Depression is a common mental health disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities that were once enjoyable. While the exact causes of depression are still not fully understood, research has shown that hormone imbalances, such as low testosterone levels, may contribute to the development of this condition.
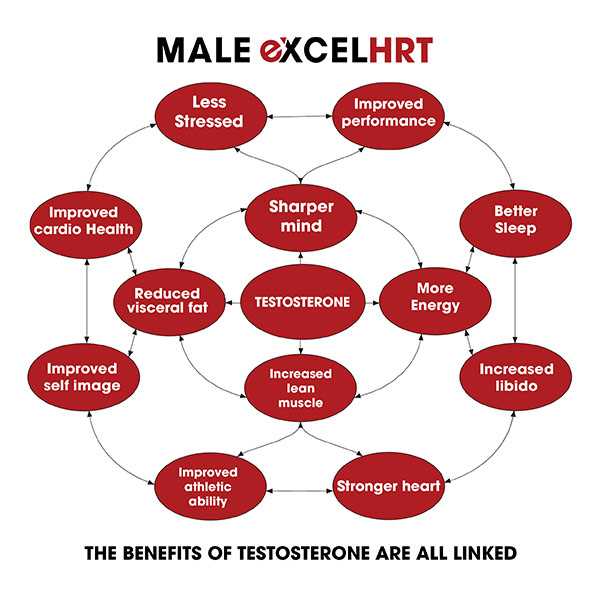
Testosterone is a hormone that is primarily produced in men’s testicles and in smaller amounts in women’s ovaries. It is commonly associated with masculinity and plays a crucial role in the development of male reproductive tissues and secondary sexual characteristics. However, testosterone also has an impact on mood, cognition, and overall well-being, both in men and women. Low levels of testosterone have been linked to an increased risk of developing depressive symptoms.
Studies have found that men with low testosterone levels are more likely to experience symptoms of depression, such as feelings of sadness, irritability, and decreased energy levels. Similarly, women who have lower levels of testosterone may also be at a higher risk of developing depression. These findings suggest that testosterone may play a role in regulating mood and may be involved in the development of depressive disorders.
It is important to note that while low testosterone levels may contribute to the development of depression, they are not the sole cause of the condition. Depression is a complex disorder influenced by various factors, including genetics, environment, and life experiences.
Treatment options for depression related to low testosterone levels may include hormone replacement therapy, antidepressant medications, talk therapy, and lifestyle changes. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying causes of depression and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
In conclusion, while the relationship between low testosterone levels and depression is still being researched, there is evidence to suggest that testosterone plays a role in regulating mood and may contribute to the development of depressive symptoms. Further studies are needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind this relationship and develop targeted treatment approaches for individuals with low testosterone and depression.
Understanding the Link between Low Testosterone Levels and Depression
Depression is a serious mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it is often thought of as a purely psychological disorder, there can be physical factors that contribute to its development. One such factor is low testosterone levels in men.
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including the regulation of mood and emotions. When testosterone levels dip below a certain threshold, it can lead to a range of symptoms that can contribute to the development or exacerbation of depression.
The Symptoms of Low Testosterone Levels
Low testosterone levels, also known as hypogonadism, can manifest in several ways. These symptoms may include:
- Low mood
- Fatigue and low energy levels
- Decreased sex drive
- Difficulty concentrating
- Decreased muscle mass and strength
- Increased body fat
- Sleep disturbances
It is important to note that experiencing one or more of these symptoms does not necessarily mean a person has low testosterone levels. However, when these symptoms are accompanied by a diagnosis of depression, it may be worth exploring a potential connection between the two.
The Role of Testosterone in Mental Health
Testosterone interacts with various neurotransmitters in the brain that regulate mood and emotions, such as serotonin and dopamine. When testosterone levels are low, these neurotransmitters may not function optimally, leading to imbalances that can contribute to the development of depressive symptoms.
Furthermore, low testosterone levels may impact the body’s stress response system. Testosterone helps regulate the release of cortisol, a hormone involved in the body’s response to stress. Imbalances in cortisol levels can have a negative impact on mood and contribute to the development of depressive symptoms.
Treating Depression and Low Testosterone Levels
If low testosterone levels are identified as a contributing factor to depression, treatment options may include hormone replacement therapy (HRT). HRT involves boosting testosterone levels through various methods, such as injections, patches, or gels.
