family dynamics. This can help improve communication, set boundaries, and provide support for both the individual with IGD and their loved ones.
- Support Groups: Support groups provide a safe and understanding space where individuals with IGD can connect with others who are going through similar experiences. Sharing stories, strategies, and offering mutual support can be invaluable in the recovery process.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of co-occurring mental health conditions, such as depression or anxiety, that often accompany IGD. It is important to note that medication should be used in conjunction with other forms of therapy and under the guidance of a medical professional.
Additionally, individuals with IGD may benefit from implementing lifestyle changes to promote healthier habits and reduce excessive gaming. These may include:
- Creating a structured schedule that includes time for other activities, such as exercise, socializing, and hobbies.
- Setting specific limits on gaming time and sticking to them.
- Engaging in activities that provide a sense of purpose and fulfillment outside of gaming.
- Building a strong support network of friends and family who can offer encouragement and accountability.
It is important for individuals with IGD and their loved ones to seek professional help and support. With the right treatment approach, individuals with IGD can regain control over their gaming habits and improve their overall quality of life.
Support for Individuals with Internet Gaming Disorder
Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) can have a significant impact on a person’s life, causing various physical, emotional, and social problems. However, there are several forms of support available to help individuals struggling with IGD. Here are some options to consider:
- Therapy: Seeking therapy is an essential step in overcoming IGD. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a commonly used approach in treating IGD. It involves identifying and challenging negative thoughts and behaviors associated with excessive gaming, replacing them with healthier alternatives.
- Support groups: Joining support groups can provide individuals with IGD a sense of community and understanding. These groups often consist of individuals who have experienced similar challenges and can offer valuable advice and support.
- Family involvement: Involving family members in the treatment process can significantly impact the recovery of individuals with IGD. Family therapy sessions can help improve communication, set boundaries, and create a supportive environment at home.
- Education and awareness: Educating oneself and others about IGD is crucial in understanding the condition and reducing stigma. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of IGD can help individuals seek help sooner and access appropriate support.
- Healthy habits and hobbies: Encouraging individuals with IGD to engage in alternative activities can help shift their focus away from excessive gaming. Encouraging physical exercise, pursuing creative hobbies, and spending time with friends and family can all contribute to a healthier lifestyle.
- Technology management: Implementing strategies to manage technology usage can be helpful in reducing the risk of IGD. This may include setting specific gaming time limits, using apps to monitor and control gaming habits, or creating a designated gaming-free zone.
Remember, seeking professional help is crucial for individuals with IGD, and support from friends, family, and communities can play a vital role in helping them overcome their addiction and lead a healthier life.
Research and Statistics on Internet Gaming Disorder
Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) is a relatively new condition, and research is still ongoing to fully understand its causes, symptoms, and treatment. However, several studies have provided valuable insights into this disorder and its prevalence.
Prevalence:
- According to a meta-analysis conducted in 2019, the prevalence of IGD worldwide is estimated to be around 6%, with higher rates among adolescents and young adults.
- In some Asian countries, such as China and South Korea, the prevalence of IGD has been found to be higher, with rates ranging from 10% to 15%.
- Prevalence rates also vary based on gender, with males showing higher rates of IGD compared to females.
Risk Factors:
- Several risk factors have been identified for the development of IGD, including younger age, male gender, high levels of impulsivity, and psychological factors such as depression and social anxiety.
- Excessive online gaming, presence of gaming environments that incentivize continuous play, and the availability of high-speed internet connections have also been identified as risk factors.
Effects on Mental Health:
- Studies have shown that individuals with IGD are more likely to experience symptoms of depression, anxiety, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and social phobia.
- Long hours spent on gaming can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to sleep disturbances and insomnia.
Treatment Options:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has been found to be effective in treating IGD, as it helps individuals develop healthier gaming habits and address underlying psychological issues.
- Other interventions, such as family therapy, support groups, and self-help techniques, may also be valuable in the treatment of IGD.
- Currently, there are no pharmacological treatments specifically approved for IGD, but medications targeting co-occurring conditions, such as depression or ADHD, may be prescribed.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, research into Internet Gaming Disorder has shed light on its prevalence, risk factors, and effects on mental health. More studies are needed to further understand the complex interplay of biological, psychological, and environmental factors in the development and treatment of this disorder.
Questions and answers
What is Internet Gaming Disorder?
Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) is a condition characterized by excessive and compulsive use of internet games, leading to significant impairment in various areas of an individual’s life.
What are the symptoms of Internet Gaming Disorder?
The symptoms of Internet Gaming Disorder include preoccupation with gaming, withdrawal symptoms when not gaming, loss of interest in other activities, continuance of gaming despite negative consequences, and deception about the extent of gaming.
What are the potential causes of Internet Gaming Disorder?
The potential causes of Internet Gaming Disorder include psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, and depression, as well as social factors such as loneliness and lack of social support. Additionally, individual characteristics such as impulsivity and poor impulse control may contribute to the development of IGD.
Is there treatment available for Internet Gaming Disorder?
Yes, there are treatment options available for Internet Gaming Disorder. These may include cognitive-behavioral therapy, which helps individuals identify and change negative thought and behavior patterns, as well as individual and group counseling sessions to support recovery and provide coping strategies. In some cases, medication may also be prescribed to address underlying mental health conditions.