Anxiety disorders are a common mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While occasional feelings of anxiety are a normal part of life, individuals with anxiety disorders experience excessive and persistent worry and fear that can significantly interfere with their daily lives.
There are several different types of anxiety disorders, each with its own unique set of symptoms and triggers. Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is characterized by excessive worry and tension about everyday events and activities. Individuals with GAD often have difficulties controlling their worry and may experience physical symptoms such as restlessness, irritability, and muscle tension.
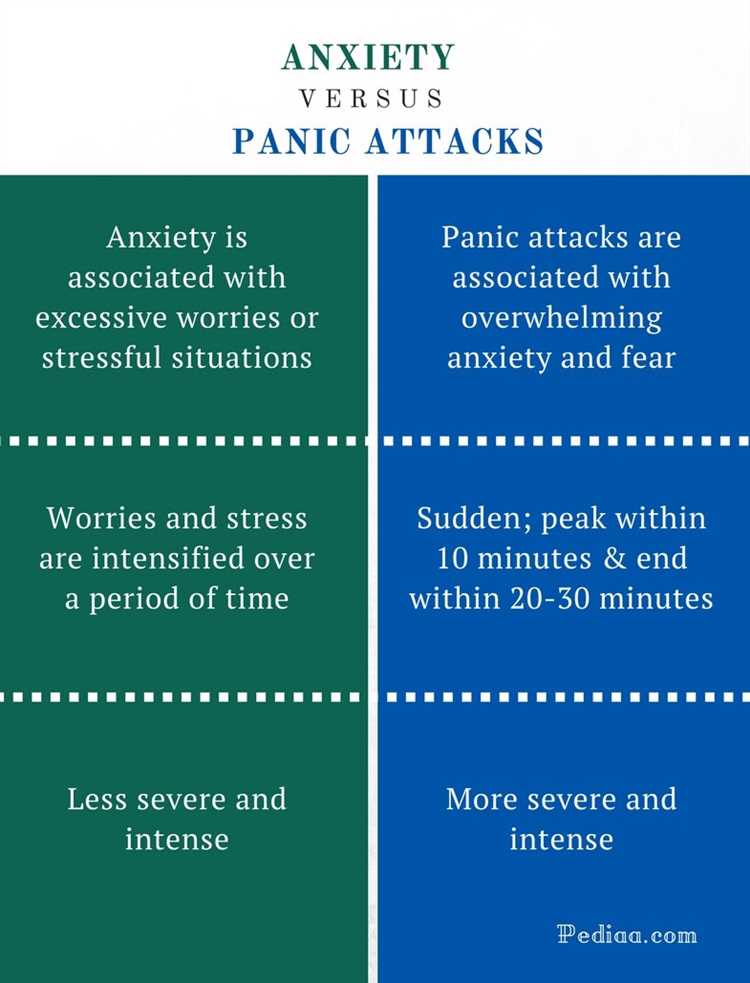
Panic disorder is another type of anxiety disorder, characterized by sudden and repeated episodes of intense fear and discomfort, known as panic attacks. During a panic attack, individuals may experience symptoms such as a rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, trembling, and feelings of impending doom. Panic attacks can be extremely distressing and may lead to avoidance of certain situations or places.
Social anxiety disorder, also known as social phobia, involves an intense fear of being judged, embarrassed, or humiliated in social situations. Individuals with social anxiety disorder often have an extreme fear of public speaking, meeting new people, or participating in social activities. This fear can significantly impact their ability to form and maintain relationships and can lead to isolation and withdrawal.
Other types of anxiety disorders include specific phobias, which are intense fears of specific objects or situations (such as heights, spiders, or flying), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), which involves intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors that individuals feel compelled to perform to alleviate anxiety. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is also considered an anxiety disorder and is characterized by flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety following a traumatic event.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder: Understanding the Symptoms
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is a common type of anxiety disorder characterized by excessive and persistent worrying about a variety of tasks or events. People with GAD often find it difficult to control their worrying, and it can interfere with their daily life and functioning.
