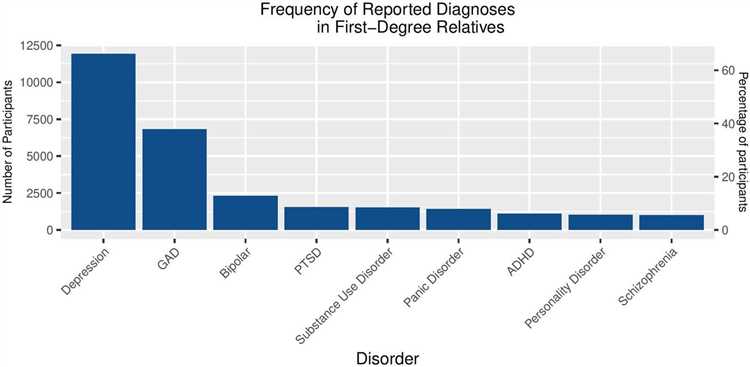
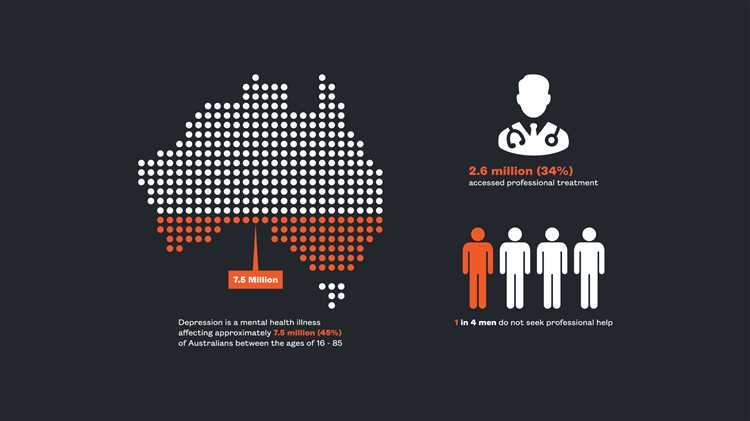
Depression is a common mental health disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. In Australia, it is estimated that over 3 million adults experience depression every year.
Depression can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or socioeconomic status. However, certain factors may increase the risk of developing depression, such as a family history of the disorder, experiencing trauma or abuse, or having a chronic medical condition.
Depression can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life, affecting their ability to function at work or school, maintain relationships, and enjoy activities they once found pleasurable. It is important to understand the key facts and statistics surrounding depression in Australia in order to raise awareness, reduce stigma, and improve access to support and treatment.
According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, depression is the leading cause of disability and the third-highest burden of disease in Australia. It is estimated to cost the Australian economy over $12.6 billion each year.
Despite the prevalence and impact of depression, many individuals do not seek help due to stigma, lack of awareness, or difficulty accessing mental health services. It is crucial for society to prioritize mental health and provide adequate support and resources for those affected by depression.
Facts about Depression in Australia
1. Prevalence: Depression is a common mental health condition in Australia, affecting a significant number of people. According to recent studies, it is estimated that one in seven Australians will experience depression in their lifetime.
2. Gender differences: Depression can affect both males and females, but there are some gender differences in terms of presentation and prevalence. While women are more likely to be diagnosed with depression, men tend to be underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed due to different symptom expressions and societal stigma.
3. Age groups: Depression can affect individuals of all ages, but certain age groups may be more vulnerable. It is commonly seen in teenagers and young adults, with around 20% of adolescents experiencing depression at some point. Older adults, especially those over 65, are also at risk due to factors such as increased health problems, loss of loved ones, and social isolation.
4. Impact on daily life: Depression can significantly impact a person’s ability to function and lead a fulfilling life. It can affect various aspects of daily life, including work productivity, relationships, self-care, and overall well-being. In severe cases, it can even lead to thoughts of self-harm or suicide.
5. Treatment options: There are several effective treatment options for depression in Australia, including medication, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes. It is important for individuals experiencing symptoms of depression to seek help from healthcare professionals to receive appropriate support and treatment.
6. Access to mental health support: Despite the availability of treatment options, there are still challenges in accessing mental health support in Australia. This can be due to factors such as stigma, lack of resources, long waiting lists, and limited funding for mental health services.
7. Suicide rates: Depression is a significant risk factor for suicide, and it is important to address mental health issues to prevent tragic outcomes. In Australia, suicide is a leading cause of death, particularly among young people. It highlights the urgent need for increased awareness, early intervention, and improved access to mental health care.
| Prevalence | Gender differences | Age groups | Impact on daily life | Treatment options | Access to mental health support | Suicide rates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One in seven Australians will experience depression in their lifetime. | Women are more likely to be diagnosed with depression, while men are often underdiagnosed. | Teenagers, young adults, and older adults are more vulnerable. | Depression can significantly affect work, relationships, self-care, and overall well-being. | Treatment options include medication, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes. | Accessing mental health support can be challenging due to various factors. | Depression is a significant risk factor for suicide, which is a leading cause of death in Australia. |
Overview of Depression in Australia
Depression is a common mental health condition that affects a significant number of people in Australia. It is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities once enjoyed. Here are some key facts and statistics about depression in Australia:
- Depression affects approximately 1 million adults in Australia every year.