In addition to HRT, traditional treatments for depression, such as therapy and medication, may also be recommended. It is essential to work with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual needs.
Conclusion
Understanding the link between low testosterone levels and depression can help improve diagnosis and treatment strategies for individuals who experience both conditions. By addressing low testosterone levels, healthcare providers can potentially alleviate depressive symptoms and improve overall mental health. However, further research is needed to fully understand the complexity of this relationship and develop targeted interventions.
The Role of Testosterone in Mental Health
Testosterone, a hormone primarily associated with male reproductive health, plays a crucial role in mental health as well. While it is well-known for its effects on muscle growth, libido, and energy levels, testosterone also influences mood, cognition, and emotional well-being.
Research has shown a strong correlation between low testosterone levels and mental health issues, particularly depression. Testosterone deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of developing depressive symptoms and a higher likelihood of experiencing persistent or recurrent depression.
One of the ways testosterone impacts mental health is through its effect on neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit signals in the brain. Testosterone influences the production and functioning of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which are essential for regulating mood and emotions.
Low testosterone levels can disrupt the balance of these neurotransmitters, leading to mood swings, irritability, and a general sense of unhappiness. Additionally, testosterone deficiency can contribute to brain fog, reduced concentration, and cognitive decline, further exacerbating feelings of depression.
In addition to its direct effects on neurotransmitters, testosterone also interacts with other hormones and systems in the body that impact mental health. For example, testosterone interacts with the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, which is responsible for regulating the body’s stress response.
Studies have shown that testosterone plays a role in modulating the stress response, and low testosterone levels can make individuals more susceptible to stress and less resilient in coping with challenging situations. Chronic stress is known to contribute to the development and worsening of depression.
It is important to note that testosterone is not the sole determinant of mental health, and other factors, such as genetics, environment, and lifestyle, also play a significant role. However, addressing testosterone deficiency through hormone replacement therapy can be a valuable approach in treating depression in individuals with low testosterone levels.
Overall, the role of testosterone in mental health encompasses its influence on neurotransmitters, stress regulation, and cognitive function. Understanding and addressing testosterone deficiency in individuals with depression can lead to improved mental health outcomes and a better overall quality of life.
Signs and Symptoms of Low Testosterone Levels
Low testosterone levels can have various signs and symptoms that may indicate a hormonal imbalance. While these symptoms can vary among individuals, here are some common signs to look out for:
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and lacking energy can be a symptom of low testosterone.
- Depression: Low testosterone levels are associated with an increased risk of depression and mood changes.
- Decreased sex drive: Testosterone plays a vital role in sexual desire, so a decrease in libido is often observed with low testosterone.
- Erectile dysfunction: Difficulty in achieving or maintaining an erection can be a result of low testosterone levels.
- Loss of muscle mass: Testosterone is crucial for muscle growth and maintenance, so a decrease in testosterone levels can lead to muscle loss and decreased strength.
- Increase in body fat: Low testosterone can contribute to an increase in body fat, particularly around the abdomen.
- Decreased bone density: Testosterone helps maintain bone density, so low levels can increase the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment options. They can conduct blood tests to measure testosterone levels and determine if low testosterone is the underlying cause of your symptoms.
Keep in mind that these symptoms can also be attributed to other conditions, so it is essential to undergo a thorough evaluation to identify the root cause of your symptoms.
Depression as a Possible Consequence of Low Testosterone
Low testosterone levels, also known as hypogonadism, can have a significant impact on the mental well-being of individuals. Depression is one possible consequence of low testosterone, and it is important to understand the relationship between these two conditions.
Testosterone is a hormone that plays a crucial role in the body, particularly in men. It is responsible for the development and maintenance of male sexual characteristics, as well as regulating mood, energy levels, and cognitive function. When testosterone levels are low, it can affect these areas and potentially contribute to the development of depression.
Research has shown a strong correlation between low testosterone levels and an increased risk of developing depression. In fact, studies have found that men with low testosterone are more likely to experience symptoms of depression, such as persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities, and changes in appetite and sleep patterns.
One possible mechanism by which low testosterone contributes to depression is through its impact on neurotransmitters. Testosterone has been found to influence the production and activity of certain neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which are known to regulate mood. When testosterone levels are low, there may be a disruption in the balance of these neurotransmitters, leading to depressive symptoms.