Here are some of the common symptoms of Generalized Anxiety Disorder:
- Excessive Worrying: People with GAD experience excessive worrying about a wide range of things, including work, health, family, finances, and more. The worrying is often out of proportion to the actual situation.
- Restlessness and Irritability: GAD can cause restlessness and irritability, making it difficult for individuals to relax or concentrate. They may feel on edge or constantly on alert for potential threats or danger.
- Physical Symptoms: GAD can also manifest in physical symptoms such as headaches, muscle tension, fatigue, and difficulty sleeping. These physical symptoms can further exacerbate the anxiety and make it harder for individuals to manage.
- Trouble with Decision-Making: People with GAD often struggle with making decisions, even small ones. The fear of making the wrong choice or the fear of potential negative consequences can be overwhelming.
- Excessive Self-Doubt: Individuals with GAD often second-guess themselves and have excessive self-doubt. They may worry about whether they said or did the right thing, or constantly seek reassurance from others.
It is important to note that everyone experiences anxiety at times, but people with Generalized Anxiety Disorder experience anxiety at a chronic and excessive level.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of GAD, it is crucial to seek professional help. Treatment options such as therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
Panic Disorder: Recognizing the Signs and Triggers
Panic disorder is a type of anxiety disorder characterized by recurring panic attacks. These episodes of intense fear and discomfort can be debilitating and may occur unexpectedly, without any specific trigger or warning. Recognizing the signs and triggers of panic disorder is crucial for both individuals experiencing it and those around them.
Signs of panic disorder:
- Recurring panic attacks: Panic attacks are the hallmark symptom of panic disorder. These are sudden and intense surges of fear or discomfort that can last for several minutes. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, rapid heart rate, sweating, trembling, chest pain, and a feeling of impending doom.
- Worry about future panic attacks: Individuals with panic disorder often live in fear of experiencing another panic attack. This worry can become overwhelming and may lead to avoidance behaviors.
- Changes in behavior: People with panic disorder may start avoiding certain places or situations where they have previously had a panic attack. They may also become overly reliant on specific people for support.
- Physical symptoms: In addition to the symptoms experienced during panic attacks, individuals with panic disorder may also experience ongoing physical symptoms such as headaches, stomachaches, and muscle tension.
Triggers of panic disorder:
Panic attacks can be triggered by a variety of factors. While they can occur unexpectedly, certain triggers may increase the likelihood of an attack:
- Stressful events: Major life changes, such as starting a new job or ending a relationship, can trigger panic attacks in some individuals.
- Phobias and fears: Certain phobias, such as a fear of flying or heights, can trigger panic attacks when confronted with the feared situation or object.
- Substance use or withdrawal: Alcohol, drugs, and certain medications can trigger panic attacks, both while using them and during withdrawal.
- Caffeine and stimulants: Consuming high amounts of caffeine or using other stimulant drugs can increase the risk of panic attacks.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hyperthyroidism, can cause symptoms similar to panic attacks and may trigger episodes.
Panic disorder can significantly impact a person’s daily life and well-being. Seeking professional help and support is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Social Anxiety Disorder: Overcoming Fear and Social Situations
Social Anxiety Disorder is a type of anxiety disorder that involves intense fear and anxiety in social situations. People with this disorder may feel self-conscious, judged, and embarrassed, leading to avoidance of social interactions and difficulties in daily life.
Common symptoms of social anxiety disorder include:
- Fear of judgment: Individuals with social anxiety disorder often have a fear of being negatively evaluated or criticized by others, leading to avoidance of social situations.
- Physical symptoms: When confronted with social situations, individuals may experience physical symptoms such as sweating, trembling, and increased heart rate.
- Avoidance behaviors: People with social anxiety disorder may go to great lengths to avoid situations that trigger their anxiety, such as parties, public speaking, or meeting new people.