- It is estimated that 1 in 6 people will experience depression at some point in their life.
- Depression can occur at any age, but it is more prevalent among adults aged 18-24.
- Women are more likely to experience depression than men, with approximately 1 in 5 women being affected compared to 1 in 8 men.
- Depression is a leading cause of disability worldwide and is associated with a significant burden on individuals, families, and society.
Depression can have a profound impact on a person’s daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. It can affect a person’s ability to function at work or school and may lead to social isolation and an increased risk of suicide.
The causes of depression are complex and can vary from person to person. It is often a combination of genetic, biological, environmental, and psychological factors. Common risk factors for depression include a history of mental health conditions, family history of depression, personal or family history of substance abuse, trauma or stressful life events, and certain medical conditions.
Early identification and appropriate treatment are essential for managing depression. This can include a combination of medication, psychotherapy, lifestyle changes, and support from healthcare professionals, friends, and family.
It is important to seek help if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of depression. There are many resources and support services available in Australia, including helplines, online forums, and local mental health services.
Prevalence of Depression in Australia
Depression is a common mental health disorder in Australia, affecting a significant portion of the population. The prevalence of depression in Australia is a cause for concern, and it is important to understand the extent of the issue.
Key statistics:
- About one in seven Australians will experience depression in their lifetime.
- Depression is more common in women than men, with approximately one in six women and one in eight men experiencing depression at some point in their lives.
- The highest prevalence of depression is found in people aged 18-24, with rates declining as age increases.
- Depression is often accompanied by other mental health disorders, such as anxiety or substance abuse.
The following table provides a comparison of depression prevalence in different age groups:
| Age Group | Percentage of Population |
|---|---|
| 18-24 | 22% |
| 25-34 | 20% |
| 35-44 | 17% |
| 45-54 | 14% |
| 55+ | 11% |
It is important to note that these statistics may underestimate the true prevalence of depression, as many people do not seek help or receive a formal diagnosis for their symptoms. However, it is clear that depression is a significant issue in Australia and efforts should be made to raise awareness, improve access to mental health services, and reduce the stigma surrounding seeking help for mental health disorders.
Risk Factors for Depression
Depression is a complex mental health condition that can be caused by a combination of factors. While the exact cause of depression is unknown, there are several risk factors that have been identified. These risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing depression:
- Genetics: There is evidence to suggest that depression can run in families. People with a family history of depression may be more likely to develop the condition themselves.
- Personal or family history: Individuals who have experienced depression in the past are at an increased risk of developing it again. Similarly, individuals with a family history of depression may be more susceptible to the condition.
- Brain chemistry: Imbalances in certain chemicals in the brain, such as serotonin, may contribute to the development of depression.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as chronic pain or cardiovascular disease, can increase the risk of developing depression.
- Stressful life events: Traumatic experiences, loss of a loved one, or other significant life events can trigger or exacerbate depression.
- Substance abuse: Drug or alcohol abuse can contribute to the development of depression. Substance abuse can also worsen the symptoms of depression.
- Gender: Women are more likely to experience depression than men. Hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause may contribute to this higher risk.
- Social factors: Certain social factors, such as isolation, lack of social support, or experiencing discrimination, can increase the risk of depression.
It is important to note that having one or more risk factors does not guarantee that an individual will develop depression, as it is a complex condition with multiple contributing factors. However, being aware of these risk factors can help individuals and healthcare professionals identify those who may be at a higher risk and take appropriate preventive or treatment measures.
Depression Statistics in Australia
Depression is a common mental health disorder that affects many individuals in Australia. Understanding the key statistics related to depression can help raise awareness and provide valuable insights into the impact of this condition. Below are some noteworthy depression statistics in Australia:
- Prevalence: Approximately 1 million adults in Australia experience depression in any given year.
- Gender Differences: Women are more likely to be diagnosed with depression compared to men. Around 1 in 6 women and 1 in 8 men will experience depression at some point in their lives.
- Age Groups: Depression can affect individuals of all ages. However, the highest prevalence of depression is observed among individuals aged 16 to 24 years old.
- Risk Factors: Various factors can increase the risk of developing depression, including a family history of mental health disorders, previous episodes of depression, chronic illnesses, and stressful life events.
- Treatment: Approximately 70% of individuals with depression do not seek appropriate treatment. Access to mental health services and stigma associated with seeking help are some of the barriers preventing people from receiving the necessary support.
It is important to remember that these statistics provide a general overview and do not capture the individual experiences and unique circumstances of each person suffering from depression. Seeking professional help, talking openly about mental health, and promoting understanding and empathy are key to combatting depression and improving the well-being of individuals in Australia.
Demographic Distribution of Depression
Depression is a common mental health disorder that affects people of all ages, genders, and backgrounds. However, there are certain demographic groups that are more vulnerable to experiencing depression.
- Age: Depression can affect individuals at any age, but it is more prevalent in certain age groups. According to research, young adults and the elderly are at a higher risk of developing depression.