In addition, low testosterone can also contribute to feelings of fatigue and low energy, which are common symptoms of depression. The lack of energy and motivation can make it difficult for individuals to engage in activities they once enjoyed, further worsening their depressive symptoms.
It is important to note that while low testosterone can be a contributing factor to depression, it is not the sole cause. Depression is a complex condition that can be influenced by various factors, including genetics, environmental factors, and other hormonal imbalances.
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
Research Findings and Studies on Testosterone and Depression
Several research studies have been conducted to explore the relationship between testosterone levels and depression. These studies have provided valuable insights into how low testosterone levels can contribute to depression and have led to further investigation in this field.
1. Study by Georgiadis et al. (2011)
- In this study, researchers examined the association between testosterone levels and depressive symptoms in a sample of middle-aged men.
- They found that low testosterone levels were significantly correlated with increased depressive symptoms.
- This study suggests that low testosterone may be a risk factor for developing depression in men.
2. Study by Seidman et al. (2001)
- This study aimed to determine the effects of testosterone replacement therapy on depression in men with low testosterone levels.
- Participants who received testosterone replacement therapy showed significant improvement in depressive symptoms compared to those who received a placebo.
- These findings indicate that increasing testosterone levels through therapy can alleviate depressive symptoms in men.
3. Study by Zarrouf et al. (2009)
- Researchers conducted a meta-analysis of studies investigating the association between low testosterone levels and depression in men.
- The analysis included data from multiple studies and found a consistent association between low testosterone levels and increased risk of depression.
- These findings provide further support for the notion that low testosterone levels contribute to the development of depression in men.
4. Study by Schneider et al. (2020)
- This study examined the relationship between testosterone levels and depression in women.
- Results showed that low testosterone levels were associated with increased depressive symptoms in women.
- This study suggests that low testosterone levels can also contribute to the development of depression in women.
In conclusion, these research findings and studies demonstrate a strong link between low testosterone levels and depression. They highlight the importance of considering testosterone levels as a potential factor in the diagnosis and treatment of depression, both in men and women.
Treatment Options for Low Testosterone and Depression
When it comes to addressing low testosterone levels and depression, there are several treatment options available. These options can help alleviate the symptoms and improve overall well-being. It is important to consult with a medical professional to determine the most appropriate treatment approach based on individual circumstances.
1. Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
Testosterone replacement therapy involves administering synthetic testosterone to raise testosterone levels in individuals with low testosterone. This treatment method can help alleviate symptoms of depression associated with low testosterone. TRT can be administered through various methods, including injections, patches, gels, or pellets.
2. Antidepressant Medication
In cases where depression is more severe or not solely attributed to low testosterone levels, antidepressant medication may be prescribed. These medications can help regulate mood and alleviate symptoms of depression. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate antidepressant medication and dosage.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can also contribute to the improvement of low testosterone levels and depression symptoms. These changes may include regular exercise, a healthy diet, stress reduction techniques, getting enough sleep, and avoiding alcohol and drug abuse.
4. Therapy
Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be beneficial for individuals with low testosterone and depression. Therapy sessions can help individuals address underlying issues contributing to their depression and develop coping mechanisms to manage their symptoms.
5. Support Groups
Participating in support groups can provide individuals with low testosterone and depression the opportunity to connect with others facing similar situations. Sharing experiences and receiving support from peers can help reduce feelings of isolation and improve overall mental well-being.
6. Hormone Regulating Medications
In some cases, medications that regulate hormone levels may be prescribed to address both low testosterone and depression. These medications can help restore hormonal balance and alleviate symptoms. A healthcare provider can guide and monitor the usage of hormone-regulating medications.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of these treatment options may vary depending on individual circumstances. It is crucial to consult with a medical professional to determine the most appropriate course of action. Combining different treatment approaches may also be necessary for maximum benefits.
Lifestyle Changes to Boost Testosterone Levels
Low testosterone levels can have a negative impact on both physical and mental health. If you are experiencing low testosterone levels, there are several lifestyle changes you can make to help boost them. Here are some tips:
- Exercise regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity can help increase testosterone levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, most days of the week.