- Low self-esteem: Social anxiety disorder is often associated with low self-esteem and a negative self-image.
Overcoming social anxiety disorder can be a challenging process, but with proper treatment and support, it is possible to lead a fulfilling social life. Here are some strategies that can help:
- Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has been found to be an effective treatment for social anxiety disorder. This therapy focuses on identifying and challenging negative thoughts and beliefs, as well as learning coping skills to manage anxiety in social situations.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage the symptoms of social anxiety disorder. Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can be used to reduce anxiety and improve functioning.
- Self-help techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, can help reduce anxiety symptoms in social situations. Gradually exposing oneself to feared situations and setting achievable goals can also be helpful.
- Social support: Seeking support from friends, family, or support groups can provide a sense of understanding and validation. It can also be beneficial to connect with others who have overcome social anxiety disorder.
It is important to remember that overcoming social anxiety disorder takes time and patience. With consistent effort and a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals with social anxiety disorder can learn to manage their fears and thrive in social situations.
Phobias: Unraveling the Fear and Irrational Beliefs
Phobias are a type of anxiety disorder characterized by an intense and irrational fear of specific objects, situations, or activities. They can cause significant distress and impairment in everyday life. Phobias are one of the most common mental health disorders, affecting millions of people around the world.
There are three main categories of phobias:
- Specific Phobias: These are phobias related to a specific object or situation, such as fear of spiders (arachnophobia), fear of heights (acrophobia), or fear of flying (aviophobia). People with specific phobias often go to great lengths to avoid their feared stimuli.
- Social Phobia (Social Anxiety Disorder): Social phobia is characterized by a fear of social situations and an intense fear of being embarrassed, humiliated, or judged by others. It often leads to avoidance of social gatherings, public speaking, or other situations where one may be the center of attention.
- Agaraphobia: Agaraphobia is a fear of being in situations or places where escape may be difficult or embarrassing, such as crowded spaces, public transportation, or open spaces. It often develops as a result of panic disorder and can lead to severe limitations in daily activities.
The symptoms of phobias can vary depending on the individual and the specific phobia. Common symptoms may include:
- Intense fear: People with phobias experience an overwhelming and irrational fear when faced with their phobic stimuli.
- Avoidance behavior: Individuals with phobias often go to great lengths to avoid situations, places, or objects that trigger their fear.
- Physical symptoms: Phobias can trigger a range of physical symptoms, including rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, trembling, sweating, and nausea.
- Interference with daily life: Phobias can significantly impact a person’s ability to carry out daily activities and may lead to social isolation and distress.
Treatment for phobias often involves a combination of therapy and medication. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective forms of treatment for phobias. It helps individuals identify and challenge their irrational beliefs and develop coping mechanisms to manage their fears. Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may also be prescribed to help reduce anxiety symptoms.
Phobias can be debilitating, but with the right treatment and support, individuals can learn to manage their fears and lead fulfilling lives.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Identifying the Obsessions and Compulsions
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a mental health disorder characterized by intrusive thoughts, known as obsessions, and repetitive behaviors, known as compulsions. People with OCD often feel a strong urge to perform these compulsions in order to alleviate anxiety or distress caused by their obsessions. It is essential to recognize and understand the obsessions and compulsions associated with OCD in order to seek appropriate treatment.
Obsessions:
- Intrusive and recurring thoughts, images, or urges that cause distress or anxiety
- Frequent worrying about contamination, germs, or dirt
- Excessive fear of making mistakes or being responsible for harm
- Unwanted thoughts of violence, aggression, or sexual content
- Feeling the need for symmetry, order, or exactness
Compulsions:
- Repetitive behaviors or mental acts performed to alleviate anxiety
- Excessive cleaning, washing, or sanitizing
- Repeated checking of locks, appliances, or other objects
- Counting, arranging, or organizing objects in a specific way
- Repeating certain words, phrases, or prayers
- Hoarding or excessive collecting of items
It is important to note that not all individuals with OCD will experience the same obsessions and compulsions. The specific obsessions and compulsions can vary significantly from person to person, and the severity of symptoms may also differ. OCD can significantly impact an individual’s daily functioning and quality of life if left untreated.