- Gender: Studies have shown that women are more likely to be diagnosed with depression compared to men. The reasons behind this gender difference are complex and may include biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors.
- Socioeconomic status: Financial stress and socio-economic factors can contribute to the development of depression. Individuals from lower socio-economic backgrounds may have limited access to mental health resources, which can further exacerbate their condition.
- Location: Geographical location can also play a role in the prevalence of depression. Research suggests that individuals living in rural or remote areas may face more challenges in accessing mental health services, resulting in higher rates of depression.
- Cultural factors: Cultural factors can influence how depression is experienced, expressed, and addressed within different communities. Some cultural groups may have different beliefs and practices related to mental health, which can impact the way depression is perceived and treated.
It is important to understand the demographics of depression in order to develop targeted interventions and support systems for those affected. By addressing the unique needs of various demographic groups, we can work towards reducing the impact of depression and promoting mental well-being for all.
Treatment and Support for Depression
1. Psychotherapy: Psychotherapy is a widely used treatment for depression. It involves talking to a trained therapist or counselor who helps you identify and change negative thoughts and behaviors. Different types of psychotherapy include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy, and psychodynamic therapy.
2. Medications: Antidepressant medications can be prescribed by a healthcare professional to help manage depression symptoms. These medications work by balancing chemicals in the brain that affect mood and emotions. It’s important to consult with a doctor to find the right medication and dosage for you.
3. Support Groups: Joining a support group can provide you with a sense of community and understanding. These groups are usually led by a mental health professional and offer a safe space for individuals experiencing similar struggles to share their experiences and provide mutual support.
4. Lifestyle Changes: Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can also play a role in managing depression. This includes regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and avoiding alcohol and drug use. Engaging in activities you enjoy and practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can also be beneficial.
5. Online Resources: There are various online platforms and websites that provide information, resources, and support for individuals dealing with depression. These resources may include self-help tools, forums, and helplines where individuals can seek guidance and connect with others experiencing similar challenges.
6. Seeking Professional Help: If you or someone you know is experiencing severe depression symptoms or having thoughts of self-harm or suicide, it’s crucial to seek immediate professional help. Contact a mental health helpline, speak to a healthcare professional, or go to the nearest emergency department for assistance.
7. Integrated Treatment Approaches: In some cases, a combination of different treatment approaches may be beneficial. This could involve a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes to provide comprehensive support for individuals with depression.
| Beyondblue | – an Australian organization providing information and support for depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues. Helpline: 1300 22 4636 |
| Lifeline Australia | – a crisis support and suicide prevention organization. 24/7 Helpline: 13 11 14 |
| Headspace | – an Australian youth mental health organization. Helpline: 1800 650 890 |
Impact of Depression on Society
Depression is a widespread mental health disorder that affects millions of people around the world, including Australia. The impact of depression on society is significant and far-reaching. Below are some key facts and statistics highlighting the impact of depression on society in Australia:
- Prevalence: Depression affects approximately 1 in 6 people in Australia at some point in their lives.
- Economic burden: The economic cost of depression in Australia is estimated to be around $12.6 billion per year, including direct healthcare costs and indirect costs such as lost productivity.
- Workforce impact: Depression is one of the leading causes of disability in the workplace. It results in decreased productivity, increased absenteeism, and higher rates of unemployment.
- Relationship strain: Depression can strain relationships with family, friends, and colleagues. It often leads to social isolation and difficulties in maintaining healthy connections with others.
- Physical health consequences: Depression is associated with an increased risk of developing chronic physical health conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
- Impact on youth: Depression among young people can have severe consequences, including poor academic performance, substance abuse, and an increased risk of suicide.
- Stigma and discrimination: Individuals with depression often face stigma and discrimination, which can prevent them from seeking help and accessing necessary treatment.
Addressing the impact of depression on society requires a comprehensive approach that includes raising awareness, increasing access to mental health services, reducing stigma, and promoting early intervention and support. By addressing depression effectively, we can minimize its impact on individuals and society as a whole.
Questions and answers
What is depression?
Depression is a mental health disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities. It can affect a person’s thoughts, feelings, behavior, and overall well-being.
How common is depression in Australia?
Depression is a prevalent mental health condition in Australia. According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS), an estimated 1 million adults in Australia suffer from depression each year.
What are the risk factors for depression in Australia?
The risk factors for depression in Australia are multifaceted. They include a family history of depression, personal history of mental health disorders, stressful life events, chronic medical conditions, substance abuse, and socioeconomic factors.
What are the symptoms of depression?
The symptoms of depression can vary from person to person, but common signs include persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities, changes in appetite or weight, sleep disturbances, fatigue, feelings of worthlessness or guilt, difficulty concentrating, and thoughts of self-harm or suicide.
How is depression treated in Australia?
Depression in Australia is commonly treated through a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. Antidepressant medications may also be prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Are there any helplines or support services available for people with depression in Australia?
Yes, there are several helplines and support services available for people with depression in Australia. Some examples include Beyond Blue (1300 22 4636), Lifeline (13 11 14), and the Black Dog Institute (1300 22 4636). These organizations offer information, support, and referrals to individuals experiencing depression.