- Manage stress: High levels of stress can contribute to low testosterone. Find healthy coping mechanisms to manage stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, getting enough sleep, and engaging in activities you enjoy.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is associated with lower testosterone levels. Focus on maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Eat a nutritious diet: Include foods that are rich in nutrients known to support testosterone production, such as zinc, vitamin D, and healthy fats. Some examples of these foods include lean meats, fish, eggs, nuts, seeds, and leafy green vegetables.
- Get enough sleep: Poor sleep can contribute to hormonal imbalances, including lower testosterone levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep every night.
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption: Alcohol can interfere with testosterone production. Limit your alcohol intake or avoid it altogether.
- Quit smoking: Smoking is known to decrease testosterone levels. If you smoke, consider quitting to help boost your testosterone levels.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration can negatively impact hormone production, including testosterone. Make sure to drink enough water throughout the day.
- Manage chronic health conditions: Certain chronic health conditions, such as diabetes and obesity, can contribute to low testosterone levels. Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations to manage these conditions effectively.
- Consider testosterone replacement therapy: If lifestyle changes alone are not sufficient to boost your testosterone levels, your healthcare provider may recommend testosterone replacement therapy. This therapy involves the use of medications or testosterone injections to increase testosterone levels in your body.
Remember, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your lifestyle or starting any new treatments. They can provide personalized advice and guidance based on your individual needs and health history.
Prevention and Early Detection of Low Testosterone and Depression
Preventing and detecting low testosterone levels and depression early on is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. Here are some strategies for prevention and early detection:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help regulate testosterone levels and improve mood. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can support optimal hormone production and mental health.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact testosterone levels and contribute to depression. Implementing stress management techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and relaxation exercises can help maintain hormone balance.
- Sufficient Sleep: Getting enough quality sleep is essential for hormone regulation. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to support optimal testosterone levels and mental well-being.
To detect low testosterone levels and depression early, it is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms. Some common signs of low testosterone include:
- Decreased libido
- Erectile dysfunction
- Fatigue
- Depressed mood
- Decreased muscle mass
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional who can order a blood test to measure your testosterone levels. Early detection can lead to early intervention and appropriate treatment.
Additionally, regularly screening for depression is important, particularly if you have risk factors such as low testosterone levels. Some common signs of depression include:
- Persistent sadness or emptiness
- Loss of interest in activities once enjoyed
- Changes in appetite or weight
- Difficulty concentrating
- Thoughts of death or suicide
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek help from a healthcare professional. They can assess your symptoms, provide a diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment options, which may include therapy, medication, or a combination of both.
| Prevention | Early Detection |
|---|---|
| Regular exercise | Awareness of signs and symptoms |
| Healthy diet | Consultation with a healthcare professional |
| Stress management | Blood test for testosterone levels |
| Sufficient sleep | Regular screening for depression |
By taking preventive measures and being proactive in detecting low testosterone levels and depression, individuals can improve their overall quality of life and reduce the potential negative impact on their mental health.
Questions and answers
What are the symptoms of low testosterone levels?
Some of the symptoms of low testosterone levels include fatigue, decreased sex drive, difficulty concentrating, irritability, and depression.
How does low testosterone contribute to depression?
Low testosterone levels can contribute to depression by affecting mood, energy levels, and overall well-being. When testosterone levels are low, it can lead to feelings of sadness, low energy, and a lack of motivation.
Are there any lifestyle factors that can contribute to low testosterone levels?
Yes, there are several lifestyle factors that can contribute to low testosterone levels. These include chronic stress, poor sleep, lack of exercise, obesity, and certain medications.
Can low testosterone levels in women also lead to depression?
Yes, low testosterone levels in women can also contribute to depression. Although testosterone is primarily thought of as a male hormone, women also produce small amounts of testosterone, and low levels can have similar effects on mood and well-being.
How is low testosterone diagnosed?
Low testosterone can be diagnosed through a blood test. A healthcare provider will measure the levels of testosterone in the blood and compare them to the normal range for the person’s age and sex.
What are the treatment options for low testosterone?
Treatment options for low testosterone may include testosterone replacement therapy, lifestyle changes such as exercise and stress reduction, and addressing any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to low testosterone levels.
Can low testosterone be prevented?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent low testosterone, there are steps that can be taken to maintain optimal levels. This includes maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.