If you or someone you know is struggling with obsessions and compulsions that interfere with daily life, it is recommended to seek professional help. Effective treatment options, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and medication, can help individuals manage and alleviate the symptoms of OCD.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: Examining the Impact of Traumatic Events
Introduction:
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. This disorder can have a significant impact on the individual’s daily life, relationships, and overall well-being.
Symptoms:
- Re-experiencing: Individuals with PTSD often experience intrusive memories or flashbacks of the traumatic event. This can include nightmares and intense emotional or physical reactions when reminded of the event.
- Avoidance: People with PTSD may try to avoid reminders of the traumatic event, such as avoiding certain places or activities that may trigger distressing memories. They may also avoid discussing or thinking about the event.
- Negative changes in thoughts and mood: PTSD can cause individuals to have negative thoughts about themselves, others, or the world. They may feel hopeless, guilty, or numb. It can also lead to a loss of interest in activities previously enjoyed.
- Hyperarousal: Those with PTSD may have heightened arousal or an exaggerated startle response. They may become easily irritable or have difficulty sleeping and concentrating. They can also be hypervigilant or constantly on guard.
Common Triggers:
PTSD can be triggered by a wide range of traumatic events, including:
- Combat exposure
- Sexual assault or abuse
- Natural disasters
- Motor vehicle accidents
- Violent personal attacks
- Being a witness to violence
- Childhood abuse or neglect
Treatment:
PTSD can be effectively treated through various therapies, including:
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This therapy helps individuals identify and change negative thoughts and behaviors related to their traumatic event.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): This therapy uses eye movements or other bilateral stimulation techniques to help reduce the distress associated with traumatic memories.
- Medication: Certain medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can be prescribed to help manage symptoms of PTSD.
Conclusion:
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder is a complex disorder that can greatly impact an individual’s life. Understanding the symptoms, triggers, and available treatment options can help those affected by PTSD find the support they need to manage their condition and improve their overall well-being.
Separation Anxiety Disorder: Navigating the Challenges of Separation
Separation anxiety is a specific type of anxiety disorder that commonly affects children, but can also occur in adults. It is characterized by an intense fear or worry about being separated from a loved one or a familiar environment. This anxiety can cause significant distress and impairment in various areas of life.
Symptoms of Separation Anxiety Disorder:
- Excessive distress when anticipating or experiencing separation from a loved one or familiar environment.
- Constant worry about the well-being of the loved one during separation.
- Physical symptoms such as headaches, stomachaches, nausea, or dizziness when separated.
- Refusal to go to school or other places where separation may occur.
- Nightmares or other sleep disturbances related to separation.
It’s important to note that while some anxiety about separation is normal, separation anxiety disorder involves an exaggerated and persistent fear that goes beyond what is developmentally appropriate.
Coping with Separation Anxiety Disorder:
Individuals with separation anxiety disorder may find it helpful to employ various coping strategies to manage their anxiety:
- Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is often an effective treatment approach for separation anxiety disorder. It helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with separation.
- Gradual exposure: Gradual exposure to separation, starting with short periods and gradually increasing the time apart, can help individuals build tolerance and reduce anxiety.
- Positive reinforcement: Rewarding individuals for successfully coping with separation can encourage them to continue practicing their coping skills.
- Open communication: Talking openly about fears and concerns related to separation with a trusted person can help alleviate anxiety and provide support.
- Self-care: Engaging in regular self-care activities such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help reduce overall anxiety levels.
The Impact of Separation Anxiety Disorder:
Separation anxiety disorder can have a significant impact on various aspects of an individual’s life, including:
| Family Life | Social Relationships | Academic Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Family members may need to adjust their routines to accommodate the individual’s anxiety. | Difficulties forming and maintaining friendships due to fear of separation. | Difficulty concentrating and participating in school activities. |
| Parents may experience increased stress and worry. | Avoidance of social situations that may involve separation. | Inconsistent attendance and falling behind in school. |
| Limitations in family activities and outings due to fear of separation. | Feelings of isolation and loneliness. | Impaired ability to achieve academic success. |
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of separation anxiety disorder, it is essential to seek professional help. With proper support and treatment, individuals with separation anxiety disorder can learn to manage their anxiety and lead fulfilling lives.
Specific Phobias: Discovering the Types and Symptoms
A specific phobia is an intense, irrational fear of a particular object or situation. People with specific phobias often go to great lengths to avoid the object or situation, leading to significant disruptions in their daily lives. Here are some common types of specific phobias along with their symptoms:
1. Animal phobias
Animal phobias involve an intense fear of specific animals, such as dogs, spiders, snakes, or insects. Symptoms of animal phobias may include:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Trembling or shaking
2. Natural environment phobias
Natural environment phobias are characterized by a fear of specific situations or objects related to nature, such as storms, heights, or water. Symptoms of natural environment phobias may include:
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Feeling of impending doom
- Panic attacks
3. Blood-injection-injury phobia
Blood-injection-injury phobia is a specific phobia that involves an intense fear of blood, needles, medical procedures, or injuries. Symptoms of blood-injection-injury phobia may include:
- Drop in blood pressure
- Dizziness or fainting
- Nausea or vomiting
- Panic attacks
4. Situational phobias
Situational phobias involve a fear of specific situations, such as flying, driving, or enclosed spaces. Symptoms of situational phobias may include:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Trembling or shaking
- Feelings of dread or terror
- Shortness of breath
5. Other specific phobias
In addition to the above types, there are various other specific phobias that people may experience. These can include fears of certain foods, specific sounds, or even specific numbers. Symptoms of other specific phobias may vary depending on the individual and the specific phobia.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a specific phobia, it is important to seek help from a mental health professional. Treatment options such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or exposure therapy can be effective in reducing phobia-related anxiety and helping individuals overcome their fears.
Questions and answers
What are the different types of anxiety disorder?
There are several different types of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, specific phobias, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
What are the symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder?
The symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder can include excessive worrying, restlessness, feeling on edge or easily fatigued, difficulty concentrating or having your mind go blank, irritability, muscle tension, and sleep disturbances.
What is panic disorder and what are its symptoms?
Panic disorder is characterized by recurrent unexpected panic attacks, which are sudden periods of intense fear that come on quickly and reach their peak within minutes. Symptoms of panic attacks can include a rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling or shaking, shortness of breath, a feeling of choking, chest pain or discomfort, nausea or abdominal distress, dizziness or lightheadedness, derealization or depersonalization, fear of losing control or going crazy, fear of dying, and numbness or tingling sensations.
What is social anxiety disorder?
Social anxiety disorder, also known as social phobia, is characterized by a persistent fear of social or performance situations, including public speaking, meeting new people, or being observed doing something embarrassing. People with social anxiety disorder may experience symptoms such as intense anxiety, fear of scrutiny or humiliation, excessive self-consciousness, avoidance of social situations, and physical symptoms like blushing, sweating, or trembling.
Can specific phobias be categorized as an anxiety disorder?
Yes, specific phobias are considered a type of anxiety disorder. They involve an intense fear or anxiety in response to a specific object or situation, such as heights, spiders, or flying. The fear or anxiety is excessive and disproportionate to the actual danger posed by the object or situation, and may result in avoidance behaviors.
What are the symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder?
Symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can include intrusive memories or flashbacks of a traumatic event, nightmares, intense distress or physical reactions when exposed to reminders of the event, avoidance of reminders of the event, negative changes in thoughts and mood, and heightened arousal or reactivity, such as being easily startled or having difficulty sleeping.